Technology
Helium: A Valuable Gas Not To Be Taken Lightly
Helium makes up 25% of the atoms in the known universe, so one would guess that the inert gas would be quite plentiful on Earth.
Unfortunately, a familiar property of helium prevents this from happening. Helium gas is lighter than air and literally rises into space, depleting the Earth of almost all valuable helium resources over time.
Where do we get helium?
So how do we actually obtain new helium gas, which is necessary for important technological applications such as MRI machines, superconductors, and even the Large Hadron Collider?
Today’s infographic from Helium One shows everything you need to know on helium, including where we can find it on Earth, as well as the most important uses of the gas.

Although helium is plentiful in the universe, on Earth it is quite rare and difficult to obtain.
Why Do We Need Helium?
Helium has several properties that make it invaluable to modern humans, particularly for technological uses:
| Helium Property | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Inert | Doesn’t react with other elements, and doesn’t explode like hydrogen |
| Non-toxic | Can be used by humans in a variety of applications |
| Lighter than air | Ability to lift and/or float |
| Melting point -272˚C | Liquid at ultra-cool temps enables superconductivity |
| Small molecular size | Can be used to find the smallest of leaks |
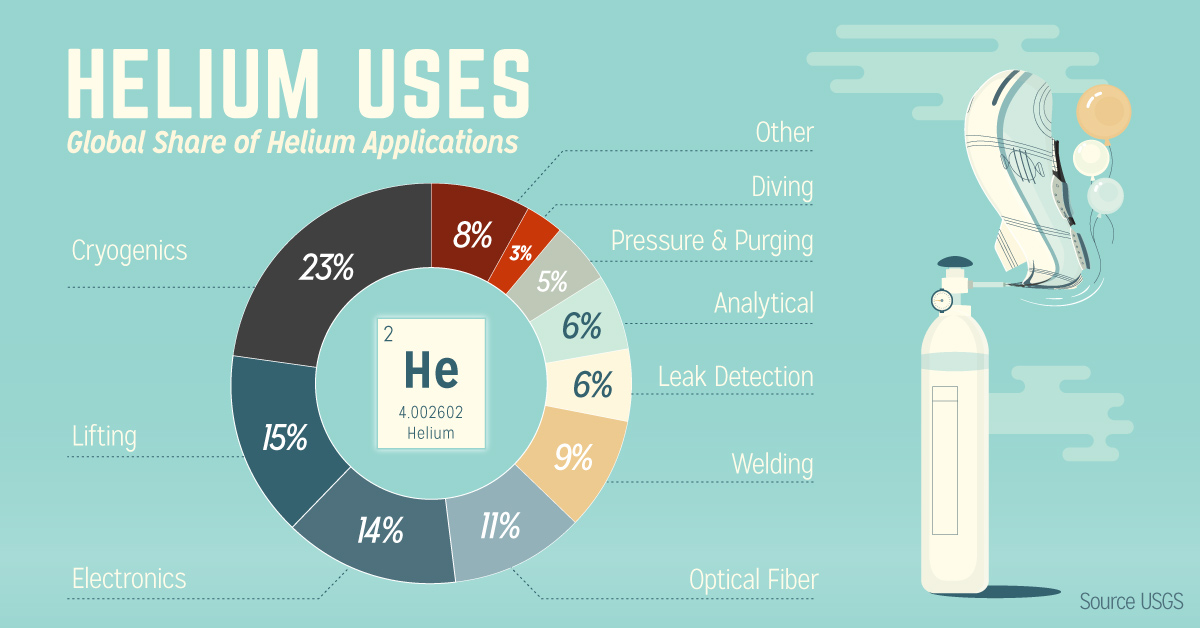
Helium Demand
Helium demand has risen consistently since 2009, and the market has been increasing at a CAGR of 10.1% since 2010. With that in mind, here are the specific constituents of helium demand today:
| Helium Use | Global Share | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cryogenics | 23% | Superconductors use ultracooled helium liquid. |
| Lifting | 15% | Used in airships and balloons |
| Electronics | 14% | Used to manufacture silicon wafers |
| Optical Fiber | 11% | Necessary to make optical fiber cables |
| Welding | 9% | Used as a shielding gas for welding |
| Leak Detection | 6% | Helium particles are small, and can find the tiniest leaks |
| Analytics | 6% | Used in chromatography and other applications |
| Pressure & Purging | 5% | Used in rocket systems |
| Diving | 3% | Mixed into commercial diving tanks for various reasons |
| Other | 8% | Helium's diverse properties give it many other minor uses |
Helium’s melting point, which is the lowest found in nature, allows it to remain as a liquid at the coolest possible temperature. This makes helium ideal for uses in superconductors, including MRI machines – one of the fastest growing components of helium demand.
Helium Supply
But where do we obtain this elusive gas?
It turns out that new helium is actually created every day in very tiny amounts within the Earth’s crust as a by-product of radioactive decay. And like other gases below the Earth’s surface (i.e. natural gas), helium gets trapped in geological formations in economical amounts.
Today, much of helium is either produced as a by-product of natural gas deposits, or from helium-primary gas deposits with concentrations up to 7% He.
Here’s helium production by country:
| Country | 2016 production (in billion cubic feet) | Share |
|---|---|---|
| USA | 2.2 | 41% |
| USA (from Cliffside Field) | 0.8 | 14% |
| Algeria | 0.4 | 6% |
| Australia | 0.1 | 3% |
| Poland | 0.1 | 1% |
| Qatar | 1.8 | 32% |
| Russia | 0.1 | 2% |
| Total | 5.4 | 100% |
USA (from Cliffside Field)
The USA government has a helium stockpile at the Cliffside Field in Texas, developed as part of a WWI initiative. It is in the process of being phased out, and by as late as 2021 it will no longer contribute to supply.
Qatar
In December 2013, the Qatar Helium 2 project was opened. This new facility combined with the first helium project makes the country the 2nd largest source of helium globally.
Russia
Russia is looking to become a player in helium as well. Gazprom’s Amur LNG project will be one of the biggest gas facilities in the world, and it will include a helium processing plant. This won’t be online until 2024, though.
Tanzania
Though not a helium player yet, scientists have recently uncovered a major helium find in the Rift Valley of Tanzania which contains an estimated 99 billion cubic feet of gas.
The Future of the Helium Market?
Because of inflated demand, especially for cryogenics in MRI machines, helium prices have risen significantly over the years.
And with these market dynamics in mind, it’s clear that the future of helium is not full of hot air.
Technology
Ranked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Did you know that some computer chips are now retailing for the price of a new BMW?
As computers invade nearly every sphere of life, so too have the chips that power them, raising the revenues of the businesses dedicated to designing them.
But how did various chipmakers measure against each other last year?
We rank the biggest semiconductor companies by their percentage share of the industry’s revenues in 2023, using data from Omdia research.
Which Chip Company Made the Most Money in 2023?
Market leader and industry-defining veteran Intel still holds the crown for the most revenue in the sector, crossing $50 billion in 2023, or 10% of the broader industry’s topline.
All is not well at Intel, however, with the company’s stock price down over 20% year-to-date after it revealed billion-dollar losses in its foundry business.
| Rank | Company | 2023 Revenue | % of Industry Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intel | $51B | 9.4% |
| 2 | NVIDIA | $49B | 9.0% |
| 3 | Samsung Electronics | $44B | 8.1% |
| 4 | Qualcomm | $31B | 5.7% |
| 5 | Broadcom | $28B | 5.2% |
| 6 | SK Hynix | $24B | 4.4% |
| 7 | AMD | $22B | 4.1% |
| 8 | Apple | $19B | 3.4% |
| 9 | Infineon Tech | $17B | 3.2% |
| 10 | STMicroelectronics | $17B | 3.2% |
| 11 | Texas Instruments | $17B | 3.1% |
| 12 | Micron Technology | $16B | 2.9% |
| 13 | MediaTek | $14B | 2.6% |
| 14 | NXP | $13B | 2.4% |
| 15 | Analog Devices | $12B | 2.2% |
| 16 | Renesas Electronics Corporation | $11B | 1.9% |
| 17 | Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation | $10B | 1.9% |
| 18 | Microchip Technology | $8B | 1.5% |
| 19 | Onsemi | $8B | 1.4% |
| 20 | KIOXIA Corporation | $7B | 1.3% |
| N/A | Others | $126B | 23.2% |
| N/A | Total | $545B | 100% |
Note: Figures are rounded. Totals and percentages may not sum to 100.
Meanwhile, Nvidia is very close to overtaking Intel, after declaring $49 billion of topline revenue for 2023. This is more than double its 2022 revenue ($21 billion), increasing its share of industry revenues to 9%.
Nvidia’s meteoric rise has gotten a huge thumbs-up from investors. It became a trillion dollar stock last year, and broke the single-day gain record for market capitalization this year.
Other chipmakers haven’t been as successful. Out of the top 20 semiconductor companies by revenue, 12 did not match their 2022 revenues, including big names like Intel, Samsung, and AMD.
The Many Different Types of Chipmakers
All of these companies may belong to the same industry, but they don’t focus on the same niche.
According to Investopedia, there are four major types of chips, depending on their functionality: microprocessors, memory chips, standard chips, and complex systems on a chip.
Nvidia’s core business was once GPUs for computers (graphics processing units), but in recent years this has drastically shifted towards microprocessors for analytics and AI.
These specialized chips seem to be where the majority of growth is occurring within the sector. For example, companies that are largely in the memory segment—Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron Technology—saw peak revenues in the mid-2010s.
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Travel1 week ago
Travel1 week agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024