Markets
How the Top Cryptocurrencies Performed in 2021
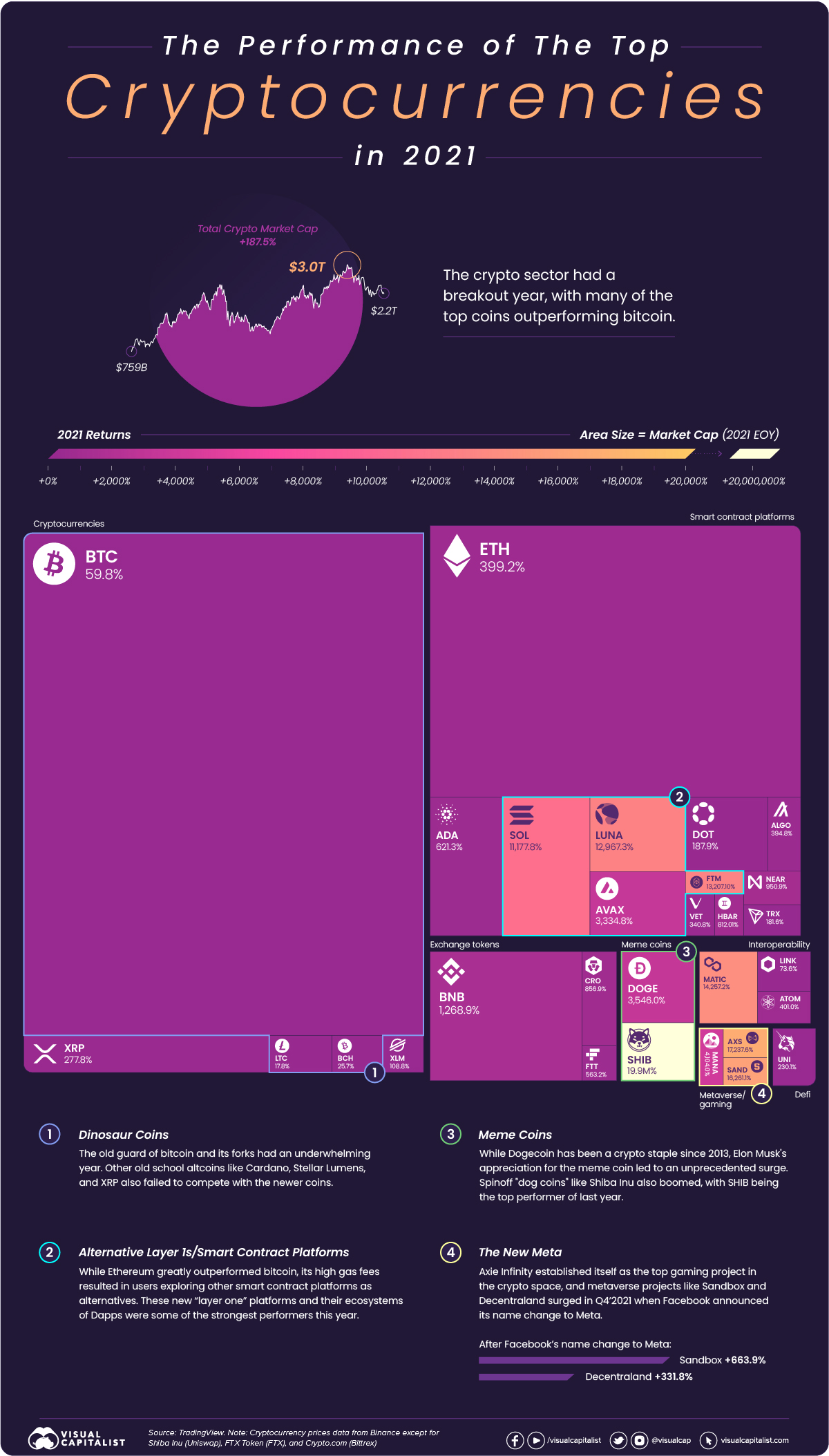
The Returns of Top Cryptocurrencies in 2021
2021 saw the crypto markets boom and mature, with different sectors flourishing and largely outperforming the market leader, bitcoin.
While bitcoin only managed to return 59.8% last year, the crypto sector’s total market cap grew by 187.5%, with many of the top coins offering four and even five-digit percentage returns.
2021 Crypto Market Roundup
Last year wasn’t just a breakout year for crypto in terms of returns, but also the growing infrastructure’s maturity and resulting decorrelation of individual crypto industries and coins.
Crypto’s infrastructure has developed significantly, and there are now many more onramps for people to buy altcoins that don’t require purchasing and using bitcoin in the process. As a result, many cryptocurrency prices were more dictated by the value and functionality of their protocol and applications rather than their correlation to bitcoin.
| Cryptocurrency | Category | 2021 Returns |
|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin | Cryptocurrency | 59.8% |
| Ethereum | Smart Contract Platform | 399.2% |
| Binance Coin | Exchange Token | 1,268.9% |
| Solana | Smart Contract Platform | 11,177.8% |
| Cardano | Smart Contract Platform | 621.3% |
| XRP | Cryptocurrency | 277.8% |
| Terra | Smart Contract Platform | 12,967.3% |
| Avalanche | Smart Contract Platform | 3,334.8% |
| Polkadot | Smart Contract Platform | 187.9% |
| Dogecoin | Meme Coin | 3,546.0% |
Sources: TradingView, Binance, Uniswap, FTX, Bittrex
Bitcoin wasn’t the only cryptocurrency that didn’t manage to reach triple-digit returns in 2021. Litecoin and Bitcoin Cash also provided meagre double-digit percentage returns, as payment-focused cryptocurrencies were largely ignored for projects with smart contract capabilities.
Other older projects like Stellar Lumens (109%) and XRP (278%) provided triple-digit returns, with Cardano (621%) being the best performer of the old guard despite not managing to ship its smart contract functionality last year.
The Rise of the Ethereum Competitors
Ethereum greatly outpaced bitcoin in 2021, returning 399.2% as the popularity boom of NFTs and creation of DeFi 2.0 protocols like Olympus (OHM) expanded possible use-cases.
But with the rise of network activity, a 50% increase in transfers in 2021, Ethereum gas fees surged. From minimums of $20 for a single transaction, to NFT mint prices starting around $40 and going into the hundreds on congested network days, crypto’s retail crowd migrated to other smart contract platforms with lower fees.
Alternative budding smart contract platforms like Solana (11,178%), Avalanche (3,335%), and Fantom (13,207%) all had 4-5 digit percentage returns, as these protocols built out their own decentralized finance ecosystems and NFT markets.
With Ethereum set to merge onto the beacon chain this year, which uses proof of stake instead of proof of work, we’ll see if 2022 brings lower gas fees and retail’s return to Ethereum if the merge is successful.
Dog Coins Meme their Way to the Top
While many new cryptocurrencies with strong functionality and unique use-cases were rewarded with strong returns, it was memes that powered the greatest returns in cryptocurrencies this past year.
Dogecoin’s surge after Elon Musk’s “adoption” saw many other dog coins follow, with SHIB benefitting the most and returning an astounding 19.85 million percent.
But ever since Dogecoin’s run from $0.07 to a high of $0.74 in Q2 of last year, the original meme coin’s price has slowly bled -77% down to $0.17 at the time of writing. After the roller coaster ride of last year, 2022 started with a positive catalyst for Dogecoin holders as Elon Musk announced DOGE can be used to purchase Tesla merchandise.
Gamifying the Crypto Industry
The intersection between crypto, games, and the metaverse became more than just a pipe dream in 2021. Axie Infinity was the first crypto native game to successfully establish a play to earn structure that combines its native token (AXS) and in-game NFTs, becoming a sensation and source of income for many in the Philippines.
Other crypto gaming projects like Defi Kingdoms are putting recognizable game interfaces on decentralized finance applications, with the decentralized exchange becoming the town’s “marketplace” and yield farms being the “gardens” where yield is harvested. This fantasy aesthetic is more than just a new coat of paint, as the project with $1.04B of total value locked is developing an underlying play-to-earn game.
Along with gamification, 2021 saw crypto native and non-crypto developers put a big emphasis on the digital worlds or metaverses users will inhabit. Facebook’s name change to Meta resulted in the two prominent metaverse projects The Sandbox (SAND) and Decentraland (MANA) surge another few hundred percent to finish off the year at 16,261% and 4,104% returns respectively.
With so many eyes on the crypto sector after the 2021’s breakout year, we’ll see how developing U.S. regulation and changing macro conditions affect cryptocurrencies in 2022.
Markets
U.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
U.S. debt interest payments have surged past the $1 trillion dollar mark, amid high interest rates and an ever-expanding debt burden.

U.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The cost of paying for America’s national debt crossed the $1 trillion dollar mark in 2023, driven by high interest rates and a record $34 trillion mountain of debt.
Over the last decade, U.S. debt interest payments have more than doubled amid vast government spending during the pandemic crisis. As debt payments continue to soar, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) reported that debt servicing costs surpassed defense spending for the first time ever this year.
This graphic shows the sharp rise in U.S. debt payments, based on data from the Federal Reserve.
A $1 Trillion Interest Bill, and Growing
Below, we show how U.S. debt interest payments have risen at a faster pace than at another time in modern history:
| Date | Interest Payments | U.S. National Debt |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $1.0T | $34.0T |
| 2022 | $830B | $31.4T |
| 2021 | $612B | $29.6T |
| 2020 | $518B | $27.7T |
| 2019 | $564B | $23.2T |
| 2018 | $571B | $22.0T |
| 2017 | $493B | $20.5T |
| 2016 | $460B | $20.0T |
| 2015 | $435B | $18.9T |
| 2014 | $442B | $18.1T |
| 2013 | $425B | $17.2T |
| 2012 | $417B | $16.4T |
| 2011 | $433B | $15.2T |
| 2010 | $400B | $14.0T |
| 2009 | $354B | $12.3T |
| 2008 | $380B | $10.7T |
| 2007 | $414B | $9.2T |
| 2006 | $387B | $8.7T |
| 2005 | $355B | $8.2T |
| 2004 | $318B | $7.6T |
| 2003 | $294B | $7.0T |
| 2002 | $298B | $6.4T |
| 2001 | $318B | $5.9T |
| 2000 | $353B | $5.7T |
| 1999 | $353B | $5.8T |
| 1998 | $360B | $5.6T |
| 1997 | $368B | $5.5T |
| 1996 | $362B | $5.3T |
| 1995 | $357B | $5.0T |
| 1994 | $334B | $4.8T |
| 1993 | $311B | $4.5T |
| 1992 | $306B | $4.2T |
| 1991 | $308B | $3.8T |
| 1990 | $298B | $3.4T |
| 1989 | $275B | $3.0T |
| 1988 | $254B | $2.7T |
| 1987 | $240B | $2.4T |
| 1986 | $225B | $2.2T |
| 1985 | $219B | $1.9T |
| 1984 | $205B | $1.7T |
| 1983 | $176B | $1.4T |
| 1982 | $157B | $1.2T |
| 1981 | $142B | $1.0T |
| 1980 | $113B | $930.2B |
| 1979 | $96B | $845.1B |
| 1978 | $84B | $789.2B |
| 1977 | $69B | $718.9B |
| 1976 | $61B | $653.5B |
| 1975 | $55B | $576.6B |
| 1974 | $50B | $492.7B |
| 1973 | $45B | $469.1B |
| 1972 | $39B | $448.5B |
| 1971 | $36B | $424.1B |
| 1970 | $35B | $389.2B |
| 1969 | $30B | $368.2B |
| 1968 | $25B | $358.0B |
| 1967 | $23B | $344.7B |
| 1966 | $21B | $329.3B |
Interest payments represent seasonally adjusted annual rate at the end of Q4.
At current rates, the U.S. national debt is growing by a remarkable $1 trillion about every 100 days, equal to roughly $3.6 trillion per year.
As the national debt has ballooned, debt payments even exceeded Medicaid outlays in 2023—one of the government’s largest expenditures. On average, the U.S. spent more than $2 billion per day on interest costs last year. Going further, the U.S. government is projected to spend a historic $12.4 trillion on interest payments over the next decade, averaging about $37,100 per American.
Exacerbating matters is that the U.S. is running a steep deficit, which stood at $1.1 trillion for the first six months of fiscal 2024. This has accelerated due to the 43% increase in debt servicing costs along with a $31 billion dollar increase in defense spending from a year earlier. Additionally, a $30 billion increase in funding for the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation in light of the regional banking crisis last year was a major contributor to the deficit increase.
Overall, the CBO forecasts that roughly 75% of the federal deficit’s increase will be due to interest costs by 2034.
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc1 week ago
Misc1 week agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes