Markets
Ranked: America’s Best States to Do Business In
Ranked: America’s Best States to Do Business In
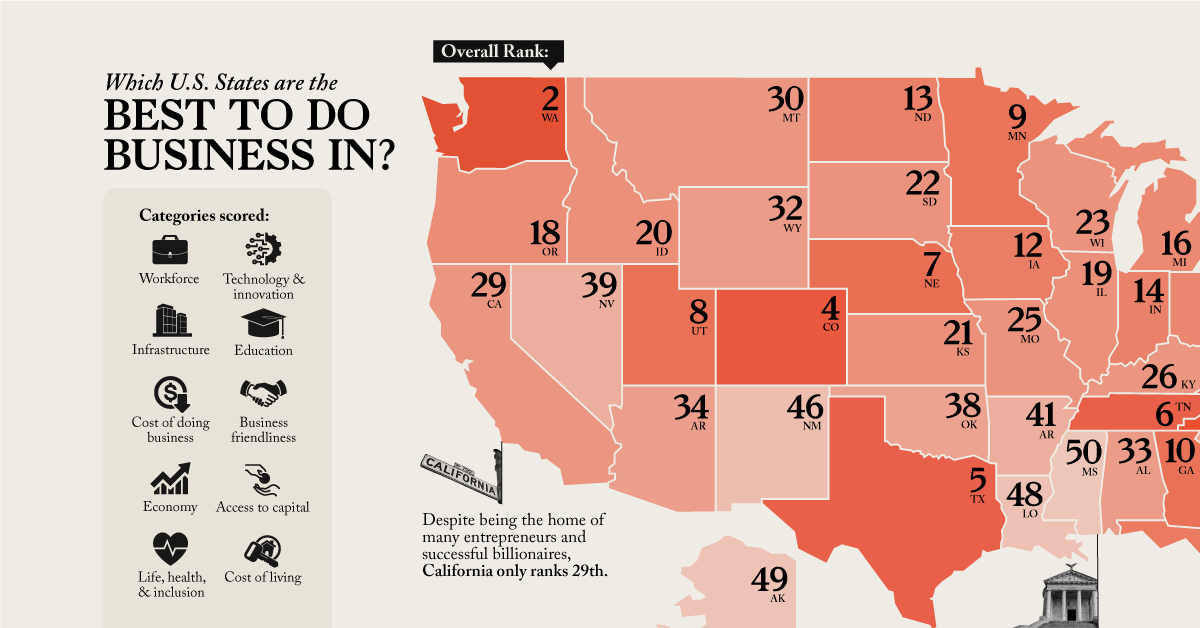
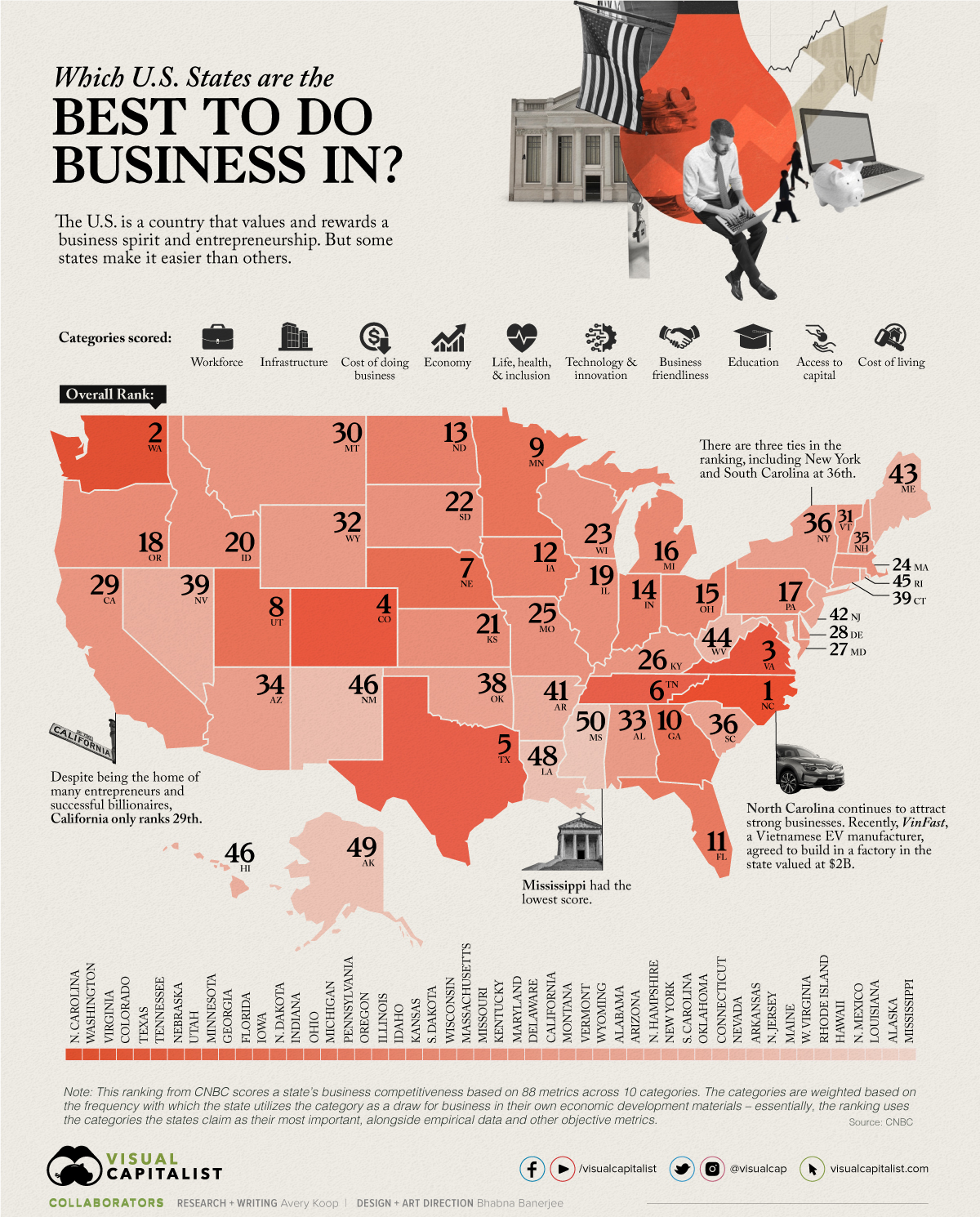
The United States often ranks as one of the best countries to start a business in, but the ease with which one can do business varies state by state. There are many considerations that factor into starting a business like the available workforce, the condition of local infrastructure, access to investors, a culture that’s open to business, and so on.
This map ranks America’s best states to do business in based on a study from CNBC which measured 88 factors across 10 broad categories.
Methodology
Here is a further breakdown of the weight given to each of the 10 categories:
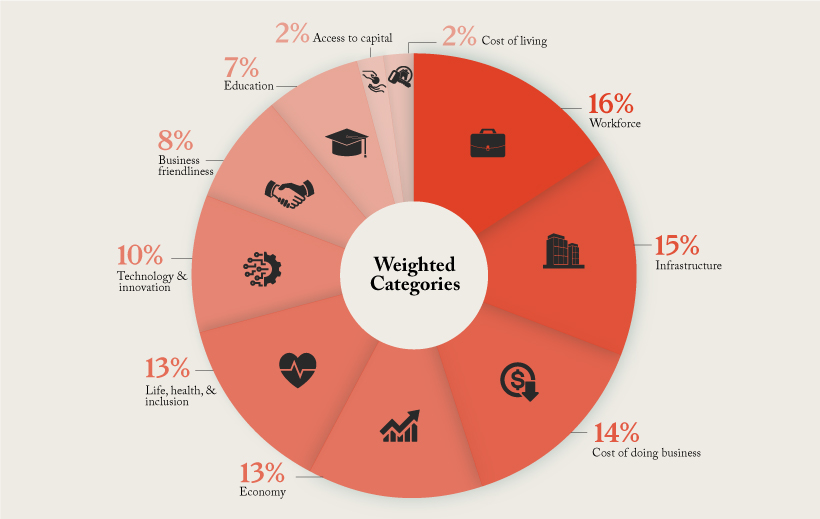
The Most Business Friendly States
North Carolina—coming in first place in the ranking—attracts an extremely talented and innovative workforce, largely thanks to the state’s investment in its Research Triangle Regional Partnership (RTRP).
| Overall Rank | State |
|---|---|
| #1 | North Carolina |
| #2 | Washington |
| #3 | Virginia |
| #4 | Colorado |
| #5 | Texas |
| #6 | Tennessee |
| #7 | Nebraska |
| #8 | Utah |
| #9 | Minnesota |
| #10 | Georgia |
| #11 | Florida |
| #12 | Iowa |
| #13 | North Dakota |
| #14 | Indiana |
| #15 | Ohio |
| #16 | Michigan |
| #17 | Pennsylvania |
| #18 | Oregon |
| #19 | Illinois |
| #20 | Idaho |
| #21 | Kansas |
| #22 | South Dakota |
| #23 | Wisconsin |
| #24 | Massachusetts |
| #25 | Missouri |
| #26 | Kentucky |
| #27 | Maryland |
| #28 | Delaware |
| #29 | California |
| #30 | Montana |
| #31 | Vermont |
| #32 | Wyoming |
| #33 | Alabama |
| #34 | Arizona |
| #35 | New Hampshire |
| #36 | New York |
| #36 | South Carolina |
| #38 | Oklahoma |
| #39 | Connecticut |
| #39 | Nevada |
| #41 | Arkansas |
| #42 | New Jersey |
| #43 | Maine |
| #44 | West Virginia |
| #45 | Rhode Island |
| #46 | Hawaii |
| #46 | New Mexico |
| #48 | Louisiana |
| #49 | Alaska |
| #50 | Mississippi |
Notably, there are three ties in the ranking: New York and South Carolina had the same score, tying for 36th, Connecticut and Nevada tied for 39th, and Hawaii and New Mexico tied for 46th.
Other states ranking high on the list are Washington, Virginia, and Colorado. One of the newest individual metrics CNBC took into consideration was an openness to the cannabis industry, likely playing into Colorado’s move up from 8th to 4th compared to last year.
Some states that perhaps surprisingly don’t crack the top 10 include California and New York, both often considered centers of finance and entrepreneurship. But with the high costs of living and of starting a business in those states, their overall score is reduced.
A Look at the Scoring — North Carolina, California, and Nevada
To better understand how this ranking works we’ve broken down three different states and how they ranked in all 10 categories that gave them their overall spot. Here’s a brief look at their place in each category:
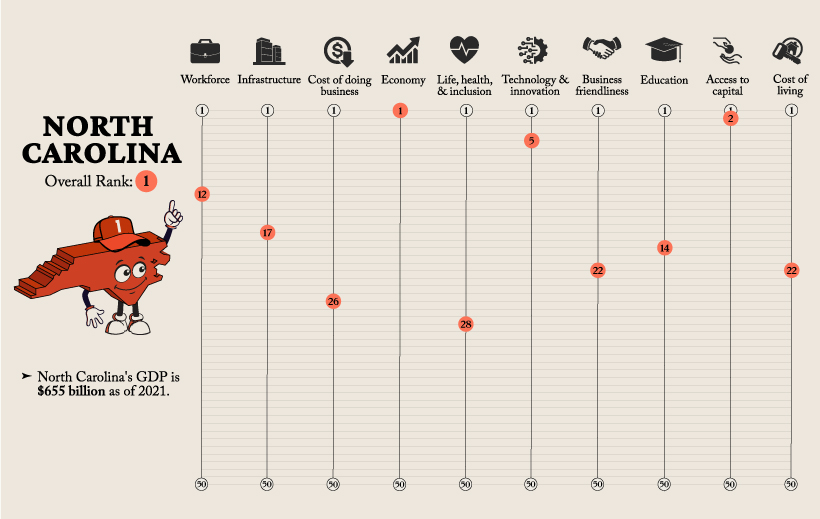
While North Carolina is the number one state to do business in and has an extremely strong economy, they are 26th when it comes to the Cost of Doing Business.
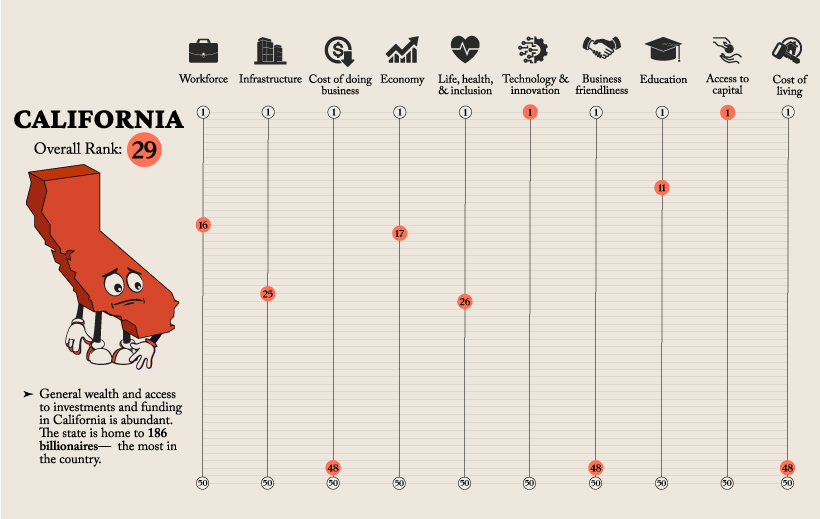
Whereas California ranks low overall, the state ranks first in terms of Technology and Innovation, as well as Access to Capital.
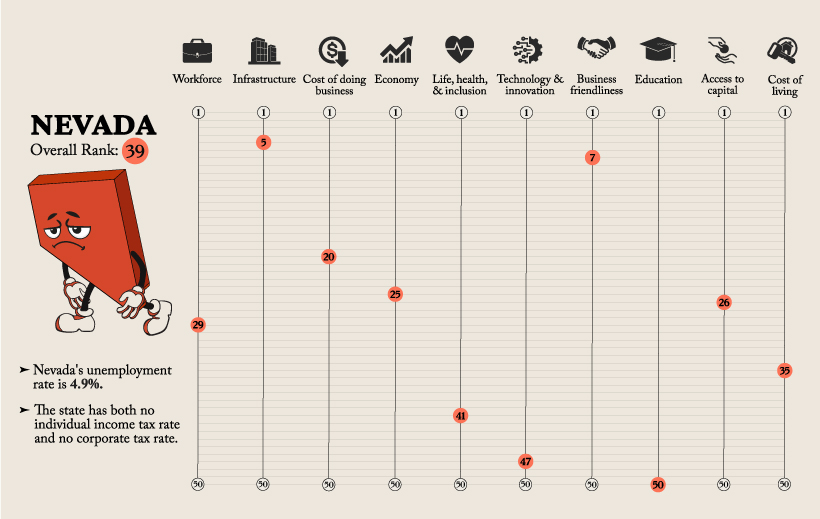
Although Nevada scored highly in the Infrastructure and Business Friendliness categories, the state scored poorly in Technology and Innovation, and was dead last in the Education category.
Doing Business in America
New business applications have actually decreased 4% this year in comparison to the same timeframe in 2021.
Here’s a look at new business applications by region as of July 2022:
- Northeast: 63,058
- Midwest: 70,827
- South: 197,663
- West: 94,150
New business applications in July were the highest in the retail trade industry, numbering around 69,000 new applications, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. Applications for professional service businesses were the second highest at 53,000, followed closely by construction businesses at 43,000.
Here’s a closer look at the industry breakdown:
| Industry | Number of Applications |
|---|---|
| Retail Trade | 68,974 |
| Professional Services | 53,321 |
| Construction | 43,442 |
| Other Services | 38,605 |
| Transportation and Warehousing | 34,952 |
| Administrative and Support | 31,602 |
| Health Care and Social Assistance | 25,725 |
| Accommodation and Food Services | 24,166 |
| Real Estate | 23,953 |
| Finance and Insurance | 18,890 |
| Arts and Entertainment | 12,684 |
| Unclassified | 12,350 |
| Wholesale Trade | 8,893 |
| Information | 7,802 |
| Educational Services | 5,762 |
| Manufacturing | 5,744 |
| Management of Companies | 4,166 |
| Agriculture | 3,703 |
| Mining | 542 |
| Utilities | 421 |
A potential looming recession, alongside rising interest rates and inflation, may be creating a sense of cautiousness among businesspeople, leading to the lower rate of business applications compared to last year. And, at existing companies, the economic situation has lead to cuts in growth forecasts and subsequently, major layoffs.
But overall, the U.S. is a country which values entrepreneurship—even during the pandemic, massive spikes in new business formations were recorded—and certain industries and states will continue to flourish in any business environment.
Markets
U.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
U.S. debt interest payments have surged past the $1 trillion dollar mark, amid high interest rates and an ever-expanding debt burden.

U.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The cost of paying for America’s national debt crossed the $1 trillion dollar mark in 2023, driven by high interest rates and a record $34 trillion mountain of debt.
Over the last decade, U.S. debt interest payments have more than doubled amid vast government spending during the pandemic crisis. As debt payments continue to soar, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) reported that debt servicing costs surpassed defense spending for the first time ever this year.
This graphic shows the sharp rise in U.S. debt payments, based on data from the Federal Reserve.
A $1 Trillion Interest Bill, and Growing
Below, we show how U.S. debt interest payments have risen at a faster pace than at another time in modern history:
| Date | Interest Payments | U.S. National Debt |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $1.0T | $34.0T |
| 2022 | $830B | $31.4T |
| 2021 | $612B | $29.6T |
| 2020 | $518B | $27.7T |
| 2019 | $564B | $23.2T |
| 2018 | $571B | $22.0T |
| 2017 | $493B | $20.5T |
| 2016 | $460B | $20.0T |
| 2015 | $435B | $18.9T |
| 2014 | $442B | $18.1T |
| 2013 | $425B | $17.2T |
| 2012 | $417B | $16.4T |
| 2011 | $433B | $15.2T |
| 2010 | $400B | $14.0T |
| 2009 | $354B | $12.3T |
| 2008 | $380B | $10.7T |
| 2007 | $414B | $9.2T |
| 2006 | $387B | $8.7T |
| 2005 | $355B | $8.2T |
| 2004 | $318B | $7.6T |
| 2003 | $294B | $7.0T |
| 2002 | $298B | $6.4T |
| 2001 | $318B | $5.9T |
| 2000 | $353B | $5.7T |
| 1999 | $353B | $5.8T |
| 1998 | $360B | $5.6T |
| 1997 | $368B | $5.5T |
| 1996 | $362B | $5.3T |
| 1995 | $357B | $5.0T |
| 1994 | $334B | $4.8T |
| 1993 | $311B | $4.5T |
| 1992 | $306B | $4.2T |
| 1991 | $308B | $3.8T |
| 1990 | $298B | $3.4T |
| 1989 | $275B | $3.0T |
| 1988 | $254B | $2.7T |
| 1987 | $240B | $2.4T |
| 1986 | $225B | $2.2T |
| 1985 | $219B | $1.9T |
| 1984 | $205B | $1.7T |
| 1983 | $176B | $1.4T |
| 1982 | $157B | $1.2T |
| 1981 | $142B | $1.0T |
| 1980 | $113B | $930.2B |
| 1979 | $96B | $845.1B |
| 1978 | $84B | $789.2B |
| 1977 | $69B | $718.9B |
| 1976 | $61B | $653.5B |
| 1975 | $55B | $576.6B |
| 1974 | $50B | $492.7B |
| 1973 | $45B | $469.1B |
| 1972 | $39B | $448.5B |
| 1971 | $36B | $424.1B |
| 1970 | $35B | $389.2B |
| 1969 | $30B | $368.2B |
| 1968 | $25B | $358.0B |
| 1967 | $23B | $344.7B |
| 1966 | $21B | $329.3B |
Interest payments represent seasonally adjusted annual rate at the end of Q4.
At current rates, the U.S. national debt is growing by a remarkable $1 trillion about every 100 days, equal to roughly $3.6 trillion per year.
As the national debt has ballooned, debt payments even exceeded Medicaid outlays in 2023—one of the government’s largest expenditures. On average, the U.S. spent more than $2 billion per day on interest costs last year. Going further, the U.S. government is projected to spend a historic $12.4 trillion on interest payments over the next decade, averaging about $37,100 per American.
Exacerbating matters is that the U.S. is running a steep deficit, which stood at $1.1 trillion for the first six months of fiscal 2024. This has accelerated due to the 43% increase in debt servicing costs along with a $31 billion dollar increase in defense spending from a year earlier. Additionally, a $30 billion increase in funding for the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation in light of the regional banking crisis last year was a major contributor to the deficit increase.
Overall, the CBO forecasts that roughly 75% of the federal deficit’s increase will be due to interest costs by 2034.
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?