Misc
Explore this Fascinating Map of Medieval Europe
View the full-size (13 MB) version of this map.
Explore this Fascinating Map of Medieval Europe
What did Europe look like in the Middle Ages? That’s a tough question to answer since Europe’s borders and territories were (and still are) constantly in flux.
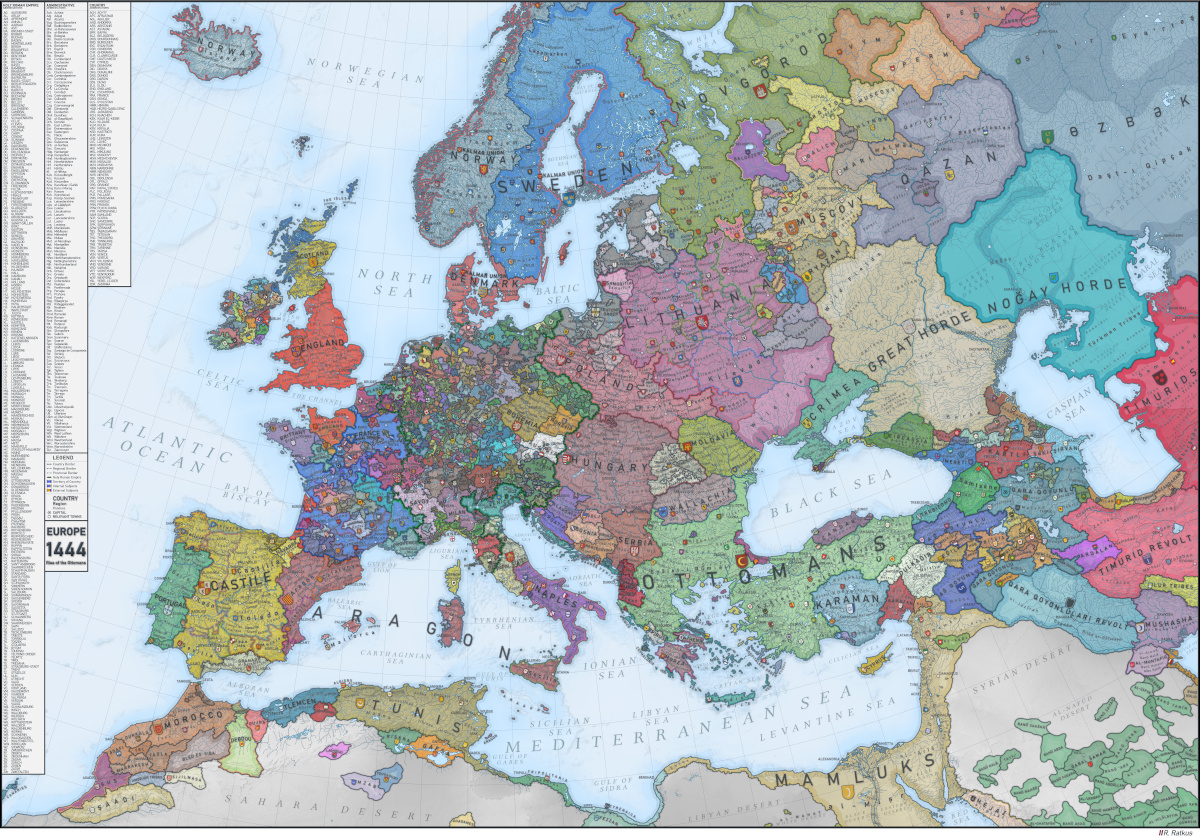
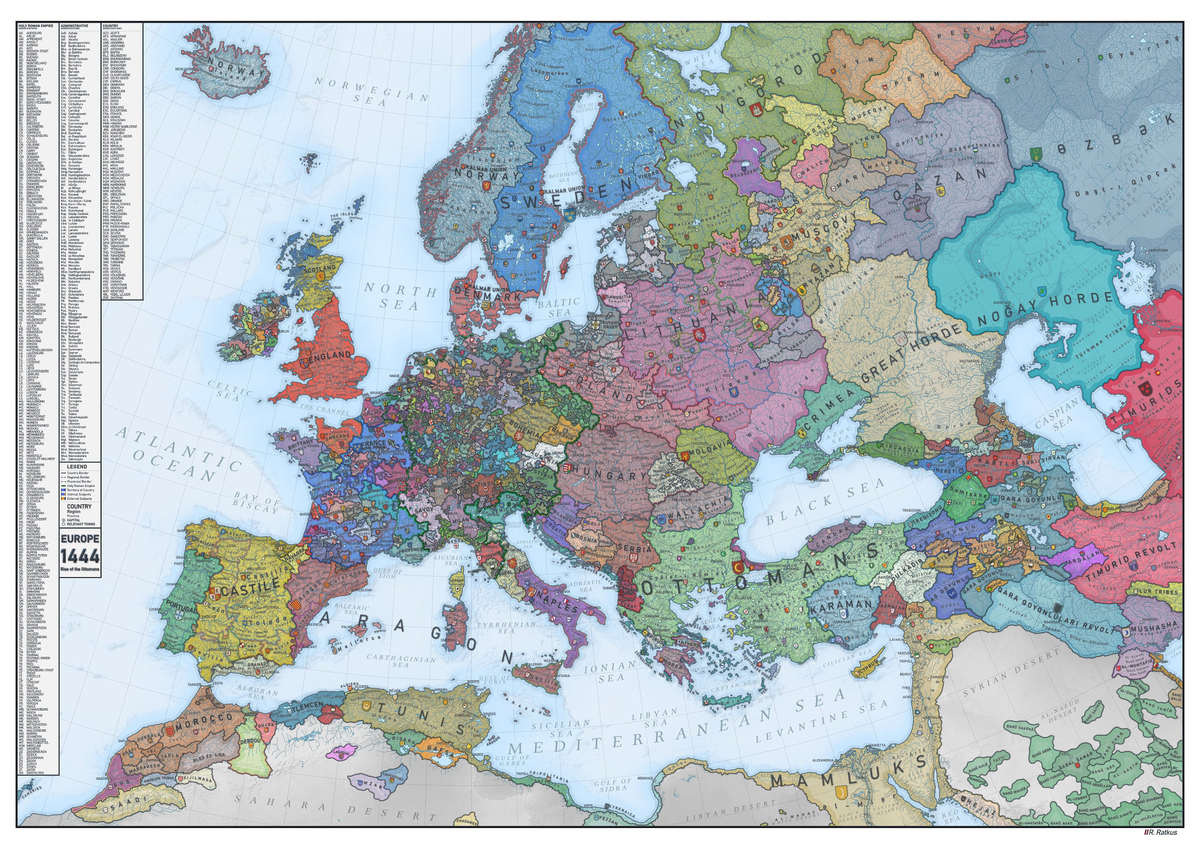
This map, shared by Reddit user /ratkatavobratka, provides a historical snapshot of Europe in 1444—a time when European society was made up mostly of independent territories that were governed by landowners rather than a centralized authority.
Below, we’ll take a closer look at some key regions on the map, and what was happening in these areas at the time.
Some Context: Why 1444?
Before we dive into the analysis, first thing’s first—what’s so special about the year 1444?
It was the year of the Battle of Varna. That’s when the Ottoman army defeated the Hungarians and allowed the Ottoman Empire to expand its reign.
It’s considered a pivotal moment for Ottoman expansion into Southern Europe. In fact, this battle is so historically significant, it was chosen as the start date for a popular video game called Europa Universalis IV.
Feudalism in Medieval Europe
One of the most immediately obvious details of this map of medieval Europe is how fragmented Western Europe was at the time.
This vast array of independent territories technically made up the Holy Roman Empire (the empire’s borders are highlighted in green on the map). But why was the Holy Roman Empire so fragmented?
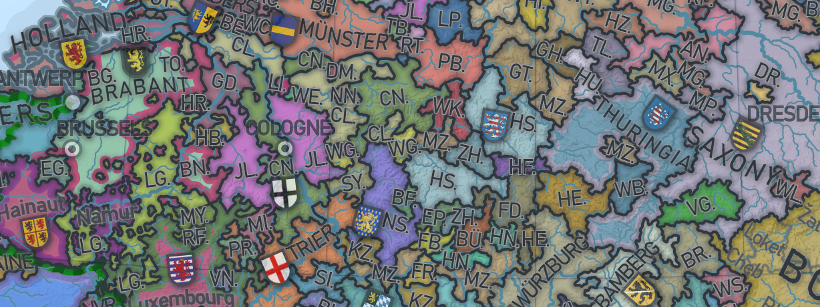
The empire was subdivided into individually governed entities at the time. These independent territories were governed by nobility rather than an absolute monarch. This was possible because the empire was run by the feudal system.
For the non-history buffs reading this, the feudal system was a socio-political system largely characterized by its lack of public authority. Theoretically, it was meant to have a distinct hierarchy:
- Monarchs
At the top of the feudal food chain, monarchs were meant to hold absolute power over their land. However, many lords held so much power over their manors that the monarch acted more as a figurehead. - Lords and Ladies (Nobility)
The nobility was supposed to act as middle management— they were in charge of managing the land and the peasants who worked on it. - Knights
Protectors of the land, knights followed a strict code of conduct, known as chivalry. If they failed to follow their chivalry, their title and land was taken from them. - Peasants
A majority of the medieval population was made up of peasants, who did all the work on the land so lords and knights could plan and prepare for war.
Between the 1200-1400s, battles between nobles and monarchs were almost constant, and the map shows a time when estates were largely governed by the nobility. However, it’s important to note that in the years following 1444, monarchs gradually began to regain their power.
Eventually, governing became more consolidated, and this gradual transition to absolute monarchy marked the early stages of what we now recognize as nation states.
Mighty Lithuania
One very prominent and perhaps surprising section of the map is the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, which today would include large portions of Poland, Belarus, and Ukraine. This snapshot depicts Lithuania at the height of its power, when their territory stretched all the way from the Baltic Sea down to the Black Sea, near Crimea.
Over time power ebbs and flows, and today Lithuania is a much more compact nation.
Staying Power
Europe’s borders have shifted constantly over the long history of the continent, but one area has remained remarkably consistent. On the map above, Portugal looks nearly identical to its present day form. This is because the country’s border with Spain–one of the world’s oldest–has barely shifted at all since the 13th century.
Zooming in on the South: The Rise of the Ottoman Empire
While the Holy Roman Empire was highly fragmented, other empires were much more unified.
For instance, the Ottoman Empire had a much more centralized governing system. In 1444, it was ruled by Fatih Sultan Mehmed (which is Turkish for Sultan Mehmed, the Conqueror). During his reign, the Ottoman Empire conquered Constantinople (now known as Istanbul), which had been ruled by the Byzantine Empire for over a thousand years before the Ottoman army seized power.
Because the Byzantine Empire was what was left of the Roman Empire, this takeover also marked the final fall of the Roman Empire.
Maps Freeze Time
Historical maps are fascinating because they provide a snapshot of the world as it once was (but no longer is).
As previously mentioned, Europe’s borders were (and still are) constantly changing. And it’s interesting to look back on previous eras to remember how far we’ve come.
VC+
VC+: Get Our Key Takeaways From the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
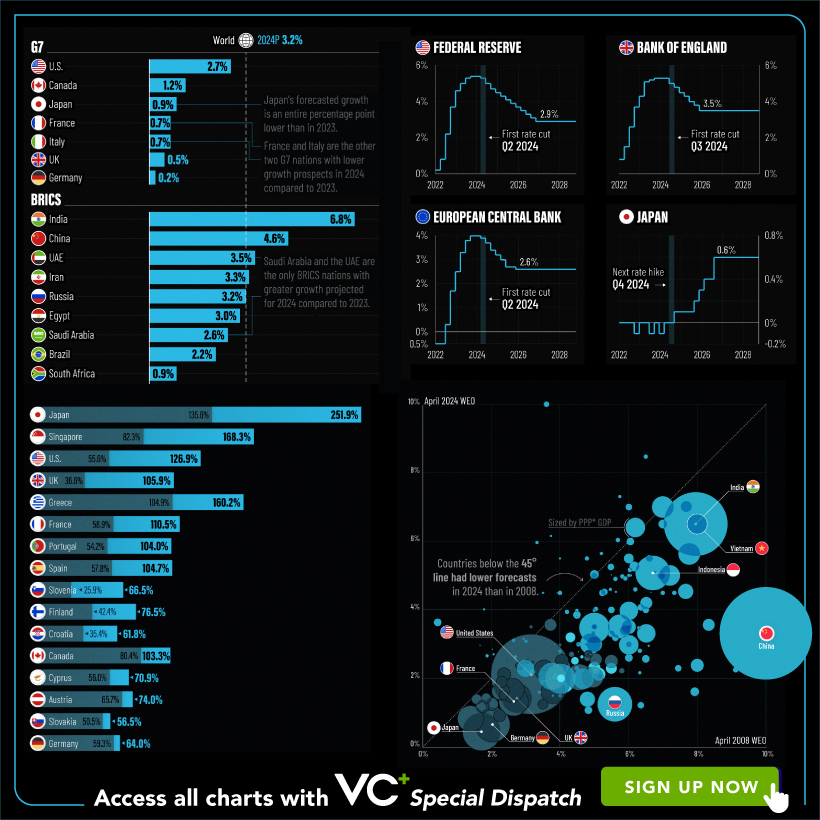
A sneak preview of the exclusive VC+ Special Dispatch—your shortcut to understanding IMF’s World Economic Outlook report.

Have you read IMF’s latest World Economic Outlook yet? At a daunting 202 pages, we don’t blame you if it’s still on your to-do list.
But don’t worry, you don’t need to read the whole April release, because we’ve already done the hard work for you.
To save you time and effort, the Visual Capitalist team has compiled a visual analysis of everything you need to know from the report—and our upcoming VC+ Special Dispatch will be available exclusively to VC+ members on Thursday, April 25th.
If you’re not already subscribed to VC+, make sure you sign up now to receive the full analysis of the IMF report, and more (we release similar deep dives every week).
For now, here’s what VC+ members can expect to receive.
Your Shortcut to Understanding IMF’s World Economic Outlook
With long and short-term growth prospects declining for many countries around the world, this Special Dispatch offers a visual analysis of the key figures and takeaways from the IMF’s report including:
- The global decline in economic growth forecasts
- Real GDP growth and inflation forecasts for major nations in 2024
- When interest rate cuts will happen and interest rate forecasts
- How debt-to-GDP ratios have changed since 2000
- And much more!
Get the Full Breakdown in the Next VC+ Special Dispatch
VC+ members will receive the full Special Dispatch on Thursday, April 25th.
Make sure you join VC+ now to receive exclusive charts and the full analysis of key takeaways from IMF’s World Economic Outlook.
Don’t miss out. Become a VC+ member today.
What You Get When You Become a VC+ Member
VC+ is Visual Capitalist’s premium subscription. As a member, you’ll get the following:
- Special Dispatches: Deep dive visual briefings on crucial reports and global trends
- Markets This Month: A snappy summary of the state of the markets and what to look out for
- The Trendline: Weekly curation of the best visualizations from across the globe
- Global Forecast Series: Our flagship annual report that covers everything you need to know related to the economy, markets, geopolitics, and the latest tech trends
- VC+ Archive: Hundreds of previously released VC+ briefings and reports that you’ve been missing out on, all in one dedicated hub
You can get all of the above, and more, by joining VC+ today.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023