Markets
From Novelty to Necessity: The Growing Tiny Home Movement
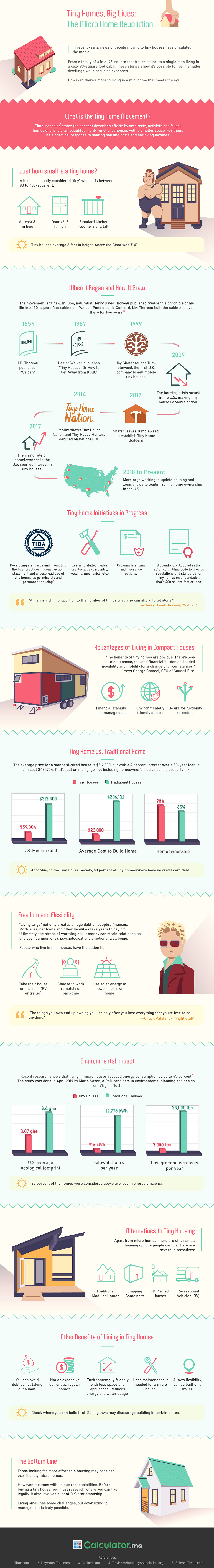
Visualizing the Rise of Tiny Homes
Born out of the desire for a simpler, more affordable way of life, the tiny home movement has spread at a furious pace—with the global market estimated to grow by a CAGR of almost 7%, adding nearly $5.2 billion in market size by 2022.
Given the economic pressures of today’s world, these alternative housing solutions have become not only a viable option for many people, but a vital one.
Today’s infographic from Calculator.me illustrates how the tiny home market got so big, and how it fares against traditional housing when it comes to providing environmentally friendly and affordable options.
How Did Tiny Homes Get So Big?
It was not until the 2009 recession hit the U.S. that tiny homes became more of a realistic option, as the benefits of downscaling became more apparent.
From then on, three things propelled the popularity of tiny homes: rising house costs, shrinking incomes, and a greater consideration for the environment.
Today, 63% of U.S. millennials would consider living in a tiny home. However, the need to go tiny is not only confined to millennials, as 40% of tiny home owners are over fifty years old.
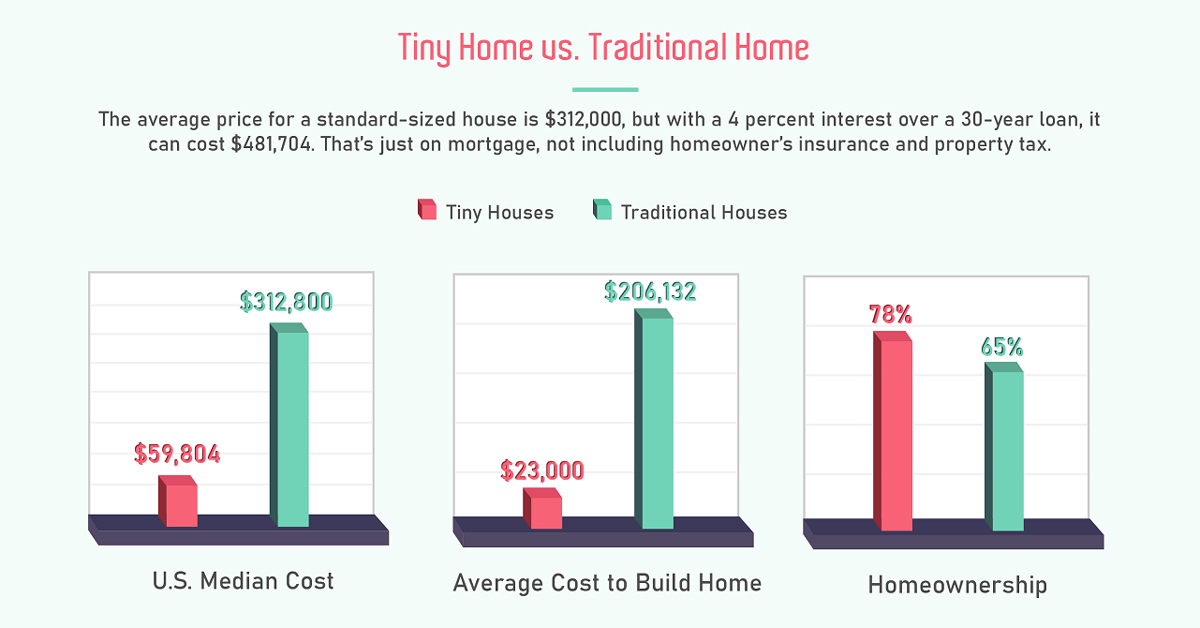
Tiny Vs. Traditional
According to the infographic, a home is considered tiny (or micro) when it is between 80-400ft², and is at least 8ft in height.
Tiny homes also come with a tiny pricetag, costing just $23,000 on average to build—meaning tiny homes are almost ⅒ the price of traditional homes.
| Metric | Tiny Homes | Traditional Homes |
|---|---|---|
| U.S. Median Cost | $59,884 | $312,800 |
| Average Cost To Build | $23,000 | $206,132 |
| Home Ownership | 78% own their home | 65% own their home |
| Mortgage | 32% have a mortgage | 64.1% have a mortgage |
| Credit Card Debt | 40% have credit card debt | 37% have credit card debt |
Other benefits of tiny home living include:
- Avoiding mortgage debt
- Less maintenance required
- Allows for a more flexible lifestyle
Further, tiny homes are providing people with alternative solutions for more sustainable living.
An Environmentally Friendly Way of Living
Certain models of tiny homes use energy from solar panels—presenting ample opportunities for an independent off-grid lifestyle. Moreover, research from Virginia Tech shows that living in tiny homes reduces energy consumption by up to 45%.
Using less energy can also be attributed to tiny homeowners using the space outside as an extension of their home. In fact, when there is usable space available outdoors, tiny home living may not seem as drastic in comparison to living in a traditional home.
Room For Improvement
There are however, some challenges for those who are considering this way of life. Zoning laws and building codes in the U.S. can be restrictive, with some states more supportive of the idea than others.
Despite these barriers, there are numerous organizations and initiatives that have been created in order to eliminate the pain points that come with tiny homes, and legitimize the industry.
Not Just a Passing Trend
With the promising trajectory of tiny homes, it is inevitable that the interest from global retailers continues to grow.
Japanese minimalist company, Muji, released their own tiny homes in 2017, costing $26,000 on average. At just under 107.6 ft², these tiny homes are prefabricated, meaning they are constructed in a factory off-site.
Amazon also recently announced their foray into the tiny home space, with dozens of models available on their website—delivering new homes right to their customers’ front doors.
The Future Comes in All Shapes and Sizes
Beyond the typical tiny home formats we see entering the market en masse, there are other alternatives which will become more readily available to consumers, including:
- Traditional modular homes
- Shipping containers
- 3D printed houses
- Recreational vehicles
It is also worth pointing out that tiny homes and these alternative models don’t have to be restricted to under 400ft². Flat packs and do-it-yourself tiny homes can be as big as 1,000ft², with some of the largest models housing up to 24 people.
It is clear that the tiny home movement is not just about going back to basics, but rather, about making home ownership a reality for everyone—potentially disrupting the current housing market in the process.
The question is not if tiny homes will become the new normal, but when.
Economy
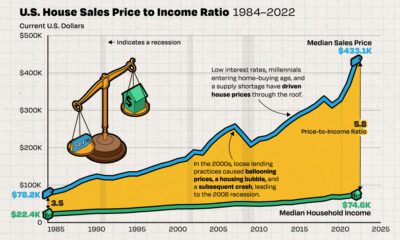
Economic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?

G7 & BRICS Real GDP Growth Forecasts for 2024
The International Monetary Fund’s (IMF) has released its real gross domestic product (GDP) growth forecasts for 2024, and while global growth is projected to stay steady at 3.2%, various major nations are seeing declining forecasts.
This chart visualizes the 2024 real GDP growth forecasts using data from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook for G7 and BRICS member nations along with Saudi Arabia, which is still considering an invitation to join the bloc.
Get the Key Insights of the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
Want a visual breakdown of the insights from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook report?
This visual is part of a special dispatch of the key takeaways exclusively for VC+ members.
Get the full dispatch of charts by signing up to VC+.
Mixed Economic Growth Prospects for Major Nations in 2024
Economic growth projections by the IMF for major nations are mixed, with the majority of G7 and BRICS countries forecasted to have slower growth in 2024 compared to 2023.
Only three BRICS-invited or member countries, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and South Africa, have higher projected real GDP growth rates in 2024 than last year.
| Group | Country | Real GDP Growth (2023) | Real GDP Growth (2024P) |
|---|---|---|---|
| G7 | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 2.5% | 2.7% |
| G7 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 1.1% | 1.2% |
| G7 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 1.9% | 0.9% |
| G7 | 🇫🇷 France | 0.9% | 0.7% |
| G7 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 0.9% | 0.7% |
| G7 | 🇬🇧 UK | 0.1% | 0.5% |
| G7 | 🇩🇪 Germany | -0.3% | 0.2% |
| BRICS | 🇮🇳 India | 7.8% | 6.8% |
| BRICS | 🇨🇳 China | 5.2% | 4.6% |
| BRICS | 🇦🇪 UAE | 3.4% | 3.5% |
| BRICS | 🇮🇷 Iran | 4.7% | 3.3% |
| BRICS | 🇷🇺 Russia | 3.6% | 3.2% |
| BRICS | 🇪🇬 Egypt | 3.8% | 3.0% |
| BRICS-invited | 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | -0.8% | 2.6% |
| BRICS | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 2.9% | 2.2% |
| BRICS | 🇿🇦 South Africa | 0.6% | 0.9% |
| BRICS | 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | 7.2% | 6.2% |
| 🌍 World | 3.2% | 3.2% |
China and India are forecasted to maintain relatively high growth rates in 2024 at 4.6% and 6.8% respectively, but compared to the previous year, China is growing 0.6 percentage points slower while India is an entire percentage point slower.
On the other hand, four G7 nations are set to grow faster than last year, which includes Germany making its comeback from its negative real GDP growth of -0.3% in 2023.
Faster Growth for BRICS than G7 Nations
Despite mostly lower growth forecasts in 2024 compared to 2023, BRICS nations still have a significantly higher average growth forecast at 3.6% compared to the G7 average of 1%.
While the G7 countries’ combined GDP is around $15 trillion greater than the BRICS nations, with continued higher growth rates and the potential to add more members, BRICS looks likely to overtake the G7 in economic size within two decades.
BRICS Expansion Stutters Before October 2024 Summit
BRICS’ recent expansion has stuttered slightly, as Argentina’s newly-elected president Javier Milei declined its invitation and Saudi Arabia clarified that the country is still considering its invitation and has not joined BRICS yet.
Even with these initial growing pains, South Africa’s Foreign Minister Naledi Pandor told reporters in February that 34 different countries have submitted applications to join the growing BRICS bloc.
Any changes to the group are likely to be announced leading up to or at the 2024 BRICS summit which takes place October 22-24 in Kazan, Russia.
Get the Full Analysis of the IMF’s Outlook on VC+
This visual is part of an exclusive special dispatch for VC+ members which breaks down the key takeaways from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook.
For the full set of charts and analysis, sign up for VC+.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries