Markets
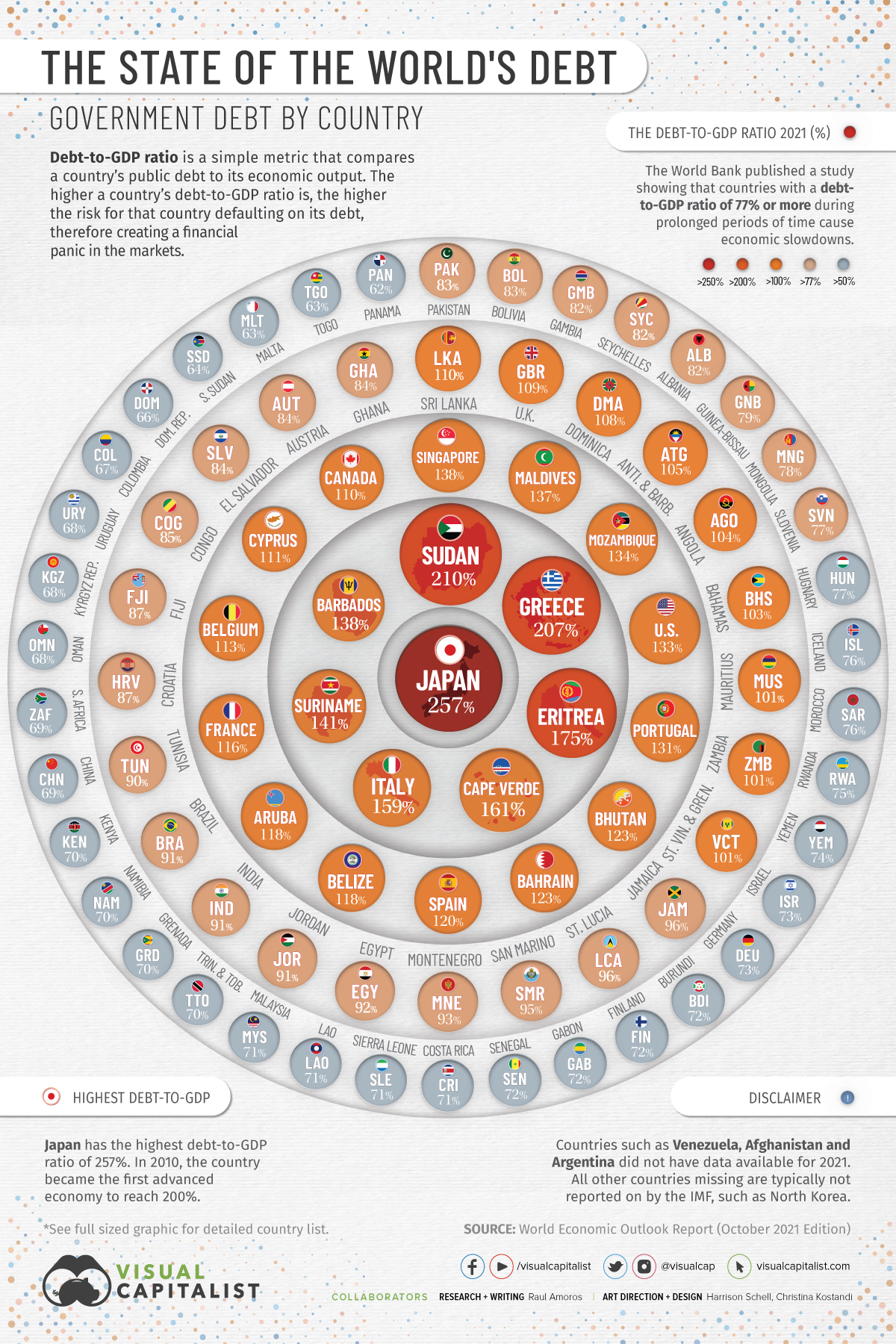
Visualizing the State of Global Debt, by Country
View the expanded version of this infographic to see all countries.
View the expanded version of this infographic to see all countries.
Visualizing the State of Global Debt, by Country
Since COVID-19 started its spread around the world in 2020, the global economy has been put to the test with supply chain disruptions, price volatility for commodities, challenges in the job market, and declining income from tourism. The World Bank has estimated that almost 97 million people have been pushed into extreme poverty as a result of the pandemic.
In order to help with this difficult situation, global governments have had to increase their expenditures to deal with higher healthcare costs, unemployment, food insecurity, and to help businesses to survive. Countries have taken on new debt to provide financial support for these measures, which has resulted in the highest global debt levels in half a century.
To analyze the extent of global debt, we’ve compiled debt-to-GDP data by country from the most recent World Economic Outlook report by the IMF.
Global Debt by Country: The Top 10 Most Indebted Nations
The debt-to-GDP ratio is a simple metric that compares a country’s public debt to its economic output. By comparing how much a country owes and how much it produces in a year, economists can measure a country’s theoretical ability to pay off its debt.
Let’s take a look at the top 10 countries in terms of debt-to-GDP:
| Rank | Country | Debt-to-GDP (2021) |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | Japan 🇯🇵 | 257% |
| #2 | Sudan 🇸🇩 | 210% |
| #3 | Greece 🇬🇷 | 207% |
| #4 | Eritrea 🇪🇷 | 175% |
| #5 | Cape Verde 🇨🇻 | 161% |
| #6 | Italy 🇮🇹 | 155% |
| #7 | Suriname 🇸🇷 | 141% |
| #8 | Barbados 🇧🇧 | 138% |
| #9 | Singapore 🇸🇬 | 138% |
| #10 | Maldives 🇲🇻 | 137% |
Source: World Economic Outlook Report (October 2021 Edition)
Japan, Sudan, and Greece top the list with debt-to-GDP ratios well above 200%, followed by Eritrea (175%), Cape Verde (160%), and Italy (154%).
Japan’s debt level won’t come as a surprise to most. In 2010, it became the first country to reach a debt-to-GDP ratio 200%, and it now sits at 257%. In order to finance new debt, the Japanese government issues bonds which get bought up primarily by the Bank of Japan.
By the end of 2020, the Bank of Japan owned 45% of government debt outstanding.
What is the main risk of a high debt-to-GDP ratio?
A rapid increase in government debt is a major cause for concern. Generally, the higher a country’s debt-to-GDP ratio is, the higher chance that country could default on its debt, therefore creating a financial panic in the markets.
The World Bank published a study showing that countries that maintained a debt-to-GDP ratio of over 77% for prolonged periods of time experienced economic slowdowns.
COVID-19 has worsened a debt crisis that has been brewing since the 2008 global recession. A report from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) shows that at least 100 countries will have to reduce expenditures on health, education, and social protection. Also, 30 countries in the developing world have high levels of debt distress, meaning they’re experiencing great difficulties in servicing their debt.
This crisis is hitting poor and middle-income countries harder than rich countries. Wealthier countries are borrowing to launch fiscal stimulus packages while low and middle income countries cannot afford such measures, potentially resulting in wider global inequality.
The IMF Warns of Interest Rates
Global debt reached $226 trillion by the end of 2020, seeing the biggest one-year increase since World War II.
Borrowing by governments accounted for slightly over half of the $28 trillion increase, bringing global public debt ratio to a record of 99% of GDP. As interest rates rise, IMF officials warn that higher interest rates will diminish the impact of fiscal spending, and cause debt sustainability concerns to intensify. “The risks will be magnified if global interest rates rise faster than expected and growth falters,” the officials wrote.
“A significant tightening of financial conditions would heighten the pressure on the most highly indebted governments, households, and firms. If the public and private sectors are forced to deleverage simultaneously, growth prospects will suffer.”
Editor’s note: All data used in our visualization was extracted from the World Economic Outlook Report (October 2021 Edition) and The World Bank. We will update this data when the new report is available in April 2022.
Markets
U.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
U.S. debt interest payments have surged past the $1 trillion dollar mark, amid high interest rates and an ever-expanding debt burden.

U.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The cost of paying for America’s national debt crossed the $1 trillion dollar mark in 2023, driven by high interest rates and a record $34 trillion mountain of debt.
Over the last decade, U.S. debt interest payments have more than doubled amid vast government spending during the pandemic crisis. As debt payments continue to soar, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) reported that debt servicing costs surpassed defense spending for the first time ever this year.
This graphic shows the sharp rise in U.S. debt payments, based on data from the Federal Reserve.
A $1 Trillion Interest Bill, and Growing
Below, we show how U.S. debt interest payments have risen at a faster pace than at another time in modern history:
| Date | Interest Payments | U.S. National Debt |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $1.0T | $34.0T |
| 2022 | $830B | $31.4T |
| 2021 | $612B | $29.6T |
| 2020 | $518B | $27.7T |
| 2019 | $564B | $23.2T |
| 2018 | $571B | $22.0T |
| 2017 | $493B | $20.5T |
| 2016 | $460B | $20.0T |
| 2015 | $435B | $18.9T |
| 2014 | $442B | $18.1T |
| 2013 | $425B | $17.2T |
| 2012 | $417B | $16.4T |
| 2011 | $433B | $15.2T |
| 2010 | $400B | $14.0T |
| 2009 | $354B | $12.3T |
| 2008 | $380B | $10.7T |
| 2007 | $414B | $9.2T |
| 2006 | $387B | $8.7T |
| 2005 | $355B | $8.2T |
| 2004 | $318B | $7.6T |
| 2003 | $294B | $7.0T |
| 2002 | $298B | $6.4T |
| 2001 | $318B | $5.9T |
| 2000 | $353B | $5.7T |
| 1999 | $353B | $5.8T |
| 1998 | $360B | $5.6T |
| 1997 | $368B | $5.5T |
| 1996 | $362B | $5.3T |
| 1995 | $357B | $5.0T |
| 1994 | $334B | $4.8T |
| 1993 | $311B | $4.5T |
| 1992 | $306B | $4.2T |
| 1991 | $308B | $3.8T |
| 1990 | $298B | $3.4T |
| 1989 | $275B | $3.0T |
| 1988 | $254B | $2.7T |
| 1987 | $240B | $2.4T |
| 1986 | $225B | $2.2T |
| 1985 | $219B | $1.9T |
| 1984 | $205B | $1.7T |
| 1983 | $176B | $1.4T |
| 1982 | $157B | $1.2T |
| 1981 | $142B | $1.0T |
| 1980 | $113B | $930.2B |
| 1979 | $96B | $845.1B |
| 1978 | $84B | $789.2B |
| 1977 | $69B | $718.9B |
| 1976 | $61B | $653.5B |
| 1975 | $55B | $576.6B |
| 1974 | $50B | $492.7B |
| 1973 | $45B | $469.1B |
| 1972 | $39B | $448.5B |
| 1971 | $36B | $424.1B |
| 1970 | $35B | $389.2B |
| 1969 | $30B | $368.2B |
| 1968 | $25B | $358.0B |
| 1967 | $23B | $344.7B |
| 1966 | $21B | $329.3B |
Interest payments represent seasonally adjusted annual rate at the end of Q4.
At current rates, the U.S. national debt is growing by a remarkable $1 trillion about every 100 days, equal to roughly $3.6 trillion per year.
As the national debt has ballooned, debt payments even exceeded Medicaid outlays in 2023—one of the government’s largest expenditures. On average, the U.S. spent more than $2 billion per day on interest costs last year. Going further, the U.S. government is projected to spend a historic $12.4 trillion on interest payments over the next decade, averaging about $37,100 per American.
Exacerbating matters is that the U.S. is running a steep deficit, which stood at $1.1 trillion for the first six months of fiscal 2024. This has accelerated due to the 43% increase in debt servicing costs along with a $31 billion dollar increase in defense spending from a year earlier. Additionally, a $30 billion increase in funding for the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation in light of the regional banking crisis last year was a major contributor to the deficit increase.
Overall, the CBO forecasts that roughly 75% of the federal deficit’s increase will be due to interest costs by 2034.
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?