Technology
Mapped: The State of Facial Recognition Around the World
View the full-size version of this infographic.
Mapping The State of Facial Recognition Around the World
View the high resolution version of this infographic by clicking here.
From public CCTV cameras to biometric identification systems in airports, facial recognition technology is now common in a growing number of places around the world.
In its most benign form, facial recognition technology is a convenient way to unlock your smartphone. At the state level though, facial recognition is a key component of mass surveillance, and it already touches half the global population on a regular basis.
Today’s visualizations from SurfShark classify 194 countries and regions based on the extent of surveillance.
| Facial Recognition Status | Total Countries |
|---|---|
| In Use | 98 |
| Approved, but not implemented | 12 |
| Considering technology | 13 |
| No evidence of use | 68 |
| Banned | 3 |
Click here to explore the full research methodology.
Let’s dive into the ways facial recognition technology is used across every region.
North America, Central America, and Caribbean
In the U.S., a 2016 study showed that already half of American adults were captured in some kind of facial recognition network. More recently, the Department of Homeland Security unveiled its “Biometric Exit” plan, which aims to use facial recognition technology on nearly all air travel passengers by 2023, to identify compliance with visa status.
Perhaps surprisingly, 59% of Americans are actually in favor of implementing facial recognition technology, considering it acceptable for use in law enforcement according to a Pew Research survey. Yet, some cities such as San Francisco have pushed to ban surveillance, citing a stand against its potential abuse by the government.
Facial recognition technology can potentially come in handy after a natural disaster. After Hurricane Dorian hit in late summer of 2019, the Bahamas launched a blockchain-based missing persons database “FindMeBahamas” to identify thousands of displaced people.
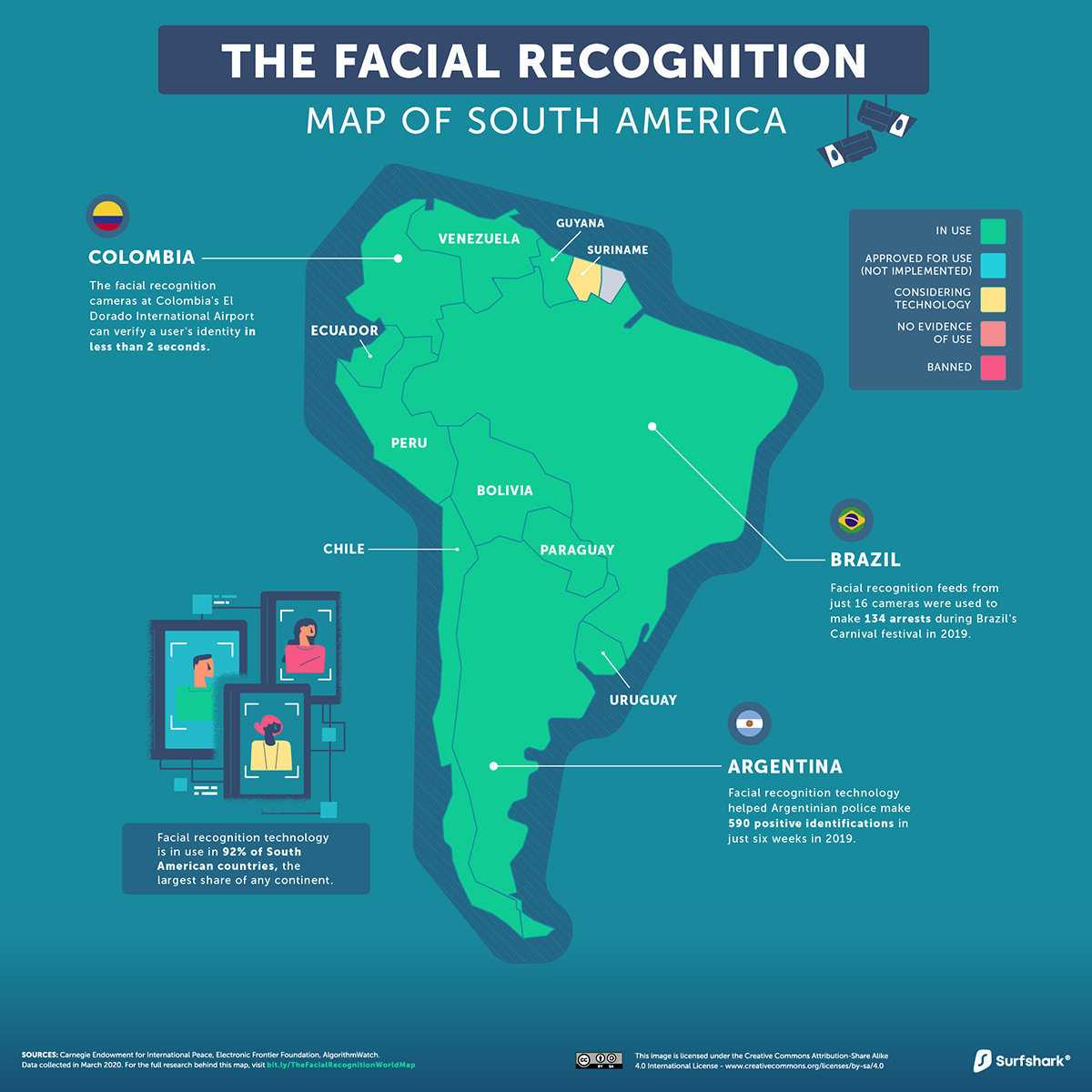
South America
The majority of facial recognition technology in South America is aimed at cracking down on crime. In fact, it worked in Brazil to capture Interpol’s second-most wanted criminal.
Home to over 209 million, Brazil soon plans to create a biometric database of its citizens. However, some are nervous that this could also serve as a means to prevent dissent against the current political order.
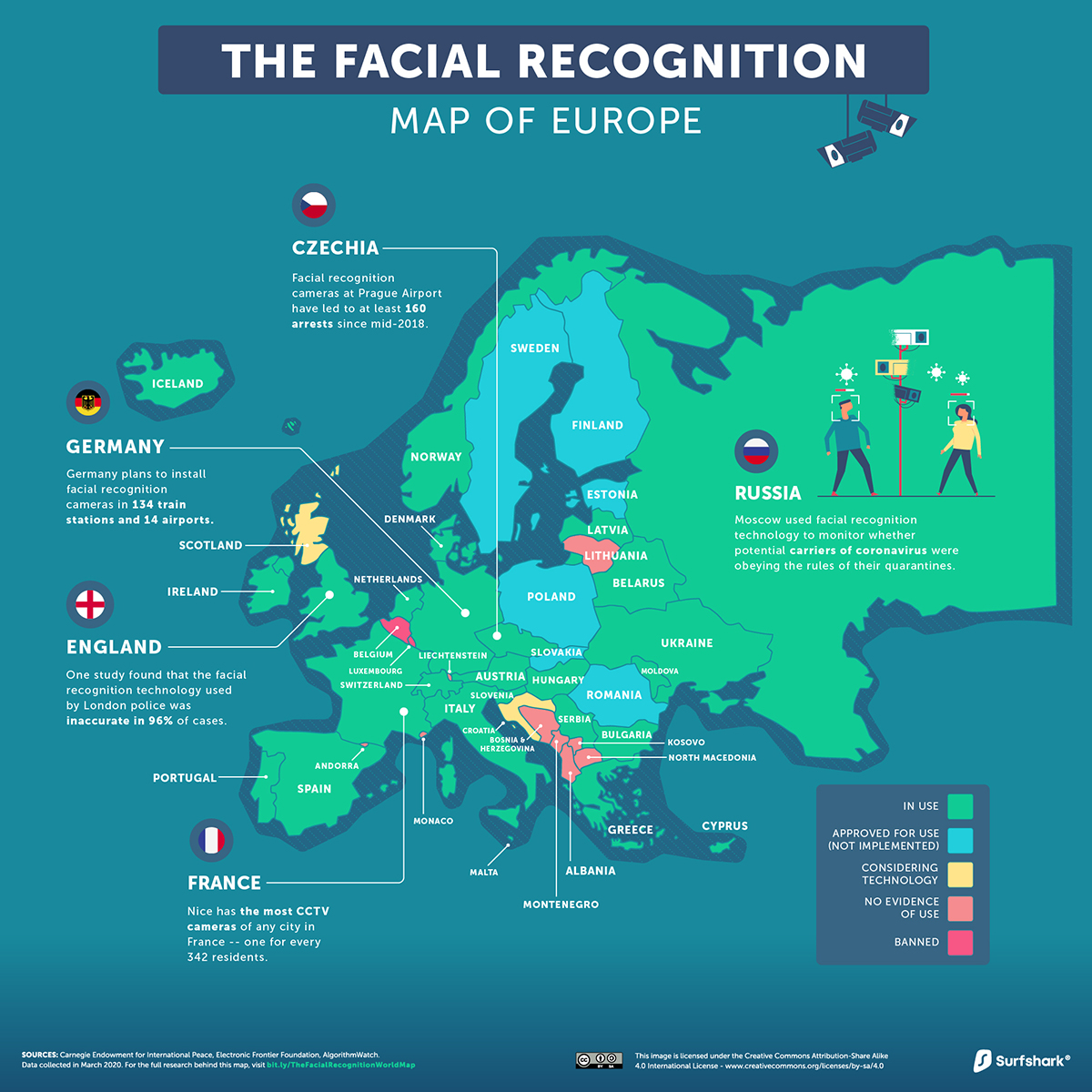
Europe
Belgium and Luxembourg are two of only three governments in the world to officially oppose the use of facial recognition technology.
Further, 80% of Europeans are not keen on sharing facial data with authorities. Despite such negative sentiment, it’s still in use across 26 European countries to date.
The EU has been a haven for unlawful biometric experimentation and surveillance.
—European Digital Rights (EDRi)
In Russia, authorities have relied on facial recognition technology to check for breaches of quarantine rules by potential COVID-19 carriers. In Moscow alone, there are reportedly over 100,000 facial recognition enabled cameras in operation.
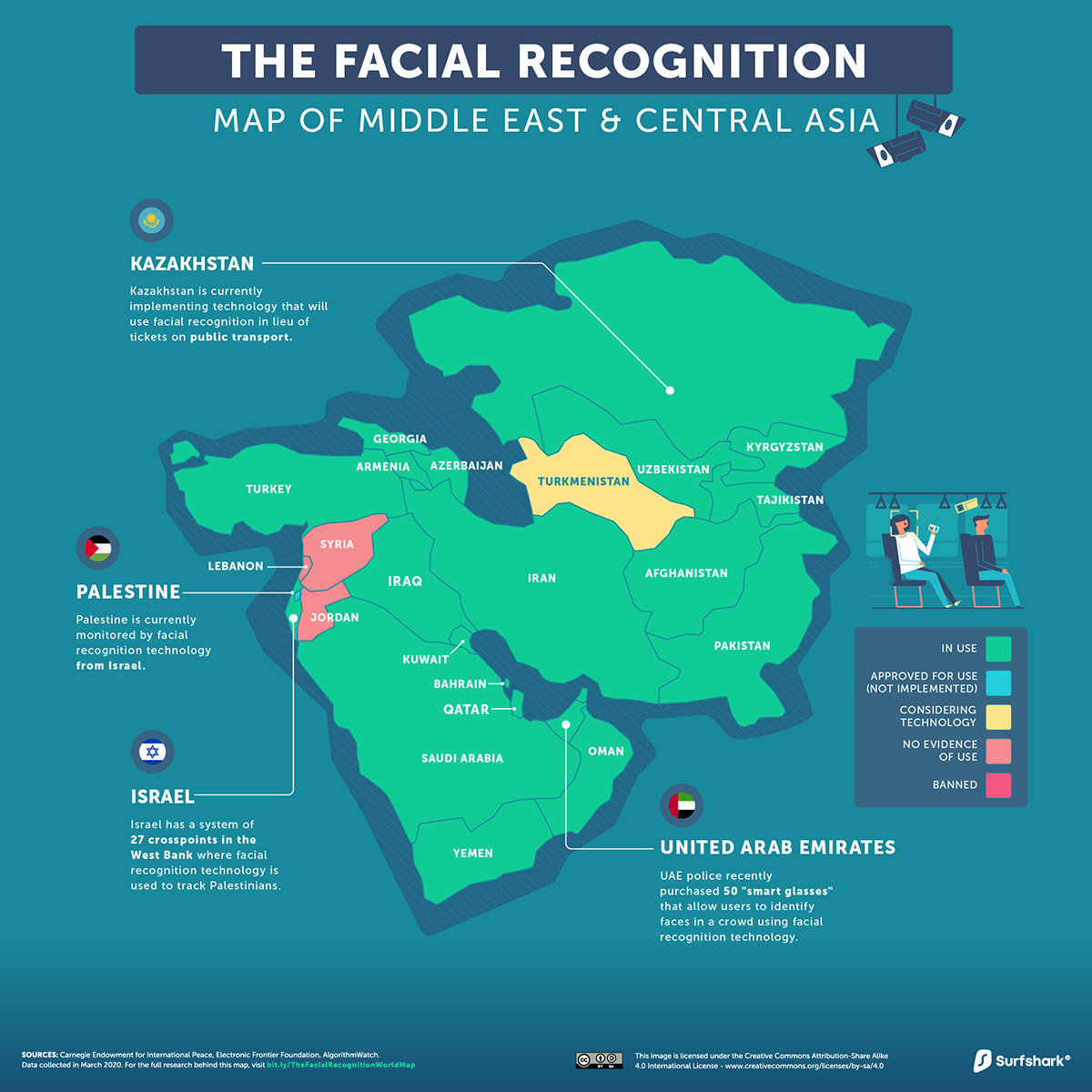
Middle East and Central Asia
Facial recognition technology is widespread in this region, notably for military purposes.
In Turkey, 30 domestically-developed kamikaze drones will use AI and facial recognition for border security. Similarly, Israel has a close eye on Palestinian citizens across 27 West Bank checkpoints.
In other parts of the region, police in the UAE have purchased discreet smart glasses that can be used to scan crowds, where positive matches show up on an embedded lens display. Over in Kazakhstan, facial recognition technology could replace public transportation passes entirely.
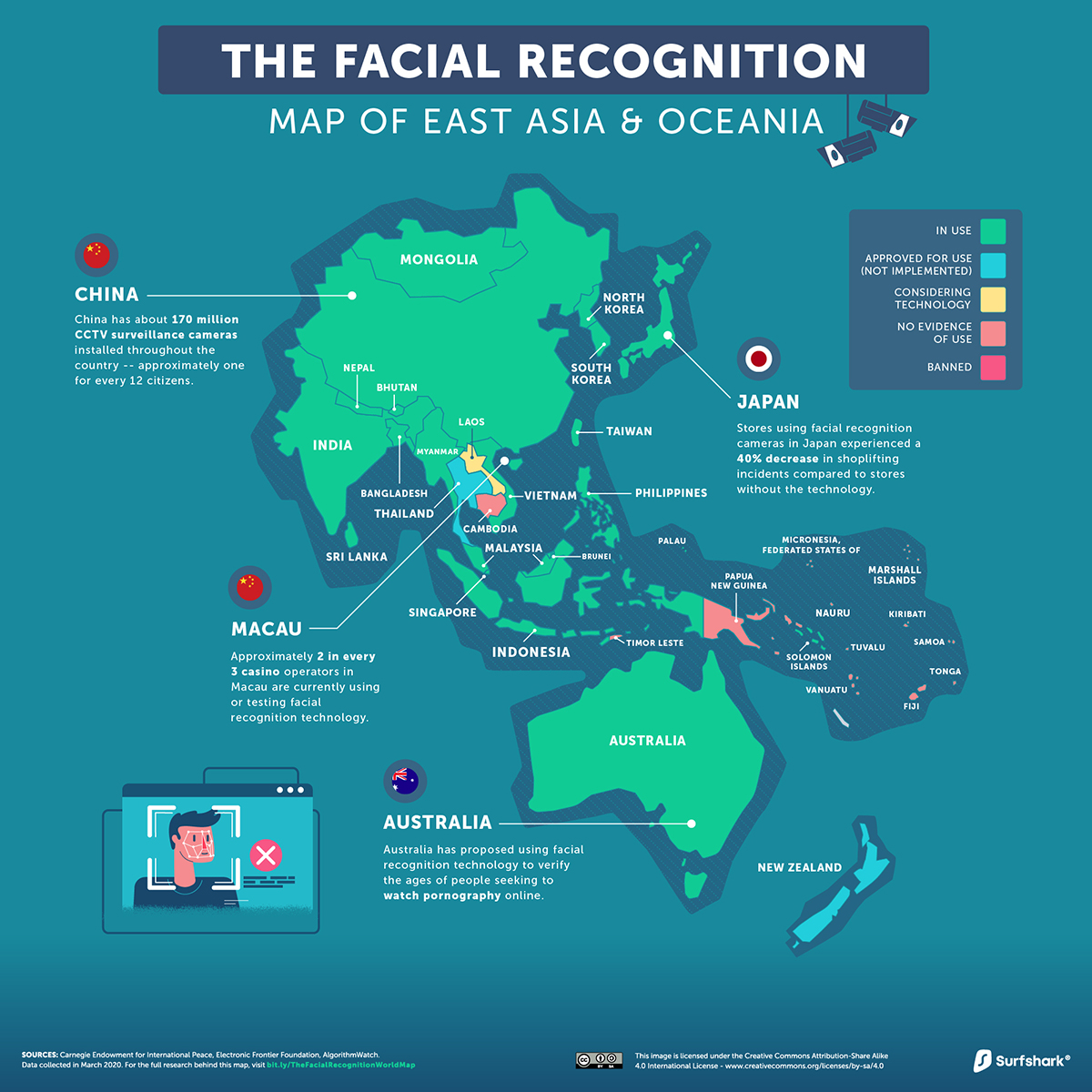
East Asia and Oceania
In the COVID-19 battle, contact tracing through biometric identification became a common tool to slow the infection rates in countries such as China, South Korea, Taiwan, and Singapore. In some instances, this included the use of facial recognition technology to monitor temperatures as well as spot those without a mask.
That said, questions remain about whether the pandemic panopticon will stop there.
China is often cited as a notorious use case of mass surveillance, and the country has the highest ratio of CCTV cameras to citizens in the world—one for every 12 people. By 2023, China will be the single biggest player in the global facial recognition market. And it’s not just implementing the technology at home–it’s exporting too.
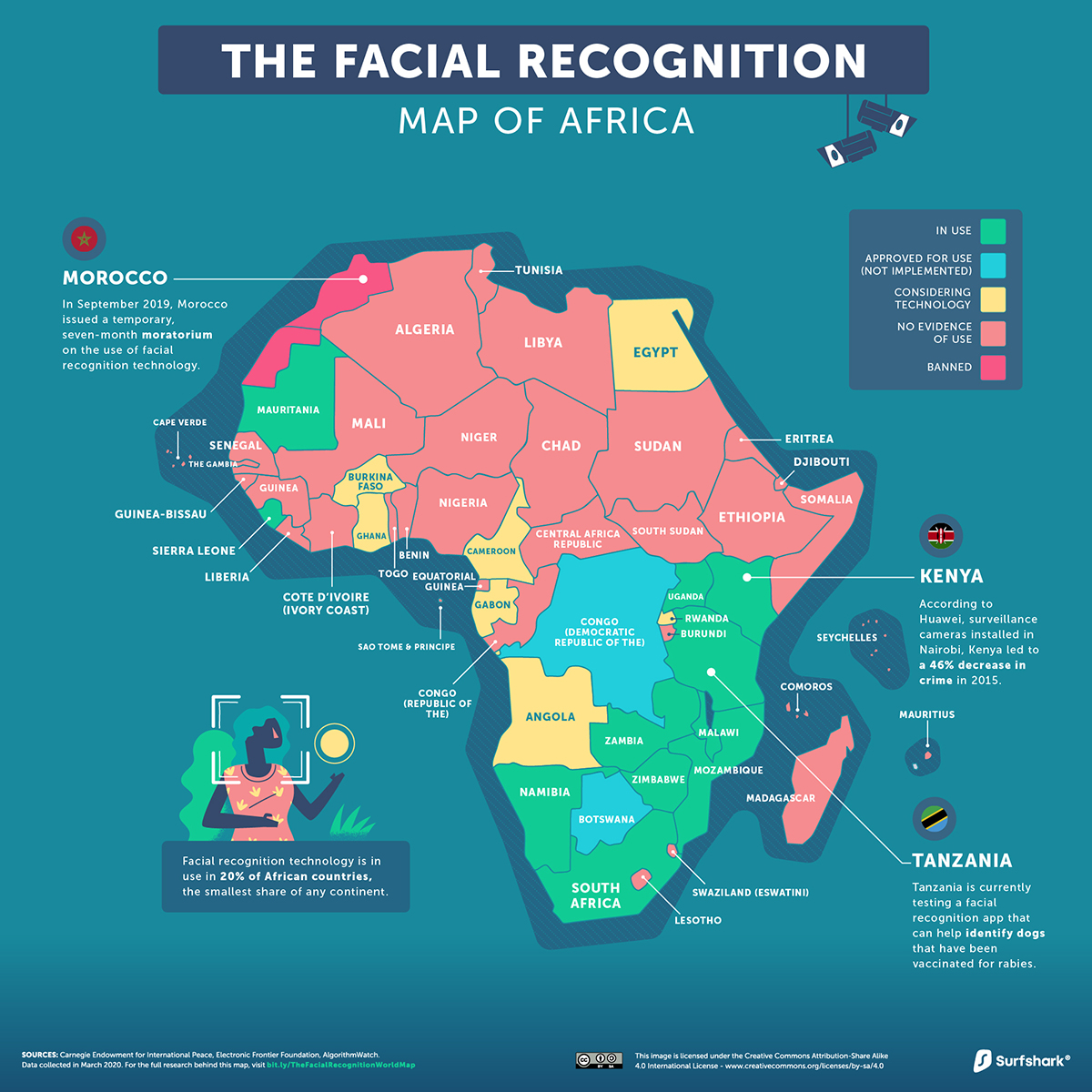
Africa
While the African continent currently has the lowest concentration of facial recognition technology in use, this deficit may not last for long.
Several African countries, such as Kenya and Uganda, have received telecommunications and surveillance financing and infrastructure from Chinese companies—Huawei in particular. While the company claims this has enabled regional crime rates to plummet, some activists are wary of the partnership.
Whether you approach facial recognition technology from public and national security lens or from an individual liberty perspective, it’s clear that this kind of surveillance is here to stay.
Brands
How Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
From complete overhauls to more subtle tweaks, these tech logos have had quite a journey. Featuring: Google, Apple, and more.

How Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
One would be hard-pressed to find a company that has never changed its logo. Granted, some brands—like Rolex, IBM, and Coca-Cola—tend to just have more minimalistic updates. But other companies undergo an entire identity change, thus necessitating a full overhaul.
In this graphic, we visualized the evolution of prominent tech companies’ logos over time. All of these brands ranked highly in a Q1 2024 YouGov study of America’s most famous tech brands. The logo changes are sourced from 1000logos.net.
How Many Times Has Google Changed Its Logo?
Google and Facebook share a 98% fame rating according to YouGov. But while Facebook’s rise was captured in The Social Network (2010), Google’s history tends to be a little less lionized in popular culture.
For example, Google was initially called “Backrub” because it analyzed “back links” to understand how important a website was. Since its founding, Google has undergone eight logo changes, finally settling on its current one in 2015.
| Company | Number of Logo Changes |
|---|---|
| 8 | |
| HP | 8 |
| Amazon | 6 |
| Microsoft | 6 |
| Samsung | 6 |
| Apple | 5* |
Note: *Includes color changes. Source: 1000Logos.net
Another fun origin story is Microsoft, which started off as Traf-O-Data, a traffic counter reading company that generated reports for traffic engineers. By 1975, the company was renamed. But it wasn’t until 2012 that Microsoft put the iconic Windows logo—still the most popular desktop operating system—alongside its name.
And then there’s Samsung, which started as a grocery trading store in 1938. Its pivot to electronics started in the 1970s with black and white television sets. For 55 years, the company kept some form of stars from its first logo, until 1993, when the iconic encircled blue Samsung logo debuted.
Finally, Apple’s first logo in 1976 featured Isaac Newton reading under a tree—moments before an apple fell on his head. Two years later, the iconic bitten apple logo would be designed at Steve Jobs’ behest, and it would take another two decades for it to go monochrome.
-

 Maps1 week ago
Maps1 week agoThe Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share