Culture
Mapped: The Most Common Illicit Drugs in the World
How to Use: The below maps will transition automatically. To pause, move your cursor on the image. Arrows on left/right navigate.
Mapped: The Most Common Illicit Drugs in the World
Despite strict prohibitory laws around much of the world, many common illicit drugs still see widespread use.
Humans have a storied and complicated relationship with drugs. Defined as chemical substances that cause a change in our physiology or psychology, many drugs are taken medicinally or accepted culturally, like caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol.
But many drugs—including medicines and non-medicinal substances taken as drugs—are taken recreationally and can be abused. Each country and people have their own relationship to drugs, with some embracing the use of specific substances while others shun them outright.
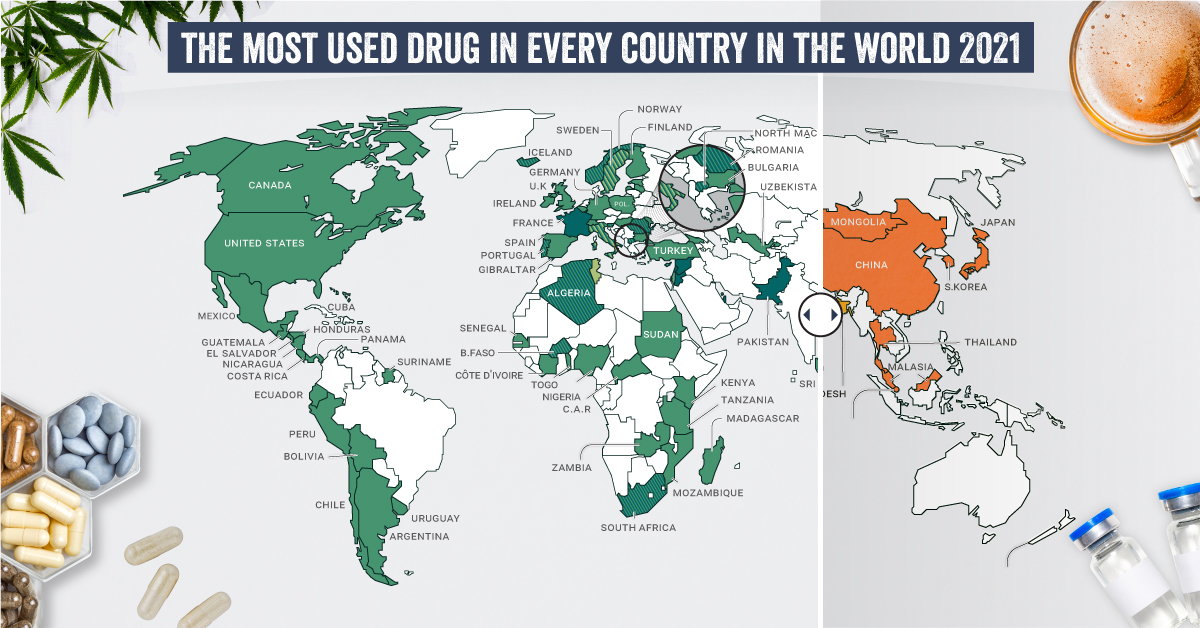
What are the most common drugs that are considered generally illicit in different parts of the world? Today’s graphics use data from the UN’s World Drug Report 2021 to highlight the most prevalent drug used in each country.
What Types of Common Drugs Are Tracked?
The World Drug Report looks explicitly at the supply and demand of the international illegal drug market, not including commonly legal substances like caffeine and alcohol.
Drugs are grouped by class and type, with six main types of drugs found as the most prevalent drugs worldwide.
- Cannabis*: Drugs derived from cannabis, including hemp. This category includes marijuana (dried flowers), hashish (resin), and other for various other parts of the plant or derived oils.
- Cocaine: Drugs derived from the leaves of coca plants. Labeled as either cocaine salts for powder form or crack for cocaine processed with baking soda and water into rock form.
- Opioids: Includes opiates which are derived directly from the opium poppy plant, including morphine, codeine, and heroin, as well as synthetic alkaloids.
- Amphetamine-type Stimulants (ATS): Amphetamine and drugs derived from amphetamine, including meth (also known as speed), MDMA, and ecstasy.
- Sedatives and Tranquilizers: Includes other drugs whose main purpose is to reduce energy, excitement, or anxiety, as well as drugs used primarily to initiate or help with sleep (also called hypnotics).
- Solvents and Inhalants: Gases or chemicals that can cause intoxication but are not intended to be drugs, including fuels, glues, and other industrial substances.
The report also tracked the prevalence of hallucinogens—psychoactive drugs which strongly affect the mind and cause a “trip”—but no hallucinogens ranked as the most prevalent drug in any one country.
*Editor’s note: Recreational cannabis is legal in five countries, and some non-federal jurisdictions (i.e. states). However, in the context of this report, it was included because it is still widely illicit in most countries globally.
The Most Prevalent Drug in Each Country
According to the report, 275 million people used drugs worldwide in 2020. Between the ages of 15–64, around 5.5% of the global population used drugs at least once.
Many countries grouped different types of the same drug class together, and a few like Saudi Arabia and North Macedonia had multiple different drug types listed as the most prevalent.
But across the board, cannabis was the most commonly prevalent drug used in 107 listed countries and territories:
| Country or territory | Most Prevalent Drug(s) |
|---|---|
| Afghanistan | Heroin, opium |
| Albania | Sedatives and tranquillizers (general) |
| Algeria | Cannabis (general) |
| Argentina | Cannabis (herb) |
| Australia | Cannabis (general) |
| Azerbaijan | Heroin |
| Bahamas | Cannabis (herb) |
| Bahrain | Cannabis (general) |
| Bangladesh | Amphetamine |
| Belarus | Opium |
| Belgium | Cannabis (herb) |
| Bolivia | Cannabis (herb) |
| Brunei | Cannabis (herb) |
| Bulgaria | Cannabis (herb) |
| Burkina Faso | Cannabis (general) |
| Canada | Cannabis (herb) |
| Central African Republic | Cannabis (herb) |
| Chile | Cannabis (herb) |
| China | Methamphetamine |
| Costa Rica | Cannabis (herb) |
| Côte d'Ivoire | Cannabis (herb) |
| Croatia | Heroin |
| Cyprus | Cannabis (general) |
| Czech Republic | Benzodiazepines |
| Dominican Republic | Cocaine (powder) |
| Ecuador | Cannabis (herb) |
| El Salvador | Cannabis (herb) |
| Estonia | Cannabis (herb) |
| Finland | Cannabis (herb) |
| France | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Georgia | Cannabis (herb) |
| Germany | Cannabis (herb) |
| Gibraltar | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Greece | Solvents and inhalants (general) |
| Guatemala | Cannabis (herb) |
| Honduras | Cannabis (herb) |
| Hong Kong | Heroin, opium, opioids |
| Hungary | Cannabis (herb) |
| Iceland | Cannabis (general) |
| India | Heroin |
| Indonesia | Cannabis (herb) |
| Iran | Opium |
| Ireland | Cannabis (herb) |
| Israel | Cannabis (herb) |
| Italy | Cannabis (general) |
| Japan | Methamphetamine |
| Jordan | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Kenya | Cannabis (herb) |
| Latvia | Cannabis (herb) |
| Lebanon | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Liechtenstein | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Lithuania | Sedatives and tranquillizers (general) |
| Luxembourg | Cannabis (general) |
| Macao | Methamphetamine |
| Madagascar | Cannabis (herb) |
| Malaysia | Methamphetamine |
| Malta | Heroin |
| Mexico | Cannabis (herb) |
| Moldova | Cannabis (herb) |
| Mongolia | Methamphetamine |
| Mozambique | Cannabis (herb) |
| Myanmar | Heroin |
| Netherlands | Benzodiazepines |
| New Zealand | Methamphetamine, solvent and inhalants |
| Nicaragua | Cannabis (herb) |
| Nigeria | Cannabis (herb) |
| North Macedonia | Multiple types |
| Norway | Cannabis (general) |
| Oman | Opium |
| Pakistan | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Panama | Cannabis (herb) |
| Peru | Cannabis (herb) |
| Philippines | Cannabis (herb) |
| Poland | Cannabis (herb) |
| Portugal | Cannabis (general) |
| Qatar | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Romania | Cannabis (general) |
| Saudi Arabia | Multiple types |
| Senegal | Cannabis (herb) |
| Serbia | Benzodiazepines |
| Singapore | Methamphetamine |
| Slovenia | Cannabis (general) |
| South Africa | Cannabis (general) |
| South Korea | Methamphetamine |
| Spain | Cannabis (herb) |
| Sri Lanka | Cannabis (herb) |
| Sudan | Cannabis (herb) |
| Suriname | Cannabis (herb) |
| Sweden | Cannabis (general) |
| Switzerland | Cannabis (herb) |
| Syrian Arab Republic | Cannabis (hashish) |
| Tajikistan | Heroin, opium |
| Tanzania | Cannabis (herb) |
| Thailand | Methamphetamine |
| Togo | Cannabis (herb) |
| Trinidad and Tobago | Cocaine (crack) |
| Tunisia | Cannabis (general) |
| Turkey | Cannabis (herb) |
| Turkmenistan | Opium |
| U.S. | Cannabis (herb) |
| UK | Cannabis (herb) |
| Ukraine | Opioids |
| Uruguay | Cannabis (herb) |
| Uzbekistan | Cannabis (herb) |
| Venezuela | Benzodiazepines |
| Vietnam | Heroin |
| Zambia | Cannabis (herb) |
How prevalent is cannabis worldwide? 72 locations or more than two-thirds of those reporting listed cannabis as the most prevalent drug.
Unsurprisingly these include countries that have legalized recreational cannabis: Canada, Georgia, Mexico, South Africa, and Uruguay.
How Common Are Opioids and Other Drugs?
Though the global prevalence of cannabis is unsurprising, especially as it becomes legalized and accepted in more countries, other drugs also have strong footholds.
Opioids (14 locations) were the most prevalent drugs in the Middle-East, South and Central Asia, including in India and Iran. Notably, Afghanistan is the world’s largest producer of opium, supplying more than 90% of illicit heroin globally.
Amphetamine-type drugs (9 locations) were the third-most common drugs overall, mainly in East Asia. Methamphetamine was the reported most prevalent drug in China, South Korea, and Japan, while amphetamine was only the most common drug in Bangladesh.
However, it’s important to note that illicit drug usage is tough to track. Asian countries where cannabis is less frequently found (or reported) might understate its usage. At the same time, the opioid epidemic in the U.S. and Canada reflects high opioid usage in the West.
As some drugs become more widespread and others face a renewed “war,” the landscape is certain to shift over the next few years.
Culture
The Highest Earning Athletes in Seven Professional Sports
We illustrate how much the highest earning athletes across seven different sports make, and where they get their money from.
The Highest Earning Athletes in Seven Professional Sports
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
How much money do the world’s biggest athletes really make? And how do they compare across different sports?
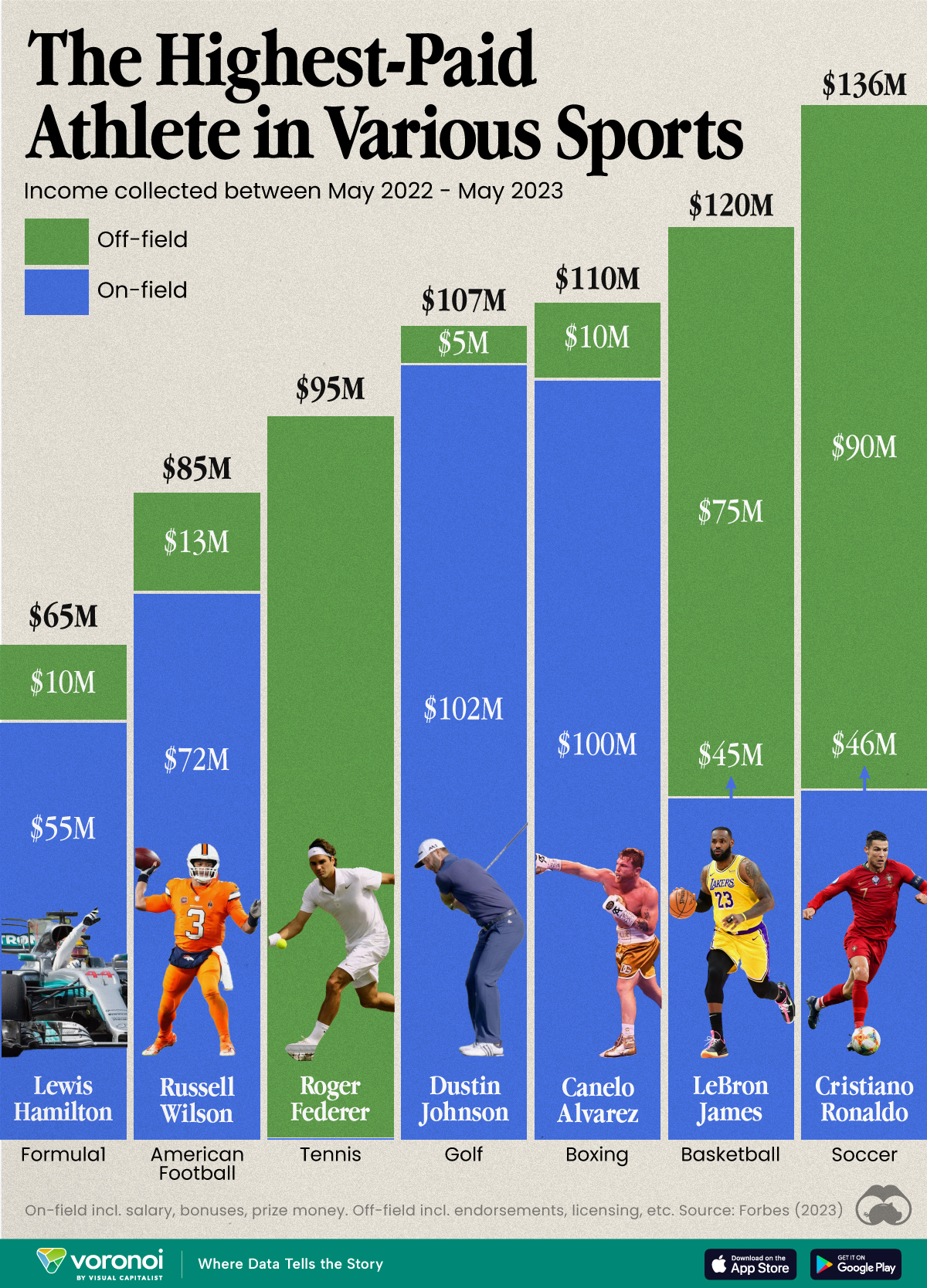
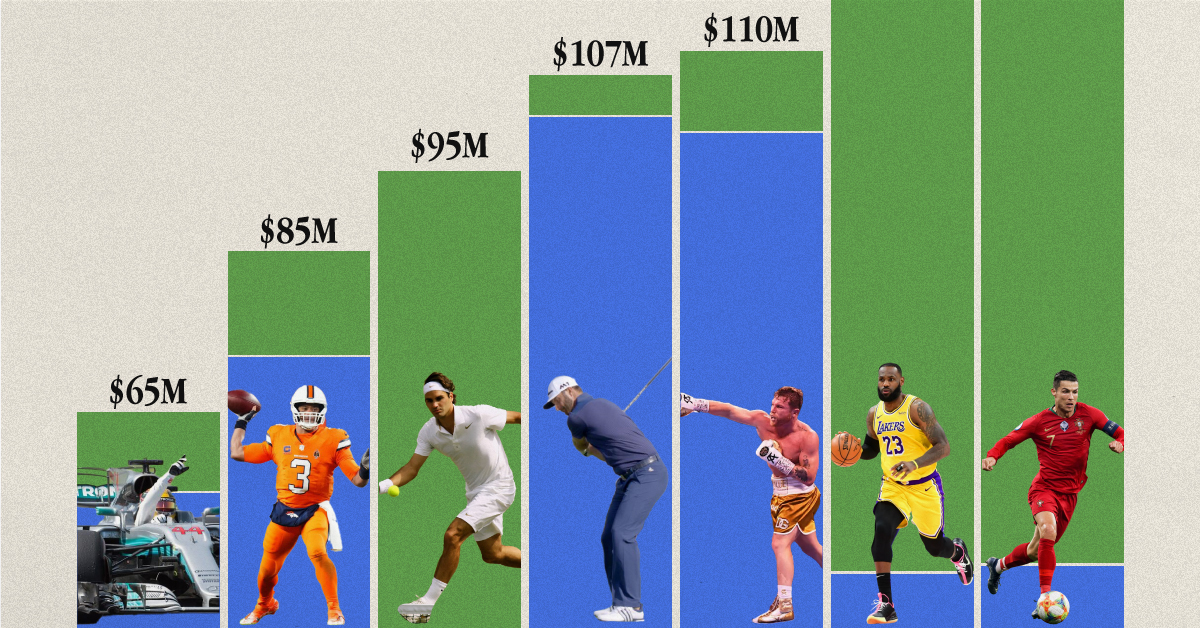
We visualized the highest earning athletes in various professional sports, according to calculations from Forbes. Earnings reported here cover the period of May 2022 to May 2023. Earnings includes on-field (salary, bonuses, prize money) and off-field (endorsements, licensing, etc).
Forbes’ research included talking to industry insiders, following news reports, and parsing salary databases. Please see their methodology page for further details.
Who is the Highest Paid Athlete in the World?
Cristiano Ronaldo was the highest-paid athlete in the world, making an estimated $136 million between May 2022 and May 2023. His move to Saudi Arabian club Al Nassr set a record for the biggest contract in the sport at the time.
Here’s how he compared to the top earners in some other sports.
| Athlete | Sport | Total Earnings (May 2022–23) |
|---|---|---|
| Cristiano Ronaldo | ⚽ Soccer | $136M |
| LeBron James | 🏀 Basketball | $120M |
| Canelo Alvarez | 🥊 Boxing | $110M |
| Dustin Johnson | ⛳ Golf | $107M |
| Roger Federer | 🎾 Tennis | $95M |
| Russell Wilson | 🏈 American Football | $85M |
| Lewis Hamilton | 🏎️ Formula 1 | $65M |
Note: Figures are rounded.
Los Angeles Lakers superstar LeBron James made the most money in basketball (just under $120 million), which is almost twice as much as Formula 1’s top earner, Lewis Hamilton, who took home about $65 million in 2022–23.
Something else to note is how off-court earnings can contribute significantly to total income for some athletes.
| Athlete | Sport | On-Field Earnings | Off-Field Earnings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cristiano Ronaldo | ⚽ Soccer | $46M | $90M |
| LeBron James | 🏀 Basketball | $45M | $75M |
| Canelo Alvarez | 🥊 Boxing | $100M | $10M |
| Dustin Johnson | ⛳ Golf | $102M | $5M |
| Roger Federer | 🎾 Tennis | $0.1M | $95M |
| Russell Wilson | 🏈 American Football | $72M | $13M |
| Lewis Hamilton | 🏎️ Formula 1 | $55M | $10M |
Note: Figures are rounded.
This is most apparent with Roger Federer, who retired in 2022, after playing his last Laver Cup. However, his massive deals with Uniqlo, Rolex, and Mercedes, as well as his stake in running company On, still keeps him towards the top of the these lists.
Together with Ronaldo and James, these three athletes are widely considered the face of their sport, undoubtedly helping them secure lucrative endorsements and business deals.
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Travel1 week ago
Travel1 week agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024