Politics
The Least and Most Trusted News Sources in America
Which news sources are the most trustworthy?
This seems like a simple question – but in the “fake news” era, things haven’t been so straightforward. As a result, the public’s level of trust in mass media has fallen to a low of just 32%.
Examining The Trust Spectrum
A new survey by the Trusting News Project helps shed more light on the state of trust in media, revealing the attitudes of 8,728 people in the United States. Administered through 28 media outlets around the country, the survey asked respondents how trusting they are of the media, whether they financially support news organizations, and which outlets are the most (and least) trustworthy.
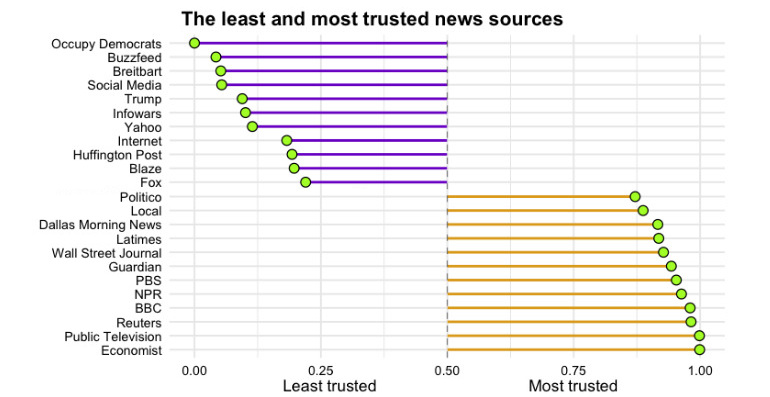
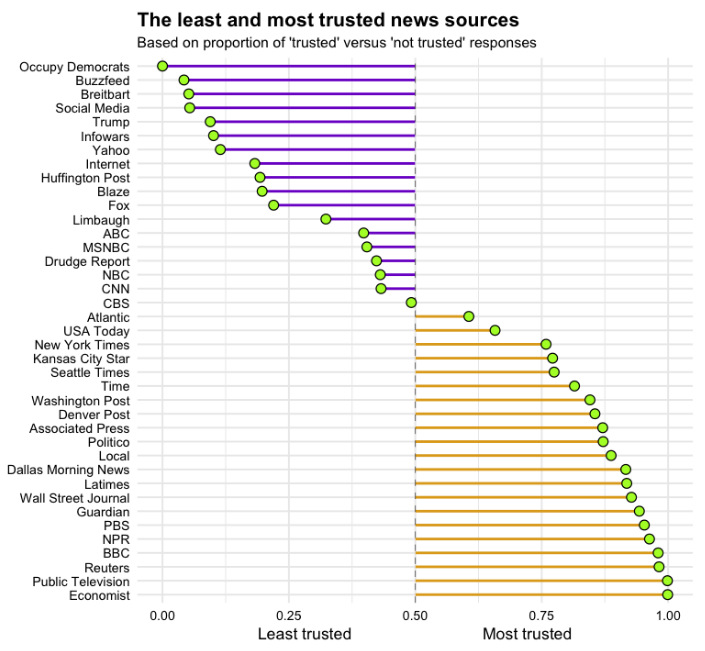
Here are results to the question about trustworthiness of specific news sources:
Before we dive into the results, it’s worth noting that respondents were self-selected and tend to skew to the liberal side of the political spectrum. More on this later in the post, but keep it in mind.
High Trust, Low Trust
According to the survey respondents, The Economist is the most trustworthy news source in media.
On the far opposite side of the spectrum? It’s Occupy Democrats, an extreme left advocacy group that claims to be the “new counterbalance to the Republican Tea Party”.
Interestingly, both The Economist and Occupy Democrats have close to the same amount of Facebook likes (8.2 million vs. 6.7 million), which shows that despite polar opposite perceptions, people are willing to grant an audience to both groups.
Also scoring well for trust included outlets such as Reuters, NPR, The Wall Street Journal, Politico, and The Guardian. Meanwhile, bad trust scores went to Buzzfeed, Breitbart, Infowars, Yahoo, and The Huffington Post.
Trust By Political Skew
It’s also worth breaking down respondents into groups based on political orientation, to see what differences this can point out regarding trust and the level of financial support being provided to news organizations.
On the following graph, the X-axis shows age groups, while the Y-axis shows levels of trust (higher is more), as well as the number of news organizations respondents claim to financially support (higher is more).
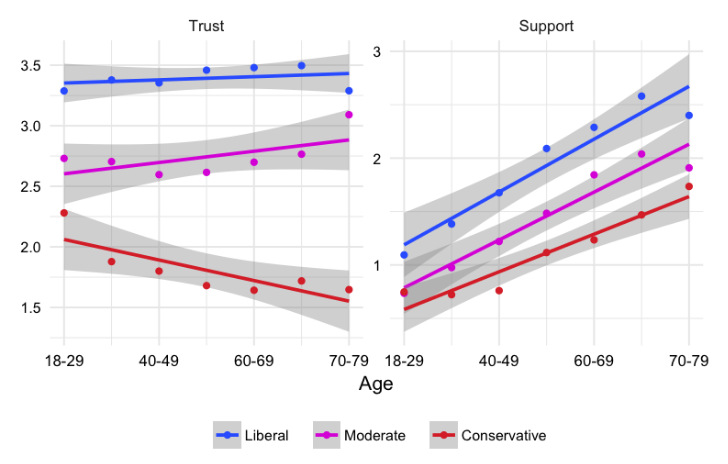
For people that identify as liberals or moderates, trust of news outlets is positively correlated with age. Interestingly, for conservatives, trust in media starts low and seems to decrease with age.
Audience Biases
As mentioned earlier, although the sample size was big (>8,000), there are a few biases worth noting:
- Survey respondents were not randomly selected, and voluntarily filled out the survey.
- Survey respondents tended to be geographically near the 28 newsrooms, many of which were local, that made the survey available on their websites.
- In terms of political orientation, the audience skews towards liberals. (See below diagram).
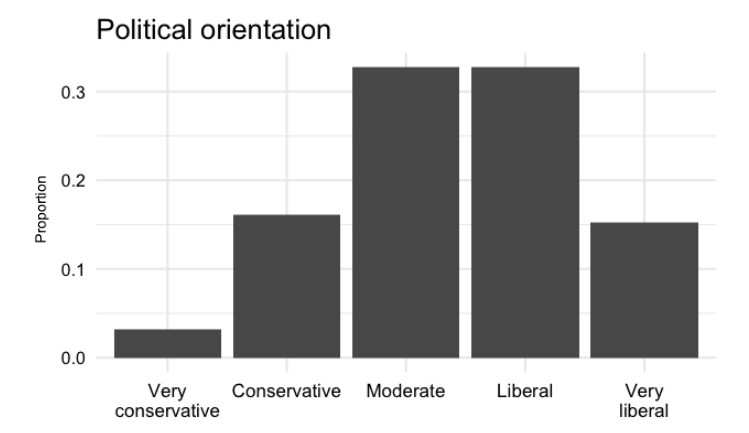
And while the audience may not be fully representative of the American public, the survey definitely does provide interesting insight on trust in media. Get access to the full report by clicking here.
War
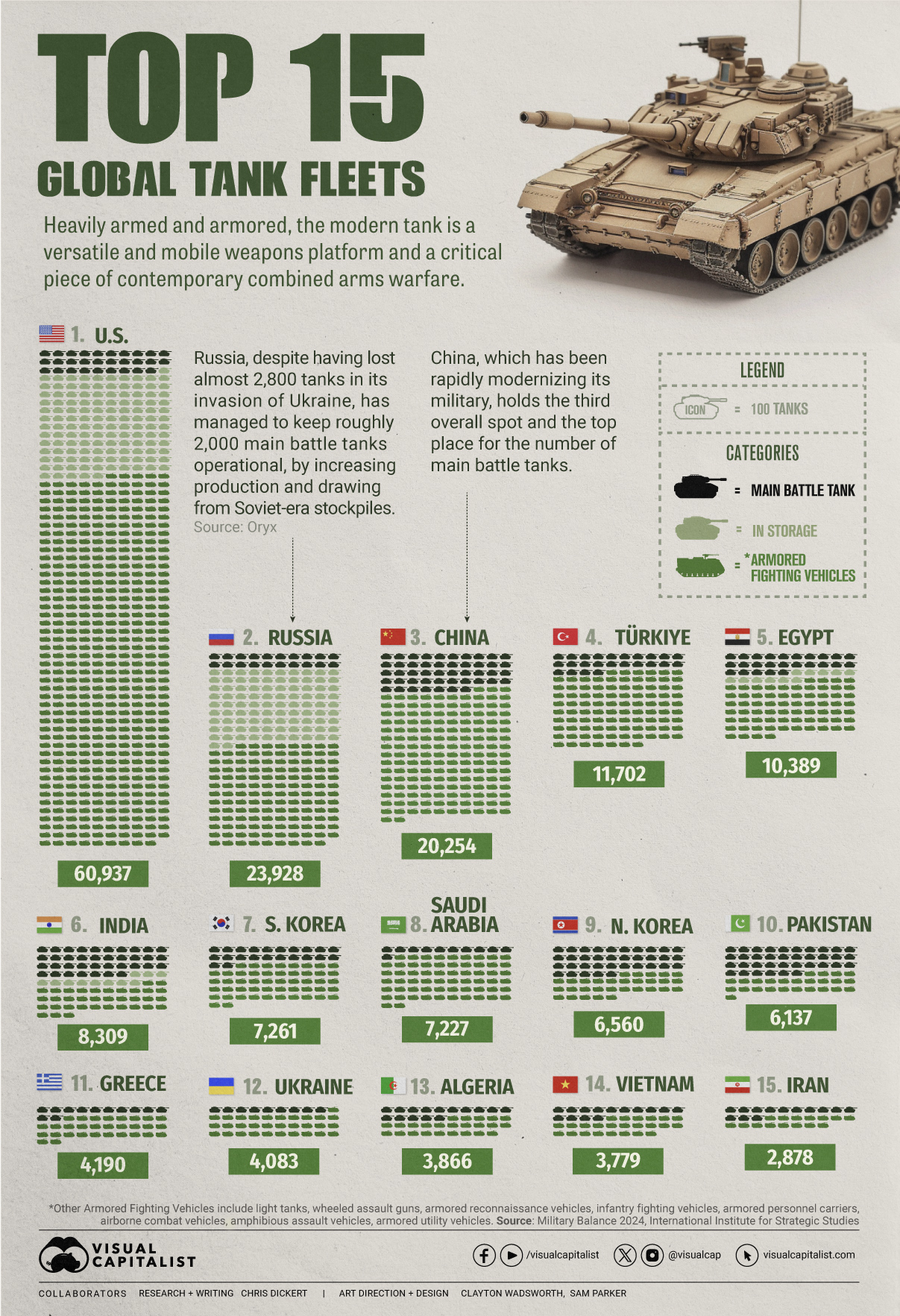
Visualized: Top 15 Global Tank Fleets
Heavily armed and armored, the modern tank is a versatile and mobile weapons platform, and a critical piece of contemporary warfare.

The Top 15 Global Tank Fleets
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Heavily armed and armored, the modern tank is a versatile and mobile weapons platform, and a critical piece of contemporary warfare.
This visualization shows the top 15 global tank fleets, using data from the 2024 Military Balance report from the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS).
Let’s take an in-depth look at the top three fleets:
1. United States
As the world’s pre-eminent military power, it’s perhaps no surprise that the United States also has the largest tank fleet, by a wide margin.
In total, they have just over 45,000 armored fighting vehicles in operation, along with 2,640 main battle tanks (MBTs), and 12,800 vehicles in storage, of which 2,000 are main battle tanks.
| Category | Vehicles | Global rank |
|---|---|---|
| Main battle tanks | 2,640 | 4 |
| Armored reconnaissance | 1,745 | 1 |
| Infantry fighting vehicles | 3,262 | 3 |
| Armored personnel carriers | 10,644 | 1 |
| Amphibious assault vehicles | 1,401 | 1 |
| Armored utility vehicles | 28,445 | 1 |
| Storage | 12,800 | 1 |
| Total | 60,937 | 1 |
The U.S. is internalizing the lessons from the ongoing invasion of Ukraine, where Western-supplied anti-tank weapons and massed Ukrainian artillery have been cutting Russian tanks to pieces. As a result, the U.S. recently canceled an upgrade of the M1 Abrams in favor of a more ambitious upgrade.
Meanwhile, the U.S. is nervously eyeing a more confident China and a potential clash over Taiwan, where air and naval forces will be critical. However, a recent war game showed that Taiwanese mechanized ground forces, kitted out with American-made tanks and armored fighting vehicles, were critical in keeping the island autonomous.
2. Russia
According to Oryx, a Dutch open-source intelligence defense website, at time of writing, Russia has lost almost 2,800 main battle tanks since invading Ukraine. Considering that in the 2022 edition of the Military Balance, Russia was estimated to have 2,927 MBTs in operation, those are some hefty losses.
Russia has been able to maintain about 2,000 MBTs in the field, in part, by increasing domestic production. Many defense plants have been taken over by state-owned Rostec and now operate around the clock. Russia is also now spending a full third of their budget on defense, equivalent to about 7.5% of GDP.
At the same time, they’ve also been drawing down their Soviet-era stockpiles, which are modernized before being sent to the front. Just how long they can keep this up is an open question; their stockpiles are large, but not limitless. Here is what their storage levels look like:
| Category | 2023 | 2024 | YOY change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main battle tanks | 5,000 | 4,000 | -20.0% |
| Armored reconnaissance | 1,000 | 100 | -90.0% |
| Infantry fighting vehicles | 4,000 | 2,800 | -30.0% |
| Armored personnel carriers | 6,000 | 2,300 | -61.7% |
| Total | 16,000 | 9,200 | -42.5% |
3. China
China holds the third overall spot and top place globally for the number of main battle tanks in operation. Untypically, the People’s Liberation Army has no armored vehicles in storage, which perhaps isn’t surprising when you consider that China has been rapidly modernizing its military and that stockpiles usually contain older models.
China also has one of the world’s largest fleets of armored fighting vehicles, second only to the United States. Breaking down that headline number, we can also see that they have the largest number of light tanks, wheeled guns, and infantry fighting vehicles.
| Category | Vehicles | Global rank |
|---|---|---|
| Main battle tanks | 4,700 | 1 |
| Light tanks | 1,330 | 1 |
| Wheeled guns | 1,250 | 1 |
| Infantry fighting vehicles | 8,200 | 1 |
| Armored personnel carriers | 3,604 | 5 |
| Airborne combat vehicles | 180 | 2 |
| Amphibious assault vehicles | 990 | 2 |
| Total | 20,254 | 3 |
This is equipment that would be integral if China were to make an attempt to reunify Taiwan with the mainland by force, where lightly armored mechanized units need to move with speed to occupy the island before Western allies can enter the fray. It’s worth noting that China also has one of the world’s largest fleets of amphibious assault vehicles.
End of the Tank?
Many commentators at the outset of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, were quick to predict the end of the tank, however, to paraphrase Mark Twain, reports of the tank’s demise are greatly exaggerated.
With the U.S. and China both developing remote and autonomous armored vehicles, tanks could be quite different in the future, but there is nothing else that matches them for firepower, mobility, and survivability on the modern battlefield today.
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc1 week ago
Misc1 week agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes