Financing a Net-Zero Future with Carbon Credit Streaming
The following content is sponsored by Carbon Streaming Corporation.

Financing a Net-Zero Future with Carbon Credit Streaming
The world is advancing towards a net-zero carbon future, but achieving it will require a larger role for carbon credits.
A carbon credit is a tradeable certificate that represents one metric ton of carbon dioxide (CO2) or the CO2 equivalent (CO2e) of another greenhouse gas (GHG) that is prevented from entering the atmosphere or is removed from the atmosphere. Organizations purchase and use these certificates to offset their emissions that are difficult to reduce or control.
This infographic sponsored by Carbon Streaming Corporation explains how the company is funding the fight against climate change by bringing the streaming model—traditionally used in mining and energy—to the growing market for carbon credits.
The Rising Need for Climate Action
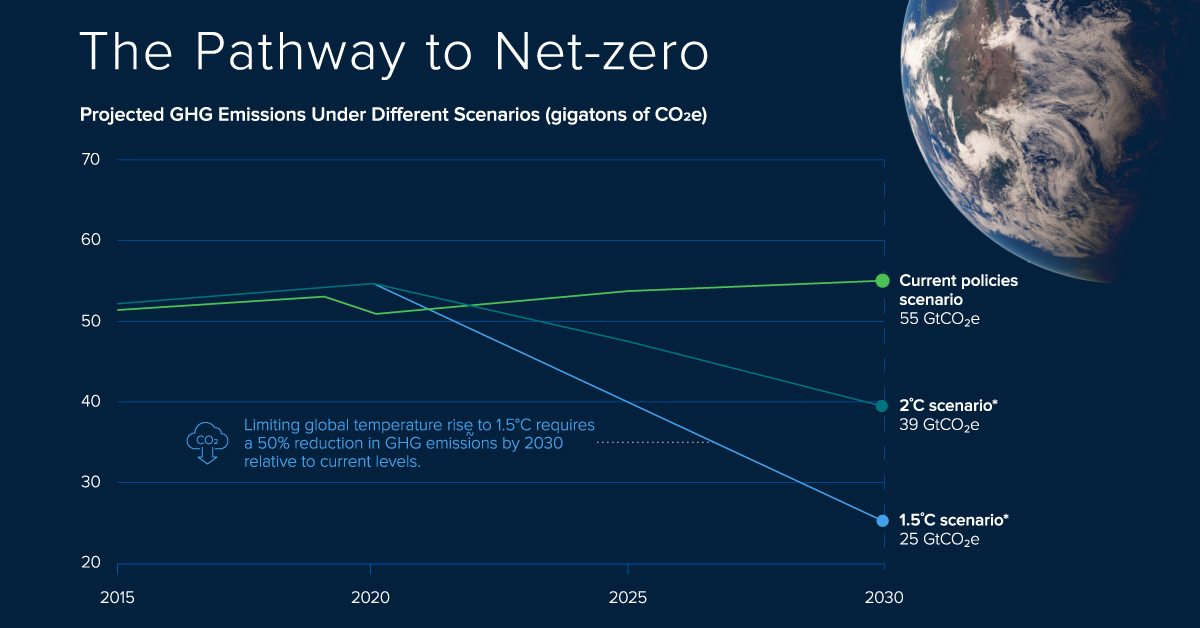
Global GHG emissions have risen alongside the expansion of industries and economies.
Since the Industrial Revolution, atmospheric concentrations of CO2 have increased at a rate at least 10 times faster than at any other time during the last 800,000 years. Consequently, global surface temperatures have risen, bringing the world closer to the devastating effects of climate change.
According to the latest United Nations Emissions Gap Report, limiting global temperature rise to 1.5°C requires a 50% reduction in GHG emissions by 2030 relative to current levels. While attaining this goal seems difficult, carbon credits can help get us closer to it.
What are Carbon Credits, and How Can They Help?
Carbon credits are generated by projects that avoid, reduce, or remove CO2e from the atmosphere. These projects include, but are not limited to:
- Reforestation and forest conservation
- Renewable energy
- Carbon capture and storage
For every metric ton of CO2e that a project avoids, reduces, or removes, it generates one carbon credit. Companies buy these carbon credits to offset emissions that are difficult to reduce or control, such as value chain emissions.
The number of companies with net-zero targets has jumped over 200% between 2019 and 2020, up from 500 to 1,565. Carbon credits can help address various gaps on a company’s path to decarbonize, including:
- Technological Gaps: Companies are limited by current reduction and removal technologies that are available at scale.
- Time Gaps: Companies will require time to implement plans to reduce their emissions.
- Cost Gaps: Companies may have emissions that are too expensive to eliminate today.
The Growing Demand for Carbon Credits
As more and more companies turn to carbon credits, the market size of both compliance and voluntary carbon markets is growing.
Compliance markets are regulated by governments to cap emissions for certain industries. Voluntary carbon markets are where carbon credits can be purchased by those that voluntarily want to offset their emissions.
| Year | Voluntary markets transaction value | Compliance markets transaction value |
|---|---|---|
| 2017 | $146M | $47B |
| 2018 | $296M | $170B |
| 2019 | $320M | $216B |
| 2020 | $473M | $261B |
| 2021* | $748M | N/A |
*As of Aug. 31, 2021.
Voluntary markets are substantially smaller than compliance markets, with a notable growth runway. Transaction values in voluntary markets have grown five-fold since 2017, and are on track to surpass $1 billion in 2021.
However, the supply of carbon credits in the voluntary markets relies on carbon offset projects, which require funding to be developed. These funds can be difficult to obtain before buyers purchase the carbon credits generated by the project. Carbon Streaming is able to provide this capital with its unique streaming model, bridging the gap in funding until credits are available for sale.
How the Carbon Streaming Model Works
The Carbon Streaming model functions in two simple steps. It involves an upfront payment from Carbon Streaming to a project developer, who then provides a stream of high-quality carbon credits in the future.
- Upfront payment to project developer: Carbon Streaming makes an upfront payment for the right to purchase future carbon credits.
- Stream of carbon credits: Carbon Streaming makes ongoing delivery payments and receives a stream of carbon credits generated by the project.
Carbon Streaming’s ability to access capital markets to raise low-cost capital provides it with a competitive advantage. The Carbon Streaming model allows the alignment of the strategic interests of Carbon Streaming and the project developer with both of them receiving multiple benefits.
Carbon Streaming acts as both:
- A long-term partner with project developers
- A trusted partner for buyers of high-quality carbon credits
Carbon Streaming provides impact investors with exposure to rising carbon prices while also financing projects that help achieve decarbonization and sustainability goals.
Carbon Streaming for a Cleaner Future
As the world shifts towards a net-zero carbon future, carbon credits will play a key role in helping countries and companies achieve their climate goals.
Carbon Streaming is funding the fight against climate change with its unique streaming model—an investment opportunity with several benefits for investors and the environment.
-

 Sponsored3 years ago
Sponsored3 years agoMore Than Precious: Silver’s Role in the New Energy Era (Part 3 of 3)
Long known as a precious metal, silver in solar and EV technologies will redefine its role and importance to a greener economy.
-

 Sponsored7 years ago
Sponsored7 years agoThe History and Evolution of the Video Games Market
Everything from Pong to the rise of mobile gaming and AR/VR. Learn about the $100 billion video games market in this giant infographic.
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Extraordinary Raw Materials in an iPhone 6s
Over 700 million iPhones have now been sold, but the iPhone would not exist if it were not for the raw materials that make the technology...
-

 Sponsored8 years ago
Sponsored8 years agoThe Industrial Internet, and How It’s Revolutionizing Mining
The convergence of the global industrial sector with big data and the internet of things, or the Industrial Internet, will revolutionize how mining works.