Technology
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): Are Companies Ready For It?
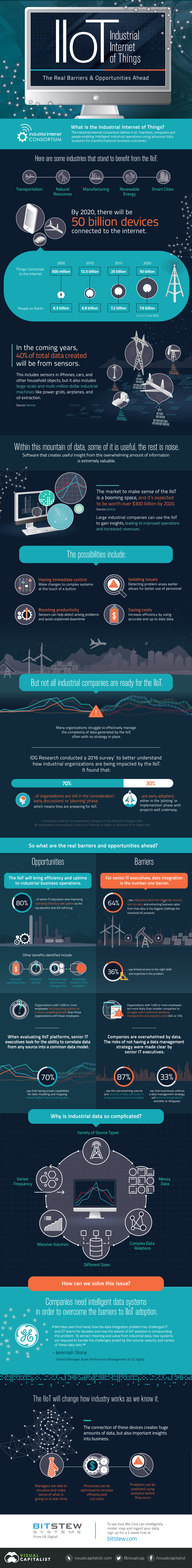
Are Companies Ready For the Industrial Internet of Things?
We’ve all heard about how the consumer version of the internet of things (IoT) will impact our lives. Smart devices in our homes, cars, and cities are already beginning to send and receive data to each other, allowing for unprecedented integration with consumer technologies.
But the implications of this revolution of connectivity extend way behind just smartphones and your home. In fact, it’s about to be applied on an industrial scale to everything from aerospace to mining in ways that people can hardly imagine.
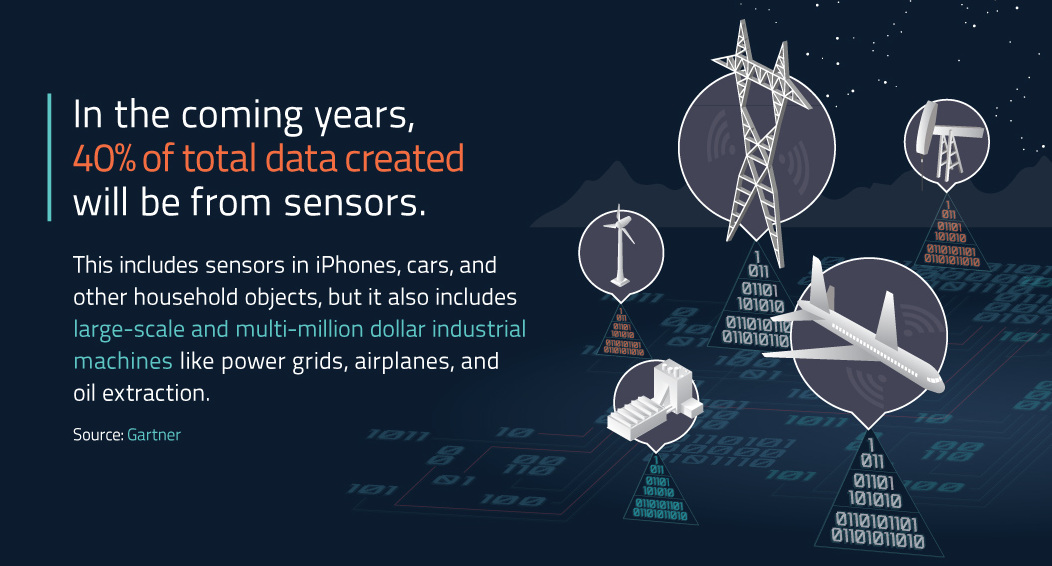
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) will pull data from millions of tiny sensors on every piece of industrial equipment fathomable. Companies will harness this data in real-time to create insights and efficiencies on a crazy scale: GE estimates it will help to generate a $10-$15 trillion increase in global GDP over the next 20 years.
But can companies handle the IIoT?
While this all sounds great in theory, the reality is that the transition to a useful IIoT is going to be an ongoing challenge. Very different types of data need to be captured and integrated, and companies will need to find ways to turn huge amounts of data into focused insights.
Bit Stew, from GE Digital, recently commissioned a survey of top IT execs to see if their respective companies were ready for the IIoT.
The survey found that only 30% of companies are currently early adopters of the IIoT, while the other 70% are still in the planning phase. Perhaps more importantly, top IT execs identified the potential barriers to their companies adopting the IIoT, as well as the opportunities that the IIoT can unlock for their operations:
Opportunities
- 80% of senior IT executives view improving operating efficiency and uptime as the top benefits that IIoT will bring.
- Other benefits identified: improved operating costs, better uptime, improved asset performance management, and knowledge transfer in the workplace.
- Larger organizations (1,000+ employees) found improving uptime to be a more compelling benefit than smaller organizations.
- 70% say that having proven capabilities for data modeling and mapping were more important for a IIoT platform than any other feature.
Barriers to Adoption
- 64% of senior IT executives said that integrating data from disparate sources and formats, and extracting business value from that data, is the biggest challenge the IIoT presents.
- Meanwhile, 36% say limited access to the right skills and expertise is the problem.
- Larger organizations (1,000+ employees) were more likely to struggle with traditional database management and analytics tools (34% vs 12%).
- 87% say that the overwhelming volume and veracity of data will result in losing valuable business insights.
- 33% say that businesses without a data management strategy will become marginalized, obsolete, or disappear.
Why is industrial data so complicated?
Industrial data comes from a variety of source types and is often messy. Combine this with its complexity, and that it comes in massive volumes and varied frequencies, and the situation is quite a quagmire for any aspiring adopter.
To enter a truly connected world where data about everything is analyzed instantaneously on an industrial scale, we must first solve these issues around data. It’s only then that the IIoT will show its true potential for business.
Brands
How Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
From complete overhauls to more subtle tweaks, these tech logos have had quite a journey. Featuring: Google, Apple, and more.

How Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
One would be hard-pressed to find a company that has never changed its logo. Granted, some brands—like Rolex, IBM, and Coca-Cola—tend to just have more minimalistic updates. But other companies undergo an entire identity change, thus necessitating a full overhaul.
In this graphic, we visualized the evolution of prominent tech companies’ logos over time. All of these brands ranked highly in a Q1 2024 YouGov study of America’s most famous tech brands. The logo changes are sourced from 1000logos.net.
How Many Times Has Google Changed Its Logo?
Google and Facebook share a 98% fame rating according to YouGov. But while Facebook’s rise was captured in The Social Network (2010), Google’s history tends to be a little less lionized in popular culture.
For example, Google was initially called “Backrub” because it analyzed “back links” to understand how important a website was. Since its founding, Google has undergone eight logo changes, finally settling on its current one in 2015.
| Company | Number of Logo Changes |
|---|---|
| 8 | |
| HP | 8 |
| Amazon | 6 |
| Microsoft | 6 |
| Samsung | 6 |
| Apple | 5* |
Note: *Includes color changes. Source: 1000Logos.net
Another fun origin story is Microsoft, which started off as Traf-O-Data, a traffic counter reading company that generated reports for traffic engineers. By 1975, the company was renamed. But it wasn’t until 2012 that Microsoft put the iconic Windows logo—still the most popular desktop operating system—alongside its name.
And then there’s Samsung, which started as a grocery trading store in 1938. Its pivot to electronics started in the 1970s with black and white television sets. For 55 years, the company kept some form of stars from its first logo, until 1993, when the iconic encircled blue Samsung logo debuted.
Finally, Apple’s first logo in 1976 featured Isaac Newton reading under a tree—moments before an apple fell on his head. Two years later, the iconic bitten apple logo would be designed at Steve Jobs’ behest, and it would take another two decades for it to go monochrome.
-

 Green1 week ago
Green1 week agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Travel2 weeks ago
Travel2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue