Misc
Millennials are Buying Their First Homes, and Here’s What They Want
Millennials are Buying Their First Homes, and Here’s What They Want
Authorities disagree on the exact birth years of the Millennial generation: for example, Pew Research defines Millennials as being born between 1981-1997, the US Census Bureau claims 1982-2000, and the National Association of Realtors says 1980-1995.
However, what all these same sources agree upon is that the Millennials are the largest and most powerful demographic force in North America.
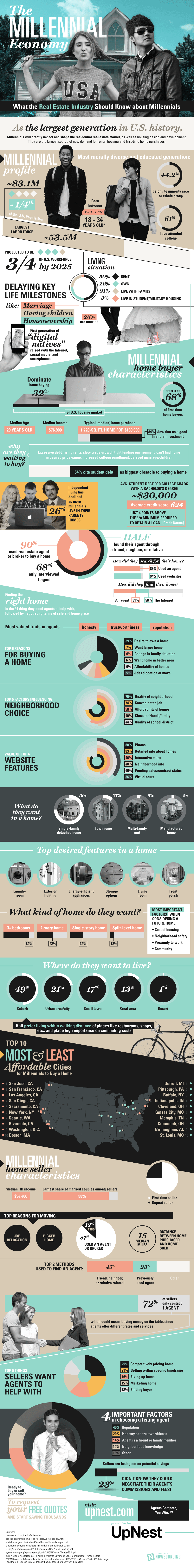
In the United States specifically, Millennials account for a quarter of the entire population with a total of 83.1 million people in the demographic. This is a group that makes up the next generation of investors, continues to struggle with mounting student debt, thinks about money differently, and is now buying homes for the first time.
Marketers in all industries have tried to nail down the preferences of Millennials for some time. Millennials have made things especially more difficult for the real estate industry, as they have delayed common life milestones such as marriage, having children, and home ownership. It is only over the last few years, as Millennials have started to buy homes in significant numbers, that the industry has truly understood what the group wants to see in a home.
Millennial home buyers make up 68% of all first-time home buyers right now, and here’s their average profile: 29 years old, a median income of $76,900, and a typical home purchase (median) of $189,900 for a 1,720 sq. ft home. Of these buyers, 84% believe a home to be a good investment.
Where do Millennials want to buy? About half of the cohort (49%) wants to buy in the suburbs, while 21% would prefer to buy in an urban area. In terms of choosing a specific neighborhood, the most-cited factors affecting Millennials’ decisions were the quality of neighborhood (75%), convenience of getting to job (74%), affordability of home (58%), proximity to friends and family (49%), and quality of the school district (44%).
Today, 32% of all home purchases are made by Millennials, but the reality is that many are still holding off on buying. The major reason for that is student debt, which 54% cited as the biggest obstacle to home ownership. In fact, about one-quarter of all Millennials still live with their parents.
Other reasons cited for not owning a home yet? They include: excessive debt, rising rents, slowing wage growth, tight-lending environment, can’t find home in desired price range, increased college enrollment, and delayed marriage/children.
Original graphic by: UpNest
VC+
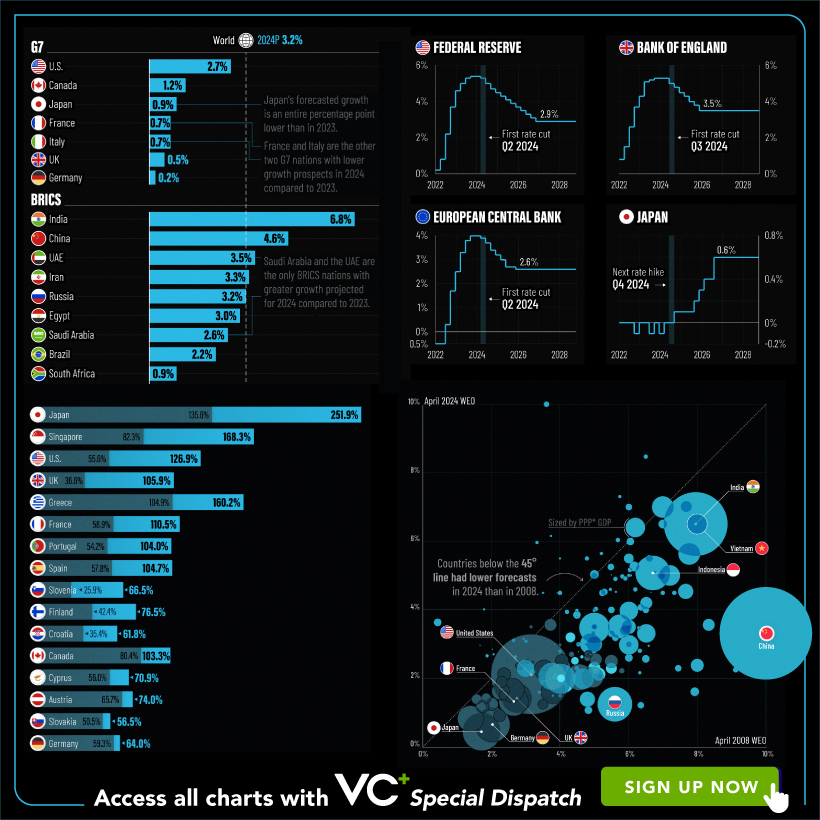
VC+: Get Our Key Takeaways From the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
A sneak preview of the exclusive VC+ Special Dispatch—your shortcut to understanding IMF’s World Economic Outlook report.

Have you read IMF’s latest World Economic Outlook yet? At a daunting 202 pages, we don’t blame you if it’s still on your to-do list.
But don’t worry, you don’t need to read the whole April release, because we’ve already done the hard work for you.
To save you time and effort, the Visual Capitalist team has compiled a visual analysis of everything you need to know from the report—and our upcoming VC+ Special Dispatch will be available exclusively to VC+ members on Thursday, April 25th.
If you’re not already subscribed to VC+, make sure you sign up now to receive the full analysis of the IMF report, and more (we release similar deep dives every week).
For now, here’s what VC+ members can expect to receive.
Your Shortcut to Understanding IMF’s World Economic Outlook
With long and short-term growth prospects declining for many countries around the world, this Special Dispatch offers a visual analysis of the key figures and takeaways from the IMF’s report including:
- The global decline in economic growth forecasts
- Real GDP growth and inflation forecasts for major nations in 2024
- When interest rate cuts will happen and interest rate forecasts
- How debt-to-GDP ratios have changed since 2000
- And much more!
Get the Full Breakdown in the Next VC+ Special Dispatch
VC+ members will receive the full Special Dispatch on Thursday, April 25th.
Make sure you join VC+ now to receive exclusive charts and the full analysis of key takeaways from IMF’s World Economic Outlook.
Don’t miss out. Become a VC+ member today.
What You Get When You Become a VC+ Member
VC+ is Visual Capitalist’s premium subscription. As a member, you’ll get the following:
- Special Dispatches: Deep dive visual briefings on crucial reports and global trends
- Markets This Month: A snappy summary of the state of the markets and what to look out for
- The Trendline: Weekly curation of the best visualizations from across the globe
- Global Forecast Series: Our flagship annual report that covers everything you need to know related to the economy, markets, geopolitics, and the latest tech trends
- VC+ Archive: Hundreds of previously released VC+ briefings and reports that you’ve been missing out on, all in one dedicated hub
You can get all of the above, and more, by joining VC+ today.
-

 Green1 week ago
Green1 week agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Travel2 weeks ago
Travel2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue