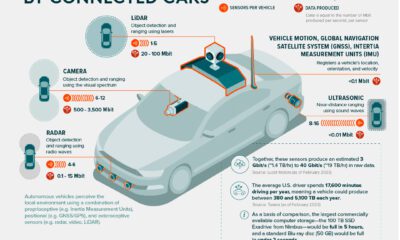
Datastream
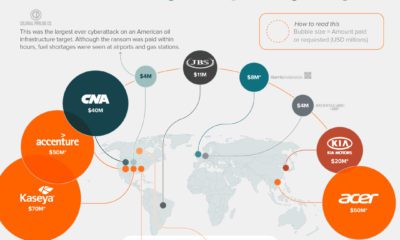
Ranked: The Top Cyberattacks Against Businesses
The following content is sponsored by Global X ETFs.

Ranked: The Top Cyberattacks Against Businesses
Cyberattacks hit a record high in 2021, continuing the momentum that had developed during the COVID-19 pandemic. One reason for this increase is the shift to remote work, which has opened up new vulnerabilities. Home networks are typically less secure, and the rapid rise in the use of online services means security is falling behind.
In this graphic sponsored by Global X ETFs, we’ve visualized survey results showing the 10 most successful types of cyberattacks in 2021.
The Results
These results are from a 2021 whitepaper by Osterman Research, a market research firm focused on cybersecurity. They surveyed 130 cybersecurity professionals from mid and large-sized organizations to see which types of attacks were the most prominent.
| Type of Attack | Percentage of respondents (%) |
|---|---|
| Business email attack was successful in tricking a lower-level employee | 53% |
| Phishing message resulted in a malware infection | 49% |
| Phishing message resulted in an account being compromised | 47% |
| Domain name was spoofed to perpetrate phishing campaigns | 38% |
| Ransomware was detected before it could be activated | 34% |
| Business email attack was successful in tricking a senior executive | 28% |
| Domain name impersonation resulted in a third-party being compromised | 16% |
| Phishing message resulted in a ransomware infection | 14% |
| A ransomware attack was successfully launched | 10% |
| A ransomware attack rendered internal IT systems non-operational | 10% |
Source: Osterman Research (2021)
The report notes that these figures may be understated because organizations are likely to downplay their security incidents. Organizations may also lack the capability to detect all types of cyberattacks.
The Impact of Phishing Attacks
Phishing refers to an attack where the perpetrator pretends to be a trusted entity. These attacks can be carried out over email, text message (SMS), and even social media apps. The goal is often to trick the victim into opening a malicious link.
According to the whitepaper, opening malicious links can result in credential theft or ransomware infections. Credential theft is when attackers gain access to internal systems. This is incredibly dangerous, as it allows attackers to commit fraud, impersonate company officials, and steal data.
A powerful tool for preventing credential theft is multi-factor authentication (MFA). This method requires users to provide multiple verification factors to access a resource (instead of a single password).
The Threat of Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of cyberattack that involves blackmail, often for financial gain. For ransomware to be successfully planted, attackers must first gain access to a company’s networks.
Access can be gained through phishing, as discussed above, or alternate means such as compromised software updates. One such attack impacted over 57,000 Asus laptop owners in Russia after hackers created a malicious update tool on an official Asus server.
Cybercriminals have become increasingly ruthless in how ransomware attacks are executed.
– Osterman Research
Researchers have warned that ransomware attacks are becoming more dangerous and sophisticated. In addition to locking organizations out from core systems, hackers are also stealing data to increase their leverage. If a ransom is not paid, the stolen data may be published or even sold to the highest bidder.
Under Siege
The rising frequency and sophistication of cybercriminal activity is a major threat to the world.
According to the World Economic Forum’s 2022 Global Risks Report, ransomware attacks have increased by 435% since 2020. Furthermore, there is an estimated shortage of 3 million cybersecurity professionals worldwide.
To catch up, businesses and governments are expected to increase their spending on cybersecurity over the next several years.
The Global X Cybersecurity ETF is a passively managed solution that can be used to gain exposure to the rising adoption of cybersecurity technologies. Click the link to learn more.
Datastream
Can You Calculate Your Daily Carbon Footprint?
Discover how the average person’s carbon footprint impacts the environment and learn how carbon credits can offset your carbon footprint.
The Briefing
- A person’s carbon footprint is substantial, with activities such as food consumption creating as much as 4,500 g of CO₂ emissions daily.
- By purchasing carbon credits from Carbon Streaming Corporation, you can offset your own emissions and fund positive climate action.
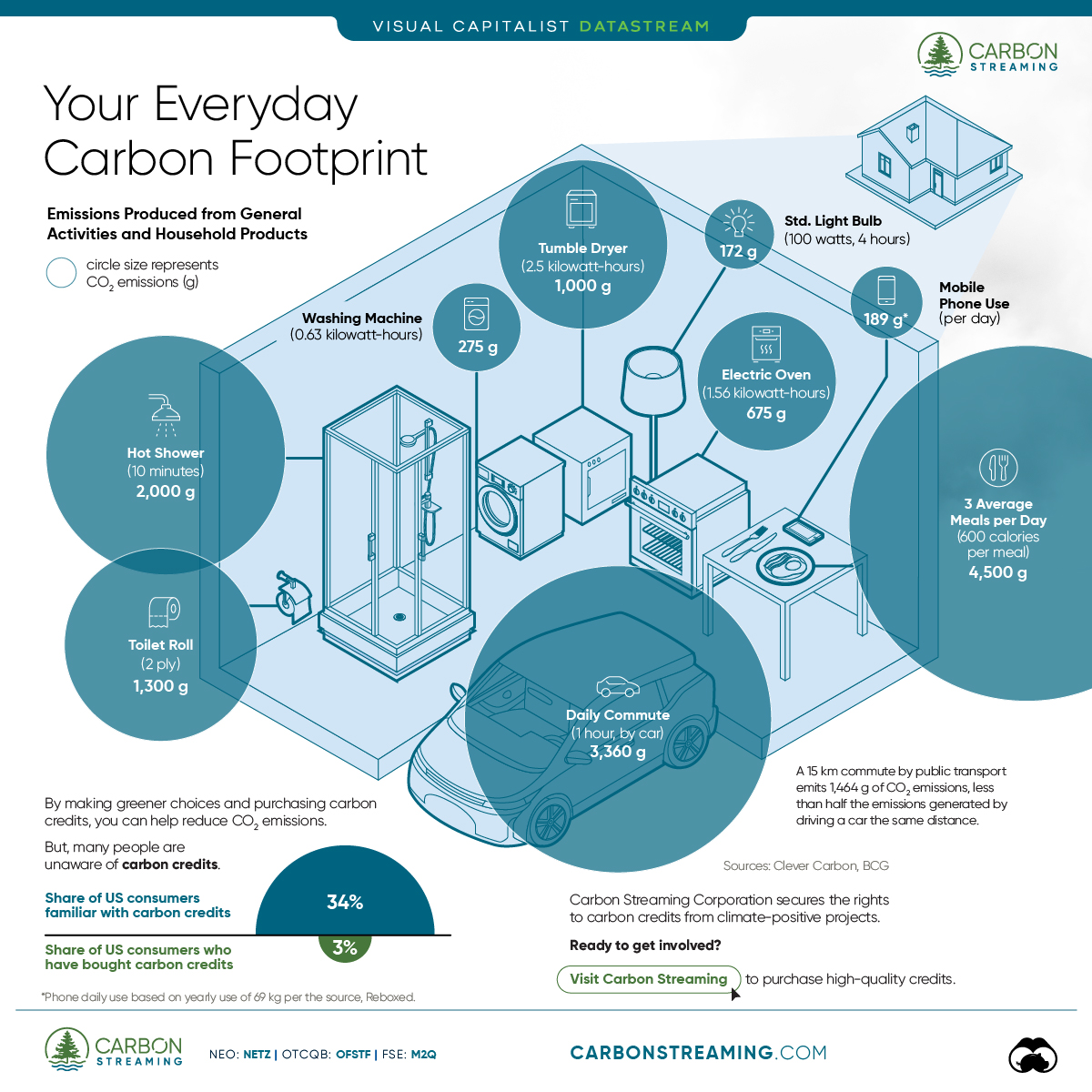
Your Everyday Carbon Footprint
While many large businesses and countries have committed to net-zero goals, it is essential to acknowledge that your everyday activities also contribute to global emissions.
In this graphic, sponsored by Carbon Streaming Corporation, we will explore how the choices we make and the products we use have a profound impact on our carbon footprint.
Carbon Emissions by Activity
Here are some of the daily activities and products of the average person and their carbon footprint, according to Clever Carbon.
| Household Activities & Products | CO2 Emissions (g) |
|---|---|
| 💡 Standard Light Bulb (100 watts, four hours) | 172 g |
| 📱 Mobile Phone Use (195 minutes per day)* | 189 g |
| 👕 Washing Machine (0.63 kWh) | 275 g |
| 🔥 Electric Oven (1.56 kWh) | 675 g |
| ♨️ Tumble Dryer (2.5 kWh) | 1,000 g |
| 🧻 Toilet Roll (2 ply) | 1,300 g |
| 🚿 Hot Shower (10 mins) | 2,000 g |
| 🚙 Daily Commute (one hour, by car) | 3,360 g |
| 🍽️ Average Daily Food Consumption (three meals of 600 calories) | 4,500 g |
| *Phone use based on yearly use of 69kg per the source, Reboxed | |
Your choice of transportation plays a crucial role in determining your carbon footprint. For instance, a 15 km daily commute to work on public transport generates an average of 1,464 g of CO₂ emissions. Compared to 3,360 g—twice the volume for a journey the same length by car.
By opting for more sustainable modes of transport, such as cycling, walking, or public transportation, you can significantly reduce your carbon footprint.
Addressing Your Carbon Footprint
One way to compensate for your emissions is by purchasing high-quality carbon credits.
Carbon credits are used to help fund projects that avoid, reduce or remove CO₂ emissions. This includes nature-based solutions such as reforestation and improved forest management, or technology-based solutions such as the production of biochar and carbon capture and storage (CCS).
While carbon credits offer a potential solution for individuals to help reduce global emissions, public awareness remains a significant challenge. A BCG-Patch survey revealed that only 34% of U.S. consumers are familiar with carbon credits, and only 3% have purchased them in the past.
About Carbon Streaming
By financing the creation or expansion of carbon projects, Carbon Streaming Corporation secures the rights to future carbon credits generated by these sustainable projects. You can then purchase these carbon credits to help fund climate solutions around the world and compensate for your own emissions.
Ready to get involved?
>> Learn more about purchasing carbon credits at Carbon Streaming
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?