Money
Visualized: The Most (and Least) Expensive Cities to Live In
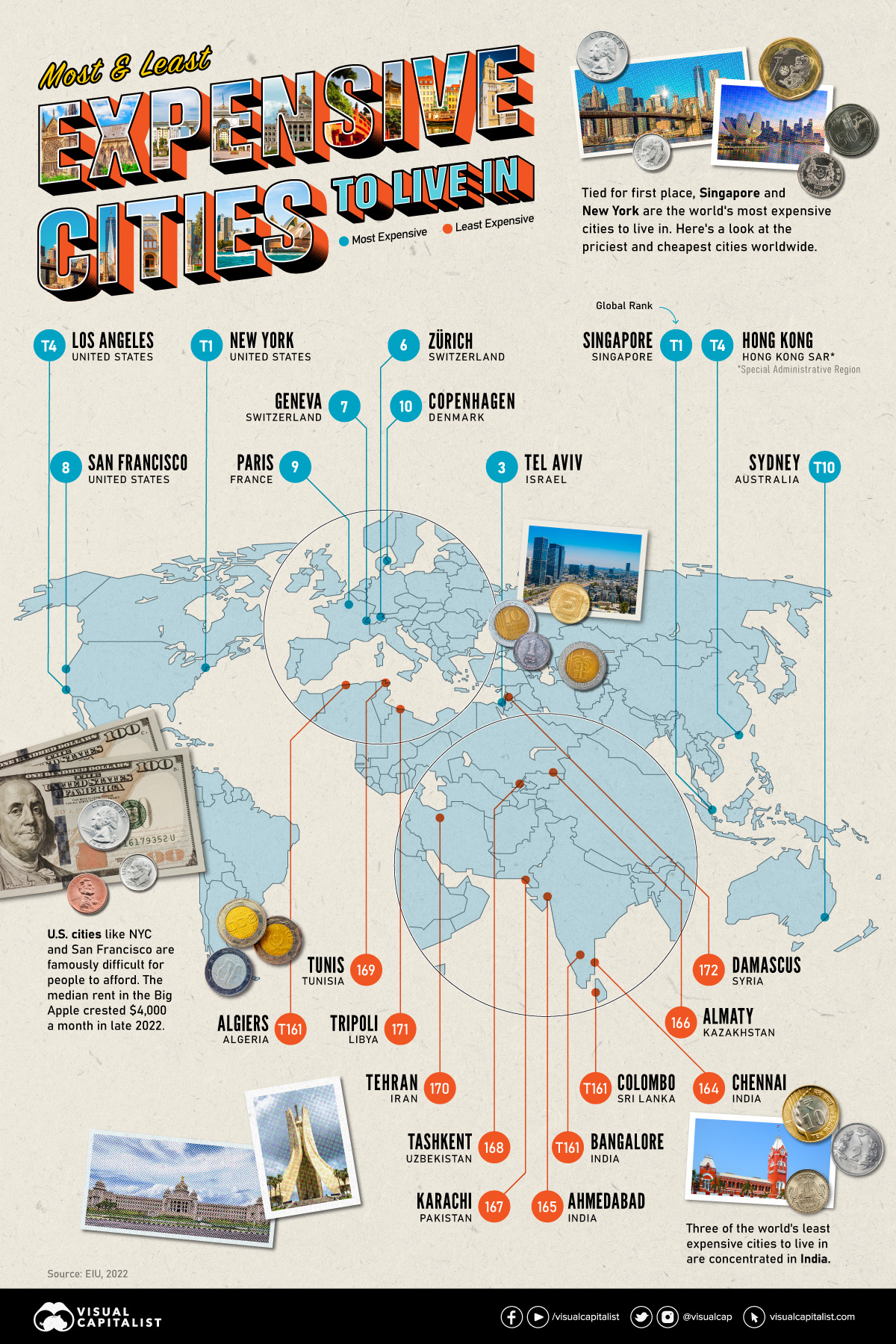
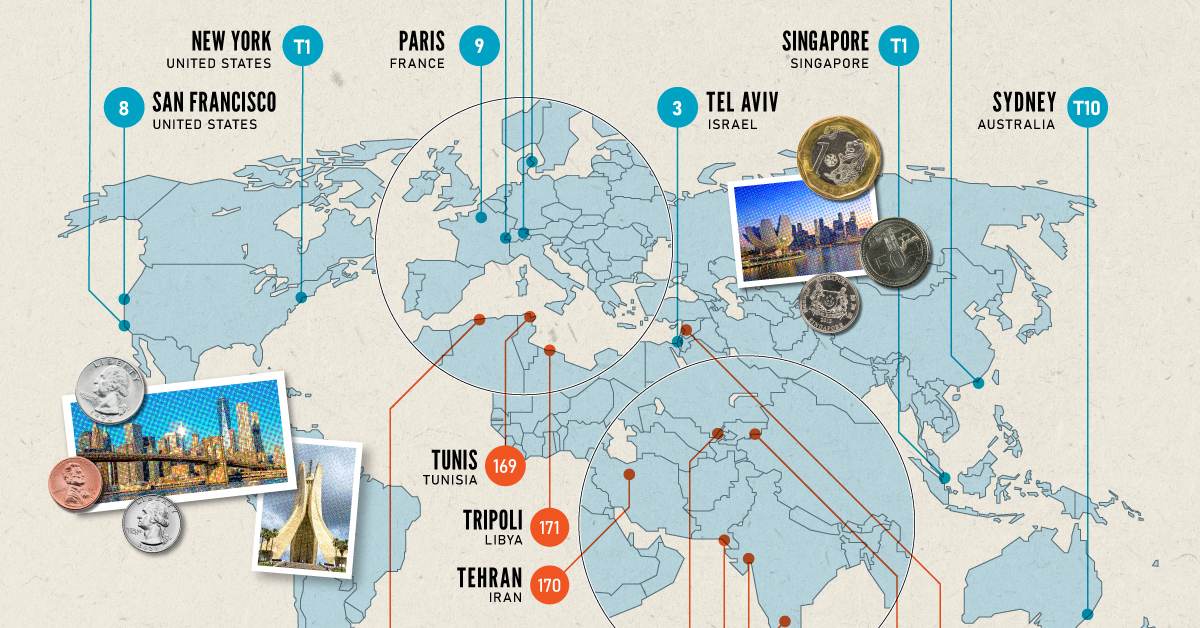
Visualizing The Most (and Least) Expensive Cities to Live In
There are many benefits to living in an iconic city like New York or Singapore, but the amenities and exclusivity can come at a high cost.
Cities become “expensive” due to a variety of factors such as high demand for housing, a concentration of high-paying businesses and industries, and a high standard of living. Additionally, factors such as taxes, transportation costs, and availability of goods and services can also contribute to the overall cost of living in global cities.
The infographic above uses data from EIU to rank the world most and least expensive cities to live in. To make the list, the EIU examines 400+ prices for over 200 products and services in 172 cities, surveying a variety of businesses to track price fluctuations over the last year.
Inflation + Strong Currency = Expensive Cities
If you live in a city where many residents find it challenging to put a roof over their heads, food on their plates, and make ends meet, you live in an expensive city.
But if this inflation is compounded with a strong national currency, you may live in one of the world’s most expensive cities.
| Rank | City | Country | Index Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Singapore | 🇸🇬 Singapore | 100 |
| #1 | New York | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 100 |
| #3 | Tel Aviv | 🇮🇱 Israel | 99 |
| #4 | Hong Kong | 🇭🇰 Hong Kong | 98 |
| #4 | Los Angeles | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 98 |
| #6 | Zurich | 🇨🇭 Switzerland | 94 |
| #7 | Geneva | 🇨🇭 Switzerland | 91 |
| #8 | San Francisco | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 85 |
| #9 | Paris | 🇫🇷 France | 84 |
| #10 | Copenhagen | 🇩🇰 Denmark | 83 |
Singapore and New York City tied for the first rank amongst the world’s most expensive cities in 2022, pushing Israel’s Tel Aviv from the first place in 2021 to the third place in 2022. Both these cities had high inflation and a strong currency. Surprisingly, this is the Big Apple’s first time atop the ranking.
The city with one of the most expensive real estate markets worldwide, Hong Kong ranked fourth in this list, followed by Los Angeles, which moved up from its ninth rank in 2021.
Poor Economies = Cheaper Cities
Asia continues to dominate the list of the world’s least expensive cities, followed by parts of North Africa and the Middle East. Though affordability sounds good at face value, sitting at the bottom of the ranking isn’t necessarily a coveted position.
While the cost of living in some of the cities in these nations is low, it comes at the price of a weak currency, poor economy, and, in many cases, political and economic turmoil.
| Rank | City | Country | Index Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| #161 | Colombo | 🇱🇰 Sri Lanka | 38 |
| #161 | Bangalore | 🇮🇳 India | 38 |
| #161 | Algiers | 🇩🇿 Algeria | 38 |
| #164 | Chennai | 🇮🇳 India | 37 |
| #165 | Ahmedabad | 🇮🇳 India | 35 |
| #166 | Almaty | 🇰🇿 Kazakhstan | 34 |
| #167 | Karachi | 🇵🇰 Pakistan | 32 |
| #168 | Tashkent | 🇺🇿 Uzbekistan | 31 |
| #169 | Tunis | 🇹🇳 Tunisia | 30 |
| #170 | Tehran | 🇮🇷 Iran | 23 |
| #171 | Tripoli | 🇱🇾 Libya | 22 |
| #172 | Dasmascus | 🇸🇾 Syria | 11 |
The decade-long conflict in Syria weakened the Syrian pound, led to a spiraling inflation and fuel shortages, and further collapsed its economy. It’s no surprise that its capital city of Damascus has maintained its position as the world’s cheapest city.
Tripoli and Tehran, the capitals of Libya and Iran, respectively, follow next on this list, reflecting their weakened economies.
Meanwhile, seven cities in Asia with the common denominator of high-income inequality and low wages dominate the list of the world’s cheapest cities. These include three Indian cities, Tashkent in Uzbekistan, Almaty in Kazakhstan, Pakistan’s most populous city of Karachi, and Sri Lankan capital–Colombo.
Money
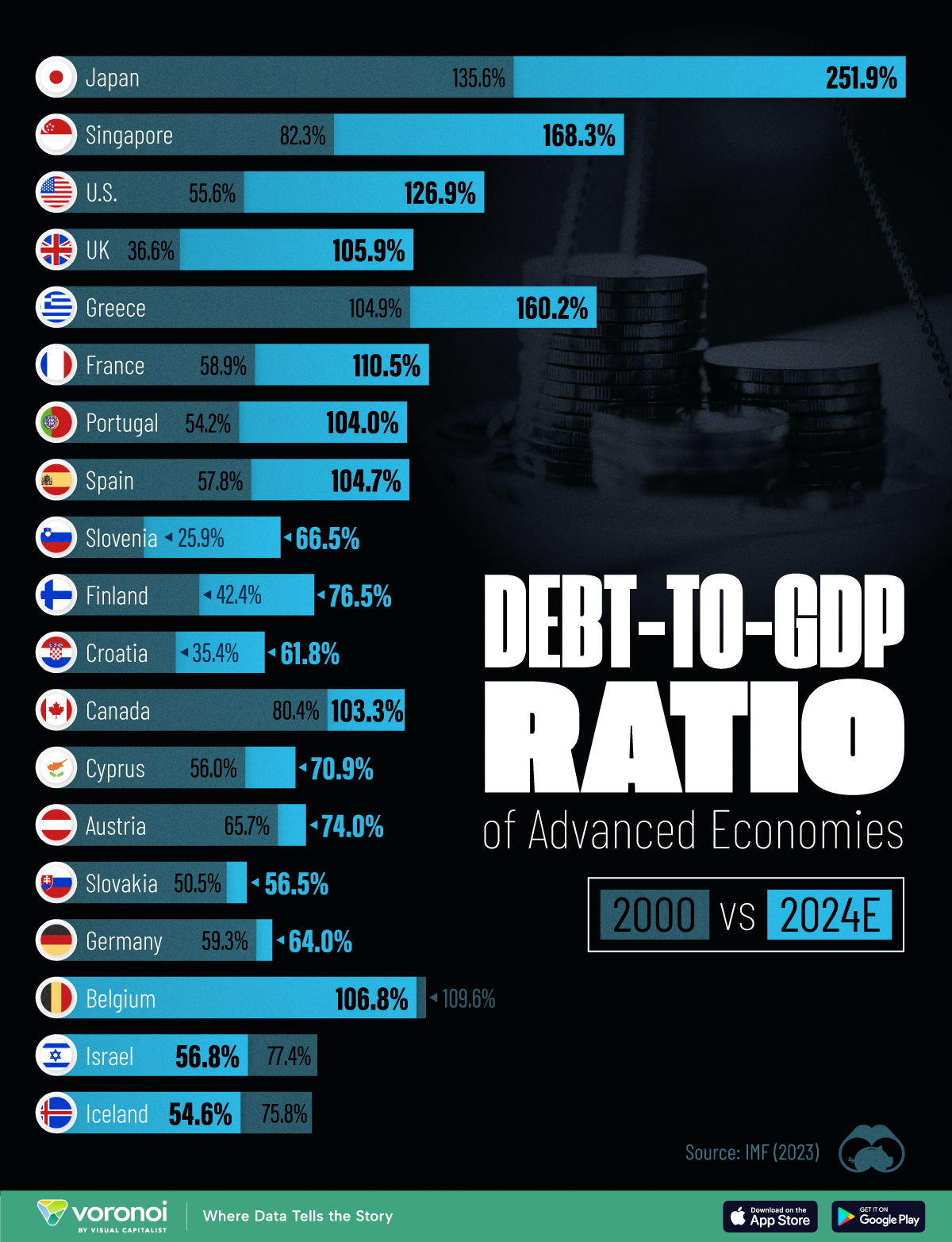
How Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
See how much the debt-to-GDP ratios of advanced economies have grown (or shrank) since the year 2000.
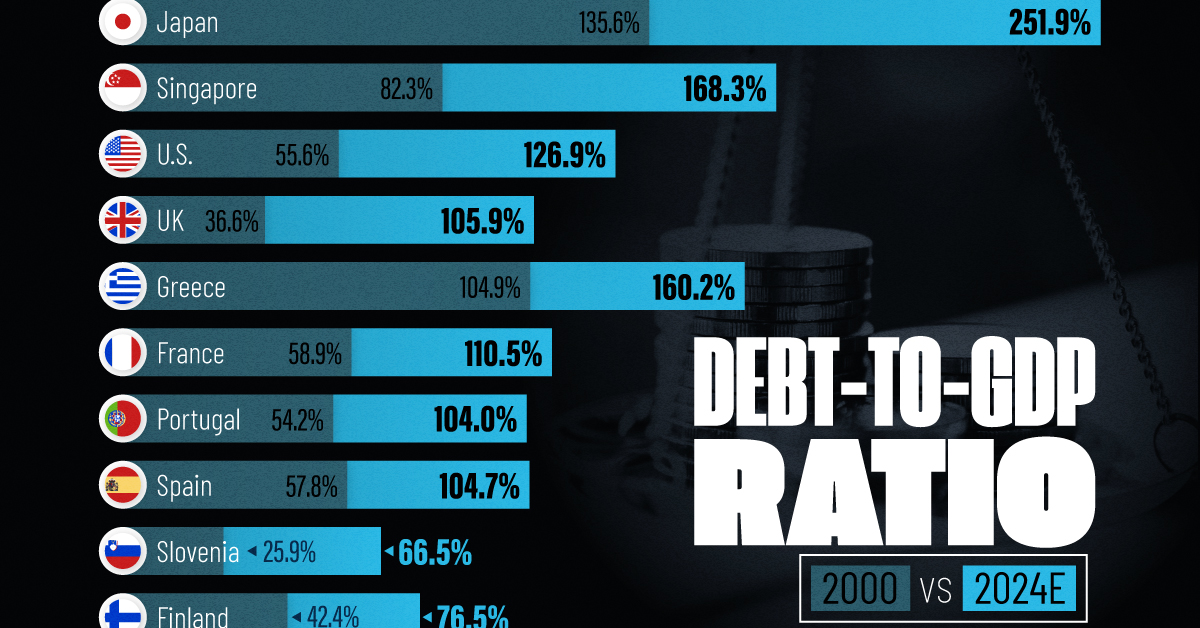
How Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Government debt levels have grown in most parts of the world since the 2008 financial crisis, and even more so after the COVID-19 pandemic.
To gain perspective on this long-term trend, we’ve visualized the debt-to-GDP ratios of advanced economies, as of 2000 and 2024 (estimated). All figures were sourced from the IMF’s World Economic Outlook.
Data and Highlights
The data we used to create this graphic is listed in the table below. “Government gross debt” consists of all liabilities that require payment(s) of interest and/or principal in the future.
| Country | 2000 (%) | 2024 (%) | Change (pp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇯🇵 Japan | 135.6 | 251.9 | +116.3 |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 82.3 | 168.3 | +86.0 |
| 🇺🇸 United States | 55.6 | 126.9 | +71.3 |
| 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 36.6 | 105.9 | +69.3 |
| 🇬🇷 Greece | 104.9 | 160.2 | +55.3 |
| 🇫🇷 France | 58.9 | 110.5 | +51.6 |
| 🇵🇹 Portugal | 54.2 | 104.0 | +49.8 |
| 🇪🇸 Spain | 57.8 | 104.7 | +46.9 |
| 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 25.9 | 66.5 | +40.6 |
| 🇫🇮 Finland | 42.4 | 76.5 | +34.1 |
| 🇭🇷 Croatia | 35.4 | 61.8 | +26.4 |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | 80.4 | 103.3 | +22.9 |
| 🇨🇾 Cyprus | 56.0 | 70.9 | +14.9 |
| 🇦🇹 Austria | 65.7 | 74.0 | +8.3 |
| 🇸🇰 Slovak Republic | 50.5 | 56.5 | +6.0 |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 59.3 | 64.0 | +4.7 |
| 🇧🇪 Belgium | 109.6 | 106.8 | -2.8 |
| 🇮🇱 Israel | 77.4 | 56.8 | -20.6 |
| 🇮🇸 Iceland | 75.8 | 54.6 | -21.2 |
The debt-to-GDP ratio indicates how much a country owes compared to the size of its economy, reflecting its ability to manage and repay debts. Percentage point (pp) changes shown above indicate the increase or decrease of these ratios.
Countries with the Biggest Increases
Japan (+116 pp), Singapore (+86 pp), and the U.S. (+71 pp) have grown their debt as a percentage of GDP the most since the year 2000.
All three of these countries have stable, well-developed economies, so it’s unlikely that any of them will default on their growing debts. With that said, higher government debt leads to increased interest payments, which in turn can diminish available funds for future government budgets.
This is a rising issue in the U.S., where annual interest payments on the national debt have surpassed $1 trillion for the first time ever.
Only 3 Countries Saw Declines
Among this list of advanced economies, Belgium (-2.8 pp), Iceland (-21.2 pp), and Israel (-20.6 pp) were the only countries that decreased their debt-to-GDP ratio since the year 2000.
According to Fitch Ratings, Iceland’s debt ratio has decreased due to strong GDP growth and the use of its cash deposits to pay down upcoming maturities.
See More Debt Graphics from Visual Capitalist
Curious to see which countries have the most government debt in dollars? Check out this graphic that breaks down $97 trillion in debt as of 2023.
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?