Politics
Ranked: The World’s Most and Least Powerful Passports in 2023
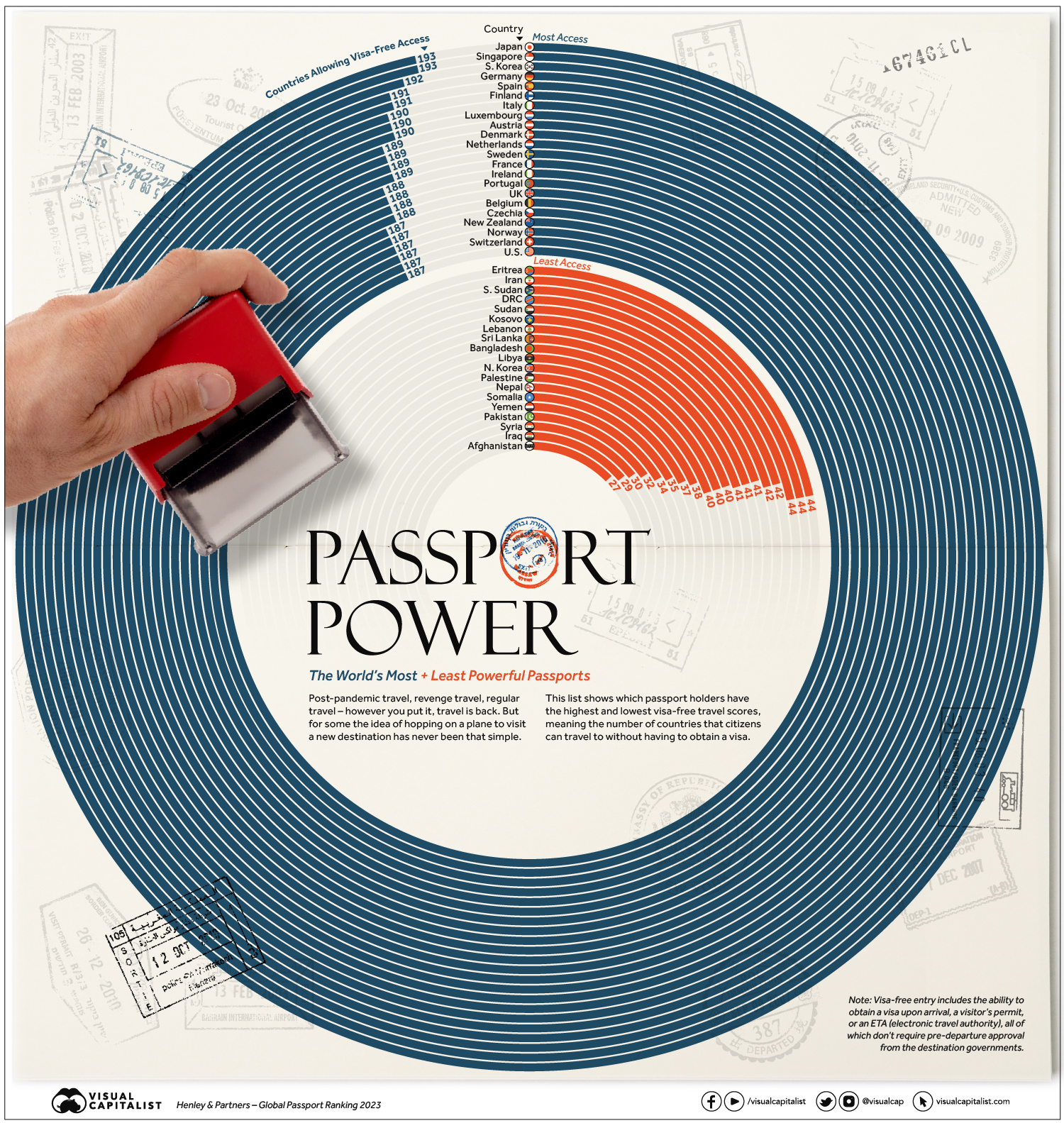
Ranked: The World’s Most and Least Powerful Passports
Depending on your passport, travel can be as simple as just booking flights, finding a hotel, and, then simply going.
But for many across the world, it’s not that easy—a number of passport holders need to obtain a travel/tourist visa prior to arrival. These visas typically require approval from the destination country’s government that can take weeks or months.
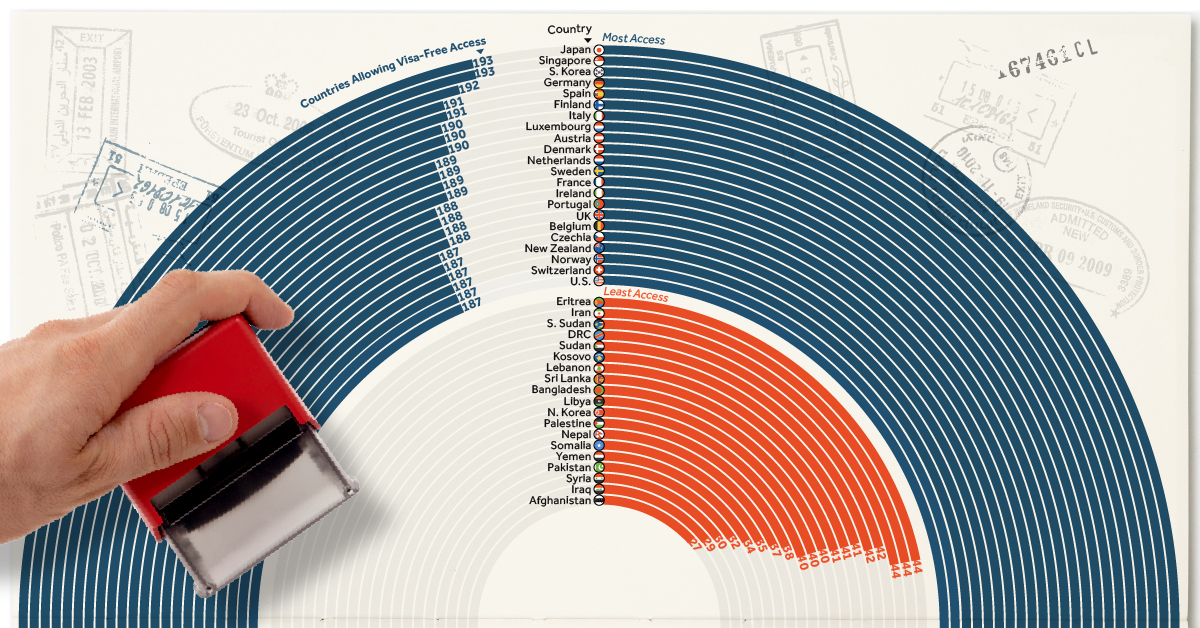
Japanese passport holders, for example, are able to visit 193 countries without pre-approval (nearly every country on Earth). Afghans, on the other hand, can only visit 27 countries with the same level of ease.
This ranking uses data from Henley & Partners, which determines the number of countries to which a passport holder has visa-free access.
The World’s Passports
First let’s look at every country’s position in the ranking in the table below:
| Rank | Passport | Number of Countries Allowing Visa-Free Access |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 193 |
| #1 | 🇸🇬 Singapore | 193 |
| #3 | 🇰🇷 South Korea | 192 |
| #4 | 🇩🇪 Germany | 191 |
| #4 | 🇪🇸 Spain | 191 |
| #6 | 🇫🇮 Finland | 190 |
| #6 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 190 |
| #6 | 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | 190 |
| #9 | 🇦🇹 Austria | 189 |
| #9 | 🇩🇰 Denmark | 189 |
| #9 | 🇳🇱 Netherlands | 189 |
| #9 | 🇸🇪 Sweden | 189 |
| #13 | 🇫🇷 France | 188 |
| #13 | 🇮🇪 Ireland | 188 |
| #13 | 🇵🇹 Portugal | 188 |
| #13 | 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 188 |
| #17 | 🇧🇪 Belgium | 187 |
| #17 | 🇨🇿 Czechia | 187 |
| #17 | 🇳🇿 New Zealand | 187 |
| #17 | 🇳🇴 Norway | 187 |
| #17 | 🇨🇭 Switzerland | 187 |
| #17 | 🇺🇸 United States | 187 |
| #23 | 🇦🇺 Australia | 186 |
| #23 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 186 |
| #23 | 🇬🇷 Greece | 186 |
| #23 | 🇲🇹 Malta | 186 |
| #27 | 🇭🇺 Hungary | 185 |
| #27 | 🇵🇱 Poland | 185 |
| #29 | 🇱🇹 Lithuania | 184 |
| #29 | 🇸🇰 Slovakia | 184 |
| #31 | 🇱🇻 Latvia | 183 |
| #31 | 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 183 |
| #33 | 🇪🇪 Estonia | 182 |
| #34 | 🇮🇸 Iceland | 181 |
| #35 | 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 180 |
| #36 | 🇱🇮 Liechtenstein | 179 |
| #37 | 🇨🇾 Cyprus | 178 |
| #37 | 🇦🇪 United Arab Emirates | 178 |
| #39 | 🇷🇴 Romania | 176 |
| #40 | 🇧🇬 Bulgaria | 175 |
| #40 | 🇨🇱 Chile | 175 |
| #40 | 🇭🇷 Croatia | 175 |
| #40 | 🇲🇨 Monaco | 175 |
| #44 | 🇭🇰 Hong Kong (SAR China) | 172 |
| #45 | 🇦🇷 Argentina | 171 |
| #46 | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 170 |
| #46 | 🇸🇲 San Marino | 170 |
| #48 | 🇦🇩 Andorra | 169 |
| #49 | 🇧🇳 Brunei | 167 |
| #50 | 🇧🇧 Barbados | 162 |
| #51 | 🇮🇱 Israel | 160 |
| #51 | 🇲🇽 Mexico | 160 |
| #53 | 🇰🇳 St. Kitts and Nevis | 156 |
| #54 | 🇧🇸 Bahamas | 155 |
| #55 | 🇻🇦 Vatican City | 154 |
| #56 | 🇸🇨 Seychelles | 153 |
| #56 | 🇺🇾 Uruguay | 153 |
| #58 | 🇻🇨 St. Vincent and the Grenadines | 151 |
| #59 | 🇦🇬 Antigua and Barbuda | 150 |
| #59 | 🇨🇷 Costa Rica | 150 |
| #59 | 🇹🇹 Trinidad and Tobago | 150 |
| #62 | 🇲🇺 Mauritius | 146 |
| #63 | 🇱🇨 St. Lucia | 146 |
| #63 | 🇹🇼 Taiwan | 146 |
| #65 | 🇬🇩 Grenada | 145 |
| #66 | 🇩🇲 Dominica | 144 |
| #66 | 🇲🇴 Macao (SAR China) | 144 |
| #66 | 🇺🇦 Ukraine | 144 |
| #69 | 🇵🇦 Panama | 143 |
| #70 | 🇵🇾 Paraguay | 141 |
| #71 | 🇷🇸 Serbia | 137 |
| #72 | 🇵🇪 Peru | 136 |
| #73 | 🇨🇴 Colombia | 133 |
| #73 | 🇬🇹 Guatemala | 133 |
| #73 | 🇭🇳 Honduras | 133 |
| #76 | 🇸🇻 El Salvador | 132 |
| #77 | 🇼🇸 Samoa | 131 |
| #77 | 🇸🇧 Solomon Islands | 131 |
| #79 | 🇹🇴 Tonga | 129 |
| #80 | 🇻🇪 Venezuela | 128 |
| #81 | 🇳🇮 Nicaragua | 127 |
| #81 | 🇹🇻 Tuvalu | 127 |
| #83 | 🇲🇰 North Macedonia | 125 |
| #84 | 🇲🇪 Montenegro | 124 |
| #85 | 🇰🇮 Kiribati | 123 |
| #86 | 🇲🇭 Marshall Islands | 122 |
| #87 | 🇲🇩 Moldova | 120 |
| #88 | 🇵🇼 Palau Islands | 119 |
| #89 | 🇧🇦 Bosnia and Herzegovina | 118 |
| #89 | 🇫🇲 Micronesia | 118 |
| #89 | 🇷🇺 Russia | 118 |
| #92 | 🇦🇱 Albania | 115 |
| #92 | 🇬🇪 Georgia | 115 |
| #94 | 🇹🇷 Türkiye | 111 |
| #95 | 🇿🇦 South Africa | 106 |
| #96 | 🇧🇿 Belize | 102 |
| #97 | 🇶🇦 Qatar | 100 |
| #98 | 🇰🇼 Kuwait | 97 |
| #98 | 🇻🇺 Vanuatu | 97 |
| #100 | 🇹🇱 Timor-Leste | 94 |
| #101 | 🇪🇨 Ecuador | 92 |
| #102 | 🇲🇻 Maldives | 89 |
| #102 | 🇳🇷 Nauru | 89 |
| #104 | 🇧🇭 Bahrain | 87 |
| #104 | 🇫🇯 Fiji | 87 |
| #104 | 🇬🇾 Guyana | 87 |
| #107 | 🇧🇼 Botswana | 86 |
| #107 | 🇯🇲 Jamaica | 86 |
| #109 | 🇴🇲 Oman | 82 |
| #109 | 🇵🇬 Papua New Guinea | 82 |
| #109 | 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | 82 |
| #112 | 🇨🇳 China | 81 |
| #113 | 🇧🇾 Belarus | 79 |
| #113 | 🇧🇴 Bolivia | 79 |
| #113 | 🇹🇭 Thailand | 79 |
| #116 | 🇳🇦 Namibia | 78 |
| #117 | 🇱🇸 Lesotho | 77 |
| #117 | 🇸🇷 Suriname | 77 |
| #119 | 🇰🇿 Kazakhstan | 75 |
| #120 | 🇸🇿 Eswatini | 74 |
| #121 | 🇲🇼 Malawi | 73 |
| #122 | 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 72 |
| #122 | 🇰🇪 Kenya | 72 |
| #124 | 🇹🇿 Tanzania | 71 |
| #124 | 🇹🇳 Tunisia | 71 |
| #126 | 🇩🇴 Dominican Republic | 70 |
| #126 | 🇿🇲 Zambia | 70 |
| #128 | 🇦🇿 Azerbaijan | 69 |
| #129 | 🇬🇲 The Gambia | 68 |
| #130 | 🇵🇭 Philippines | 67 |
| #131 | 🇺🇬 Uganda | 66 |
| #132 | 🇦🇲 Armenia | 65 |
| #132 | 🇨🇻 Cape Verde Islands | 65 |
| #132 | 🇲🇦 Morocco | 65 |
| #132 | 🇿🇼 Zimbabwe | 65 |
| #136 | 🇨🇺 Cuba | 64 |
| #136 | 🇬🇭 Ghana | 64 |
| #136 | 🇸🇱 Sierra Leone | 64 |
| #139 | 🇰🇬 Kyrgyzstan | 63 |
| #140 | 🇲🇳 Mongolia | 61 |
| #140 | 🇲🇿 Mozambique | 61 |
| #142 | 🇧🇯 Benin | 60 |
| #142 | 🇮🇳 India | 60 |
| #142 | 🇷🇼 Rwanda | 60 |
| #145 | 🇸🇹 Sao Tome and Principe | 59 |
| #145 | 🇹🇯 Tajikistan | 59 |
| #145 | 🇺🇿 Uzbekistan | 59 |
| #148 | 🇲🇷 Mauritania | 58 |
| #149 | 🇧🇫 Burkina Faso | 57 |
| #150 | 🇨🇮 Cote d'Ivoire | 56 |
| #150 | 🇬🇦 Gabon | 56 |
| #150 | 🇸🇳 Senegal | 56 |
| #153 | 🇬🇶 Equatorial Guinea | 55 |
| #153 | 🇬🇳 Guinea | 55 |
| #153 | 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 55 |
| #156 | 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 54 |
| #156 | 🇲🇬 Madagascar | 54 |
| #156 | 🇹🇬 Togo | 54 |
| #159 | 🇪🇬 Egypt | 53 |
| #159 | 🇯🇴 Jordan | 53 |
| #159 | 🇲🇱 Mali | 53 |
| #159 | 🇳🇪 Niger | 53 |
| #163 | 🇩🇿 Algeria | 52 |
| #163 | 🇧🇹 Bhutan | 52 |
| #163 | 🇨🇫 Central African Republic | 52 |
| #163 | 🇹🇩 Chad | 52 |
| #163 | 🇰🇲 Comoros | 52 |
| #163 | 🇬🇼 Guinea-Bissau | 52 |
| #163 | 🇹🇲 Turkmenistan | 52 |
| #170 | 🇨🇲 Cameroon | 51 |
| #171 | 🇦🇴 Angola | 50 |
| #171 | 🇱🇦 Laos | 50 |
| #173 | 🇧🇮 Burundi | 49 |
| #173 | 🇨🇬 Congo (Rep.) | 49 |
| #173 | 🇱🇷 Liberia | 49 |
| #176 | 🇩🇯 Djibouti | 48 |
| #176 | 🇭🇹 Haiti | 48 |
| #178 | 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 47 |
| #179 | 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | 46 |
| #179 | 🇳🇬 Nigeria | 46 |
| #181 | 🇪🇷 Eritrea | 44 |
| #181 | 🇮🇷 Iran | 44 |
| #181 | 🇸🇸 South Sudan | 44 |
| #184 | 🇨🇩 Democratic Republic of the Congo | 42 |
| #184 | 🇸🇩 Sudan | 42 |
| #186 | 🇽🇰 Kosovo | 41 |
| #186 | 🇱🇧 Lebanon | 41 |
| #186 | 🇱🇰 Sri Lanka | 41 |
| #189 | 🇧🇩 Bangladesh | 40 |
| #189 | 🇱🇾 Libya | 40 |
| #189 | 🇰🇵 North Korea | 40 |
| #192 | 🇵🇸 Palestine | 38 |
| #193 | 🇳🇵 Nepal | 37 |
