Misc
Mapped: Each Region’s Median Age Since 1950
Mapped: Each Region’s Median Age Since 1950
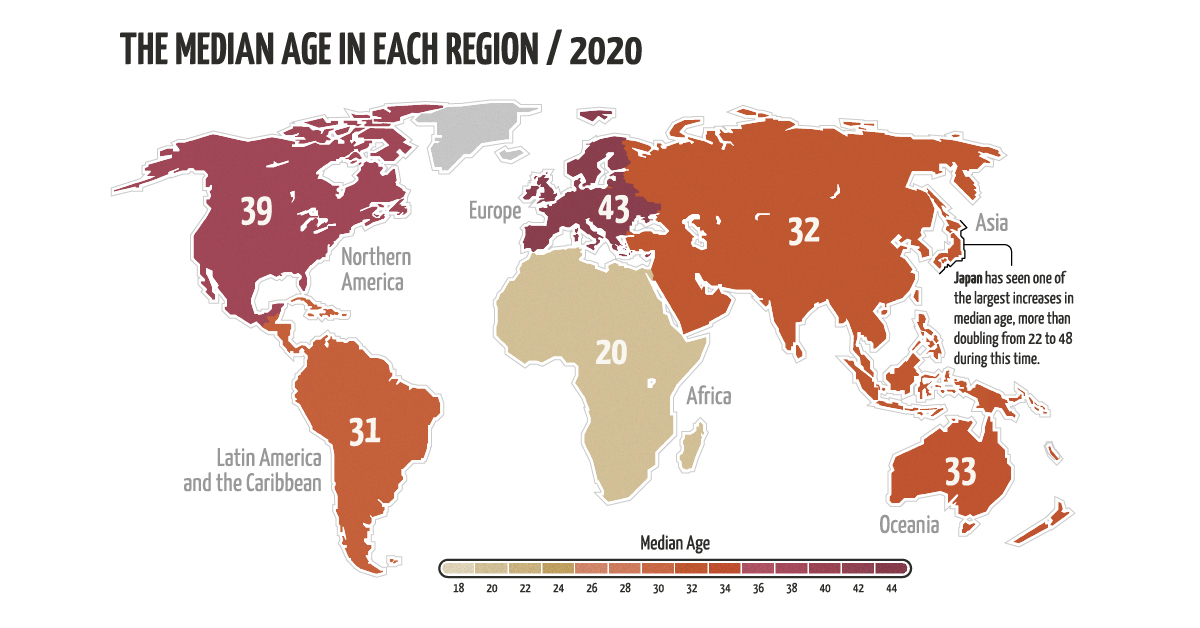
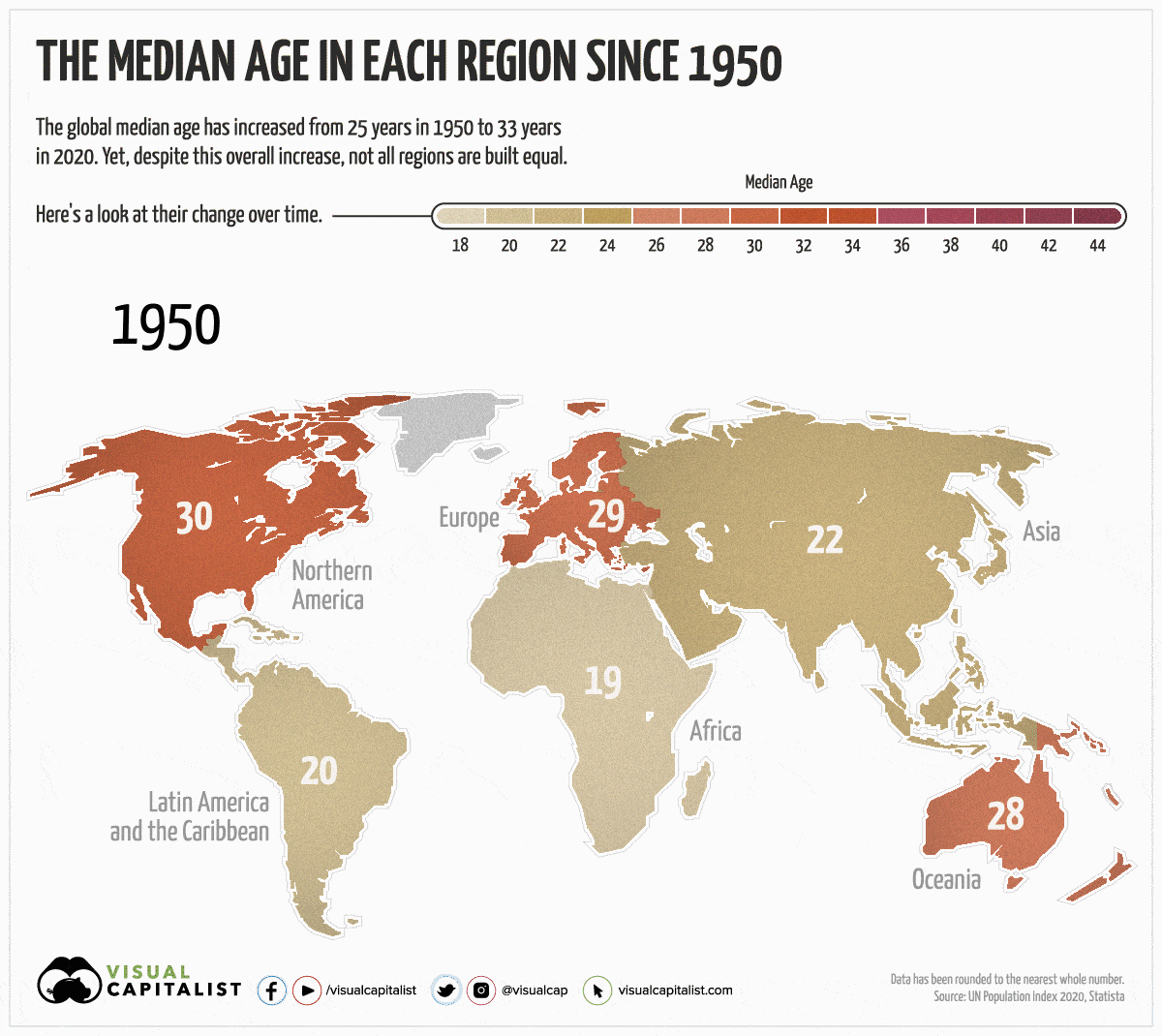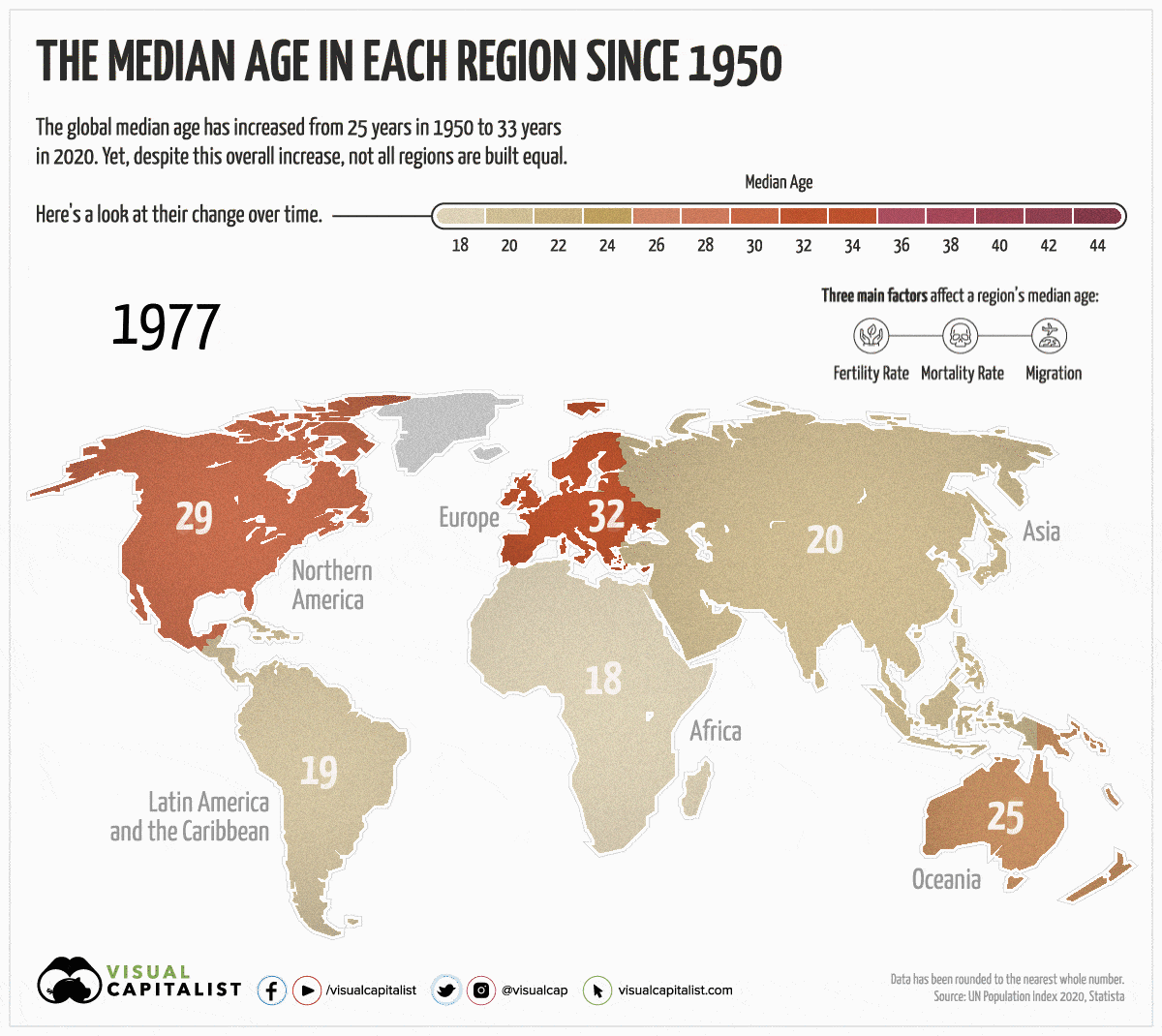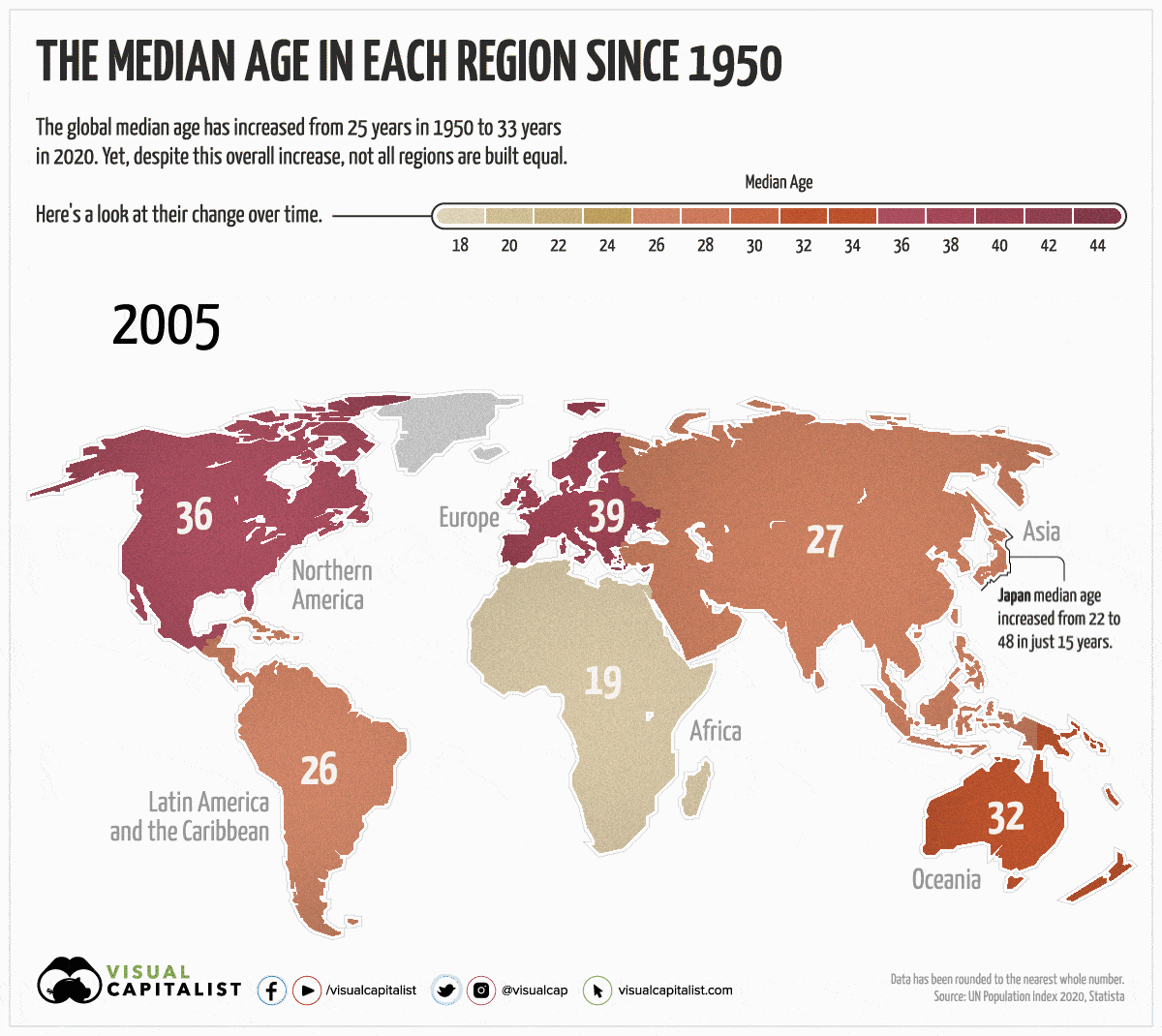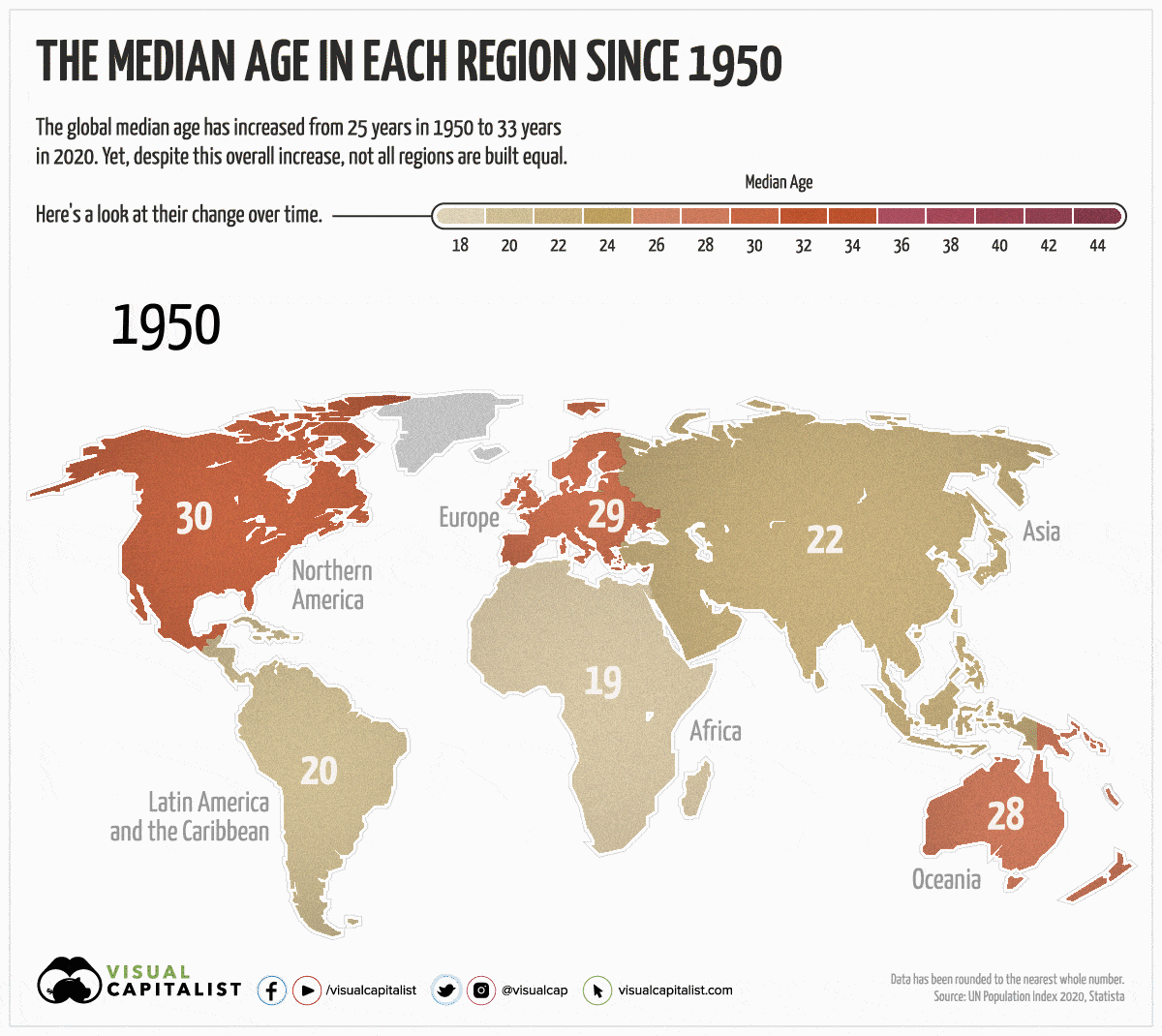
Over the last 70 years, the global population has gotten older. Since 1950, the worldwide median age has gone from 25 years to 33 years.
Yet, despite an overall increase globally, not all regions have aged at the same rate. For instance, Europe’s median age has grown by 14 years, while Africa’s has only increased by 1 year.
Today’s animated map uses data from the UN Population Index to highlight the changes in median age over the last 70 years, and to visualize the differences between each region. We also explain why some regions skew older than others.
Factors that Affect a Region’s Median Age
Before diving into the numbers, it’s important to understand the key factors that influence a region’s median age:
- Fertility Rate
The average number of children that women give birth to in their reproductive years. The higher the fertility rate, the younger a population skews. Since 1950, the global fertility rate has dropped by 50%. - Mortality Rate
The number of deaths in a particular region, usually associated with a certain demographic or period in time. For example, global child mortality (children who have died under five years of age) has been on the decline, which has contributed to an increase in the average life expectancy across the globe. - Migration
International migration may lower a region’s population since migrants are usually younger or working age. In 2019, there were 272 million migrants globally.
The Change in Median Age
As mentioned, not all regions are created equal. Here’s how much the median age has changed in each region since 1950:
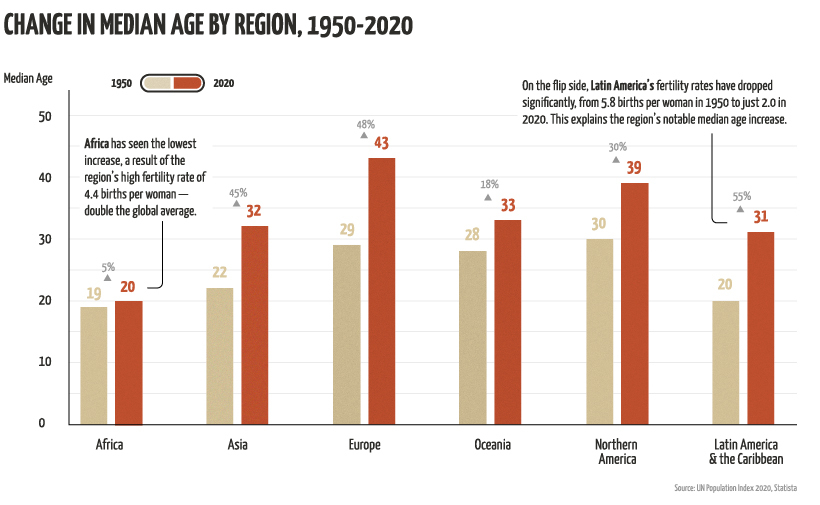
The Highs
Regions that have seen the most growth and generally skew older are Latin America, followed by Europe and Asia.
Interestingly, Asia’s notable increase is largely influenced by Japan, which has the oldest population on the planet. The country has seen a significant increase in median age since 1950—it’s gone from 22 to 48 years in 2020. This can be explained by its considerably low fertility rate, which is 1.4 births per woman—that’s less than half the global average.
But why is Japan’s fertility rate so low? There are more women in the workforce than ever before, and they are too busy to take on the burden of running a household. Yet, while women are more prosperous than ever, the workforce in general has taken a hit.
Japan’s recession in the early 1990s led to an increase in temporary jobs, which has had lasting effects on the region’s workforce—in 2019, about 1 in 5 men were working contract jobs with little stability or job growth.
The Lows
In contrast to Asia’s growth, Africa has seen the lowest increase in median age. The region’s population skews young, with over 60% of its population under the age of 25.
Africa’s young population can be explained by its high birth rate of 4.4 births per woman. It also has a relatively low life expectancy, at 65 years for women and 61 years for men. To put things into perspective, the average life expectancy across the globe is 75 years for women and 70 years for men.
Another trend worth noting is Oceania’s relatively small growth. It’s interesting because the region’s fertility rate is almost on par with the global average, at 2.4 births per woman, and the average life expectancy doesn’t differ much from the norm either.
The most likely reason for Oceania’s stagnant growth in median age is its high proportion of migrants. In 2019, the country had 8.9 million international migrants, which is 21% of its overall population. In contrast, migrants only make up 10% of North America’s population.
Unique Challenges for Every Region
Age composition has significant impacts on a region’s labor force, health services, and economic productivity.
Regions with a relatively high median age face several challenges such as shrinking workforce, higher taxes, and increasing healthcare costs. On the other end of the spectrum, regions with a younger population face increased demand for educational services and a lack of employment opportunities.
As our population worldwide continues to grow and age, it’s important to bring attention to issues that impact our global community. World Population Day on July 11, 2020, was established by the UN to try and solve worldwide population issues.
“The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development is the world’s blueprint for a better future for all on a healthy planet. On World Population Day, we recognize that this mission is closely interrelated with demographic trends including population growth, aging, migration, and urbanization.”
– UN Secretary-General António Guterres
Maps
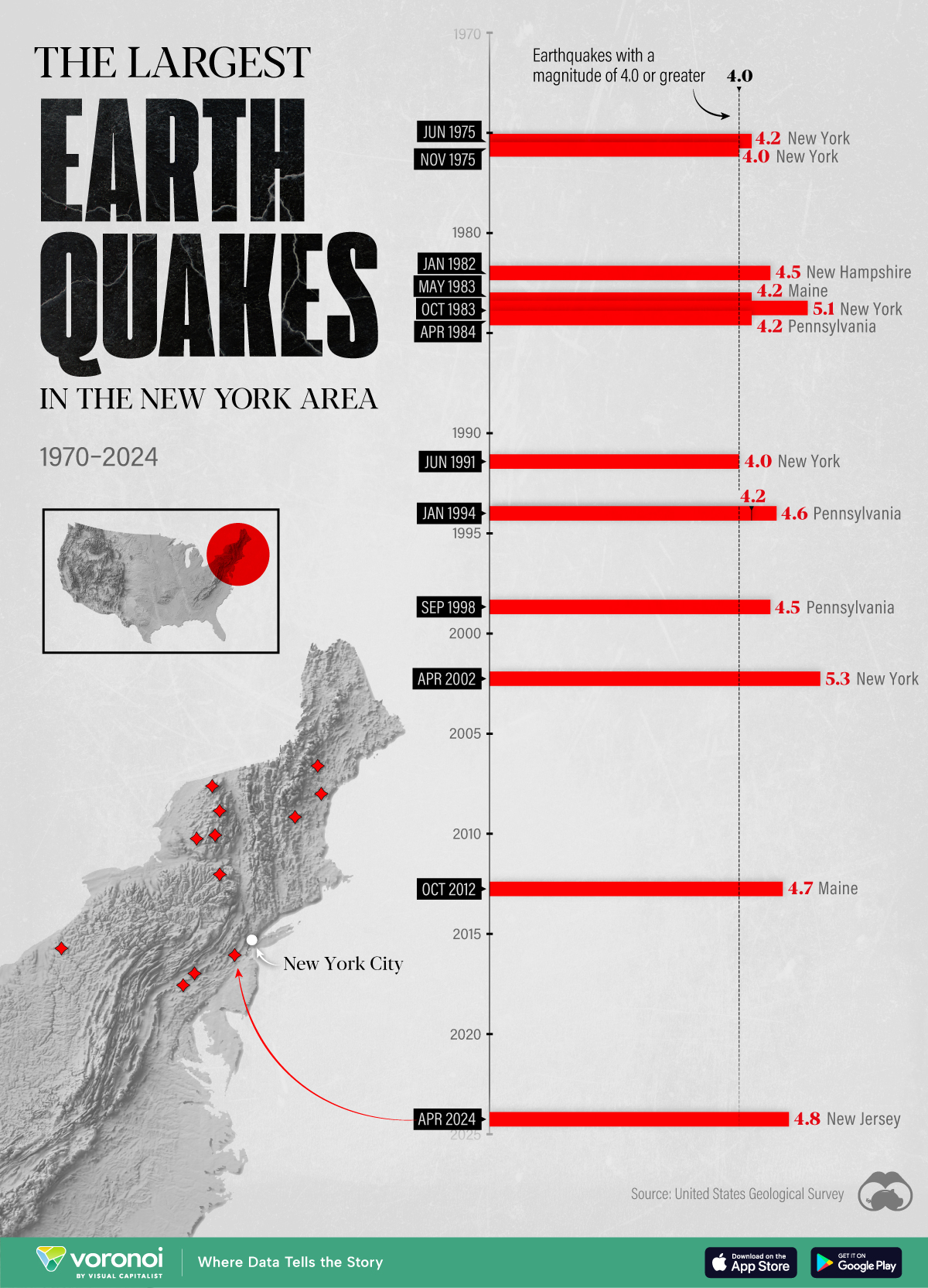
The Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
The earthquake that shook buildings across New York in April 2024 was the third-largest quake in the Northeast U.S. over the past 50 years.

The Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The 4.8 magnitude earthquake that shook buildings across New York on Friday, April 5th, 2024 was the third-largest quake in the U.S. Northeast area over the past 50 years.
In this map, we illustrate earthquakes with a magnitude of 4.0 or greater recorded in the Northeastern U.S. since 1970, according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS).
Shallow Quakes and Older Buildings
The earthquake that struck the U.S. Northeast in April 2024 was felt by millions of people from Washington, D.C., to north of Boston. It even caused a full ground stop at Newark Airport.
The quake, occurring just 5 km beneath the Earth’s surface, was considered shallow, which is what contributed to more intense shaking at the surface.
According to the USGS, rocks in the eastern U.S. are significantly older, denser, and harder than those on the western side, compressed by time. This makes them more efficient conduits for seismic energy. Additionally, buildings in the Northeast tend to be older and may not adhere to the latest earthquake codes.
Despite disrupting work and school life, the earthquake was considered minor, according to the Michigan Technological University magnitude scale:
| Magnitude | Earthquake Effects | Estimated Number Each Year |
|---|---|---|
| 2.5 or less | Usually not felt, but can be recorded by seismograph. | Millions |
| 2.5 to 5.4 | Often felt, but only causes minor damage. | 500,000 |
| 5.5 to 6.0 | Slight damage to buildings and other structures. | 350 |
| 6.1 to 6.9 | May cause a lot of damage in very populated areas. | 100 |
| 7.0 to 7.9 | Major earthquake. Serious damage. | 10-15 |
| 8.0 or greater | Great earthquake. Can totally destroy communities near the epicenter. | One every year or two |
The largest earthquake felt in the area over the past 50 years was a 5.3 magnitude quake that occurred in Au Sable Forks, New York, in 2002. It damaged houses and cracked roads in a remote corner of the Adirondack Mountains, but caused no injuries.
| Date | Magnitude | Location | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| April 20, 2002 | 5.3 | Au Sable Forks | New York |
| October 7, 1983 | 5.1 | Newcomb | New York |
| April 5, 2024 | 4.8 | Whitehouse Station | New Jersey |
| October 16, 2012 | 4.7 | Hollis Center | Maine |
| January 16, 1994 | 4.6 | Sinking Spring | Pennsylvania |
| January 19, 1982 | 4.5 | Sanbornton | New Hampshire |
| September 25, 1998 | 4.5 | Adamsville | Pennsylvania |
| June 9, 1975 | 4.2 | Altona | New York |
| May 29, 1983 | 4.2 | Peru | Maine |
| April 23, 1984 | 4.2 | Conestoga | Pennsylvania |
| January 16, 1994 | 4.2 | Sinking Spring | Pennsylvania |
| November 3, 1975 | 4 | Long Lake | New York |
| June 17, 1991 | 4 | Worcester | New York |
The largest earthquake in U.S. history, however, was the 1964 Good Friday quake in Alaska, measuring 9.2 magnitude and killing 131 people.
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Popular Smartphone Brands in the U.S.
-

 Automotive1 week ago
Automotive1 week agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoVisualizing the Size of the Global Senior Population