Is Vertical Farming the Future?
The following content is sponsored by Global X ETFs.
The Briefing
- Land degradation is a long-term sustainability risk
- Vertical farms can grow food indoors with less land and water than traditional methods
Is Vertical Farming the Future?
According to the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), half of the Earth’s topsoil has been lost over the past 150 years. This issue is known as land degradation, and it’s caused by natural and human forces such as droughts, overfarming, and pollution.
In this graphic sponsored by Global X ETFs, we’ve illustrated an innovative solution to land degradation known as vertical farming.
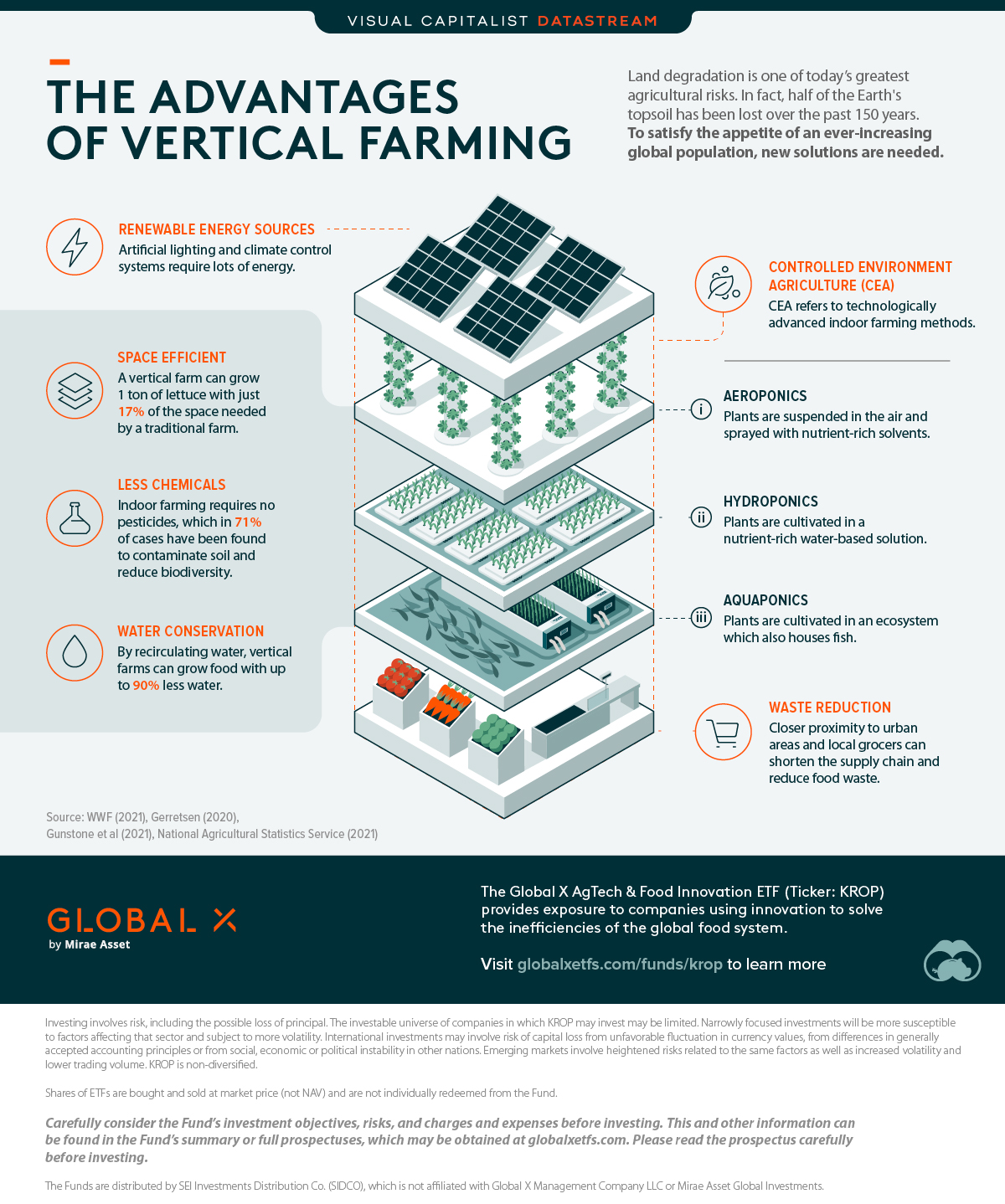
Advantages of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming is best defined as growing food indoors and on vertically stacked layers. It utilizes technologies known as controlled environment agriculture (CEA):
- Aeroponics: Plants are suspended in the air and sprayed with nutrient-rich solvents
- Hydroponics: Plants are cultivated in a nutrient-rich water-based solution
- Aquaponics: Plants are cultivated in an ecosystem which also houses fish
Vertical farms can grow 1 ton of lettuce with just 17% of the space needed for a traditional farm, meaning they are much more space efficient. This is a direct solution for land degradation, but the benefits don’t end there.
Farming in a controlled environment cuts down on chemical usage because there is no longer a need for pesticides. A recent U.S. study found that in 71% of usage cases, pesticides have contaminated soil and reduced biodiversity.
Furthermore, vertical farms can reduce water use by up to 90% thanks to recirculation. This is a massive improvement when considering that traditional farms account for 70% of global water consumption.
What’s the Trade-off?
Like most things in life, vertical farms also have their drawbacks.
The first challenge is high energy consumption due to the lack of natural sunlight and water. Both of these inputs must be provided by using electricity, which may not be ideal depending on location. The second challenge is costs, not just because of energy consumption, but also due to the equipment needed for CEA systems.
The table below compares a traditional outdoor farm with a theoretical vertical farm. These estimates illustrate a clear trade-off between i) greater output and less water usage; and ii) a larger carbon footprint.
| Metric | Traditional Outdoor Farm | Vertical Farm | Percentage Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lettuce output per 1 acre | 16 tons | 126 tons | +787% |
| Kg CO₂ emitted per ton of lettuce | 160 kg | 540 kg | +337% |
| KL of water used per ton of lettuce | 118 kL | 6 kL | -95% |
Traditional farm yields are based on the U.S. 2020 average. Source: Global X ETFs
With global population expected to reach 10 billion people by 2060, more efficient methods of farming are needed. Vertical farms, alongside other innovations in agriculture and food, could be the answer.
Source: Global X ETFs, WWF
-
 Datastream10 months ago
Datastream10 months agoCan You Calculate Your Daily Carbon Footprint?
Discover how the average person's carbon footprint impacts the environment and learn how carbon credits can offset your carbon footprint.
-
 Datastream11 months ago
Datastream11 months agoThe 10 Longest Range EVs for 2023
This infographic lists 10 of the longest range EVs currently for sale in the U.S. in 2023. The Lucid Air takes first place at 516 miles.
-

 Economy11 months ago
Economy11 months agoCharted: Public Trust in the Federal Reserve
Public trust in the Federal Reserve chair has hit its lowest point in 20 years. Get the details in this infographic.
-
 Datastream1 year ago
Datastream1 year agoHow Gen Z Feels About Its Financial Future
Despite the looming uncertainty, members of Gen Z maintains an optimistic outlook about their financial future
-
 Datastream1 year ago
Datastream1 year agoMore U.S. Tech Companies are Adopting Unequal Dual-Class Voting Structures
Dual-class share structures are rising in popularity, and they give executives much more voting power within a public company.
-

 Datastream1 year ago
Datastream1 year agoThe Link Between Entrepreneurship and Mental Health Conditions
Research explores the link between entrepreneurship and mental health conditions such as ADHD and bipolar disorder


