Technology
How Machines Destroy and Create Jobs
“There’s just doesn’t seem to be many blacksmith jobs these days.”
At first glance, this would be a ridiculous thing to say. Of course there aren’t many blacksmiths around. We live in a modern society and machines do a way better job of making things from metal anyways.
However, it also raises an important point.
What if machines are better at driving long-haul trucks? What if machines are better servers at McDonald’s? What if robots did your taxes for you?
While some of these ideas are contentious today, in the future we may look back thinking that our fears were ill-placed. The truth is that the job landscape is constantly in flux as technology changes.
Some of today’s jobs with high automation potential may be the future “blacksmiths”, and we should not be surprised if they go away. The best thing that we can do is to understand these trends and build a set of skills that will be in demand in any market.
The Trend is Your Friend
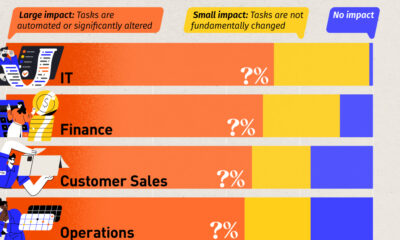
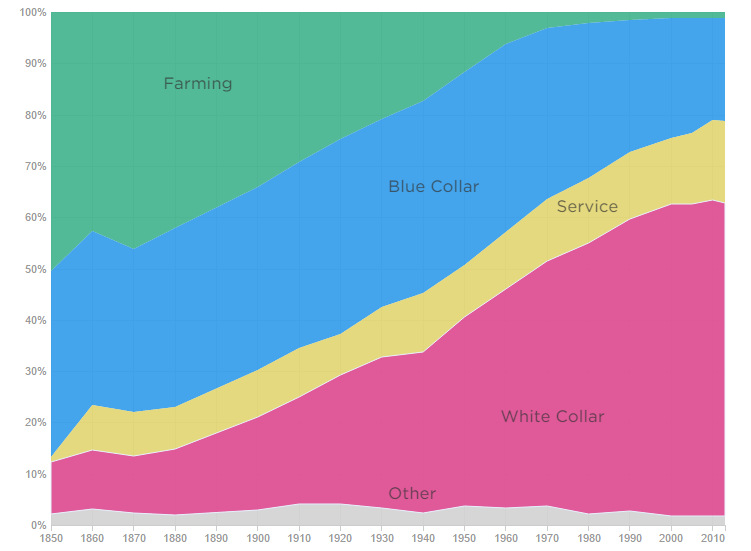
The following graphics from NPR shows the evolution of jobs over time in the United States.
The first divides jobs into four main categories: white collar, blue collar, farming, and services. It shows how the composition of the overall job market has changed over the last 165 years:
The second shows the same information, but plotted by the total number of jobs:
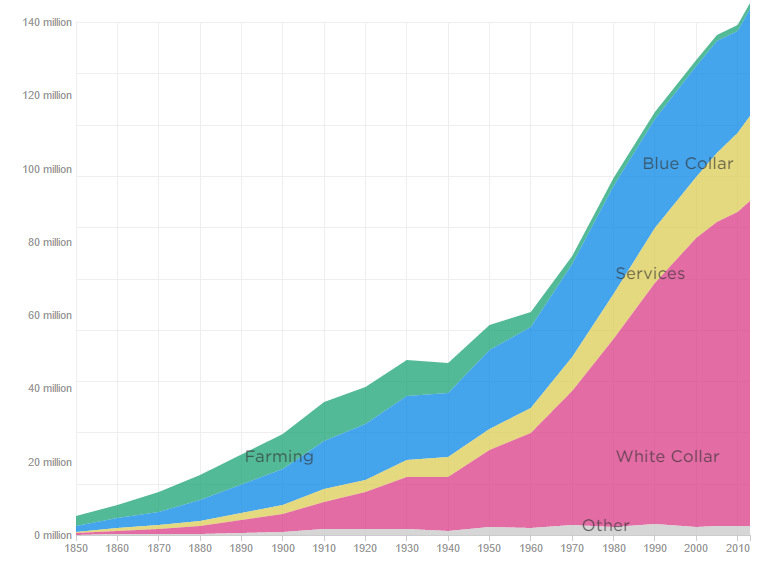
There were 10 million farmers in America in the early 20th century.
Now there’s closer to one million, and yet those farmers produce way more food. Technology may have “killed off” the majority of farm jobs, but at the same time new technology created jobs in the service, blue collar, and white collar industries.
We may now be at a similar inflection point for other careers – this interactive graphic shows some of the jobs that have been on the decline in recent years.
In 1960, a whopping 11% of the workforce was employed in factories. Today only 4% are employed in factories.
In the late 1970s, almost 5% of the workforce was secretaries. Today, we’re at about half that, but professionals can be just as productive without a secretary thanks to better computer software.
Yes, there are globalization issues at play here as well, but even a modern domestic factory such as the Tesla Gigafactory (which has the largest building by footprint in the world) will only employ about 6,000 people. The majority of the work will be done by robots.
And while it seems scary to think about the rise of machines and a faster pace of technological advancement, it’s important to recognize that these types of sweeping changes to the job market have happened throughout history.
The point is, try not to be the 21st century version of a “blacksmith”.
Technology
Ranked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Did you know that some computer chips are now retailing for the price of a new BMW?
As computers invade nearly every sphere of life, so too have the chips that power them, raising the revenues of the businesses dedicated to designing them.
But how did various chipmakers measure against each other last year?
We rank the biggest semiconductor companies by their percentage share of the industry’s revenues in 2023, using data from Omdia research.
Which Chip Company Made the Most Money in 2023?
Market leader and industry-defining veteran Intel still holds the crown for the most revenue in the sector, crossing $50 billion in 2023, or 10% of the broader industry’s topline.
All is not well at Intel, however, with the company’s stock price down over 20% year-to-date after it revealed billion-dollar losses in its foundry business.
| Rank | Company | 2023 Revenue | % of Industry Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intel | $51B | 9.4% |
| 2 | NVIDIA | $49B | 9.0% |
| 3 | Samsung Electronics | $44B | 8.1% |
| 4 | Qualcomm | $31B | 5.7% |
| 5 | Broadcom | $28B | 5.2% |
| 6 | SK Hynix | $24B | 4.4% |
| 7 | AMD | $22B | 4.1% |
| 8 | Apple | $19B | 3.4% |
| 9 | Infineon Tech | $17B | 3.2% |
| 10 | STMicroelectronics | $17B | 3.2% |
| 11 | Texas Instruments | $17B | 3.1% |
| 12 | Micron Technology | $16B | 2.9% |
| 13 | MediaTek | $14B | 2.6% |
| 14 | NXP | $13B | 2.4% |
| 15 | Analog Devices | $12B | 2.2% |
| 16 | Renesas Electronics Corporation | $11B | 1.9% |
| 17 | Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation | $10B | 1.9% |
| 18 | Microchip Technology | $8B | 1.5% |
| 19 | Onsemi | $8B | 1.4% |
| 20 | KIOXIA Corporation | $7B | 1.3% |
| N/A | Others | $126B | 23.2% |
| N/A | Total | $545B | 100% |
Note: Figures are rounded. Totals and percentages may not sum to 100.
Meanwhile, Nvidia is very close to overtaking Intel, after declaring $49 billion of topline revenue for 2023. This is more than double its 2022 revenue ($21 billion), increasing its share of industry revenues to 9%.
Nvidia’s meteoric rise has gotten a huge thumbs-up from investors. It became a trillion dollar stock last year, and broke the single-day gain record for market capitalization this year.
Other chipmakers haven’t been as successful. Out of the top 20 semiconductor companies by revenue, 12 did not match their 2022 revenues, including big names like Intel, Samsung, and AMD.
The Many Different Types of Chipmakers
All of these companies may belong to the same industry, but they don’t focus on the same niche.
According to Investopedia, there are four major types of chips, depending on their functionality: microprocessors, memory chips, standard chips, and complex systems on a chip.
Nvidia’s core business was once GPUs for computers (graphics processing units), but in recent years this has drastically shifted towards microprocessors for analytics and AI.
These specialized chips seem to be where the majority of growth is occurring within the sector. For example, companies that are largely in the memory segment—Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron Technology—saw peak revenues in the mid-2010s.
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc1 week ago
Misc1 week agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes