Agriculture
How to Make Quality Cannabis, and the Role of Organic Farming

How to Make Quality Cannabis, and the Role of Organic Farming
The cannabis industry is picking up speed across the continent.
Canada has now become the first G7 country to legalize recreational cannabis nationwide – and across the border, more U.S. states are also entering what could become a $95 billion market by 2026.
As the industry matures, product quality will become a strong differentiator between those competing for market share. But what makes for a top-notch cannabis product, and does organic farming play a role in this?
How Quality Cannabis is Made
Today’s infographic from The Green Organic Dutchman explains what goes into making a high quality cannabis product, and why the industry could be gearing towards embracing organic farming.
The first major factor that affects quality is where it is grown.
For most of its 6,000-year history, cannabis was predominantly grown outdoors. In a more modern setting, however, indoor cultivation has increased in popularity.
Here are the pros and cons of both environments:
| Benefits |
|
|
| Drawbacks |
|
|
| Impact on Quality |
|
|
Interestingly, many modern cannabis producers do not rely on soil as a growing medium anymore. Instead, they use the latest technology to improve upon traditional methods:
- Aeroponics: Plant roots are sprayed directly with a nutrient-rich mist
- Hydroponics: Plant roots are submerged in a nutrient solution
- Micro-propagation: Plant samples are multiplied in agar gel
While growing cannabis using innovative methods can result in healthy and high-yield products, this also increases operational and labor costs. At the same time, it’s clear that the way cannabis is grown significantly affects the final product and its environmental footprint.
The Issue with Modern Cannabis
Even with all of these other innovations that help in achieving a superior product, many cannabis growers use “super chemicals” or pesticides to achieve rapid growth for their plants. The catch? Cannabis plants are effective at leaching toxins from soil, which means they can easily wind up in the final product.
What’s more, commonly used pesticides such as pyrethins can be safe for consumption in trace amounts. But when cannabis is smoked, the heat can make these chemicals much more toxic for humans.
There’s also mother nature to consider. In modern farming, leftover byproducts often run off into the groundwater, polluting nearby bodies of water.
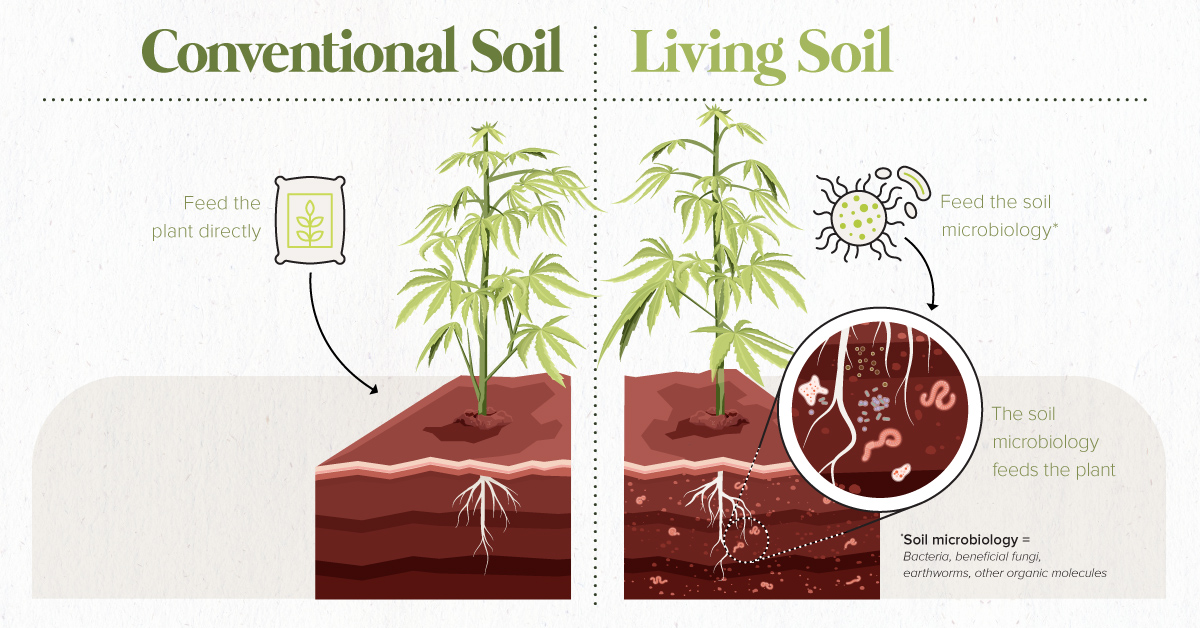
Growing cannabis organically in living soil avoids all the above problems.
- No pesticides, herbicides, or fertilizers are present in the environment
- Cannabis plant and soil microbiology have a symbiotic relationship
- Maintains an ecological balance among the plant and its surroundings
The result of this all-natural process? A safe and premium consumer cannabis product.
As the cannabis green rush progresses, we will dive further into the push towards organic products in the agri-food industry, and what this means for the rapidly-maturing cannabis space.
Markets
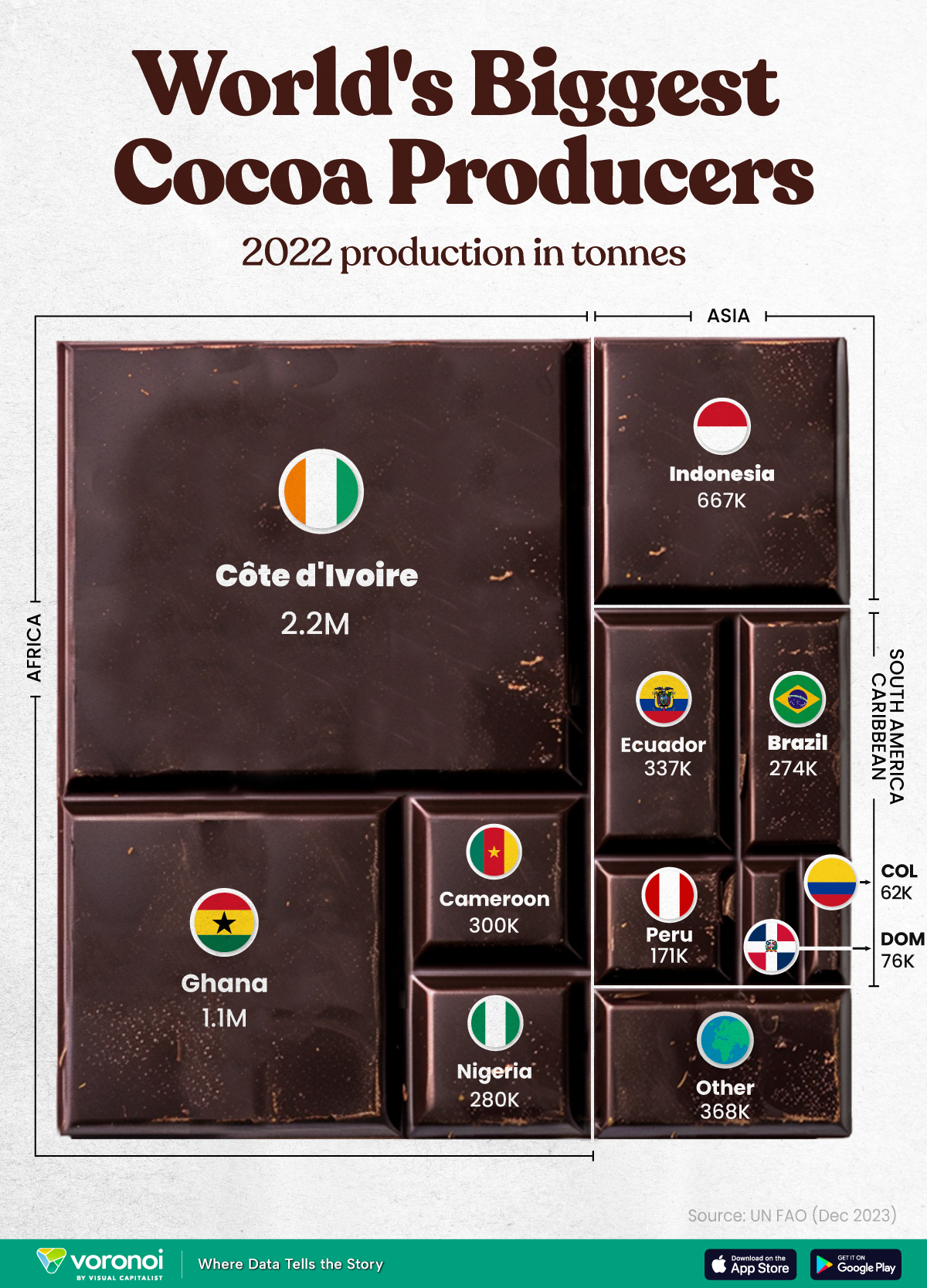
The World’s Top Cocoa Producing Countries
Here are the largest cocoa producing countries globally—from Côte d’Ivoire to Brazil—as cocoa prices hit record highs.

The World’s Top Cocoa Producing Countries
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
West Africa is home to the largest cocoa producing countries worldwide, with 3.9 million tonnes of production in 2022.
In fact, there are about one million farmers in Côte d’Ivoire supplying cocoa to key customers such as Nestlé, Mars, and Hershey. But the massive influence of this industry has led to significant forest loss to plant cocoa trees.
This graphic shows the leading producers of cocoa, based on data from the UN FAO.
Global Hotspots for Cocoa Production
Below, we break down the top cocoa producing countries as of 2022:
| Country | 2022 Production, Tonnes |
|---|---|
| 🇨🇮 Côte d'Ivoire | 2.2M |
| 🇬🇭 Ghana | 1.1M |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 667K |
| 🇪🇨 Ecuador | 337K |
| 🇨🇲 Cameroon | 300K |
| 🇳🇬 Nigeria | 280K |
| 🇧🇷 Brazil | 274K |
| 🇵🇪 Peru | 171K |
| 🇩🇴 Dominican Republic | 76K |
| 🌍 Other | 386K |
With 2.2 million tonnes of cocoa in 2022, Côte d’Ivoire is the world’s largest producer, accounting for a third of the global total.
For many reasons, the cocoa trade in Côte d’Ivoire and Western Africa has been controversial. Often, farmers make about 5% of the retail price of a chocolate bar, and earn $1.20 each day. Adding to this, roughly a third of cocoa farms operate on forests that are meant to be protected.
As the third largest producer, Indonesia produced 667,000 tonnes of cocoa with the U.S., Malaysia, and Singapore as major importers. Overall, small-scale farmers produce 95% of cocoa in the country, but face several challenges such as low pay and unwanted impacts from climate change. Alongside aging trees in the country, these setbacks have led productivity to decline.
In South America, major producers include Ecuador and Brazil. In the early 1900s, Ecuador was the world’s largest cocoa producing country, however shifts in the global marketplace and crop disease led its position to fall. Today, the country is most known for its high-grade single-origin chocolate, with farms seen across the Amazon rainforest.
Altogether, global cocoa production reached 6.5 million tonnes, supported by strong demand. On average, the market has grown 3% annually over the last several decades.
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Travel1 week ago
Travel1 week agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024