Energy
Mapped: The 1.2 Billion People Without Access to Electricity
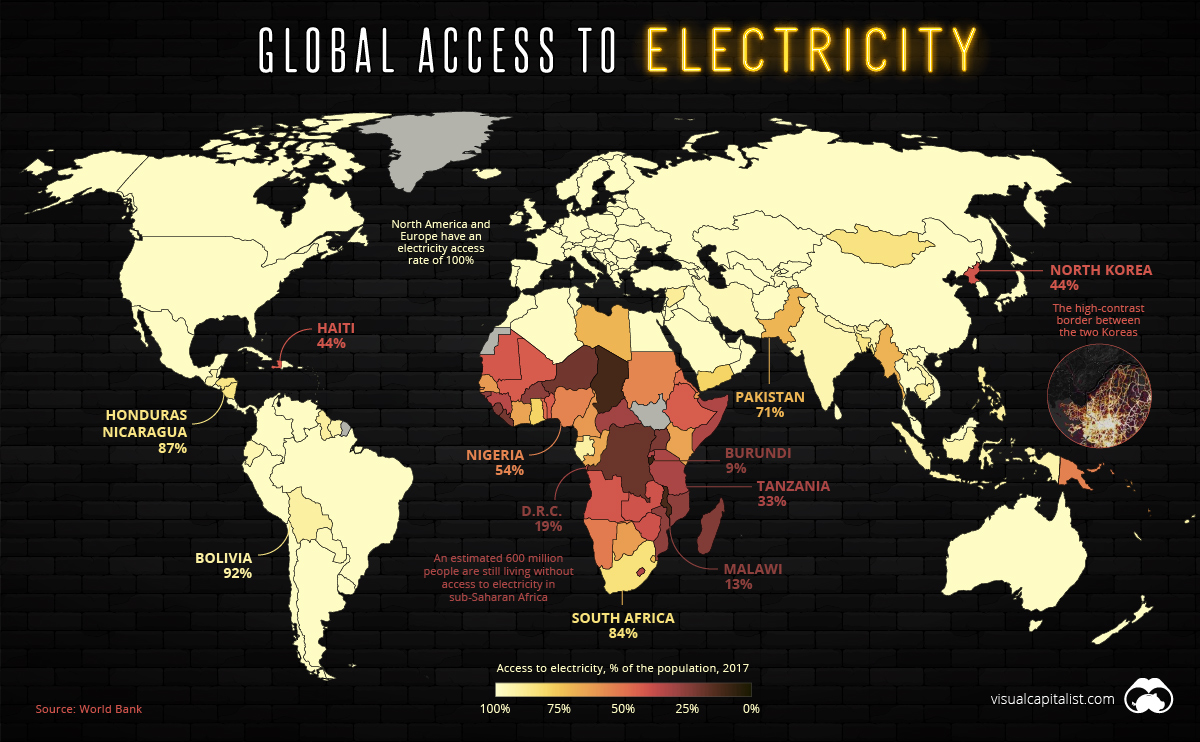
For anyone reading this article, the benefits of electricity need not be explained.
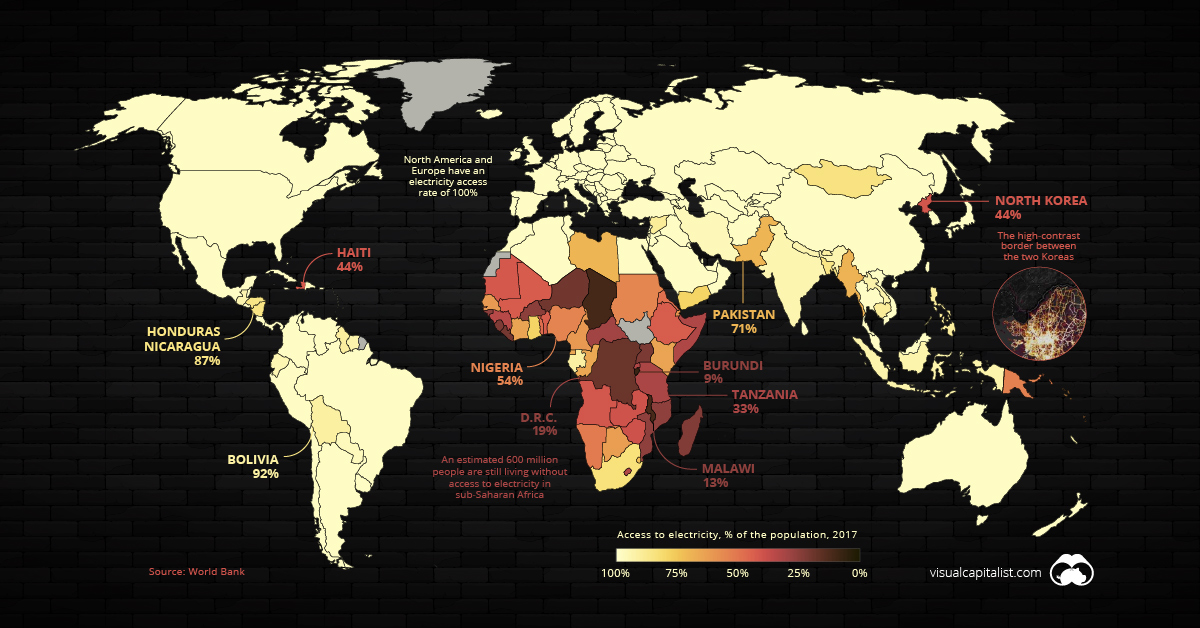
Access to electricity is now an afterthought in most parts of the world, so it may come as a surprise to learn that 16% of the world’s population — an estimated 1.2 billion people — are still living without this basic necessity. Lack of access to electricity, or “energy poverty”, is the ultimate economic hindrance as it prevents people from participating in the modern economy.
Where are people still living in the dark, and how are these energy challenges being addressed? Let’s dive in.
Where the Grid Reaches, and Beyond
At this point in time, a majority of countries have 100% electricity access rates, and many more have rates above 95%. This includes most of the world’s high-population countries, such as China, Brazil, and the United States.
India is fast approaching that benchmark for access. The massive country has made great strides in a short amount of time, jumping from a 70% to 93% access rate in a single decade.
Meanwhile, North Korea is an obvious outlier in East Asia. The Hermit Kingdom’s lack of electrification isn’t just conspicuous in the data — it’s even visible from space. The border between the two Koreas is clearly visible where the dark expanse of North Korea runs up against the glow of South Korea’s urban areas.
It’s been estimated that more than half of North Korea’s people are living in energy poverty.
Africa’s Access to Electricity
In 1995, a mere 20% of sub-Saharan Africa’s population had access to power. While today’s figure is above 40%, that still means roughly 600 million people in the region are living without access to electricity.
Not surprisingly, energy poverty disproportionately impacts rural Africans. Nearly all of the countries with the lowest levels of electricity access have rural-majority populations:
| Global Rank | Country | Electricity Access | Rural Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| #197 | 🇧🇮 Burundi | 9% | 87% |
| #196 | 🇹🇩 Chad | 11% | 77% |
| #195 | 🇲🇼 Malawi | 13% | 83% |
| #194 | 🇨🇩 D.R.C. | 19% | 56% |
| #193 | 🇳🇪 Niger | 20% | 84% |
| #192 | 🇱🇷 Liberia | 21% | 49% |
| #191 | 🇺🇬 Uganda | 22% | 77% |
| #190 | 🇸🇱 Sierra Leone | 23% | 58% |
| #189 | 🇲🇬 Madagascar | 24% | 63% |
| #188 | 🇧🇫 Burkina Faso | 25% | 71% |
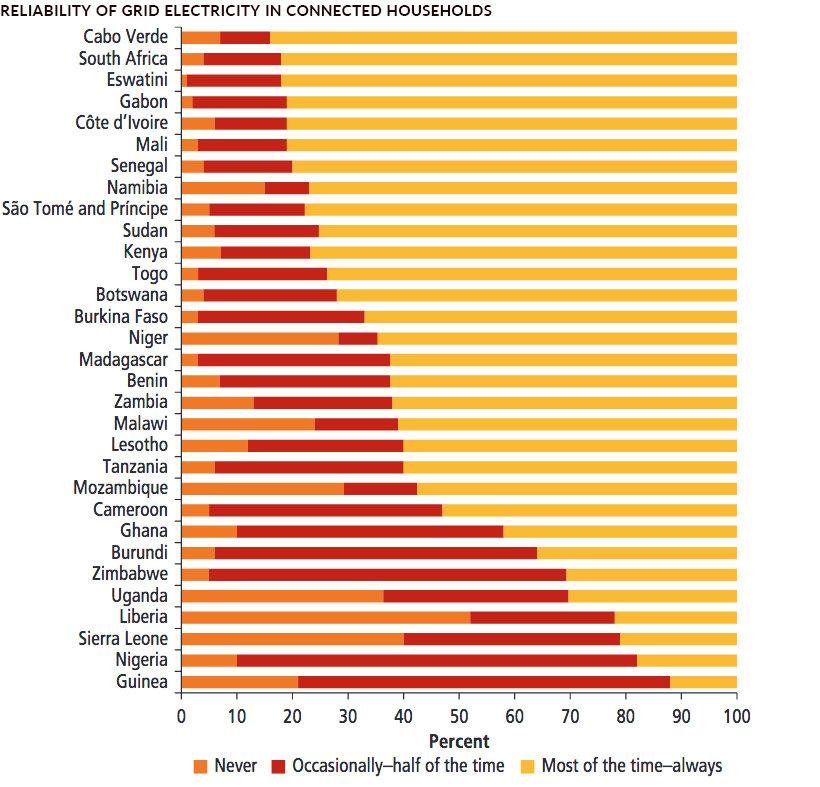
Nonexistent and unreliable electricity isn’t just an issue confined to rural Africa. Even Nigeria — Africa’s largest economy — has an electrification rate of just 54%.
Where there is an electrical grid, instability is also causing problems. A recent survey found that a majority of Nigerian tech firms face 30 or more power outages per month, and more than half ranked electricity as a “major” or “severe” constraint to doing business.
This is pattern that is repeated in a number of countries in Africa:
Mini-Grids, Big Impact
It has taken an average of 25 years for countries to move from 20% to 80% access, so history suggests that it may be a number of years before sub-Saharan Africa fully catches up with other parts of the world. That said, Vietnam was able to close that gap in only nine years.
Traditional utility companies continue to make inroads in the region, but it might be a smaller-scale solution that brings electricity to people in harder-to-reach rural villages.
Between 2009 and 2015, solar PV module prices fell by 80%, ushering in a new era of affordability. Solar powered mini-grids don’t just have the potential to bring electricity to new markets, it can also replace the diesel-powered generators commonly used in Africa.
For the 600 million people in sub-Saharan Africa who are still unable to fully participate in the modern world, these innovations can’t come soon enough.
Energy
The World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
China has grown its nuclear capacity over the last decade, now ranking second on the list of top nuclear energy producers.

The World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Scientists in South Korea recently broke a record in a nuclear fusion experiment. For 48 seconds, they sustained a temperature seven times that of the sun’s core.
But generating commercially viable energy from nuclear fusion still remains more science fiction than reality. Meanwhile, its more reliable sibling, nuclear fission, has been powering our world for many decades.
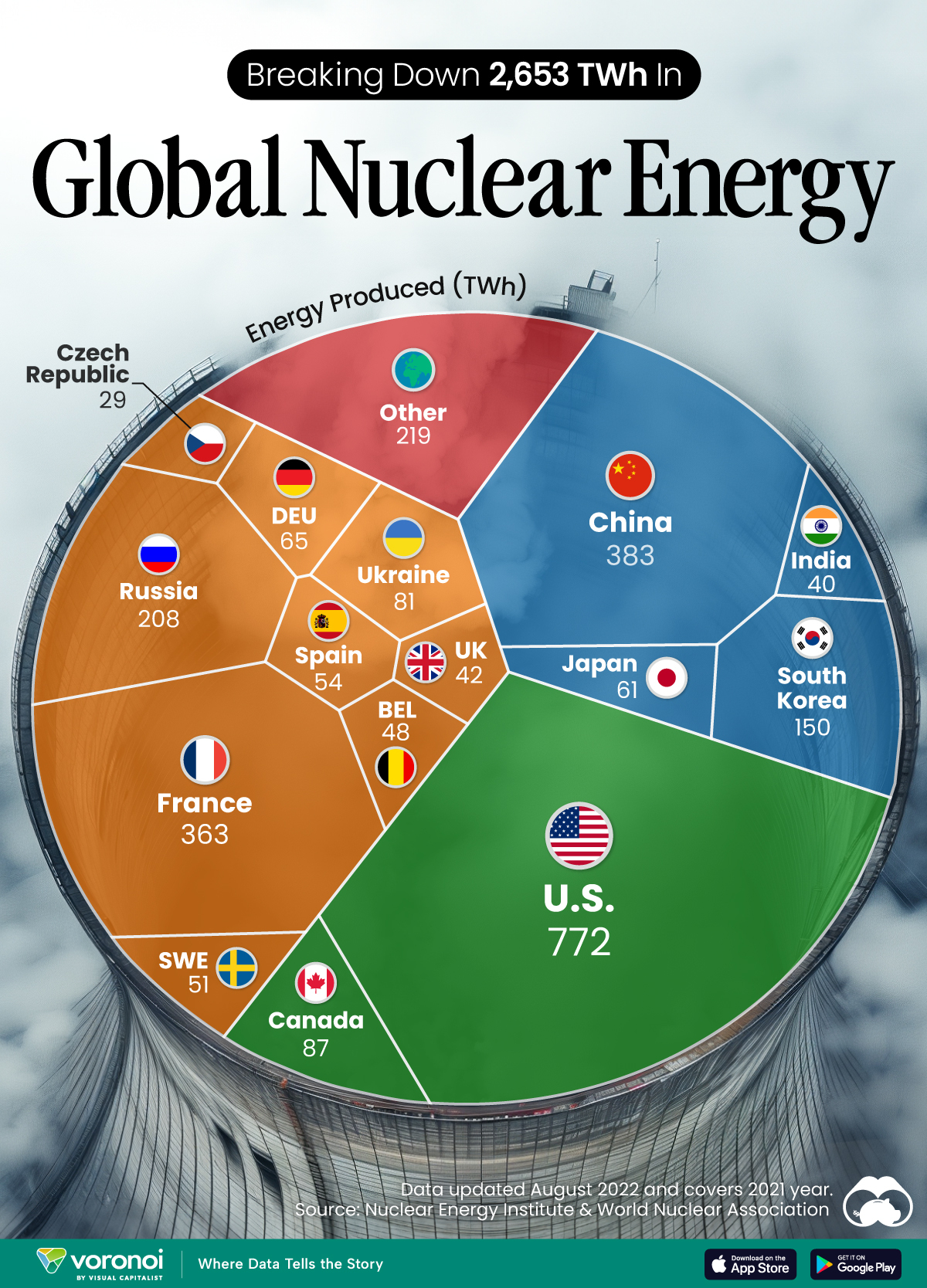
In this graphic, we visualized the top producers of nuclear energy by their share of the global total, measured in terawatt hours (TWh). Data for this was sourced from the Nuclear Energy Institute, last updated in August 2022.
Which Country Generates the Most Nuclear Energy?
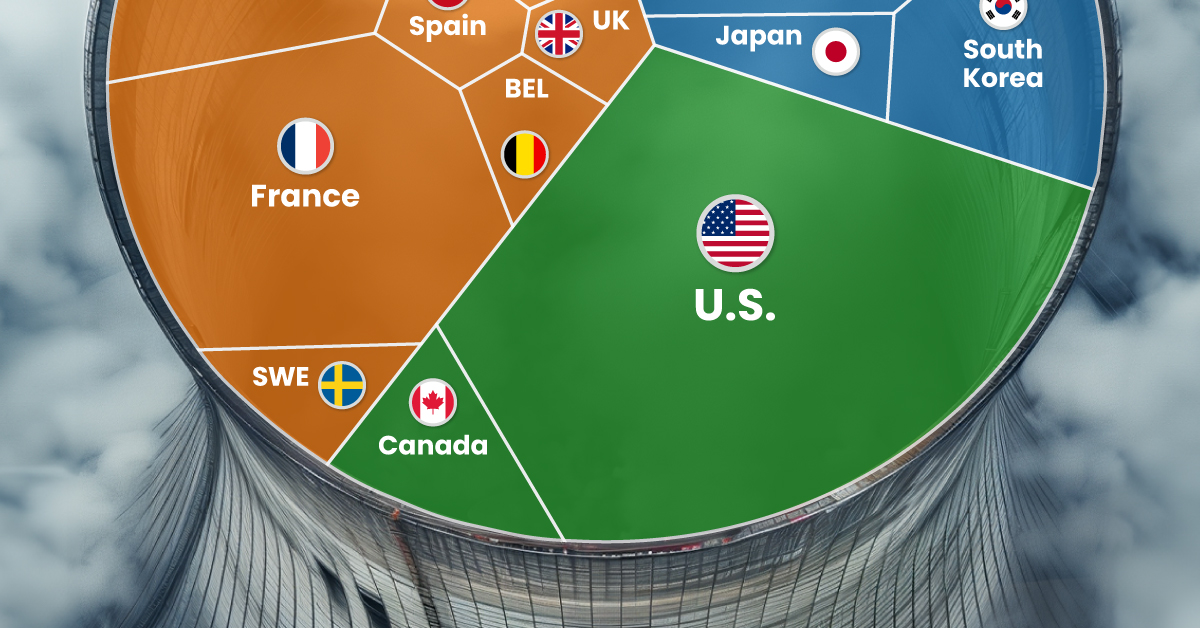
Nuclear energy production in the U.S. is more than twice the amount produced by China (ranked second) and France (ranked third) put together. In total, the U.S. accounts for nearly 30% of global nuclear energy output.
However, nuclear power only accounts for one-fifth of America’s electricity supply. This is in contrast to France, which generates 60% of its electricity from nuclear plants.
| Rank | Country | Nuclear Energy Produced (TWh) | % of Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 772 | 29% |
| 2 | 🇨🇳 China | 383 | 14% |
| 3 | 🇫🇷 France | 363 | 14% |
| 4 | 🇷🇺 Russia | 208 | 8% |
| 5 | 🇰🇷 South Korea | 150 | 6% |
| 6 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 87 | 3% |
| 7 | 🇺🇦 Ukraine | 81 | 3% |
| 8 | 🇩🇪 Germany | 65 | 2% |
| 9 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 61 | 2% |
| 10 | 🇪🇸 Spain | 54 | 2% |
| 11 | 🇸🇪 Sweden | 51 | 2% |
| 12 | 🇧🇪 Belgium | 48 | 2% |
| 13 | 🇬🇧 UK | 42 | 2% |
| 14 | 🇮🇳 India | 40 | 2% |
| 15 | 🇨🇿 Czech Republic | 29 | 1% |
| N/A | 🌐 Other | 219 | 8% |
| N/A | 🌍 Total | 2,653 | 100% |
Another highlight is how China has rapidly grown its nuclear energy capabilities in the last decade. Between 2016 and 2021, for example, it increased its share of global nuclear energy output from less than 10% to more than 14%, overtaking France for second place.
On the opposite end, the UK’s share has slipped to 2% over the same time period.
Meanwhile, Ukraine has heavily relied on nuclear energy to power its grid. In March 2022, it lost access to its key Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Station after Russian forces wrested control of the facility. With six 1,000 MW reactors, the plant is one of the largest in Europe. It is currently not producing any power, and has been the site of recent drone attacks.
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?