Technology
Mapped: The Fastest (and Slowest) Internet Speeds in the World
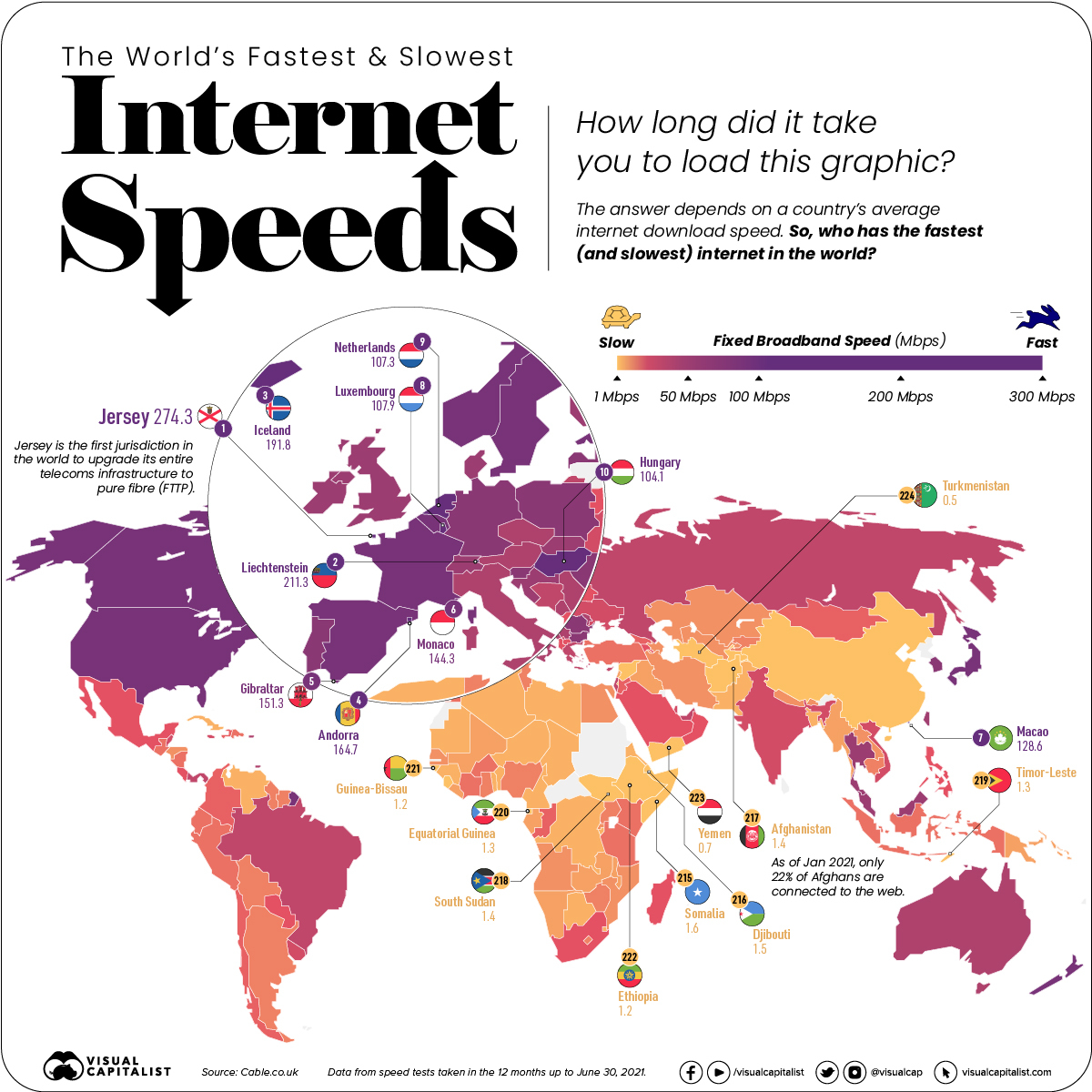
Mapped: The World’s Fastest (and Slowest) Internet Speeds
How quickly did this page load for you?
The answer depends on the device you’re using, and where in the world you’re located. Average internet speeds vary wildly from country to country.
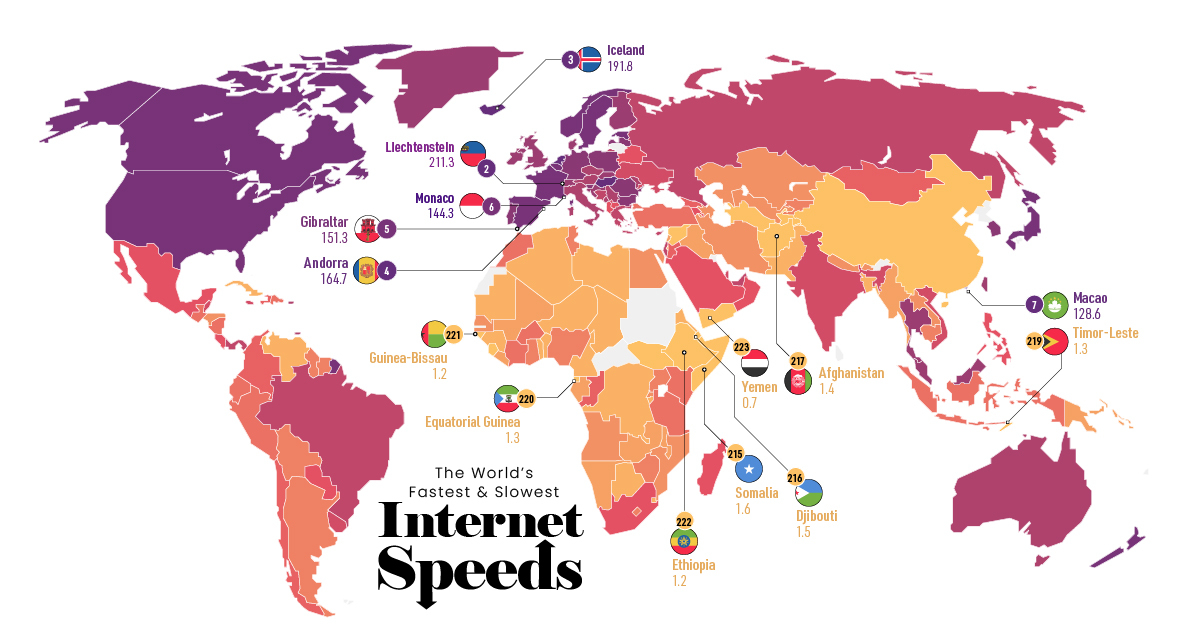
Which countries have the fastest internet connection? Using data from the Cable.co.uk, this map ranks the fastest (and slowest) internet speeds worldwide by comparing the fixed broadband speeds of over 200 countries.
What Factors Affect Internet Speed?
Before diving in, it’s important to understand the key factors that impact a country’s internet speed. Generally speaking, internet speed depends on:
- Infrastructure or the type of cabling (copper or fiber-optic) that a country’s utilizing to support their internet service. Typically, the newer the infrastructure, the faster the connection.
- Proximity/connection to submarine cables is important, as these massive undersea fiber-optic cables transmit about 97% of the world’s communication data.
- The size of a country, since landmass affects how much it costs to upgrade infrastructure. The smaller the country, the cheaper it is to upgrade cabling.
- Investment makes a difference, or how much a country’s government prioritizes internet accessibility.
Of course, other factors may influence a country’s internet speed too, such as government regulation and intentional bandwidth throttling, which is the case in countries like Turkmenistan.
Ranked: Fixed Broadband Speeds
To measure fixed broadband speeds across the globe, Cable.co.uk used more than 1.1 billion speed tests, sourced from over 200 countries.
The region with the fastest connection is Jersey, which is one of the islands that make up the British Isles. It has an average download speed of 274.27 mbps—almost 9x the overall average.
| Rank | Country | Mean download speed (Mbps) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇯🇪 Jersey | 274.27 |
| 2 | 🇱🇮 Liechtenstein | 211.26 |
| 3 | 🇮🇸 Iceland | 191.83 |
| 4 | 🇦🇩 Andorra | 164.66 |
| 5 | 🇬🇮 Gibraltar | 151.34 |
| 6 | 🇲🇨 Monaco | 144.29 |
| 7 | 🇲🇴 Macao SAR | 128.56 |
| 8 | 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | 107.94 |
| 9 | 🇳🇱 Netherlands | 107.3 |
| 10 | 🇭🇺 Hungary | 104.07 |
| 11 | 🇸🇬 Singapore | 97.61 |
| 12 | 🇧🇲 Bermuda | 96.54 |
| 13 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 96.36 |
| 14 | 🇺🇸 United States | 92.42 |
| 15 | 🇭🇰 Hong Kong SAR | 91.04 |
| 16 | 🇪🇸 Spain | 89.59 |
| 17 | 🇸🇪 Sweden | 88.98 |
| 18 | 🇳🇴 Norway | 88.67 |
| 19 | 🇫🇷 France | 85.96 |
| 20 | 🇳🇿 New Zealand | 85.95 |
| 21 | 🇲🇹 Malta | 85.2 |
| 22 | 🇪🇪 Estonia | 84.72 |
| 23 | 🇦🇽 Aland Islands | 81.31 |
| 24 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 79.96 |
| 25 | 🇧🇪 Belgium | 78.46 |
| 26 | 🇻🇦 Vatican City | 73.49 |
| 27 | 🇰🇾 Cayman Islands | 71.47 |
| 28 | 🇦🇼 Aruba | 70.66 |
| 29 | 🇷🇴 Romania | 67.4 |
| 30 | 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 67.2 |
| 31 | 🇵🇱 Poland | 63.84 |
| 32 | 🇧🇬 Bulgaria | 63.41 |
| 33 | 🇱🇻 Latvia | 63.28 |
| 34 | 🇵🇹 Portugal | 63.02 |
| 35 | 🇰🇷 Republic of Korea | 61.72 |
| 36 | 🇩🇪 Germany | 60.55 |
| 37 | 🇱🇹 Republic of Lithuania | 56.17 |
| 38 | 🇧🇧 Barbados | 55.92 |
| 39 | 🇫🇮 Finland | 55.08 |
| 40 | 🇸🇰 Slovak Republic | 54.92 |
| 41 | 🇹🇭 Thailand | 53.95 |
| 42 | 🇮🇲 Isle of Man | 52.1 |
| 43 | 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 51.48 |
| 44 | 🇮🇪 Ireland | 51.41 |
| 45 | 🇨🇭 Switzerland | 50.83 |
| 46 | 🇭🇷 Croatia | 49.77 |
| 47 | 🇩🇰 Denmark | 49.24 |
| 48 | 🇵🇲 Saint Pierre and Miquelon | 47.92 |
| 49 | 🇹🇼 Taiwan | 46.43 |
| 50 | 🇷🇪 Réunion | 43.62 |
| 51 | 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 42.83 |
| 52 | 🇬🇱 Greenland | 41.56 |
| 53 | 🇸🇲 San Marino | 40.55 |
| 54 | 🇵🇷 Puerto Rico | 40.52 |
| 55 | 🇦🇺 Australia | 40.5 |
| 56 | 🇲🇫 Saint Martin | 40.19 |
| 57 | 🇲🇪 Montenegro | 40.14 |
| 58 | 🇧🇸 Bahamas | 39.71 |
| 59 | 🇦🇹 Austria | 37.99 |
| 60 | 🇨🇿 Czechia | 37.23 |
| 61 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 36.69 |
| 62 | 🇷🇸 Serbia | 36.59 |
| 63 | 🇲🇩 Republic of Moldova | 36.47 |
| 64 | 🇹🇨 Turks and Caicos Islands | 36.09 |
| 65 | 🇹🇹 Trinidad and Tobago | 35.81 |
| 66 | 🇷🇺 Russian Federation | 35.73 |
| 67 | 🇮🇱 Israel | 34.97 |
| 68 | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 33.34 |
| 69 | 🇳🇨 New Caledonia | 31.79 |
| 70 | 🇧🇦 Bosnia and Herzegovina | 31.72 |
| 71 | 🇬🇬 Guernsey | 31.2 |
| 72 | 🇵🇦 Panama | 30.58 |
| 73 | 🇦🇪 United Arab Emirates | 29.9 |
| 74 | 🇬🇷 Greece | 29.76 |
| 75 | 🇻🇮 Virgin Islands, U.S. | 29.34 |
| 76 | 🇨🇾 Cyprus | 28.3 |
| 77 | 🇺🇦 Ukraine | 25.26 |
| 78 | 🇶🇦 Qatar | 24.16 |
| 79 | 🇧🇿 Belize | 23.12 |
| 80 | 🇮🇳 India | 22.53 |
| 81 | 🇽🇰 Kosovo | 22.21 |
| 82 | 🇺🇾 Uruguay | 21.73 |
| 83 | 🇫🇴 Faroe Islands | 21.59 |
| 84 | 🇬🇵 Guadeloupe | 21.32 |
| 85 | 🇯🇲 Jamaica | 20.96 |
| 86 | 🇬🇺 Guam | 20.76 |
| 87 | 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 20.66 |
| 88 | 🇬🇩 Grenada | 20.49 |
| 89 | 🇨🇼 Curaçao | 20.18 |
| 90 | 🇿🇦 South Africa | 19.94 |
| 91 | 🇲🇶 Martinique | 19.88 |
| 92 | 🇧🇾 Belarus | 19.86 |
| 93 | 🇧🇶 Bonaire, Saint Eustatius and Saba | 19.6 |
| 94 | 🇵🇾 Paraguay | 19.41 |
| 95 | 🇻🇬 Virgin Islands, British | 19.4 |
| 96 | 🇦🇱 Albania | 19.36 |
| 97 | 🇨🇷 Costa Rica | 19.02 |
| 98 | 🇲🇽 Mexico | 18.83 |
| 99 | 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | 18.1 |
| 100 | 🇰🇼 Kuwait | 18.06 |
| 101 | 🇦🇲 Armenia | 18.05 |
| 102 | 🇵🇭 Philippines | 16.84 |
| 103 | 🇴🇲 Oman | 16.73 |
| 104 | 🇧🇭 Bahrain | 16.37 |
| 105 | 🇲🇬 Madagascar | 16.28 |
| 106 | 🇧🇳 Brunei | 15.79 |
| 107 | 🇲🇰 North Macedonia | 15.38 |
| 108 | 🇯🇴 Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan | 15.25 |
| 109 | 🇱🇨 Saint Lucia | 15.02 |
| 110 | 🇲🇳 Mongolia | 14.94 |
| 111 | 🇻🇨 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | 14.32 |
| 112 | 🇬🇪 Georgia | 13.83 |
| 113 | 🇨🇱 Chile | 13.76 |
| 114 | 🇲🇵 Northern Mariana Islands | 13.15 |
| 115 | 🇨🇴 Colombia | 13.13 |
| 116 | 🇰🇳 Saint Kitts and Nevis | 12.96 |
| 117 | 🇩🇲 Dominica | 12.41 |
| 118 | 🇧🇱 Saint Barthélemy | 12.25 |
| 119 | 🇭🇹 Haiti | 12.12 |
| 120 | 🇨🇬 Republic of the Congo | 12.07 |
| 121 | 🇸🇨 Seychelles | 12.04 |
| 122 | 🇩🇴 Dominican Republic | 11.87 |
| 123 | 🇦🇸 American Samoa | 11.76 |
| 124 | 🇹🇷 Turkey | 11.58 |
| 125 | 🇵🇪 Peru | 11.35 |
| 126 | 🇰🇪 Kenya | 11.27 |
| 127 | 🇬🇫 French Guiana | 10.99 |
| 128 | 🇧🇫 Burkina Faso | 10.73 |
| 129 | 🇲🇦 Morocco | 10.33 |
| 130 | 🇪🇨 Ecuador | 10.25 |
| 131 | 🇸🇻 El Salvador | 9.95 |
| 132 | 🇱🇰 Sri Lanka | 9.95 |
| 133 | 🇬🇹 Guatemala | 9.85 |
| 134 | 🇳🇮 Nicaragua | 9.75 |
| 135 | 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 9.58 |
| 136 | 🇨🇮 Cote D'Ivoire | 9.54 |
| 137 | 🇫🇯 Fiji | 9.4 |
| 138 | 🇬🇾 Guyana | 9.26 |
| 139 | 🇬🇭 Ghana | 9.23 |
| 140 | 🇦🇮 Anguilla | 9 |
| 141 | 🇦🇬 Antigua and Barbuda | 8.69 |
| 142 | 🇳🇬 Nigeria | 8.68 |
| 143 | 🇦🇷 Argentina | 8.68 |
| 144 | 🇹🇿 United Republic of Tanzania | 8.6 |
| 145 | 🇲🇺 Mauritius | 8.53 |
| 146 | 🇺🇬 Uganda | 8.52 |
| 147 | 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 8.49 |
| 148 | 🇱🇸 Lesotho | 8.46 |
| 149 | 🇨🇻 Cape Verde | 7.94 |
| 150 | 🇿🇼 Zimbabwe | 7.92 |
| 151 | 🇾🇹 Mayotte | 7.7 |
| 152 | 🇵🇫 French Polynesia | 7.67 |
| 153 | 🇹🇳 Tunisia | 7.46 |
| 154 | 🇲🇻 Maldives | 7.45 |
| 155 | 🇰🇬 Kyrgyzstan | 7.44 |
| 156 | 🇸🇷 Suriname | 7.44 |
| 157 | 🇧🇴 Bolivia | 7.36 |
| 158 | 🇲🇿 Mozambique | 7.17 |
| 159 | 🇭🇳 Honduras | 7.17 |
| 160 | 🇮🇷 Iran | 7.05 |
| 161 | 🇸🇳 Senegal | 7.02 |
| 162 | 🇪🇬 Egypt | 6.94 |
| 163 | 🇳🇵 Nepal | 6.84 |
| 164 | 🇼🇸 Samoa | 6.8 |
| 165 | 🇲🇭 Marshall Islands | 6.71 |
| 166 | 🇺🇿 Uzbekistan | 6.64 |
| 167 | 🇦🇿 Azerbaijan | 6.63 |
| 168 | 🇧🇹 Bhutan | 6.44 |
| 169 | 🇷🇼 Rwanda | 6.29 |
| 170 | 🇸🇽 Sint Maarten | 6.15 |
| 171 | 🇱🇦 Lao People's Democratic Republic | 5.91 |
| 172 | 🇦🇴 Angola | 5.88 |
| 173 | 🇰🇿 Kazakhstan | 5.83 |
| 174 | 🇱🇧 Lebanon | 5.67 |
| 175 | 🇮🇶 Iraq | 5.58 |
| 176 | 🇿🇲 Zambia | 5.48 |
| 177 | 🇸🇧 Solomon Islands | 5.33 |
| 178 | 🇱🇷 Liberia | 5.23 |
| 179 | 🇵🇬 Papua New Guinea | 5.1 |
| 180 | 🇬🇦 Gabon | 4.99 |
| 181 | 🇲🇼 Malawi | 4.96 |
| 182 | 🇵🇼 Palau | 4.84 |
| 183 | 🇲🇱 Mali | 4.72 |
| 184 | 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 4.58 |
| 185 | 🇳🇦 Namibia | 4.42 |
| 186 | 🇰🇲 Comoros | 3.99 |
| 187 | 🇸🇿 Eswatini | 3.73 |
| 188 | 🇱🇾 Libya | 3.73 |
| 189 | 🇧🇼 Botswana | 3.65 |
| 190 | 🇵🇸 Palestine | 3.65 |
| 191 | 🇨🇩 DR Congo | 3.63 |
| 192 | 🇹🇬 Togo | 3.54 |
| 193 | 🇳🇪 Niger | 3.23 |
| 194 | 🇩🇿 Algeria | 3.08 |
| 195 | 🇨🇲 Cameroon | 3.04 |
| 196 | 🇨🇺 Cuba | 2.92 |
| 197 | 🇧🇩 Bangladesh | 2.9 |
| 198 | 🇻🇺 Vanuatu | 2.9 |
| 199 | 🇵🇰 Pakistan | 2.82 |
| 200 | 🇧🇮 Burundi | 2.82 |
| 201 | 🇻🇪 Venezuela | 2.62 |
| 202 | 🇧🇯 Benin | 2.59 |
| 203 | 🇲🇷 Mauritania | 2.54 |
| 204 | 🇸🇹 São Tomé and Príncipe | 2.43 |
| 205 | 🇪🇷 Eritrea | 2.41 |
| 206 | 🇬🇳 Guinea | 2.39 |
| 207 | 🇹🇩 Chad | 2.39 |
| 208 | 🇸🇱 Sierra Leone | 2.19 |
| 209 | 🇨🇳 China | 2.06 |
| 210 | 🇬🇲 Gambia | 2.04 |
| 211 | 🇹🇯 Tajikistan | 1.82 |
| 212 | 🇸🇩 Sudan | 1.8 |
| 213 | 🇸🇾 Syrian Arab Republic | 1.67 |
| 214 | 🇫🇲 Federated States of Micronesia | 1.63 |
| 215 | 🇸🇴 Somalia | 1.59 |
| 216 | 🇩🇯 Djibouti | 1.46 |
| 217 | 🇦🇫 Afghanistan | 1.41 |
| 218 | 🇸🇸 South Sudan | 1.4 |
| 219 | 🇹🇱 Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste | 1.33 |
| 220 | 🇬🇶 Equatorial Guinea | 1.3 |
| 221 | 🇬🇼 Guinea-Bissau | 1.24 |
| 222 | 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | 1.2 |
| 223 | 🇾🇪 Yemen | 0.68 |
| 224 | 🇹🇲 Turkmenistan | 0.5 |
Infrastructure is a major reason behind Jersey’s speedy internet. It’s the first jurisdiction in the world to upgrade its entire system to pure fibre (FTTP). But the region’s size also plays a factor, since its landmass and population size are both relatively small compared to the rest of the world.
Second on the list is another small region, Liechtenstein, with an average download speed of 211.26 mbps. Liechtenstein is one of the richest countries in the world per capita, and its government has invested heavily in its telecommunications infrastructure, aiming to be fully fibre optic by 2022.
Like Jersey, Liechtenstein also has a relatively small population. At the time of this article’s publication, the region is home to approximately 38,000 people. In fact, it’s worth noting that of the top ten regions, only two have populations over one million—the Netherlands, and Hungary.
At the opposite end of the spectrum, Turkmenistan has the slowest fixed broadband, with a speed of 0.5 mbps. As mentioned above, this is largely because of government regulation and intervention.
The Future is 5G
Innovation and new technologies are changing the digital landscape, and things like 5G networks are becoming more mainstream across the globe.
Because of the rapidly changing nature of this industry, the data behind this ranking is updated monthly to provide the latest look at internet speeds across the globe.
This means the bar is gradually raising when it comes to internet speed, as faster, stronger internet connections become the norm. And countries that aren’t equipped to handle these souped-up networks will lag behind even further.
Technology
Ranked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Did you know that some computer chips are now retailing for the price of a new BMW?
As computers invade nearly every sphere of life, so too have the chips that power them, raising the revenues of the businesses dedicated to designing them.
But how did various chipmakers measure against each other last year?
We rank the biggest semiconductor companies by their percentage share of the industry’s revenues in 2023, using data from Omdia research.
Which Chip Company Made the Most Money in 2023?
Market leader and industry-defining veteran Intel still holds the crown for the most revenue in the sector, crossing $50 billion in 2023, or 10% of the broader industry’s topline.
All is not well at Intel, however, with the company’s stock price down over 20% year-to-date after it revealed billion-dollar losses in its foundry business.
| Rank | Company | 2023 Revenue | % of Industry Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intel | $51B | 9.4% |
| 2 | NVIDIA | $49B | 9.0% |
| 3 | Samsung Electronics | $44B | 8.1% |
| 4 | Qualcomm | $31B | 5.7% |
| 5 | Broadcom | $28B | 5.2% |
| 6 | SK Hynix | $24B | 4.4% |
| 7 | AMD | $22B | 4.1% |
| 8 | Apple | $19B | 3.4% |
| 9 | Infineon Tech | $17B | 3.2% |
| 10 | STMicroelectronics | $17B | 3.2% |
| 11 | Texas Instruments | $17B | 3.1% |
| 12 | Micron Technology | $16B | 2.9% |
| 13 | MediaTek | $14B | 2.6% |
| 14 | NXP | $13B | 2.4% |
| 15 | Analog Devices | $12B | 2.2% |
| 16 | Renesas Electronics Corporation | $11B | 1.9% |
| 17 | Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation | $10B | 1.9% |
| 18 | Microchip Technology | $8B | 1.5% |
| 19 | Onsemi | $8B | 1.4% |
| 20 | KIOXIA Corporation | $7B | 1.3% |
| N/A | Others | $126B | 23.2% |
| N/A | Total | $545B | 100% |
Note: Figures are rounded. Totals and percentages may not sum to 100.
Meanwhile, Nvidia is very close to overtaking Intel, after declaring $49 billion of topline revenue for 2023. This is more than double its 2022 revenue ($21 billion), increasing its share of industry revenues to 9%.
Nvidia’s meteoric rise has gotten a huge thumbs-up from investors. It became a trillion dollar stock last year, and broke the single-day gain record for market capitalization this year.
Other chipmakers haven’t been as successful. Out of the top 20 semiconductor companies by revenue, 12 did not match their 2022 revenues, including big names like Intel, Samsung, and AMD.
The Many Different Types of Chipmakers
All of these companies may belong to the same industry, but they don’t focus on the same niche.
According to Investopedia, there are four major types of chips, depending on their functionality: microprocessors, memory chips, standard chips, and complex systems on a chip.
Nvidia’s core business was once GPUs for computers (graphics processing units), but in recent years this has drastically shifted towards microprocessors for analytics and AI.
These specialized chips seem to be where the majority of growth is occurring within the sector. For example, companies that are largely in the memory segment—Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron Technology—saw peak revenues in the mid-2010s.
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?