Investor Education
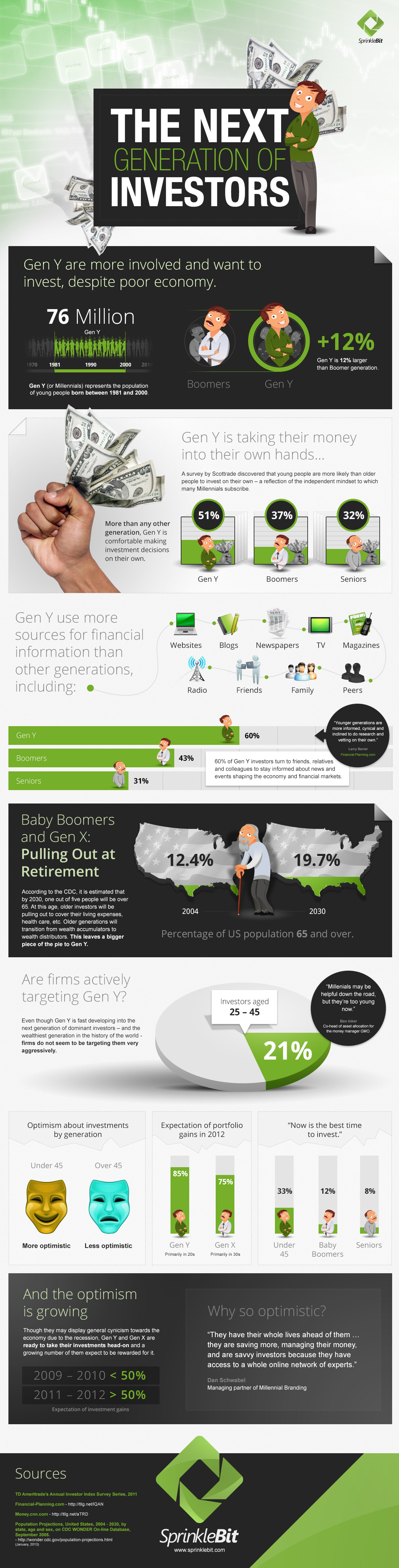
Gen Y: The Next Generation of Investors
Gen Y: The Next Generation of Investors
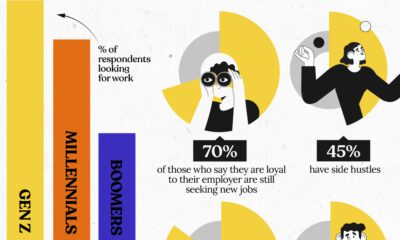
Move over Baby Boomers, the next generation of investors is here and they plan on doing big things.
With Gen Y youth (born between 1981 and 2000) coming to an earning stage of their lives, it is worth noting that they behave differently from investors of the previous generations.
Gen Y, also known as Millennials, have grown up with the abundance of quality and timely information always within an arm’s reach. Young investors today use multiple sources of information that were not available to previous generations to make informed financial decisions. Therefore, investors of this era have become more independent and are inclined to perform research for their investments and finances on their own.
Side note: This is why we created Visual Capitalist. We want to inform the modern investor as quickly and efficiently as possible as they are inundated with a myriad of information every moment of every day. We believe visual learning is the best way to consume and retain useful information.
As Baby Boomers, and eventually Gen X, start to age and pull their investments to cover cost of retirement, more investment opportunities are opening up for Gen Y. In America, almost 20% of the population will be over the age of 65 by 2030. The older generation will go from being “wealth accumulators” to “wealth distributors”.
The economic collapse in the late 2000s led many young people to see their parents’ financial well-being fall apart. The newest generation of investors has learned that they need to be smart with their money and stay ahead of the game to avoid a similar fate.
Source: Sprinklebit blog – The Next Generation of Investors
Investor Education
How MSCI Builds Thematic Indexes: A Step-by-Step Guide
From developing an index objective to choosing relevant stocks, this graphic breaks down how MSCI builds thematic indexes using examples.
How MSCI Builds Thematic Indexes: A Step-by-Step Guide
Have you ever wondered how MSCI builds its thematic indexes?
To capture long-term, structural trends that could drive business performance in the future, the company follows a systematic approach. This graphic from MSCI breaks down each step in the process used to create its thematic indexes.
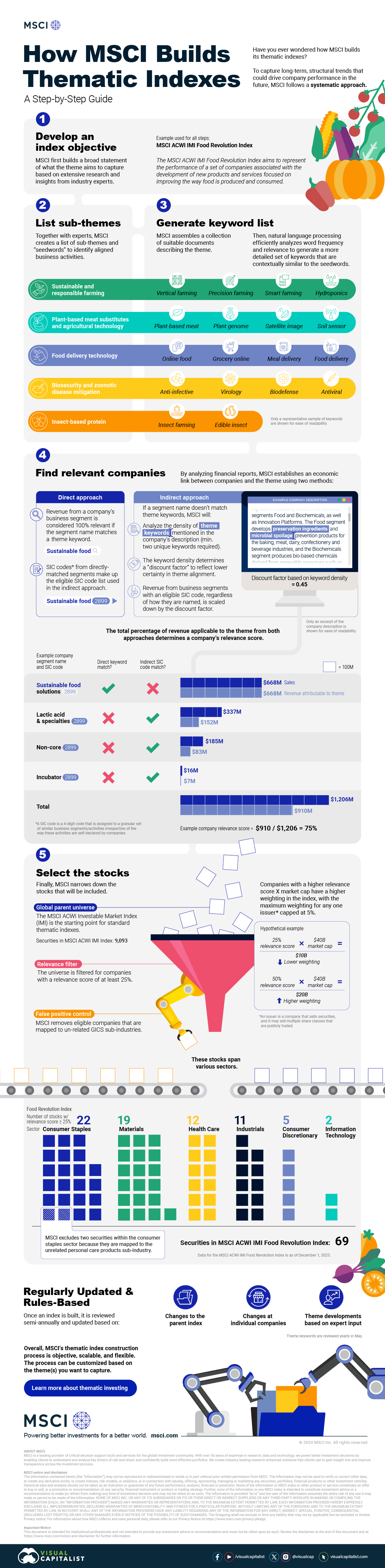
Step 1: Develop an Index Objective
MSCI first builds a broad statement of what the theme aims to capture based on extensive research and insights from industry experts.
Steps 2 and 3: List Sub-Themes, Generate Keyword List
Together with experts, MSCI creates a list of sub-themes or “seedwords” to identify aligned business activities.
The team then assembles a collection of suitable documents describing the theme. Natural language processing efficiently analyzes word frequency and relevance to generate a more detailed set of keywords contextually similar to the seedwords.
Step 4: Find Relevant Companies
By analyzing financial reports, MSCI picks companies relevant to the theme using two methods:
- Direct approach: Revenue from a company’s business segment is considered 100% relevant if the segment name matches a theme keyword. Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) codes from these directly-matched segments make up the eligible SIC code list used in the indirect approach.
- Indirect approach: If a segment name doesn’t match theme keywords, MSCI will:
- Analyze the density of theme keywords mentioned in the company’s description. A minimum of two unique keywords is required.
- The keyword density determines a “discount factor” to reflect lower certainty in theme alignment.
- Revenue from business segments with an eligible SIC code, regardless of how they are named, is scaled down by the discount factor.
The total percentage of revenue applicable to the theme from both approaches determines a company’s relevance score.
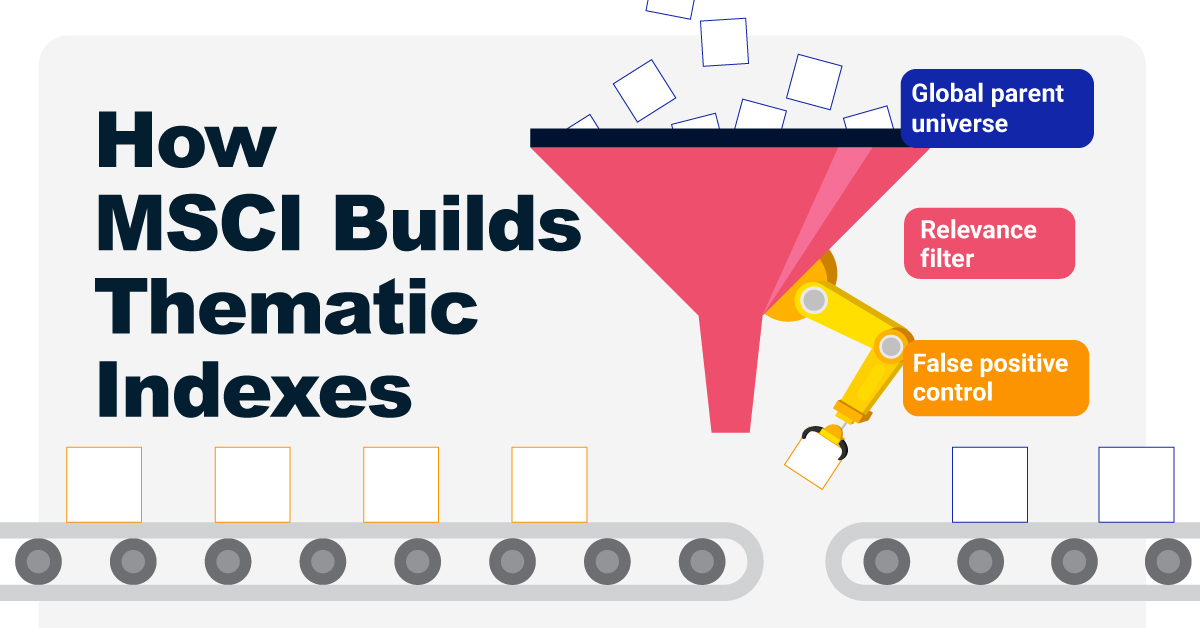
Step 5: Select the Stocks
Finally, MSCI narrows down the stocks that will be included:
- Global parent universe: The ACWI Investable Market Index (IMI) is the starting point for standard thematic indexes.
- Relevance filter: The universe is filtered for companies with a relevance score of at least 25%.
- False positive control: Eligible companies that are mapped to un-related GICS sub-industries are removed.
Companies with higher relevance scores and market caps have a higher weighting in the index, with the maximum weighting for any one issuer capped at 5%. The final selected stocks span various sectors.
MSCI Thematic Indexes: Regularly Updated and Rules-Based
Once an index is built, it is reviewed semi-annually and updated based on:
- Changes to the parent index
- Changes at individual companies
- Theme developments based on expert input
Theme keywords are reviewed yearly in May. Overall, MSCI’s thematic index construction process is objective, scalable, and flexible. The process can be customized based on the theme(s) you want to capture.

Learn more about MSCI’s thematic indexes.

-

 Investor Education6 months ago
Investor Education6 months agoThe 20 Most Common Investing Mistakes, in One Chart
Here are the most common investing mistakes to avoid, from emotionally-driven investing to paying too much in fees.
-
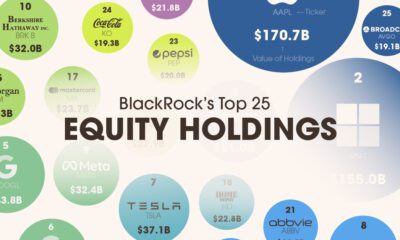
 Stocks10 months ago
Stocks10 months agoVisualizing BlackRock’s Top Equity Holdings
BlackRock is the world’s largest asset manager, with over $9 trillion in holdings. Here are the company’s top equity holdings.
-
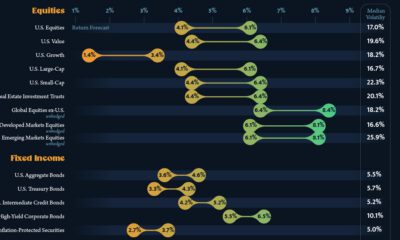
 Investor Education10 months ago
Investor Education10 months ago10-Year Annualized Forecasts for Major Asset Classes
This infographic visualizes 10-year annualized forecasts for both equities and fixed income using data from Vanguard.
-

 Investor Education1 year ago
Investor Education1 year agoVisualizing 90 Years of Stock and Bond Portfolio Performance
How have investment returns for different portfolio allocations of stocks and bonds compared over the last 90 years?
-
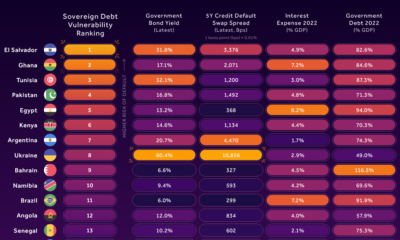
 Debt2 years ago
Debt2 years agoCountries with the Highest Default Risk in 2022
In this infographic, we examine new data that ranks the top 25 countries by their default risk.
-
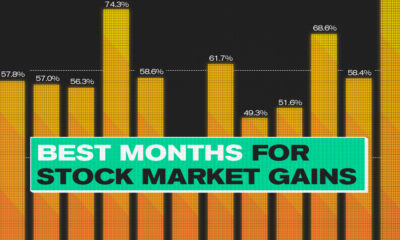
 Markets2 years ago
Markets2 years agoThe Best Months for Stock Market Gains
This infographic analyzes over 30 years of stock market performance to identify the best and worst months for gains.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023