| #194 | 🇸🇴 Somalia | 35 |
| #195 | 🇾🇪 Yemen | 34 |
| #196 | 🇵🇰 Pakistan | 32 |
| #197 | 🇸🇾 Syria | 30 |
| #198 | 🇮🇶 Iraq | 29 |
| #199 | Afghanistan | 27 |
Visas are imposed by some countries to make it easier to track visitors, allowing a country to assess whether said passport-holder may be a risk for illegal immigration, crime, acts of terror, or covert surveillance.
For example, both Russia and China require American passport holders to obtain visas prior to travel, and vice versa.
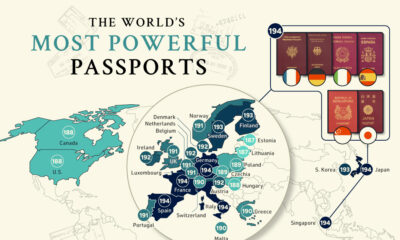
The Most Powerful Passports
When it comes to the most powerful passports, most of the top 20 are issued by countries in Asia or Europe, with the exception of New Zealand and the United States.
Due to multiple ties in the rankings the U.S. technically ranks 17th, having visa-free access to 187 countries, on par with Norway, New Zealand, and Switzerland.
Ranking 66th, Ukraine’s passport has actually seen drastic improvement over the last decade, currently getting visa-free access to 144 countries. It has yet to be seen how this will change in the wake of the Russia/Ukraine conflict.
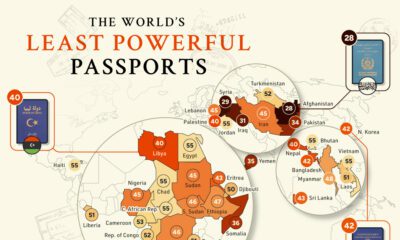
The Least Powerful Passports
Many of least powerful passports come out of war-torn and politically unstable nations. As visas for travel are typically required to counter illicit activity, these nations are often flagged whether justly or not.
One immediate standout among the least powerful passports is North Korea. The insular nation has visa-free access to 40 countries, ranking it above eight other passports on the list.
Most North Koreans who travel abroad do so only in extremely special circumstances for work, study, or athletic competitions. Leisure travel out of North Korea does not happen, but technically, North Koreans can visit countries like Haiti, St. Vincent & the Grenadines, Palestine, and Kyrgyzstan, among others without a visa.
The Biggest Gainers & Losers Over Time
From a big picture standpoint, the world’s travelers have seen their access improve significantly over the last 10 years. If you’re a citizen of the UAE, for example, your prospects for visa-free travel have improved by 100+ countries over the last decade.
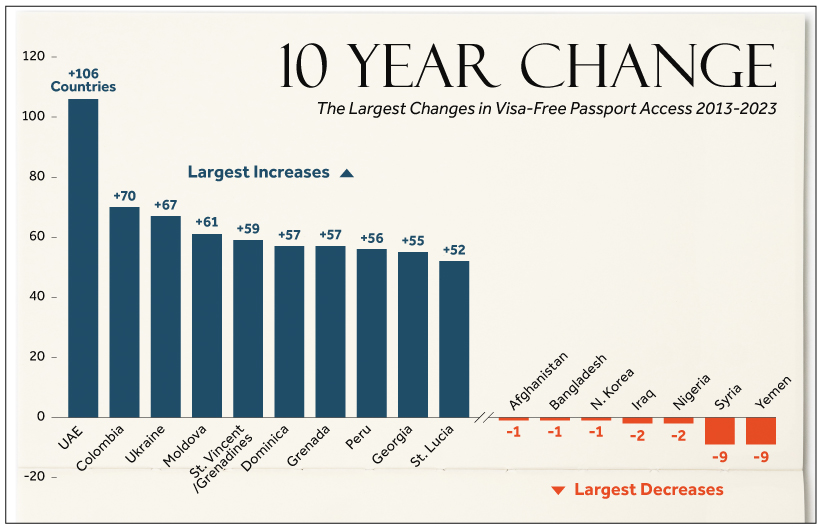
Here’s a closer look at 15 countries with the greatest change in visa-free access:
| Rank | Country | 2013 Visa-Free Access | 2023 Visa-Free Access | 10 Year Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 🇦🇪 United Arab Emirates | 72 | 178 | +106 |
| #2 | 🇨🇴 Colombia | 63 | 133 | +70 |
| #3 | 🇺🇦 Ukraine | 77 | 144 | +67 |
| #4 | 🇲🇩 Moldova | 59 | 120 | +61 |
| #5 | 🇻🇨 St. Vincent and the Grenadines | 92 | 151 | +59 |
| #6 | 🇩🇲 Dominica | 87 | 144 | +57 |
| #6 | 🇬🇩 Grenada | 88 | 145 | +57 |
| #8 | 🇵🇪 Peru | 80 | 136 | +56 |
| #9 | 🇬🇪 Georgia | 60 | 115 | +55 |
| #10 | 🇱🇨 St. Lucia | 94 | 146 | +52 |
| #11 | 🇼🇸 Samoa | 81 | 131 | +50 |
| #11 | 🇹🇹 Trinidad and Tobago | 100 | 150 | +50 |
| #13 | 🇹🇴 Tonga | 80 | 129 | +49 |
| #14 | 🇸🇧 Solomon Islands | 84 | 131 | +47 |
| #15 | 🇭🇷 Croatia | 129 | 175 | +46 |
On the other hand, other countries have fared poorly, with some actually losing access to destinations since 2013. Yemen and Syria are tied for first place, having lost visa-free access to nine countries over the last 10 years.
Here’s a look at 15 countries who experienced the biggest negative change:
| Rank | Country | 2013 Visa-Free Access | 2023 Visa-Free Access | 10 Year Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 🇾🇪 Yemen | 43 | 34 | -9 |
| #1 | 🇸🇾 Syria | 39 | 30 | -9 |
| #3 | 🇳🇬 Nigeria | 48 | 46 | -2 |
| #3 | 🇮🇶 Iraq | 31 | 29 | -2 |
| #5 | 🇰🇵 North Korea | 41 | 40 | -1 |
| #5 | 🇧🇩 Bangladesh | 41 | 40 | -1 |
| #5 | 🇦🇫 Afghanistan | 28 | 27 | -1 |
| #8 | 🇻🇪 Venezuela | 128 | 128 | 0 |
| #8 | 🇬🇲 The Gambia | 68 | 68 | 0 |
| #8 | 🇵🇰 Pakistan | 32 | 32 | 0 |
| #8 | 🇳🇪 Niger | 53 | 53 | 0 |
| #8 | 🇳🇵 Nepal | 37 | 37 | 0 |
| #8 | 🇲🇱 Mali | 53 | 53 | 0 |
| #14 | 🇹🇬 Togo | 53 | 54 | +1 |
| #14 | 🇸🇱 Sierra Leone | 63 | 64 | +1 |
Looking at the tables above, it’s apparent that the world has generally become more open in recent years.
Overall, the power of a passport is almost directly reflective of the political state of the world. World powers and rich nations typically have free flow of travel, but those facing instability or war are often also face barriers when wanting to go abroad.
Economy
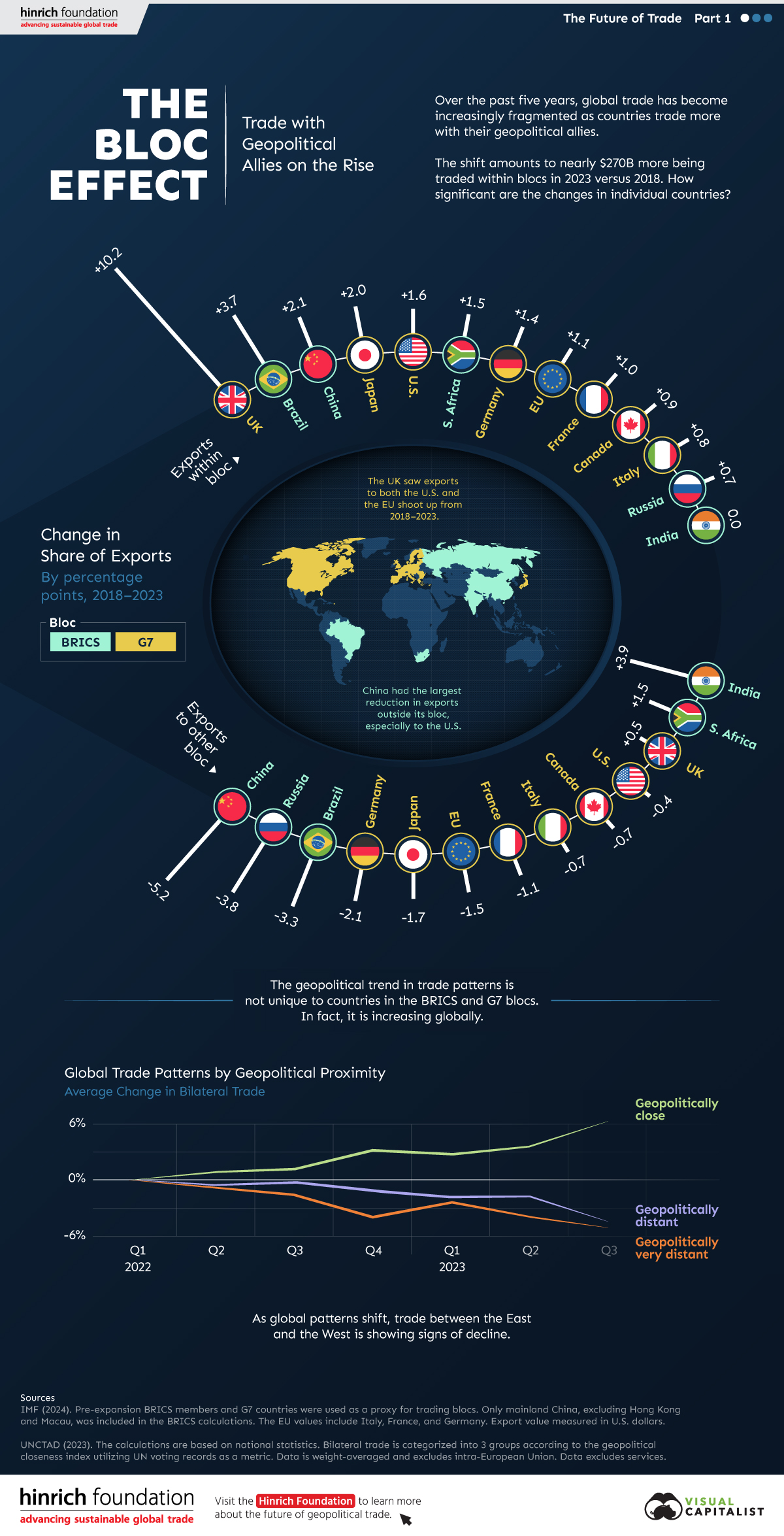
The Bloc Effect: International Trade with Geopolitical Allies on the Rise
Rising geopolitical tensions are shaping the future of international trade, but what is the effect on trading among G7 and BRICS countries?

The Bloc Effect: International Trade with Allies on the Rise
International trade has become increasingly fragmented over the last five years as countries have shifted to trading more with their geopolitical allies.
This graphic from The Hinrich Foundation, the first in a three-part series covering the future of trade, provides visual context to the growing divide in trade in G7 and pre-expansion BRICS countries, which are used as proxies for geopolitical blocs.
Trade Shifts in G7 and BRICS Countries
This analysis uses IMF data to examine differences in shares of exports within and between trading blocs from 2018 to 2023. For example, we looked at the percentage of China’s exports with other BRICS members as well as with G7 members to see how these proportions shifted in percentage points (pp) over time.
Countries traded nearly $270 billion more with allies in 2023 compared to 2018. This shift came at the expense of trade with rival blocs, which saw a decline of $314 billion.
Country Change in Exports Within Bloc (pp) Change in Exports With Other Bloc (pp)
🇮🇳 India 0.0 3.9
🇷🇺 Russia 0.7 -3.8
🇮🇹 Italy 0.8 -0.7
🇨🇦 Canada 0.9 -0.7
🇫🇷 France 1.0 -1.1
🇪🇺 EU 1.1 -1.5
🇩🇪 Germany 1.4 -2.1
🇿🇦 South Africa 1.5 1.5
🇺🇸 U.S. 1.6 -0.4
🇯🇵 Japan 2.0 -1.7
🇨🇳 China 2.1 -5.2
🇧🇷 Brazil 3.7 -3.3
🇬🇧 UK 10.2 0.5
All shifts reported are in percentage points. For example, the EU saw its share of exports to G7 countries rise from 74.3% in 2018 to 75.4% in 2023, which equates to a 1.1 percentage point increase.
The UK saw the largest uptick in trading with other countries within the G7 (+10.2 percentage points), namely the EU, as the post-Brexit trade slump to the region recovered.
Meanwhile, the U.S.-China trade dispute caused China’s share of exports to the G7 to fall by 5.2 percentage points from 2018 to 2023, the largest decline in our sample set. In fact, partly as a result of the conflict, the U.S. has by far the highest number of harmful tariffs in place.
The Russia-Ukraine War and ensuing sanctions by the West contributed to Russia’s share of exports to the G7 falling by 3.8 percentage points over the same timeframe.
India, South Africa, and the UK bucked the trend and continued to witness advances in exports with the opposing bloc.
Average Trade Shifts of G7 and BRICS Blocs
Though results varied significantly on a country-by-country basis, the broader trend towards favoring geopolitical allies in international trade is clear.
Bloc Change in Exports Within Bloc (pp) Change in Exports With Other Bloc (pp)
Average 2.1 -1.1
BRICS 1.6 -1.4
G7 incl. EU 2.4 -1.0
Overall, BRICS countries saw a larger shift away from exports with the other bloc, while for G7 countries the shift within their own bloc was more pronounced. This implies that though BRICS countries are trading less with the G7, they are relying more on trade partners outside their bloc to make up for the lost G7 share.
A Global Shift in International Trade and Geopolitical Proximity
The movement towards strengthening trade relations based on geopolitical proximity is a global trend.
The United Nations categorizes countries along a scale of geopolitical proximity based on UN voting records.
According to the organization’s analysis, international trade between geopolitically close countries rose from the first quarter of 2022 (when Russia first invaded Ukraine) to the third quarter of 2023 by over 6%. Conversely, trade with geopolitically distant countries declined.
The second piece in this series will explore China’s gradual move away from using the U.S. dollar in trade settlements.

Visit the Hinrich Foundation to learn more about the future of geopolitical trade

-

 Economy1 day ago
Economy1 day agoEconomic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?
-

 United States1 week ago
United States1 week agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
We visualized the top U.S. companies by employees, revealing the massive scale of retailers like Walmart, Target, and Home Depot.
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
We visualized product categories that saw the highest % increase in price due to U.S. inflation as of March 2024.
-

 Economy4 weeks ago
Economy4 weeks agoG20 Inflation Rates: Feb 2024 vs COVID Peak
We visualize inflation rates across G20 countries as of Feb 2024, in the context of their COVID-19 pandemic peak.
-

 Economy1 month ago
Economy1 month agoMapped: Unemployment Claims by State
This visual heatmap of unemployment claims by state highlights New York, California, and Alaska leading the country by a wide margin.
-
 Economy2 months ago
Economy2 months agoConfidence in the Global Economy, by Country
Will the global economy be stronger in 2024 than in 2023?
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries