Demographics
Interactive: How Do Americans Differ by Age?
var divElement = document.getElementById(‘viz1563771062413’); var vizElement = divElement.getElementsByTagName(‘object’)[0]; if ( divElement.offsetWidth > 800 ) { vizElement.style.width=’1125px’;vizElement.style.height=’1002px’;} else if ( divElement.offsetWidth > 500 ) { vizElement.style.width=’100%’;vizElement.style.height=’927px’;} else { vizElement.style.width=’100%’;vizElement.style.height=’1327px’;} var scriptElement = document.createElement(‘script’); scriptElement.src = ‘https://public.tableau.com/javascripts/api/viz_v1.js’; vizElement.parentNode.insertBefore(scriptElement, vizElement);
Interactive: How Do Americans Differ by Age?
The human experience changes dramatically over the course of a lifetime.
While we each intrinsically know that our days as teenagers will be vastly different from those as senior citizens, it is interesting to see how this looks from a 10,000-foot perspective.
Using demographic data on the American populace, we can spot key differences between age groups, including some aspects that make each generation of Americans unique.
The U.S. Population, by Age
Today’s interactive data visualization comes to us from Overflow Data, and it charts out the entire U.S. population by age group.
The graphic allows you to sort demographics based on data pertaining to specific topics—such as whether people own or rent their house—to see how age affects answers to these different questions. The interactive visualization also allows you to filter results by geographic region, sex, marital status, or employment status.
Data here comes from the 2017 Public Use Microdata Sample (PUMS) via the American Community Survey, which is published by the U.S. Census Bureau.
Gauging Differences
Let’s dive into how American differ by age, by looking at some specific charts:
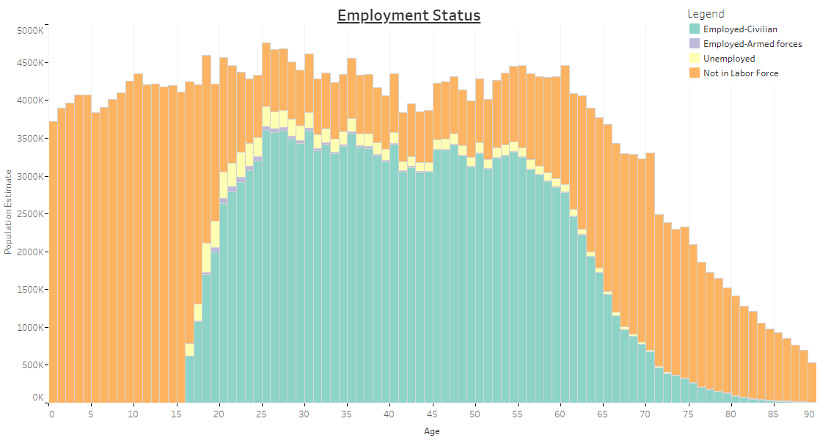
Employment Status, by Age
This is a simple one to start with, but it makes it easy to see how the data works. In the below chart, it’s evident that most younger and older Americans are not in the labor force, while the majority of working age Americans are employed or seeking work (unemployed).
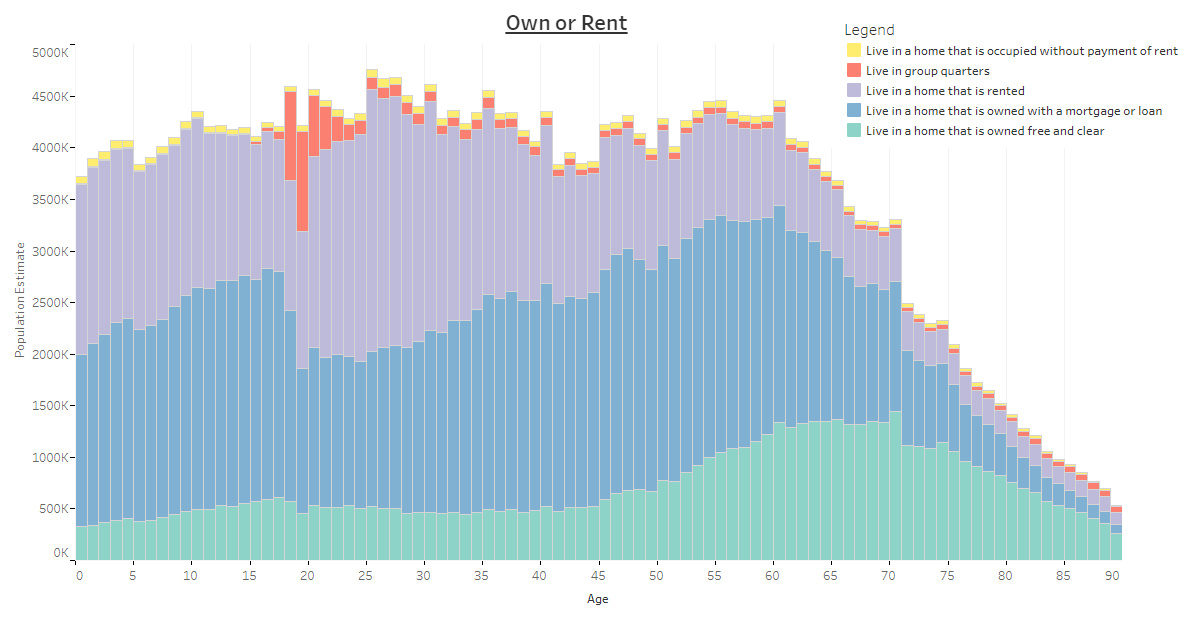
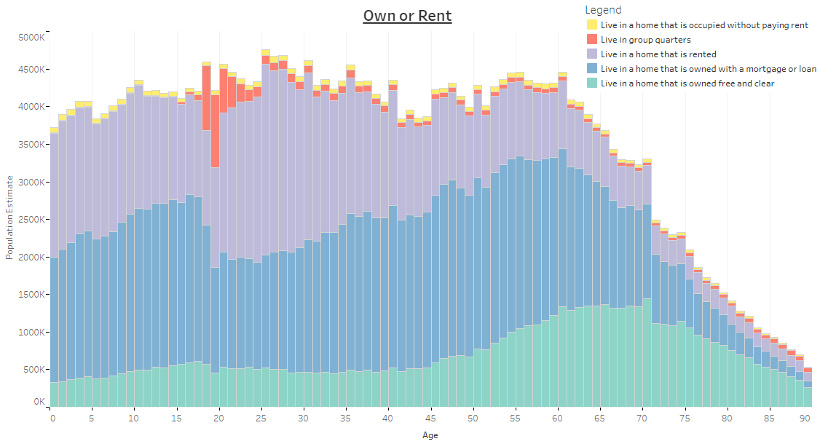
Own or Rent, by Age
How about looking at whether Americans own or rent, or even if they live in a group quarters?
Race, by Age
The below chart is sorted by percentile, and it shows the percentage of individuals by race according to their age group. As the population skews younger, so does its racial diversity.
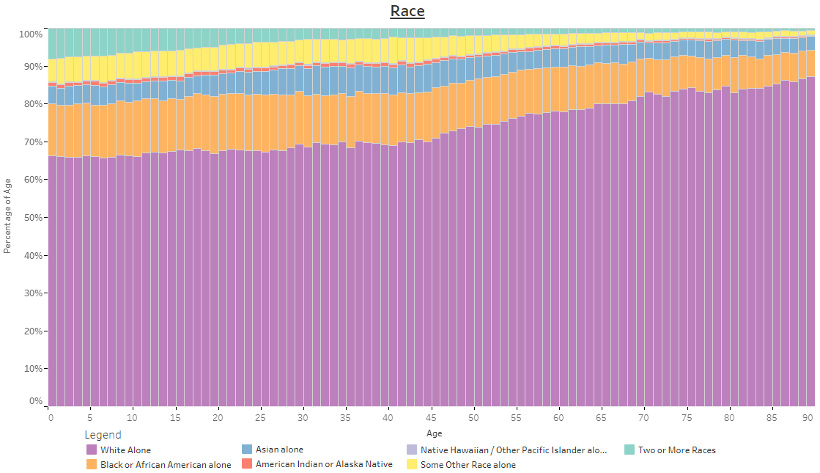
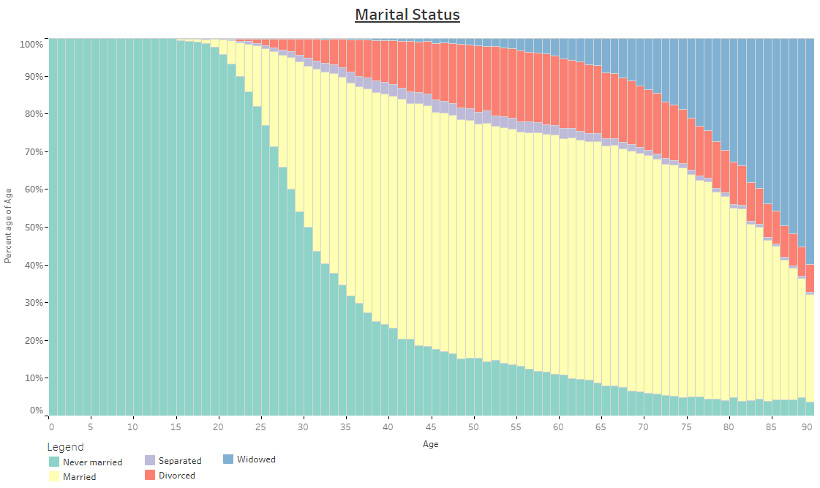
Marital Status, by Age
The below chart is sorted by percentile, and it shows the marital status (married, divorced, etc.) of different age groups.
The Generational Effect
For more on how Americans differ by age, learn about how different generations approach the workplace, as well as how they think about investing.
Demographics
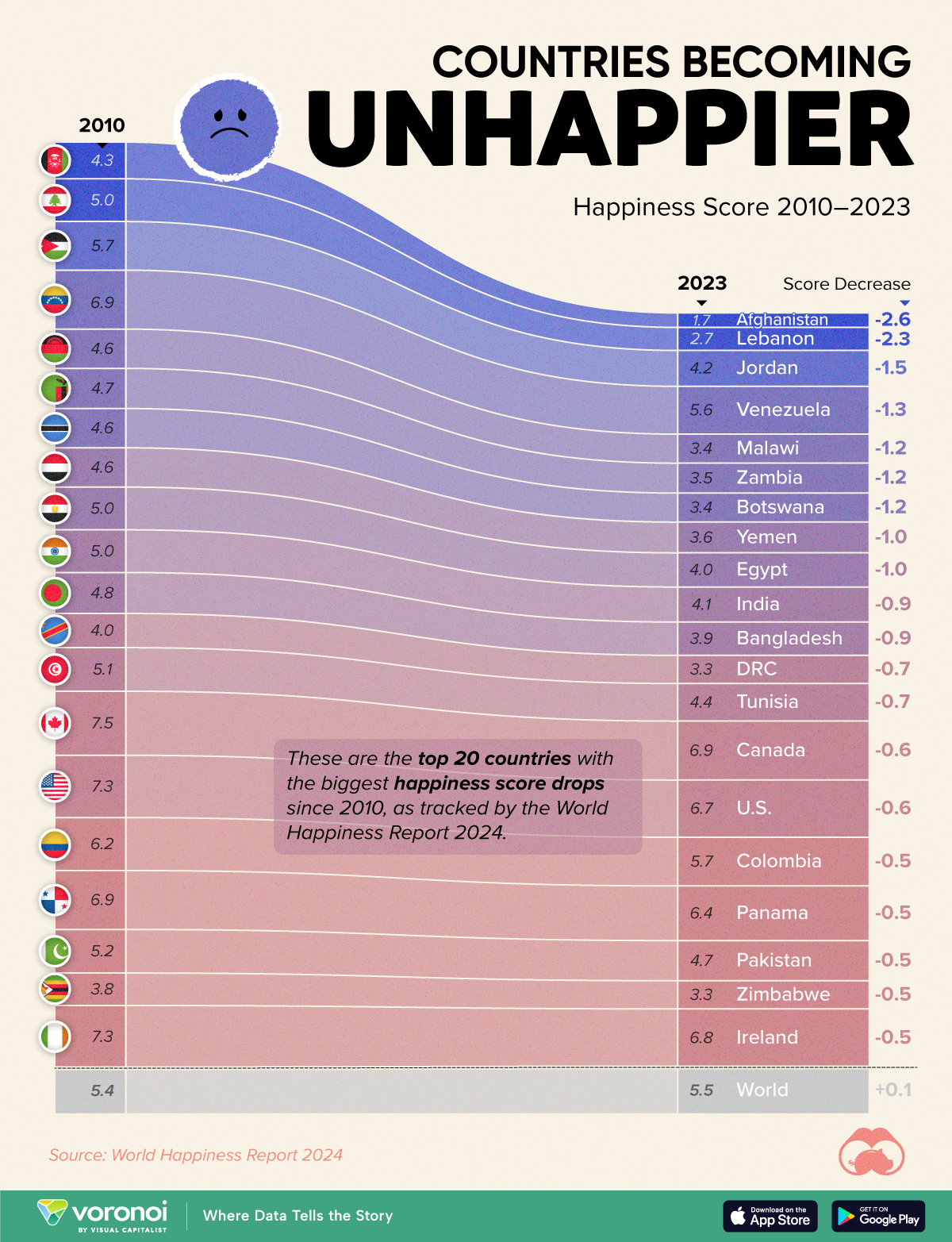
The Countries That Have Become Sadder Since 2010
Tracking Gallup survey data for more than a decade reveals some countries are witnessing big happiness declines, reflecting their shifting socio-economic conditions.
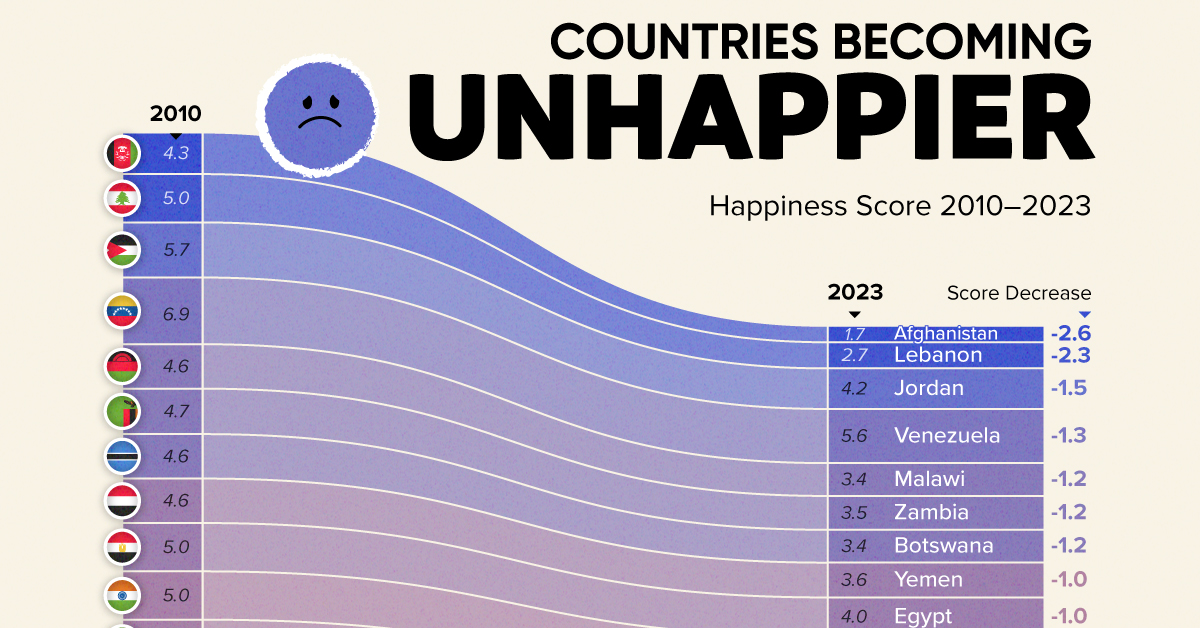
The Countries That Have Become Sadder Since 2010
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Can happiness be quantified?
Some approaches that try to answer this question make a distinction between two differing components of happiness: a daily experience part, and a more general life evaluation (which includes how people think about their life as a whole).
The World Happiness Report—first launched in 2012—has been making a serious go at quantifying happiness, by examining Gallup poll data that asks respondents in nearly every country to evaluate their life on a 0–10 scale. From this they extrapolate a single “happiness score” out of 10 to compare how happy (or unhappy) countries are.
More than a decade later, the 2024 World Happiness Report continues the mission. Its latest findings also include how some countries have become sadder in the intervening years.
Which Countries Have Become Unhappier Since 2010?
Afghanistan is the unhappiest country in the world right now, and is also 60% unhappier than over a decade ago, indicating how much life has worsened since 2010.
In 2021, the Taliban officially returned to power in Afghanistan, after nearly two decades of American occupation in the country. The Islamic fundamentalist group has made life harder, especially for women, who are restricted from pursuing higher education, travel, and work.
On a broader scale, the Afghan economy has suffered post-Taliban takeover, with various consequent effects: mass unemployment, a drop in income, malnutrition, and a crumbling healthcare system.
| Rank | Country | Happiness Score Loss (2010–24) | 2024 Happiness Score (out of 10) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇦🇫 Afghanistan | -2.6 | 1.7 |
| 2 | 🇱🇧 Lebanon | -2.3 | 2.7 |
| 3 | 🇯🇴 Jordan | -1.5 | 4.2 |
| 4 | 🇻🇪 Venezuela | -1.3 | 5.6 |
| 5 | 🇲🇼 Malawi | -1.2 | 3.4 |
| 6 | 🇿🇲 Zambia | -1.2 | 3.5 |
| 7 | 🇧🇼 Botswana | -1.2 | 3.4 |
| 8 | 🇾🇪 Yemen | -1.0 | 3.6 |
| 9 | 🇪🇬 Egypt | -1.0 | 4.0 |
| 10 | 🇮🇳 India | -0.9 | 4.1 |
| 11 | 🇧🇩 Bangladesh | -0.9 | 3.9 |
| 12 | 🇨🇩 DRC | -0.7 | 3.3 |
| 13 | 🇹🇳 Tunisia | -0.7 | 4.4 |
| 14 | 🇨🇦 Canada | -0.6 | 6.9 |
| 15 | 🇺🇸 U.S. | -0.6 | 6.7 |
| 16 | 🇨🇴 Colombia | -0.5 | 5.7 |
| 17 | 🇵🇦 Panama | -0.5 | 6.4 |
| 18 | 🇵🇰 Pakistan | -0.5 | 4.7 |
| 19 | 🇿🇼 Zimbabwe | -0.5 | 3.3 |
| 20 | 🇮🇪 Ireland | -0.5 | 6.8 |
| N/A | 🌍 World | +0.1 | 5.5 |
Nine countries in total saw their happiness score drop by a full point or more, on the 0–10 scale.
Noticeably, many of them have seen years of social and economic upheaval. Lebanon, for example, has been grappling with decades of corruption, and a severe liquidity crisis since 2019 that has resulted in a banking system collapse, sending poverty levels skyrocketing.
In Jordan, unprecedented population growth—from refugees leaving Iraq and Syria—has aggravated unemployment rates. A somewhat abrupt change in the line of succession has also raised concerns about political stability in the country.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
-

 Green3 weeks ago
Green3 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?