Demographics
Meet Generation Z: The Newest Member to the Workforce
Every generation approaches the workplace differently.
While talk over the last decade has largely focused on understanding the work habits and attitudes of Millennials, it’s already time for a new generation to enter the fold.
Generation Z, the group born after the Millennials, is entering their early adult years and starting their young careers. What makes them different, and how will they approach things differently than past generations?
Meet Generation Z
Today’s infographic comes to us from ZeroCater, and it will help introduce you to the newest entrant to the modern workforce: Generation Z.
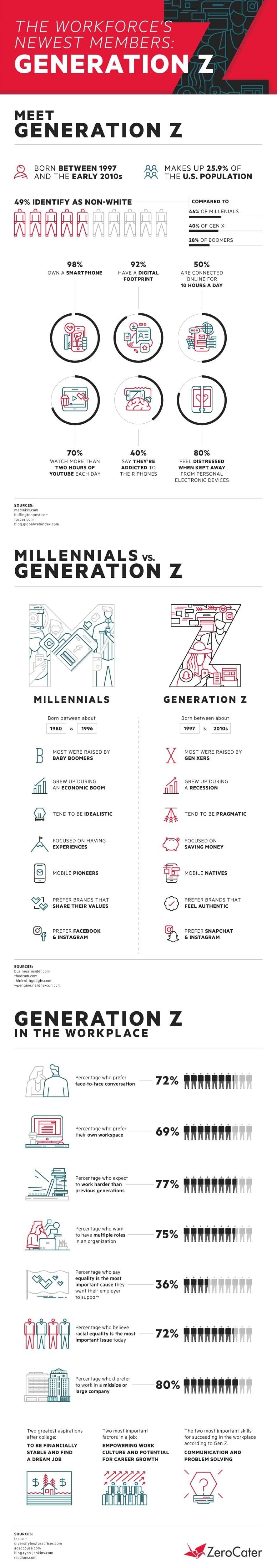
There is no exact consensus on the definition of Generation Z, and demographers can differ on where it starts. Some have Gen Z beginning as early as the mid-1990s, while others see it starting in the mid-2000s.
Regardless, Generation Z is the group that follows the Millennials – and many Gen Zers are wrapping up high school, finishing up their university degrees, or looking to get their first real jobs.
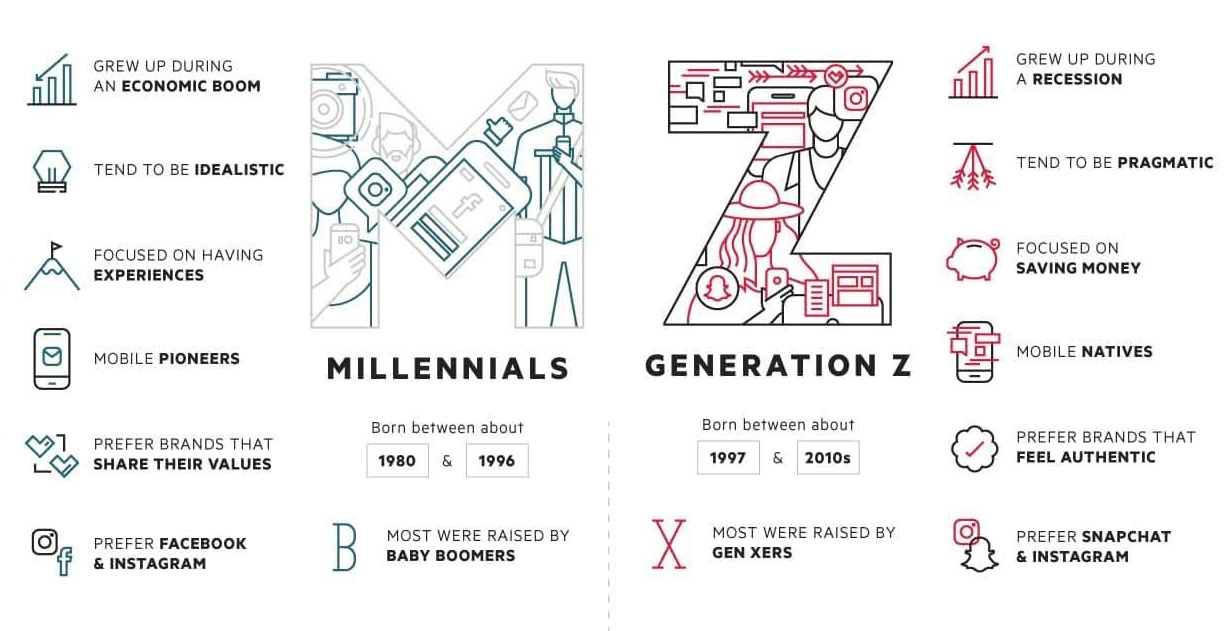
Millennials vs. Gen Z
While generational differences cast a wide net and don’t necessarily apply to every individual, here is what demographers say are some key similarities and differences between Gen Z and Millennials.
| Millennials | Generation Z |
|---|---|
| Raised by Baby Boomers | Raised by Gen Xers |
| Grew up during an economic boom | Grew up during a recession |
| Tend to be idealistic | Tend to be pragmatic |
| Focused on having experiences | Focused on saving money |
| Mobile pioneers | Mobile natives |
| Prefer brands that share their values | Prefer brands that feel authentic |
| Prefer Facebook and Instagram | Prefer Snapchat and Instagram |
Generation Z tends to be more pragmatic, approaching both their education and career differently than Millennials. It appears that Gen Z is also approaching money in a unique way compared to past groups.
What to Expect?
Generation Z does not remember a time when the internet did not exist – and as such, it’s not surprising to learn that 50% of Gen Z spends 10 hours a day connected online, and 70% watches YouTube for two hours a day or more.
But put aside this ultra-connectivity, and Gen Zers have some unique and possibly unexpected traits. Gen Z prefers face-to-face interactions in the workplace, and also expects to work harder than past groups. Gen Z is also the most diverse generation (49% non-white) and values racial equality as a top issue. Finally, Gen Z is possibly one of the most practical generations, valuing things like saving money and getting stable jobs.
You may already have Gen Zers in your workplace – but if you don’t, you will soon.
Demographics
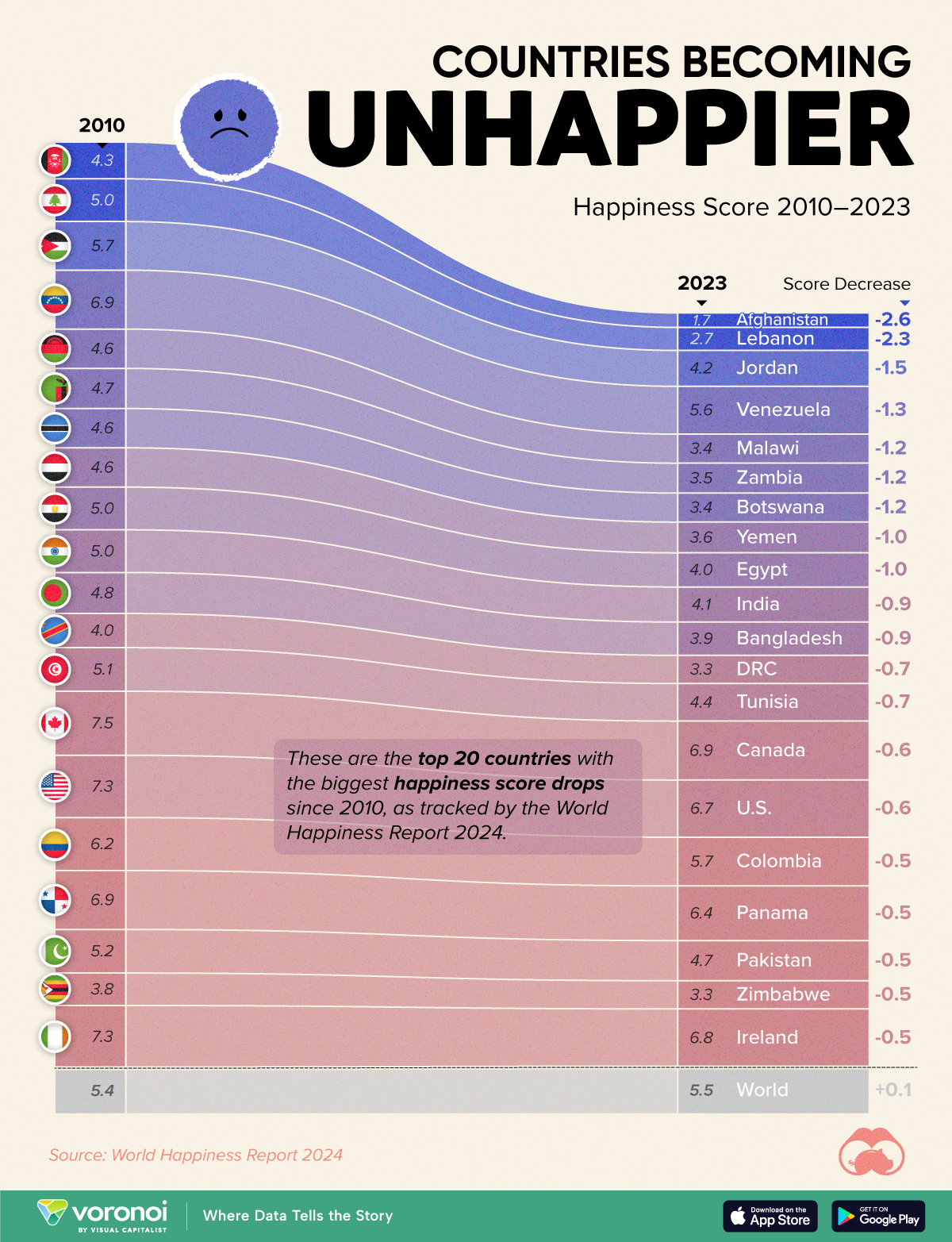
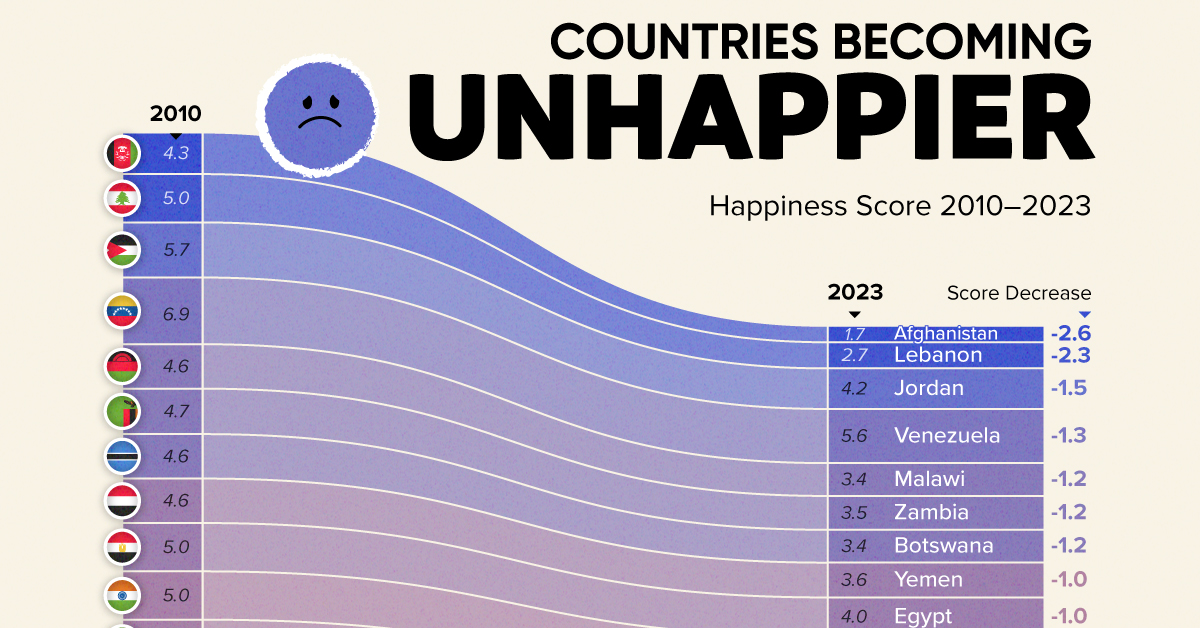
The Countries That Have Become Sadder Since 2010
Tracking Gallup survey data for more than a decade reveals some countries are witnessing big happiness declines, reflecting their shifting socio-economic conditions.
The Countries That Have Become Sadder Since 2010
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Can happiness be quantified?
Some approaches that try to answer this question make a distinction between two differing components of happiness: a daily experience part, and a more general life evaluation (which includes how people think about their life as a whole).
The World Happiness Report—first launched in 2012—has been making a serious go at quantifying happiness, by examining Gallup poll data that asks respondents in nearly every country to evaluate their life on a 0–10 scale. From this they extrapolate a single “happiness score” out of 10 to compare how happy (or unhappy) countries are.
More than a decade later, the 2024 World Happiness Report continues the mission. Its latest findings also include how some countries have become sadder in the intervening years.
Which Countries Have Become Unhappier Since 2010?
Afghanistan is the unhappiest country in the world right now, and is also 60% unhappier than over a decade ago, indicating how much life has worsened since 2010.
In 2021, the Taliban officially returned to power in Afghanistan, after nearly two decades of American occupation in the country. The Islamic fundamentalist group has made life harder, especially for women, who are restricted from pursuing higher education, travel, and work.
On a broader scale, the Afghan economy has suffered post-Taliban takeover, with various consequent effects: mass unemployment, a drop in income, malnutrition, and a crumbling healthcare system.
| Rank | Country | Happiness Score Loss (2010–24) | 2024 Happiness Score (out of 10) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇦🇫 Afghanistan | -2.6 | 1.7 |
| 2 | 🇱🇧 Lebanon | -2.3 | 2.7 |
| 3 | 🇯🇴 Jordan | -1.5 | 4.2 |
| 4 | 🇻🇪 Venezuela | -1.3 | 5.6 |
| 5 | 🇲🇼 Malawi | -1.2 | 3.4 |
| 6 | 🇿🇲 Zambia | -1.2 | 3.5 |
| 7 | 🇧🇼 Botswana | -1.2 | 3.4 |
| 8 | 🇾🇪 Yemen | -1.0 | 3.6 |
| 9 | 🇪🇬 Egypt | -1.0 | 4.0 |
| 10 | 🇮🇳 India | -0.9 | 4.1 |
| 11 | 🇧🇩 Bangladesh | -0.9 | 3.9 |
| 12 | 🇨🇩 DRC | -0.7 | 3.3 |
| 13 | 🇹🇳 Tunisia | -0.7 | 4.4 |
| 14 | 🇨🇦 Canada | -0.6 | 6.9 |
| 15 | 🇺🇸 U.S. | -0.6 | 6.7 |
| 16 | 🇨🇴 Colombia | -0.5 | 5.7 |
| 17 | 🇵🇦 Panama | -0.5 | 6.4 |
| 18 | 🇵🇰 Pakistan | -0.5 | 4.7 |
| 19 | 🇿🇼 Zimbabwe | -0.5 | 3.3 |
| 20 | 🇮🇪 Ireland | -0.5 | 6.8 |
| N/A | 🌍 World | +0.1 | 5.5 |
Nine countries in total saw their happiness score drop by a full point or more, on the 0–10 scale.
Noticeably, many of them have seen years of social and economic upheaval. Lebanon, for example, has been grappling with decades of corruption, and a severe liquidity crisis since 2019 that has resulted in a banking system collapse, sending poverty levels skyrocketing.
In Jordan, unprecedented population growth—from refugees leaving Iraq and Syria—has aggravated unemployment rates. A somewhat abrupt change in the line of succession has also raised concerns about political stability in the country.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
-

 Green3 weeks ago
Green3 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?