Technology
The Industrial Internet of Things as the Next Big Growth Driver?

The Industrial Internet of Things as the Next Big Growth Driver?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is often marketed as a consumer-based technology phenomenon that will combine the potential of low-cost sensors and big data with wide-scale internet connectivity.
The promise of this consumer-focused vision of IoT is to change how we interact with daily objects in our lives. When people talk about the IoT, they often bring up ideas such as the connected home, automobiles, or health – concepts that will change how we live on a personal level.
But flying under the radar is a less sexy sub-sector of the IoT that could ultimately prove to be the most transformative – the marriage of the internet of things with industrial applications such as mining, oil and gas, infrastructure, aviation, locomotives, cities, farming, manufacturing, and power generation.
It’s been coined the “Industrial Internet of Things” (IIoT) by giants like GE, AT&T, Cisco, Intel, and IBM– and today’s infographic from RS Components shows that the economic growth stemming from this industrial internet revolution could be game-changing.
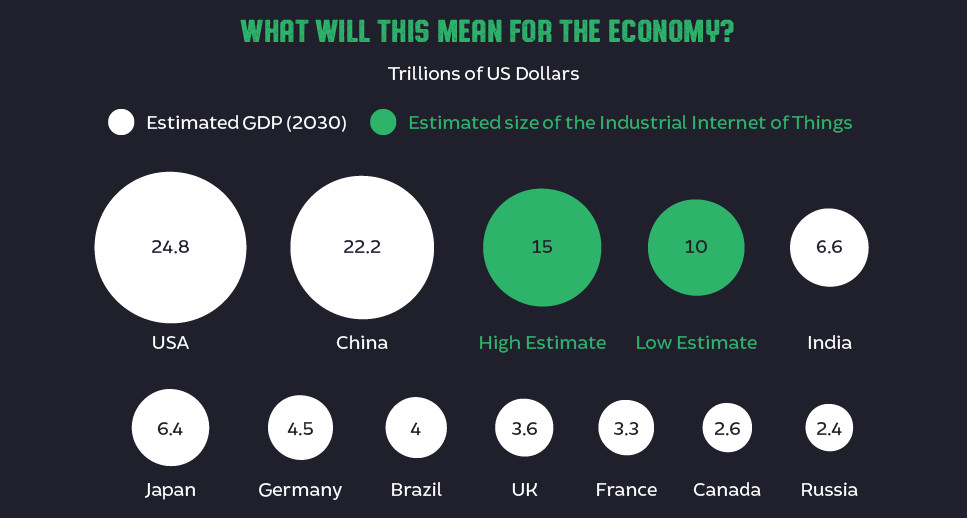
Industrial Internet of Things
The opportunity behind the IIoT is massive, and it’s measured in the trillions of dollars.
GE, for example, expects that by 2030 that it will add $10 to $15 trillion to global GDP, and that it could raise average income significantly throughout the world.
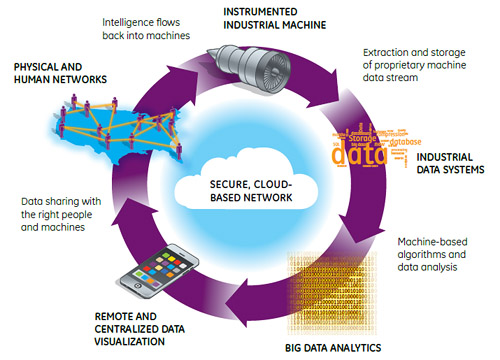
Like previous industrial revolutions, the IIoT will allow for greater automation of previously human-intensive work, creating greater productivity per man-hour invested.
Some potential applications:
Smart Farming: Making use of the vast amounts of information from crop yields, soil-mapping, fertilizer applications, weather data, machinery, and animal health, to improve yields and cut costs in the modern farming environment.
Smart Manufacturing: Using the industrial internet to create a fundamental shift in how products are invented, manufactured, shipped and sold. Intelligent networks will power the value chain – connecting people, processes and data and generating new best practices.
Smart Cities: Cities could stand to benefit significantly from connecting people, processes, data, and things together. City assets such as libraries, transportation systems, power plants, water supply networks, waste management systems, law enforcement, hospitals and other community services could feed off each other. Local governments will understand what is happening on micro and macro levels, and how the city is evolving.
Smart Energy: Power generation can be improved by combining sensors, big data, and connectivity. Imagine wind farms that make slight mechanical adjustments to capitalize on the small changes in wind velocity or direction, to be more efficient – this is only scratching the surface of what is possible.
Technology
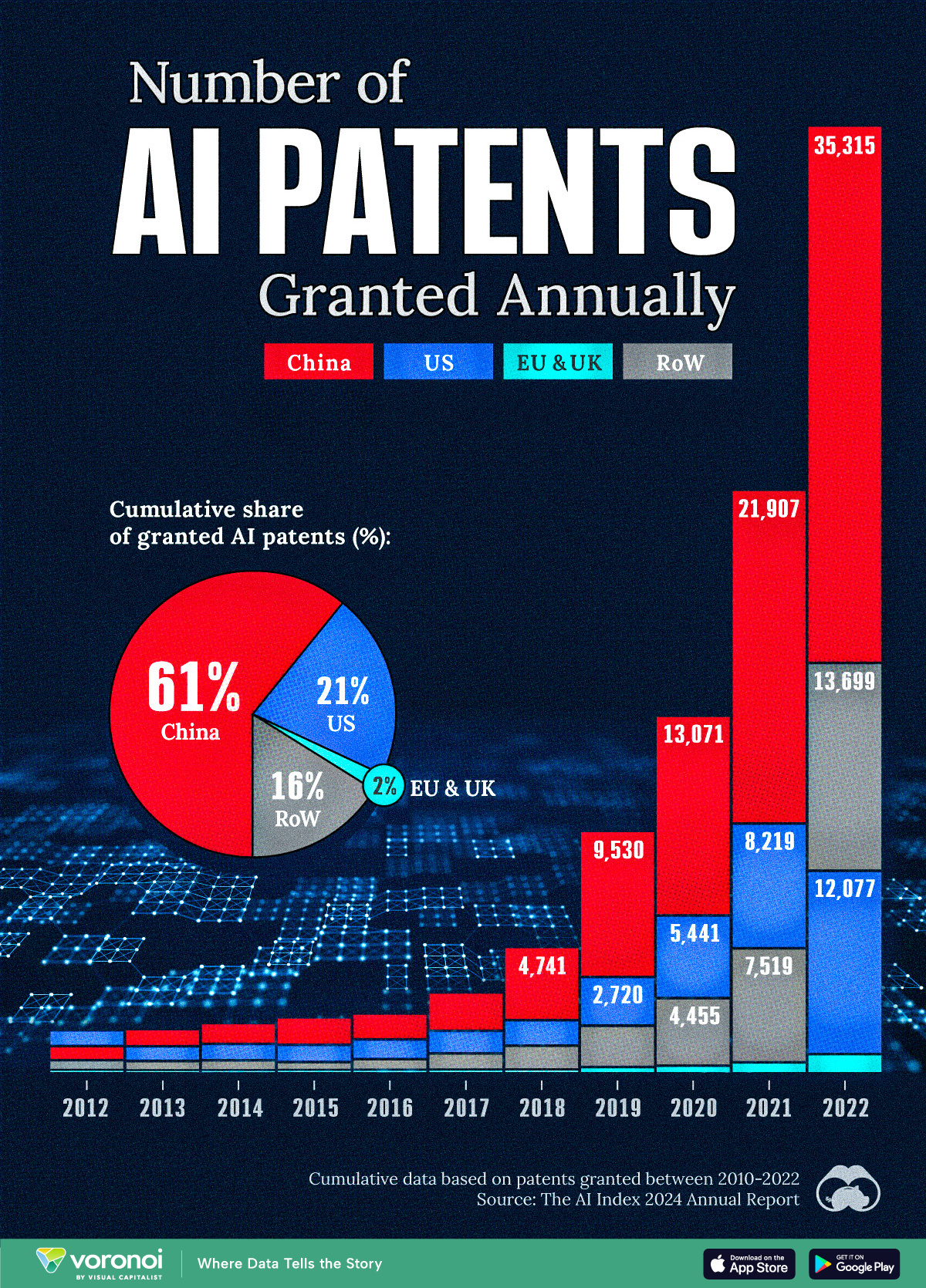
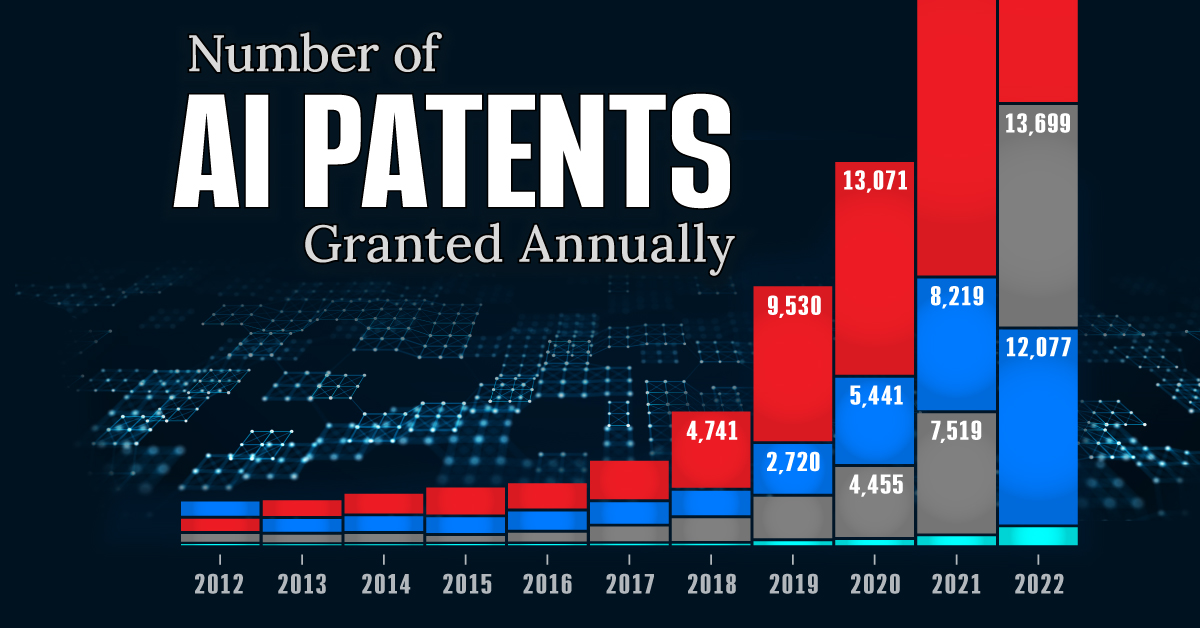
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This infographic shows the number of AI-related patents granted each year from 2010 to 2022 (latest data available). These figures come from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET), accessed via Stanford University’s 2024 AI Index Report.
From this data, we can see that China first overtook the U.S. in 2013. Since then, the country has seen enormous growth in the number of AI patents granted each year.
| Year | China | EU and UK | U.S. | RoW | Global Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 307 | 137 | 984 | 571 | 1,999 |
| 2011 | 516 | 129 | 980 | 581 | 2,206 |
| 2012 | 926 | 112 | 950 | 660 | 2,648 |
| 2013 | 1,035 | 91 | 970 | 627 | 2,723 |
| 2014 | 1,278 | 97 | 1,078 | 667 | 3,120 |
| 2015 | 1,721 | 110 | 1,135 | 539 | 3,505 |
| 2016 | 1,621 | 128 | 1,298 | 714 | 3,761 |
| 2017 | 2,428 | 144 | 1,489 | 1,075 | 5,136 |
| 2018 | 4,741 | 155 | 1,674 | 1,574 | 8,144 |
| 2019 | 9,530 | 322 | 3,211 | 2,720 | 15,783 |
| 2020 | 13,071 | 406 | 5,441 | 4,455 | 23,373 |
| 2021 | 21,907 | 623 | 8,219 | 7,519 | 38,268 |
| 2022 | 35,315 | 1,173 | 12,077 | 13,699 | 62,264 |
In 2022, China was granted more patents than every other country combined.
While this suggests that the country is very active in researching the field of artificial intelligence, it doesn’t necessarily mean that China is the farthest in terms of capability.
Key Facts About AI Patents
According to CSET, AI patents relate to mathematical relationships and algorithms, which are considered abstract ideas under patent law. They can also have different meaning, depending on where they are filed.
In the U.S., AI patenting is concentrated amongst large companies including IBM, Microsoft, and Google. On the other hand, AI patenting in China is more distributed across government organizations, universities, and tech firms (e.g. Tencent).
In terms of focus area, China’s patents are typically related to computer vision, a field of AI that enables computers and systems to interpret visual data and inputs. Meanwhile America’s efforts are more evenly distributed across research fields.
Learn More About AI From Visual Capitalist
If you want to see more data visualizations on artificial intelligence, check out this graphic that shows which job departments will be impacted by AI the most.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries