Technology
How Technology is Disrupting the Construction Industry
View the full-resolution version of this infographic
How Technology is Disrupting the Construction Industry
See the full resolution version of this infographic.
The rate of digital disruption is escalating in almost every industry. However, despite being one of the fastest-growing industries globally—construction has been one of the last to get hit.
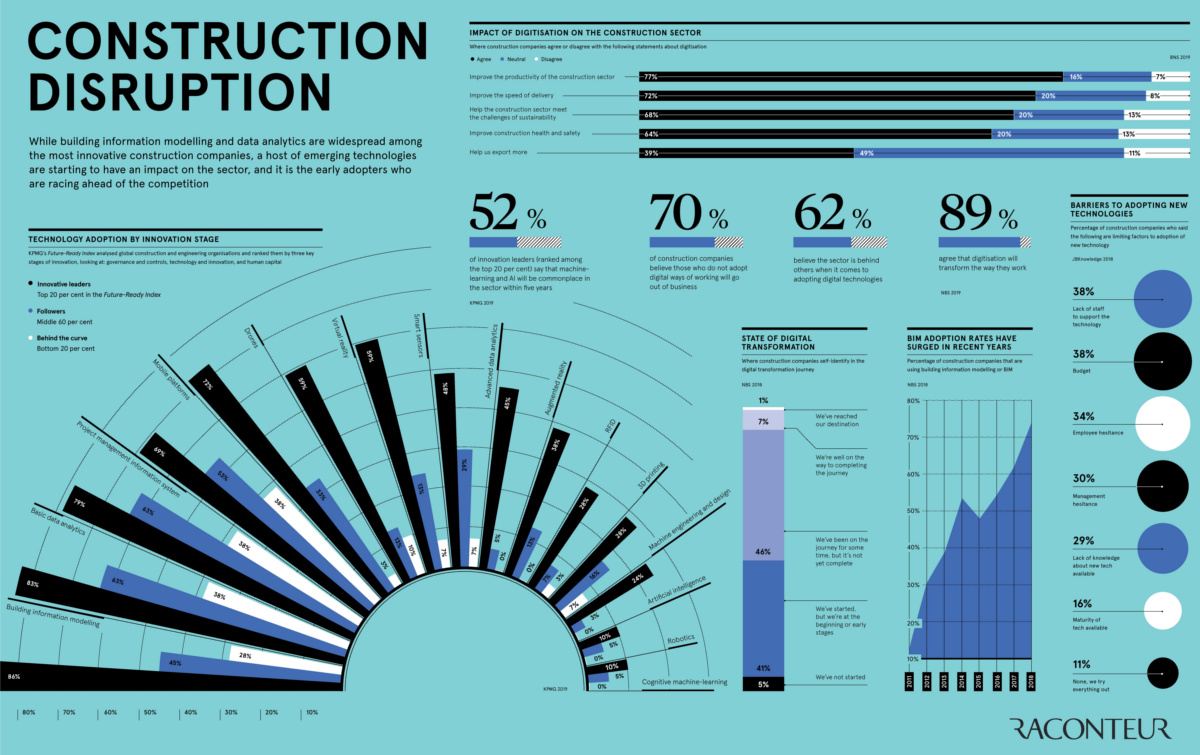
Today’s infographic from Raconteur ranks the adoption of emerging technologies that will have a major impact on the industry’s processes and bottom line. The technologies help solve four major challenge areas that the construction industry struggles with: productivity, safety and training, labor shortages, and collaboration.
Which technologies could improve the lives of industry workers, and which technologies may pose a threat to their jobs?
Towards a New Dimension
Output from the global construction industry is expected to rise to $12.7 trillion in 2022, up from $10.6 trillion in 2017. Despite this promising outlook, the industry has gained only 1% of productivity in the last 20 years due to lack of digitization. This creates an opportunity for an added $1.6 trillion by innovating in this area.
According to the infographic, the industry is divided when it comes to the current state of digital transformation. Almost half (46%) of construction companies self-identify as having been on a path towards digital transformation for some time, while 41% see their company as only in the very early stages of digital transformation.
The Spectrum of Tech Adoption
The technology adoption spectrum ranks construction companies by their stages of innovation and rate of technological adoption, using data from the KPMG Future-Ready Index.
Technologies that have the highest adoption rates in the top 20% of companies (considered innovative leaders), are as follows:
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): 86%
- Basic data analytics: 83%
- Project management and information systems: 79%
- Drones: 72%
- Mobile platforms: 69%
BIM is a 3D modeling system that creates depictions of manufacturing facilities, buildings, and highways. While 3D modeling is widely used in construction today, next-generation 5D BIM represents both the physical and functional aspects of a project, and considers a project’s cost and schedule in addition to the standard parameters of 3D BIM.
Meanwhile, for the bottom 20% of companies (considered behind the curve), the rate of adoption can be low or even non-existent for many key technologies. Here are the ones with the lowest adoption rates within this group:
- Cognitive machine learning: 0%
- Robotics: 0%
- Artificial intelligence: 0%
- Machine engineering and design: 3%
- 3D printing: 7%
Both employers and employees are hesitant about adopting new technologies, due in part to the lack of knowledge surrounding them. More specifically, 29% of companies agree that lack of knowledge is a barrier for adoption, while 38% believe that it is due to lack of budget. A further 38% believe it is the lack of support from employees that inhibits mass adoption.
Despite these barriers, 52% of innovation leaders claim that technologies like artificial intelligence and cognitive machine learning will become commonplace within the industry over the next five years.
The Long-term Impact
Construction companies are now in a race to go digital, with the hope that technology will enhance profitability while also fending off competitors.
In total, 70% of construction companies believe that those who do not adopt digital tools will go out of business. Further, most believe digitization will improve productivity, speed of delivery, and help meet sustainability challenges.
Technology
Ranked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Did you know that some computer chips are now retailing for the price of a new BMW?
As computers invade nearly every sphere of life, so too have the chips that power them, raising the revenues of the businesses dedicated to designing them.
But how did various chipmakers measure against each other last year?
We rank the biggest semiconductor companies by their percentage share of the industry’s revenues in 2023, using data from Omdia research.
Which Chip Company Made the Most Money in 2023?
Market leader and industry-defining veteran Intel still holds the crown for the most revenue in the sector, crossing $50 billion in 2023, or 10% of the broader industry’s topline.
All is not well at Intel, however, with the company’s stock price down over 20% year-to-date after it revealed billion-dollar losses in its foundry business.
| Rank | Company | 2023 Revenue | % of Industry Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intel | $51B | 9.4% |
| 2 | NVIDIA | $49B | 9.0% |
| 3 | Samsung Electronics | $44B | 8.1% |
| 4 | Qualcomm | $31B | 5.7% |
| 5 | Broadcom | $28B | 5.2% |
| 6 | SK Hynix | $24B | 4.4% |
| 7 | AMD | $22B | 4.1% |
| 8 | Apple | $19B | 3.4% |
| 9 | Infineon Tech | $17B | 3.2% |
| 10 | STMicroelectronics | $17B | 3.2% |
| 11 | Texas Instruments | $17B | 3.1% |
| 12 | Micron Technology | $16B | 2.9% |
| 13 | MediaTek | $14B | 2.6% |
| 14 | NXP | $13B | 2.4% |
| 15 | Analog Devices | $12B | 2.2% |
| 16 | Renesas Electronics Corporation | $11B | 1.9% |
| 17 | Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation | $10B | 1.9% |
| 18 | Microchip Technology | $8B | 1.5% |
| 19 | Onsemi | $8B | 1.4% |
| 20 | KIOXIA Corporation | $7B | 1.3% |
| N/A | Others | $126B | 23.2% |
| N/A | Total | $545B | 100% |
Note: Figures are rounded. Totals and percentages may not sum to 100.
Meanwhile, Nvidia is very close to overtaking Intel, after declaring $49 billion of topline revenue for 2023. This is more than double its 2022 revenue ($21 billion), increasing its share of industry revenues to 9%.
Nvidia’s meteoric rise has gotten a huge thumbs-up from investors. It became a trillion dollar stock last year, and broke the single-day gain record for market capitalization this year.
Other chipmakers haven’t been as successful. Out of the top 20 semiconductor companies by revenue, 12 did not match their 2022 revenues, including big names like Intel, Samsung, and AMD.
The Many Different Types of Chipmakers
All of these companies may belong to the same industry, but they don’t focus on the same niche.
According to Investopedia, there are four major types of chips, depending on their functionality: microprocessors, memory chips, standard chips, and complex systems on a chip.
Nvidia’s core business was once GPUs for computers (graphics processing units), but in recent years this has drastically shifted towards microprocessors for analytics and AI.
These specialized chips seem to be where the majority of growth is occurring within the sector. For example, companies that are largely in the memory segment—Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron Technology—saw peak revenues in the mid-2010s.
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc1 week ago
Misc1 week agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes