Technology
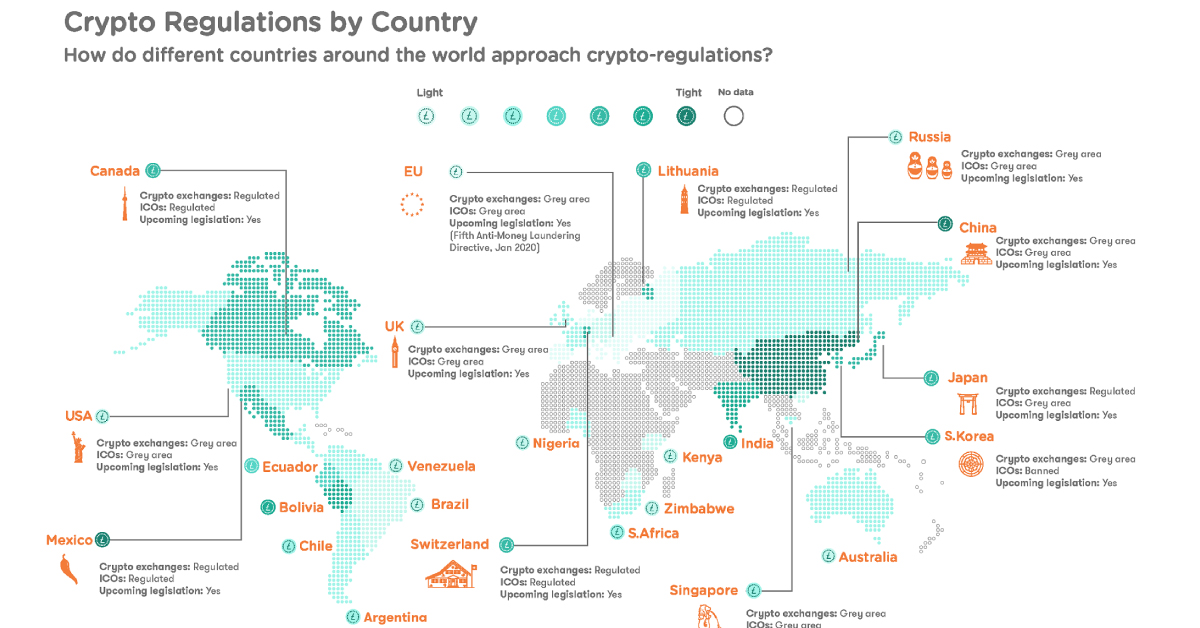
Mapped: Cryptocurrency Regulations Around the World
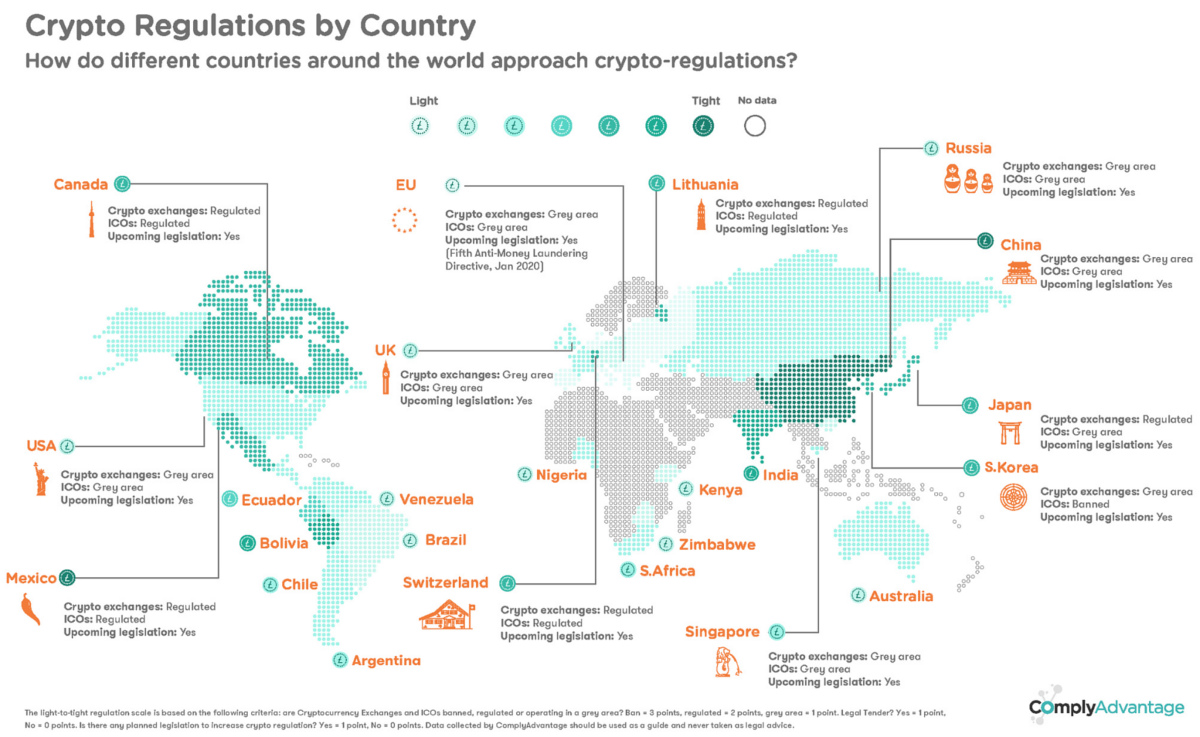
Mapped: Cryptocurrency Regulations Around the World
Following the unprecedented cryptocurrency boom in 2017, investors and governments alike could no longer ignore the growth of decentralized finance.
The world has become increasingly fascinated with cryptocurrencies and the ways they are enabling greater access, such as being able to send funds to remote places or securing capital for small businesses.
To aid this, cryptocurrency regulations are being slowly introduced into global financial markets. Regulations help to monitor these emerging digital currencies, and to allow for clearer guidelines and a measure of security.
The Regulatory Landscape
Today’s graphic from ComplyAdvantage maps out major regulatory cryptocurrency and exchange landscapes around the world, showing how sentiments towards digital currencies are evolving.
To do this, ComplyAdvantage measured cryptocurrency regulatory environments using their own Light-to-Tight scale, based on the following criteria:
- Cryptocurrencies and exchanges status? (Ban = 3 points, Regulated = 2 points, Grey Area = 1 point)
- Cryptocurrency considered legal tender? (Yes = 1 point, No = 0 points)
- Planned legislation to increase crypto regulation? (Yes = 1 point, No = 0 points)
Which jurisdictions have the strictest and most relaxed regulations for cryptocurrencies?
Regulations by Region
Global attitudes towards the rise of cryptocurrencies have shifted greatly over the past few years. While the term cryptocurrency is a bit of a misnomer, some countries do consider digital currencies legal tender, with many viewing cryptocurrencies as commodities.
Below is a table of the major countries that are pursuing cryptocurrency regulations:
| Country | Cryptocurrencies | Exchanges | Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | Legal; treated as property | Legal, must register with AUSTRAC | Regulated |
| Switzerland | Legal; generally accepted as payment | Legal, regulated by SFTA | Regulated |
| Malta | Not legal tender | Legal, regulated under the VFA Act | Regulated |
| Estonia | Not legal tender | Legal, must register with the Financial Intelligence Unit | Regulated |
| Gibraltar | Not legal tender | Legal, must register with the GFSC | Regulated |
| Luxembourg | Not legal tender | Legal, must register with the CSSF | Regulated |
| Canada | Not legal tender; some retailers accept as payment | Legal, regulation varies by province; final federal regulations expected late 2019 | Regulated |
| Mexico | Legal, accepted as payment in some contexts | Grey area; first crypto exchange in opened mid 2019 | Regulated |
| Lithuania | Not legal tender | Legal, must register with the Lithuanian Finance Ministry | Grey area |
| United States | Not legal tender; some retailers accept as payment | Legal, regulation varies by state; SEC expected to publish updated crypto regulations late 2019 | Grey area |
| UK | Not legal tender; considered assets | Legal, registration requirements with FCA | Grey area |
| Russia | Not legal tender | Grey area; regulations to be determined by the end of 2019 | Grey area |
| Japan | Legal; treated as property | Legal, must register with the Financial Services Agency | Grey area |
| Nigeria | Legal | Grey area; regulations upcoming from Central Bank of Nigeria | Grey area |
| Singapore | Not legal tender | Legal, no registration required | Grey area |
| South Korea | Not legal tender | Legal and regulated, must register with FSS | Banned |
| India | Not legal tender; digital rupee may be in the works | Effectively illegal, but global and federal regulations being considered | Banned |
| China | Bitcoin considered property; all other cryptocurrencies banned | Illegal, but a global regulatory framework being considered | Banned |
Sources: ComplyAdvantage, HedgeTrade, CoinDesk
Asia
Japan has one of the most progressive regulatory climates for cryptocurrencies, widely considering bitcoin as legal tender and passing a law in mid-2017 recognizing cryptocurrencies as legal property. In late 2018, Japan also approved self-regulation for the crypto industry.
By contrast, China currently has one of the most restrictive environments in the world for cryptocurrency. China banned bitcoin transactions in 2013, as well as ICOs and crypto exchanges in 2017─though many have found workarounds through sites not yet firewalled.
Europe
Cryptocurrency and exchange regulations in the EU are determined by individual member states, and are considered legal across the bloc.
Digital currency offers great promise, through its ability to reach people and businesses in remote and marginalized regions.
—Christine Lagarde, Managing Director of IMF
Perhaps unsurprisingly, Switzerland has one of the most open climates for cryptocurrencies and exchanges in Europe. In 2016, the city of Zug, known as “Crypto Valley”, started accepting bitcoin as payment for city fees. Swiss Economics Minister Johann Schneider-Ammann announced his goal in 2018 to make Switzerland the world’s first “crypto-nation”.
North America
Both Canada and the U.S. take a similar approach to cryptocurrency legislation at the federal level, as both countries view cryptocurrencies as securities. However, provincial and state regulations differ widely in their taxation requirements of profits from crypto investments.
Latin America
Regulations throughout Latin and South America run the full legislative spectrum.
- Bolivia: unilateral ban on cryptocurrencies and exchanges
- Ecuador: the first country to launch its own token; ban on all cryptocurrencies aside from its government-issued SDE token (Sistema de Dinero Electrónico = electronic money system)
- Mexico, Argentina, Brazil, Chile: cryptocurrencies widely accepted as payment
- Venezuela: cryptocurrencies widely accepted; this makes sense, considering the economic crisis and subsequent freefall of the bolívar
The Importance of Cryptocurrency Regulations
Cryptocurrency’s journey is the story of a technology rapidly outpacing the laws that govern it.
Governments around the world are keenly aware of this problem. Members of the G20 published a request in June 2019 for a global regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies to be implemented to better manage the benefits and challenges that cryptocurrencies bring.
Regulation for both cryptocurrencies and crypto exchanges is essential for the future of digital finance─bringing legitimacy to the digital financial market, and making it more attractive for new businesses, established banks, and investors worldwide to more easily conduct business within this emerging ecosystem.
Technology
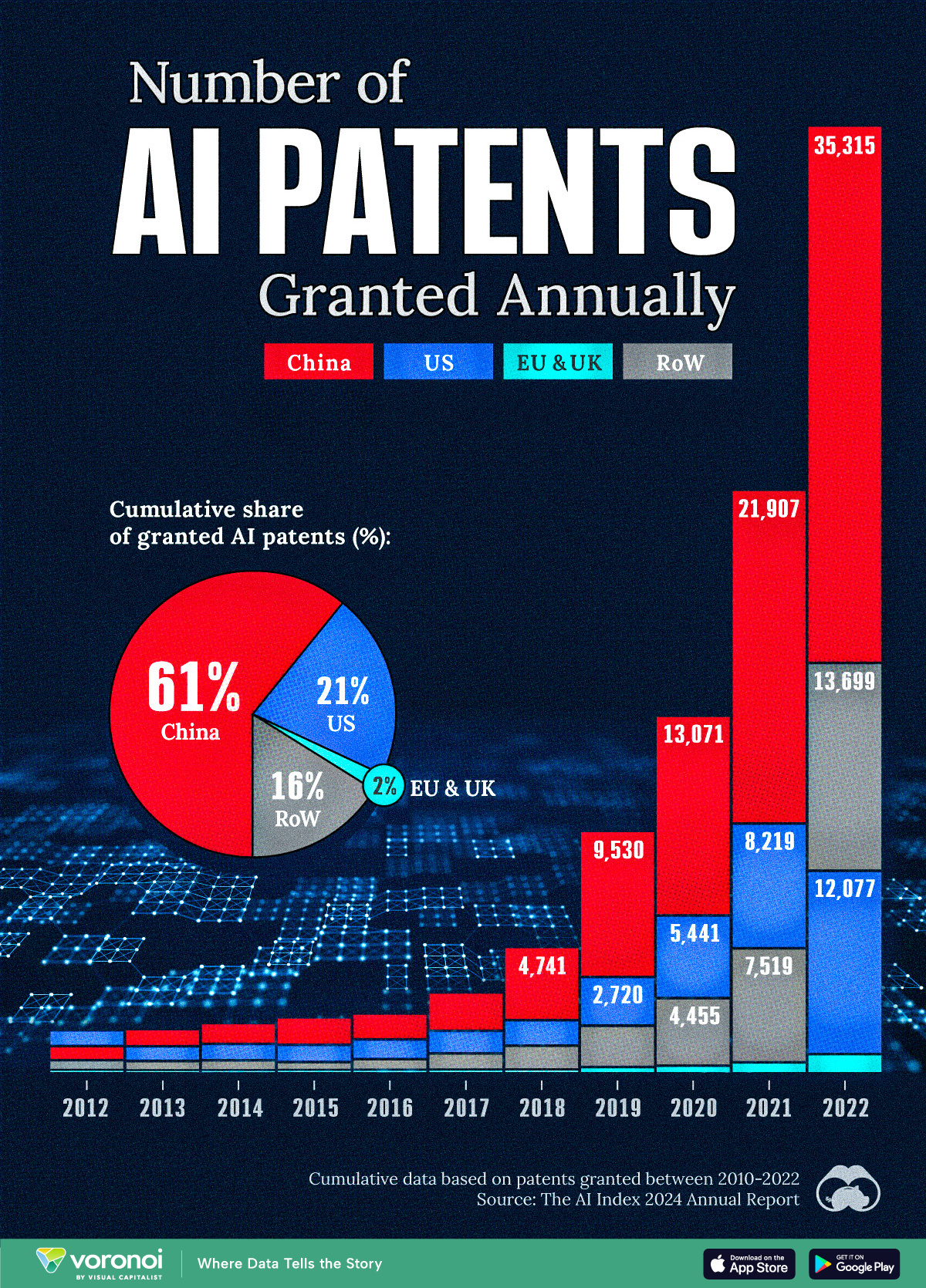
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
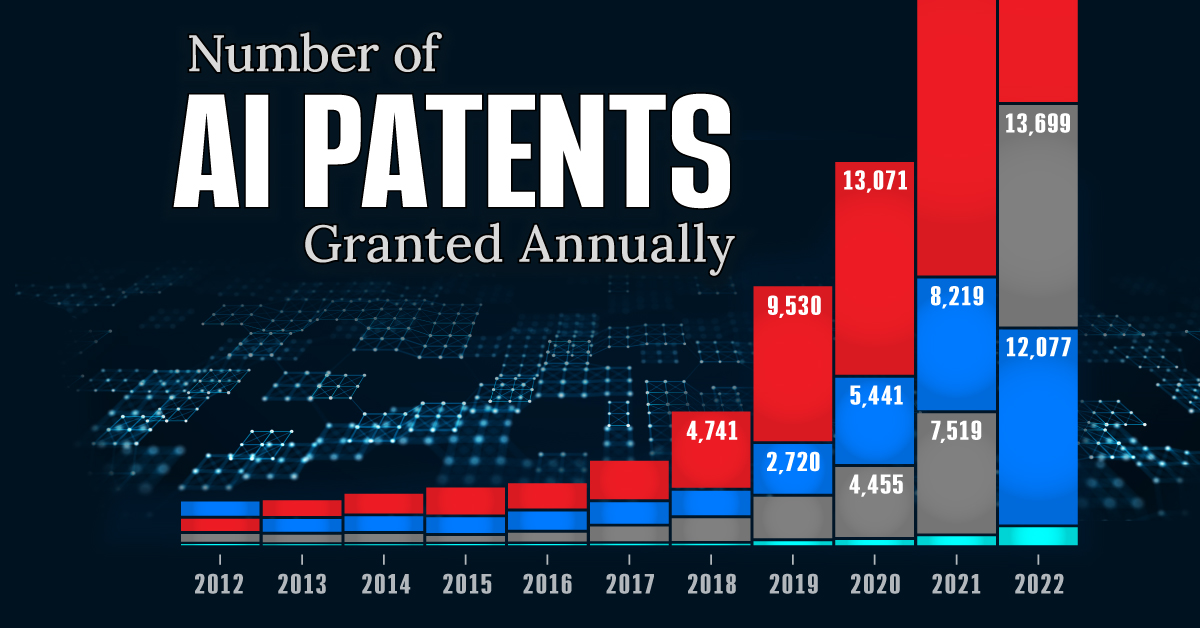
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This infographic shows the number of AI-related patents granted each year from 2010 to 2022 (latest data available). These figures come from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET), accessed via Stanford University’s 2024 AI Index Report.
From this data, we can see that China first overtook the U.S. in 2013. Since then, the country has seen enormous growth in the number of AI patents granted each year.
| Year | China | EU and UK | U.S. | RoW | Global Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 307 | 137 | 984 | 571 | 1,999 |
| 2011 | 516 | 129 | 980 | 581 | 2,206 |
| 2012 | 926 | 112 | 950 | 660 | 2,648 |
| 2013 | 1,035 | 91 | 970 | 627 | 2,723 |
| 2014 | 1,278 | 97 | 1,078 | 667 | 3,120 |
| 2015 | 1,721 | 110 | 1,135 | 539 | 3,505 |
| 2016 | 1,621 | 128 | 1,298 | 714 | 3,761 |
| 2017 | 2,428 | 144 | 1,489 | 1,075 | 5,136 |
| 2018 | 4,741 | 155 | 1,674 | 1,574 | 8,144 |
| 2019 | 9,530 | 322 | 3,211 | 2,720 | 15,783 |
| 2020 | 13,071 | 406 | 5,441 | 4,455 | 23,373 |
| 2021 | 21,907 | 623 | 8,219 | 7,519 | 38,268 |
| 2022 | 35,315 | 1,173 | 12,077 | 13,699 | 62,264 |
In 2022, China was granted more patents than every other country combined.
While this suggests that the country is very active in researching the field of artificial intelligence, it doesn’t necessarily mean that China is the farthest in terms of capability.
Key Facts About AI Patents
According to CSET, AI patents relate to mathematical relationships and algorithms, which are considered abstract ideas under patent law. They can also have different meaning, depending on where they are filed.
In the U.S., AI patenting is concentrated amongst large companies including IBM, Microsoft, and Google. On the other hand, AI patenting in China is more distributed across government organizations, universities, and tech firms (e.g. Tencent).
In terms of focus area, China’s patents are typically related to computer vision, a field of AI that enables computers and systems to interpret visual data and inputs. Meanwhile America’s efforts are more evenly distributed across research fields.
Learn More About AI From Visual Capitalist
If you want to see more data visualizations on artificial intelligence, check out this graphic that shows which job departments will be impacted by AI the most.
-

 Mining1 week ago
Mining1 week agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries