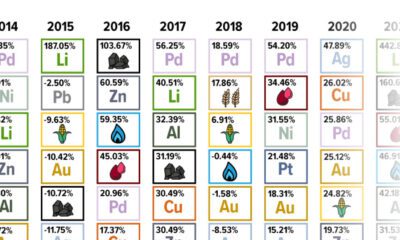
Mining
Global Gold Mine and Deposit Rankings 2013
For a second year in a row, we have worked with Roy Sebag of Natural Resource Holdings to produce an in-depth report of all gold deposits hold be public, private, and government backed companies.
— View the full 40 page PDF report. —
Results Discussion
We were able to identify a total of 580 deposits that have over 1,000,000 ounces of gold for a total of 3.72 billion in-situ ounces. The average grade of all deposits is 1.01 g/t Au.
These deposits are owned by 312 entities including public, private, and government sponsored corporations. 261 of the deposits were owned (or partially owned) by independent junior miners.
2013 vs Previous Years
It is our belief that this is by far the most comprehensive report yet. That said, those that compare this report to 2012 will notice significant differences in the final metrics. Most notably:
- Total deposits over 1 million oz increased from 439 to 580 worldwide.
- Total ounces have increased from 3.02 billion oz to 3.72 billion oz of Au.
- Average grade has increased from 0.82 g/t to 1.01 g/t Au.
The chief difference is that this year we decided to include all African deposits and mines, including projects that we believe will never be mined because they did not meet our thresholds of grade or depth. However, by including these projects, which add up to about 350 million oz alone, we believe the report is much more encompassing.
Trends in Size and Grade
The project economics of gold deposits are mostly dependent on two major factors: size and grade. Without a sizeable ore body, a mining operation cannot acquire the economies of scale to bring down the cost of production. Likewise, a project without grade may not have the margins for each ton of ore processed to justify production.
The average grade differed significantly between producing and undeveloped deposits. The average grade of all producing mines is 1.18 g/t Au, which is 32.6% higher than the average of all projects still in the development phase (0.89 g/t Au). This has significant implications on future gold production. In the near term, with significant volatility and the gold price at a three-year low, many of these projects are simply not economically feasible. In the medium to long term, unless major discoveries are made, either gold production must decrease (with a focus on only higher grade deposits) or the price of gold must rise to make these projects economical.
A key take home point of this report each year is the rarity of large, high-grade projects. There are only 51 (8.8%) projects in the world that are more than 5 million oz and have an average grade of higher than 3 g/t Au. Of these, there are only 21 that are not yet in production.
By Geography
While North America shows the largest amount of contained gold, Africa continues to be home to some of the highest grade (and highest risk) projects on the planet.
The highest grade deposits in the world are in countries such as South Africa, Tanzania, DRC, Mali, Russia, Ghana, Ivory Coast, Ecuador, Kyrgyzstan, and Papua New Guinea.
The Future of Gold Supply
Our figure for in-situ ounces that we have provided (3.72 billion oz Au) is a comprehensive view of what is below ground in terms of reserves and resources.
However, to come up with a clear picture of what is actually recoverable, the reality is that there are several limitations to the amount of gold that will actually become part of the future supply chain:
- Economic pit outlines have not yet been applied.
- Metallurgical recovery rates have not yet been applied.
- Inferred resources have been included in global contained ounces.
- Undeveloped deposits with no clear path towards permitting remain included.
To project an accurate figure, we need to take our 3.72 billion oz number and apply some math:
Total in-situ ounces in database:
3,720,865,356 oz
70% of total become mines:
2,604,605,749 oz
70% metallurgical recovery rate:
1,823,224,024 oz
This number, 1.82 billion oz, becomes really interesting when we look at annual extractable supply. Averaged over 50 years, the supply is equal to 1,134 tonnes (36,464,480 oz) of gold per year.
This figure is equal to only 42.0% of the 2,700 tonnes (86,807,016 oz) of worldwide gold production in 2012.
Conclusion
Led by countries such as Russia and China, central banks have recently become net buyers of gold. Meanwhile, ETF gold outflows have been a temporary source of supply this year, but obviously this cannot persist. It’s also unreasonable to assume that recycling will make up a significantly greater piece of supply without the price of gold increasing substantially.
With the grade of current producing gold mines being 32.6% higher than undeveloped deposits, it makes the supply scenario even more clear. Not only is the current yearly mine supply difficult to sustain, but future mines coming online will be challenged by grade and margins to be economical at today’s prices.
Mathematically, unless we have high-grade, high ounce deposits that are being fast tracked online, it will be very difficult to find a way to get supply to match demand.
Copper
Brass Rods: The Secure Choice
This graphic shows why brass rods are the secure choice for precision-machined and forged parts.

Brass Rods: The Secure Choice
The unique combination of machinability and recyclability makes brass rods the secure choice for manufacturers seeking future-proof raw material solutions.
This infographic, from the Copper Development Association, shows three ways brass rods give manufacturers greater control and a license to grow in the competitive market for precision-machined and forged products.
Future-Proof Investments in New Machine Tools
A material’s machinability directly impacts machine throughput, which typically has the largest impact on machine shop profitability.
The high-speed machining capabilities of brass rods maximize machine tool performance, allowing manufacturers to run the material faster and longer without sacrificing tool life, chip formation, or surface quality.
The high machining efficiency of brass leads to reduced per-part costs, quicker return on investment (ROI) for new machine tools, and expanded production capacity for new projects.
Supply Security Through Closed Loop Recycling
Brass, like its parent element copper, can be infinitely recycled.
In 2022, brass- and wire-rod mills accounted for the majority of the 830,000 tonnes of copper recycled from scrap in the United States.
Given that scrap ratios for machined parts typically range from 60-70% by weight, producing mills benefit from a secure and steady supply of clean scrap returned directly from customers, which is recycled to create new brass rods.
The high residual value of brass scrap creates a strong recycling incentive. Scrap buy back programs give manufacturers greater control over raw material net costs as scrap value is often factored into supplier purchase agreements.
Next Generation Alloys for a Lead-Free Future
Increasingly stringent global regulations continue to pressure manufacturers to minimize the use of materials containing trace amounts of lead and other harmful impurities.
The latest generation of brass-rod alloys is engineered to meet the most demanding criteria for lead leaching in drinking water and other sensitive applications.
Seven brass-rod alloys passed rigorous testing to become the only ‘Acceptable Materials’ against lower lead leaching criteria recently adopted in the national U.S. drinking water quality standard, NSF 61.

Learn more about the advantages of brass rods solutions.

-

 Base Metals1 year ago
Base Metals1 year agoRanked: The World’s Largest Copper Producers
Many new technologies critical to the energy transition rely on copper. Here are the world’s largest copper producers.
-
 Silver2 years ago
Silver2 years agoMapped: Solar Power by Country in 2021
In 2020, solar power saw its largest-ever annual capacity expansion at 127 gigawatts. Here’s a snapshot of solar power capacity by country.
-

 Batteries5 years ago
Batteries5 years agoVisualizing Copper’s Role in the Transition to Clean Energy
A clean energy transition is underway as wind, solar, and batteries take center stage. Here’s how copper plays the critical role in these technologies.
-
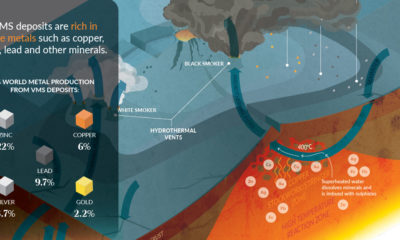
 Science5 years ago
Science5 years agoEverything You Need to Know on VMS Deposits
Deep below the ocean’s waves, VMS deposits spew out massive amounts of minerals like copper, zinc, and gold, making them a key source of the metals…
-
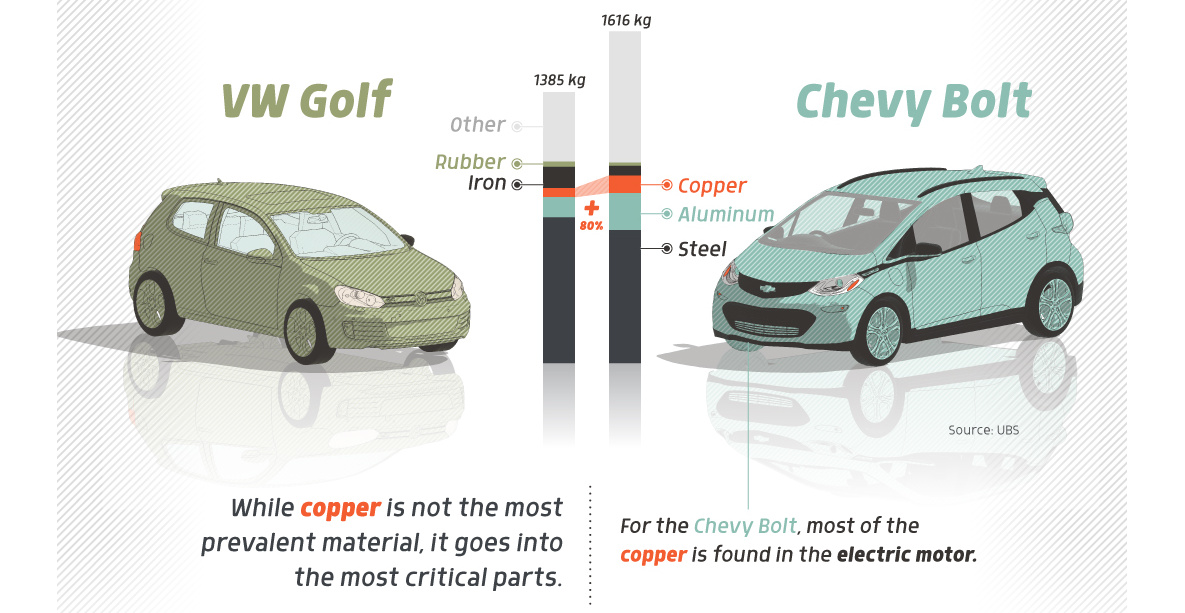
 Copper5 years ago
Copper5 years agoHow Much Copper is in an Electric Vehicle?
Have you ever wondered how much copper is in an electric vehicle? This infographic shows the metal’s properties as well as the quantity of copper used.
-
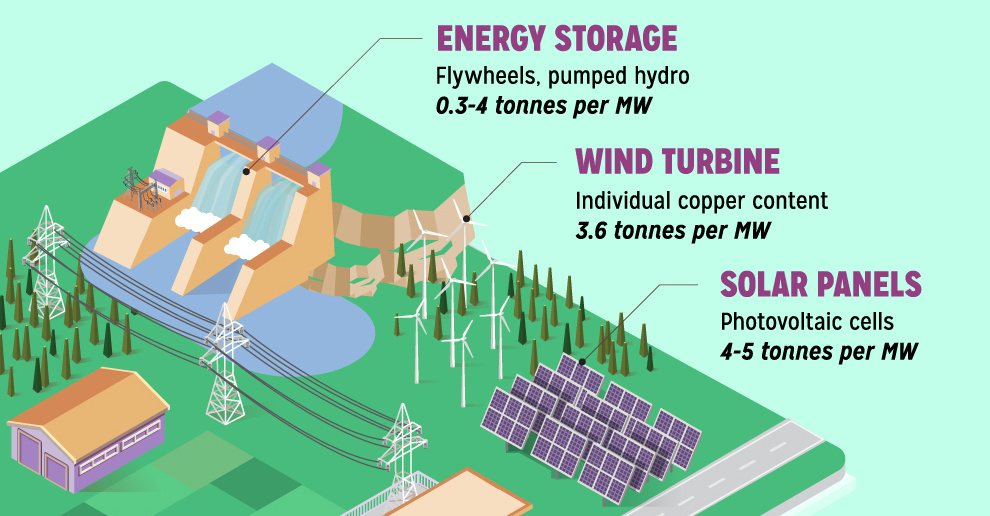
 Copper6 years ago
Copper6 years agoCopper: Driving the Green Energy Revolution
Renewable energy is set to fuel a new era of copper demand – here’s how much copper is used in green applications from EVs to photovoltaics.
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?