Misc
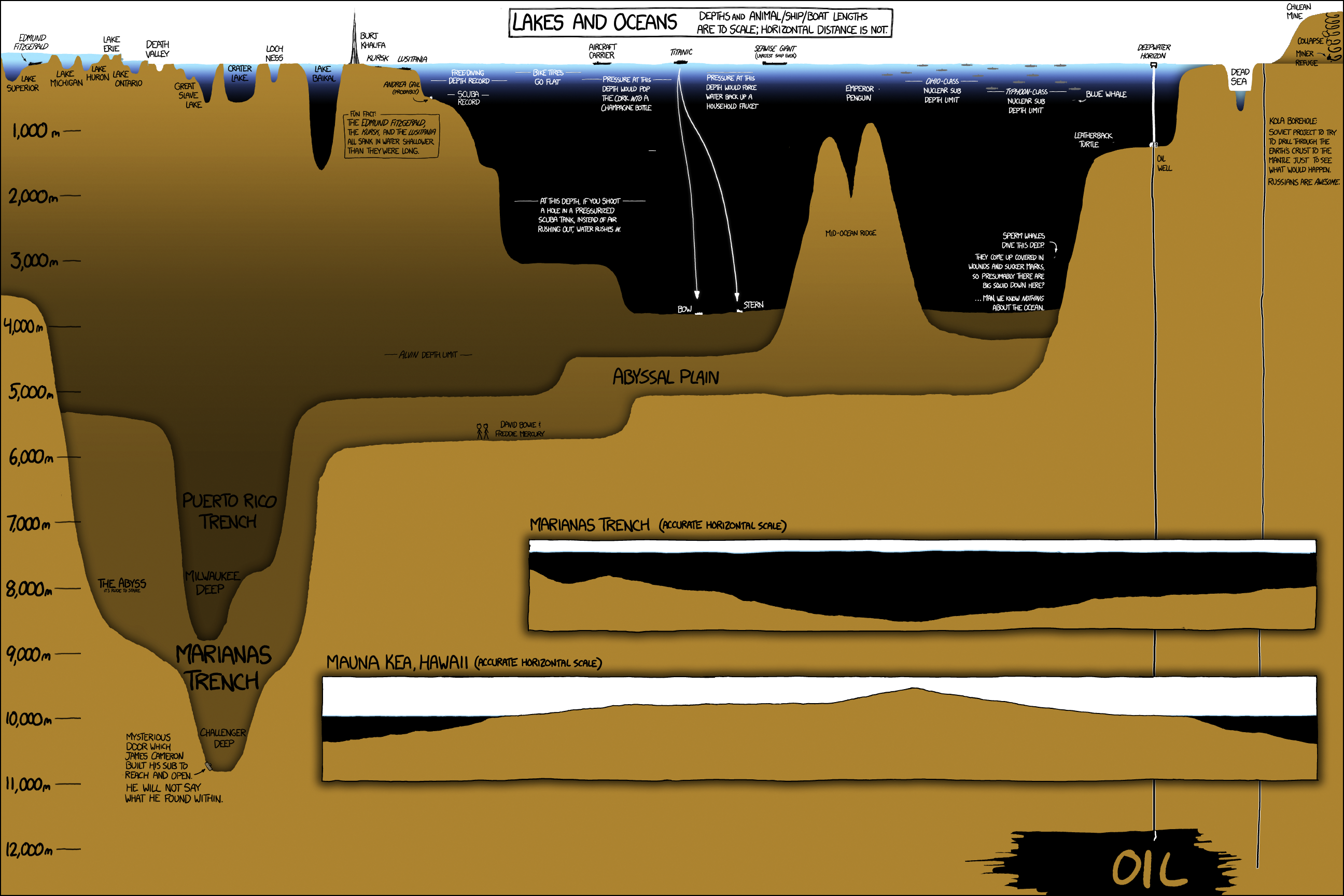
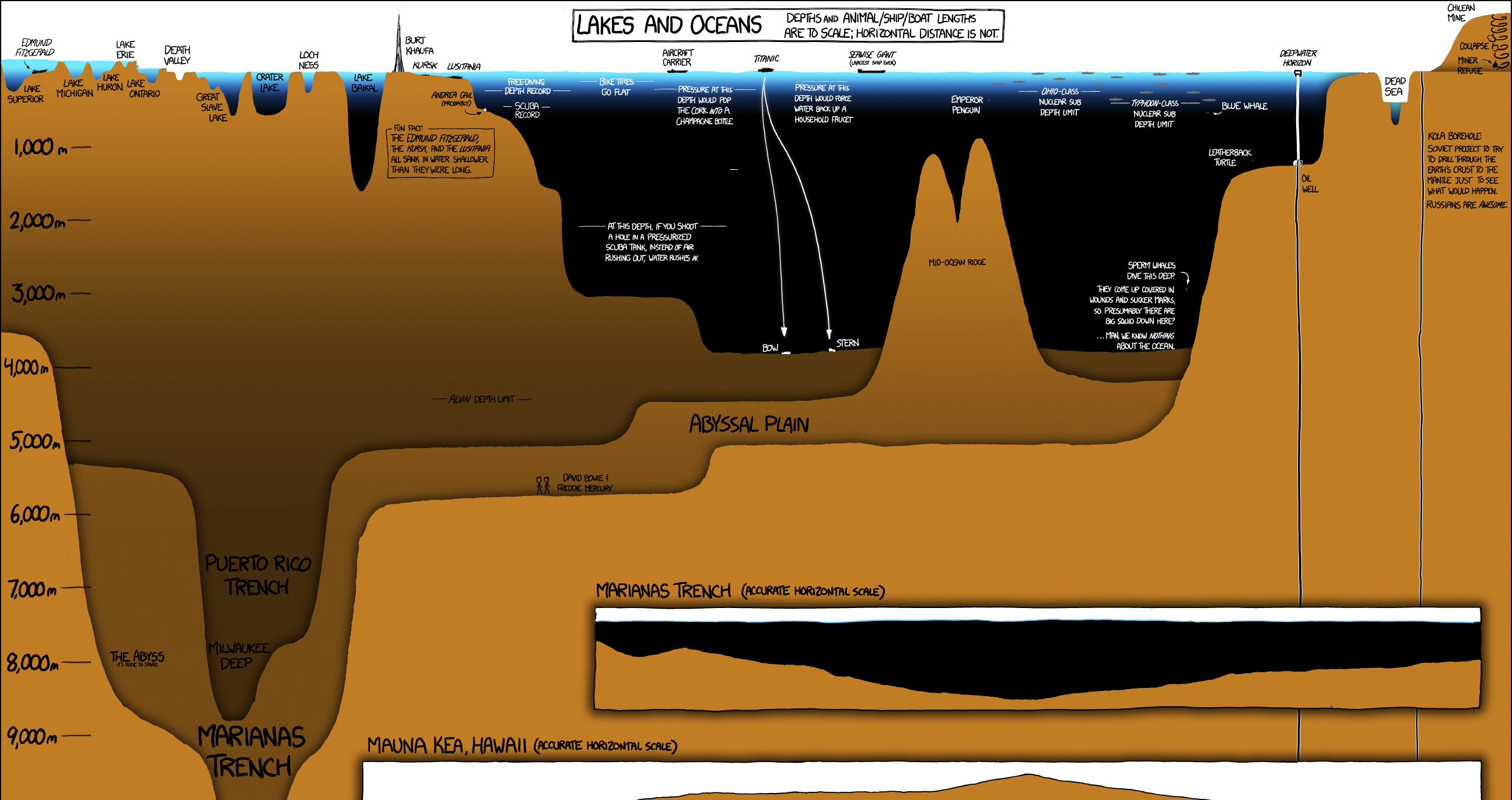
A Deep Dive Into the World’s Oceans, Lakes, and Drill Holes
Explore the full-size version of this visualization by clicking here.
Credit: xkcd
Today’s chart is best viewed full-screen. Explore the high resolution version by clicking here.
Sailors have been circumnavigating the high seas for centuries now, but what could be found beneath the sunlit surface of the ocean remained a mystery until far more recently. In fact, it wasn’t until 1875, during the Challenger expedition, that humanity got it’s first concrete idea of how deep the ocean actually was.
Today’s graphic, another fantastic piece by xkcd, is a unique and entertaining look at everything from Lake Superior’s ice encrusted shoreline down to blackest, inhospitable trench (which today bears the name of the expedition that first discovered it).
The graphic is packed with detail, so we’ll only highlight a few points of interest.
Deep Thoughts with Lake Baikal
Deep in Siberia, abutting a mountainous stretch of the Mongolian border, is the one of the most remarkable bodies of water on Earth: Lake Baikal. There are a number of qualities that make Lake Baikal stand out.
Depth: Baikal, located in a massive continental rift, is the deepest lake in the world at 1,642m (5,387ft). That extreme depth holds a lot of fresh water. In fact, an estimated 22% of all the world’s fresh water can be found in the lake.
Age: Baikal (which is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site) is estimated to be over 25 million years old, making it the most ancient lake on the planet.
Clarity: Interestingly, the water in the lake is exceptionally clear. In winter, visibility can extend over 30m (98ft) below the surface.
Biodiversity: The unique ecosystem of Lake Baikal provides a home for thousands of plant and animal species. In fact, upwards of 80% of those species are endemic, meaning they are unique to that region.
Who is Alvin?
Since 1964, a hard-working research submersible named Alvin has been helping us better understand the deep ocean. Alvin explored the wreckage of RMS Titanic in 1986, and helped confirm the existence of black smokers (one of the weirdest ecosystems in the world).
Though most of the components of the vessel have been replaced and upgraded over the years, it’s still in use today. In 2020, Alvin received an $8 million upgrade, and is now capable of exploring 99% of the ocean floor.
We know more about the surface of Venus than the bottom of the ocean. The potential for discovery is huge.– Anna-Louise Reysenbach, Professor of Microbiology, PSU
The Ocean’s Deepest Point
The deepest point in the ocean is the Mariana Trench, at 11,034 meters (36,201 feet).
This trench is located in the Pacific Ocean, near Guam and the trench’s namesake, the Mariana Islands. While the trench is the most extreme example of ocean depths, when compared to surface level distance, it’s depth is shorter than Manhattan.
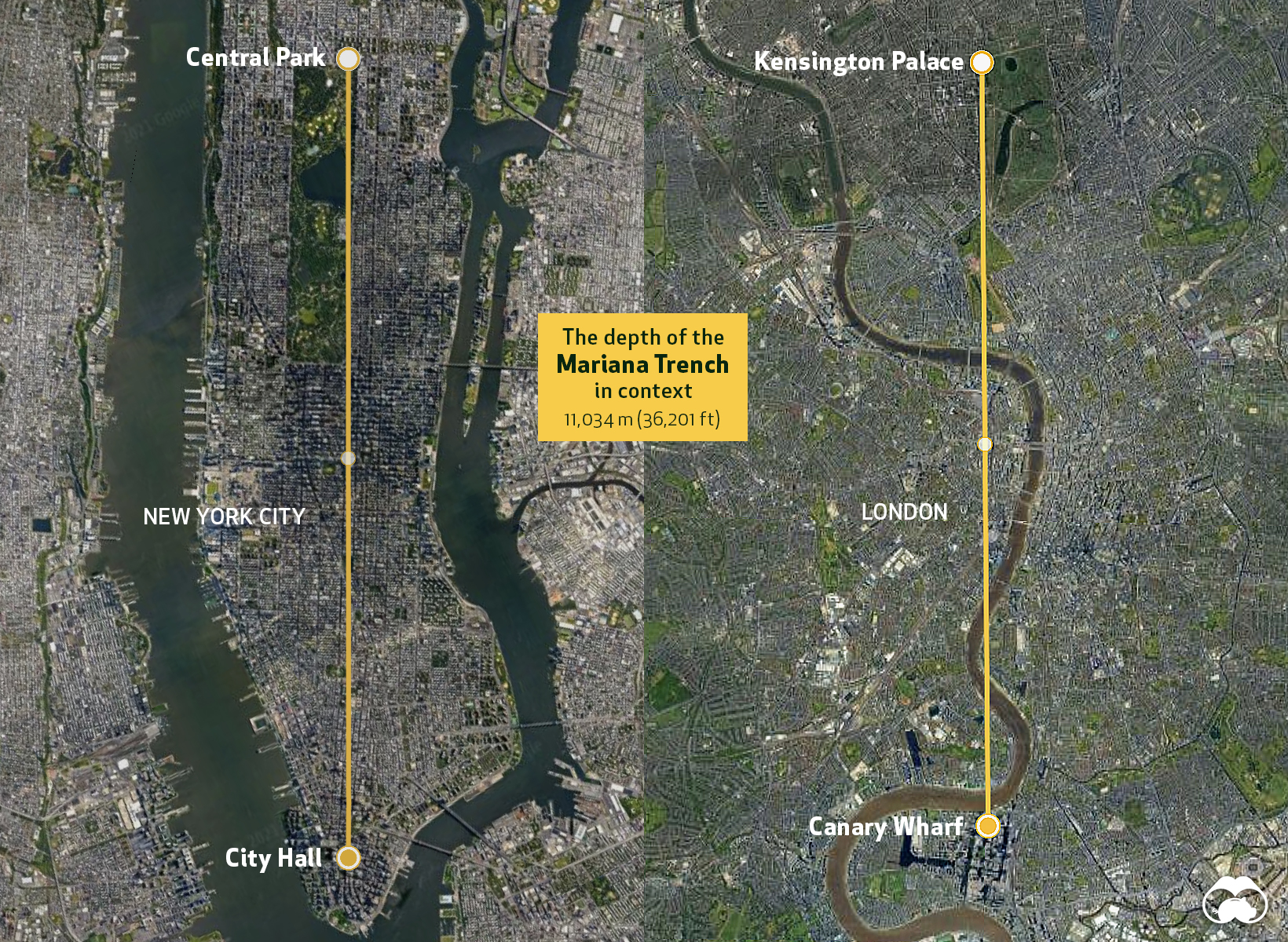
Obviously, the context of surface distance is wildly different than vertical distance, but it serves as a reminder of how narrow the “explorable” band of the Earth’s surface is.
Polymetallic Nodules
The ancient Greek word, ábyssos, roughly means “unfathomable, bottomless gulf”. While there is a bottom (the abyssopelagic zone comprises around 75% of the ocean floor), the enormous scale of this ecosystem is certainly unfathomable.
Objectively, the abyssal plain is not the prettiest part of the ocean. It’s nearly featureless, and lacks the panache of, say, a coral reef, but there are still some very compelling reasons we’re eager to explore it. Resource companies are chiefly interested in polymetallic nodules, which are essentially rich manganese formations scattered about on the sea bottom.
Manganese is already essential in steel production, but demand is also getting a substantial lift from the fast-growing electric vehicle market. The first company to find an economical way to harvest nodules from the ocean floor could reap a significant windfall.
Drill Baby, Drill
Demand for resources can force humans into some very inhospitable places, and in the case of Deepwater Horizon, we chased oil to a depth even surpassing the famed Marianas Trench.
Drilling that far below the surface is a complicated endeavor, and when the drill platform was put into service in 2001, it was hailed as an engineering marvel. To this day, Deepwater Horizon holds the record for the deepest offshore hole ever made.
After the rig’s infamous explosion and subsequent spill in 2010, that depth record for drilling may stand the test of time.
Maps
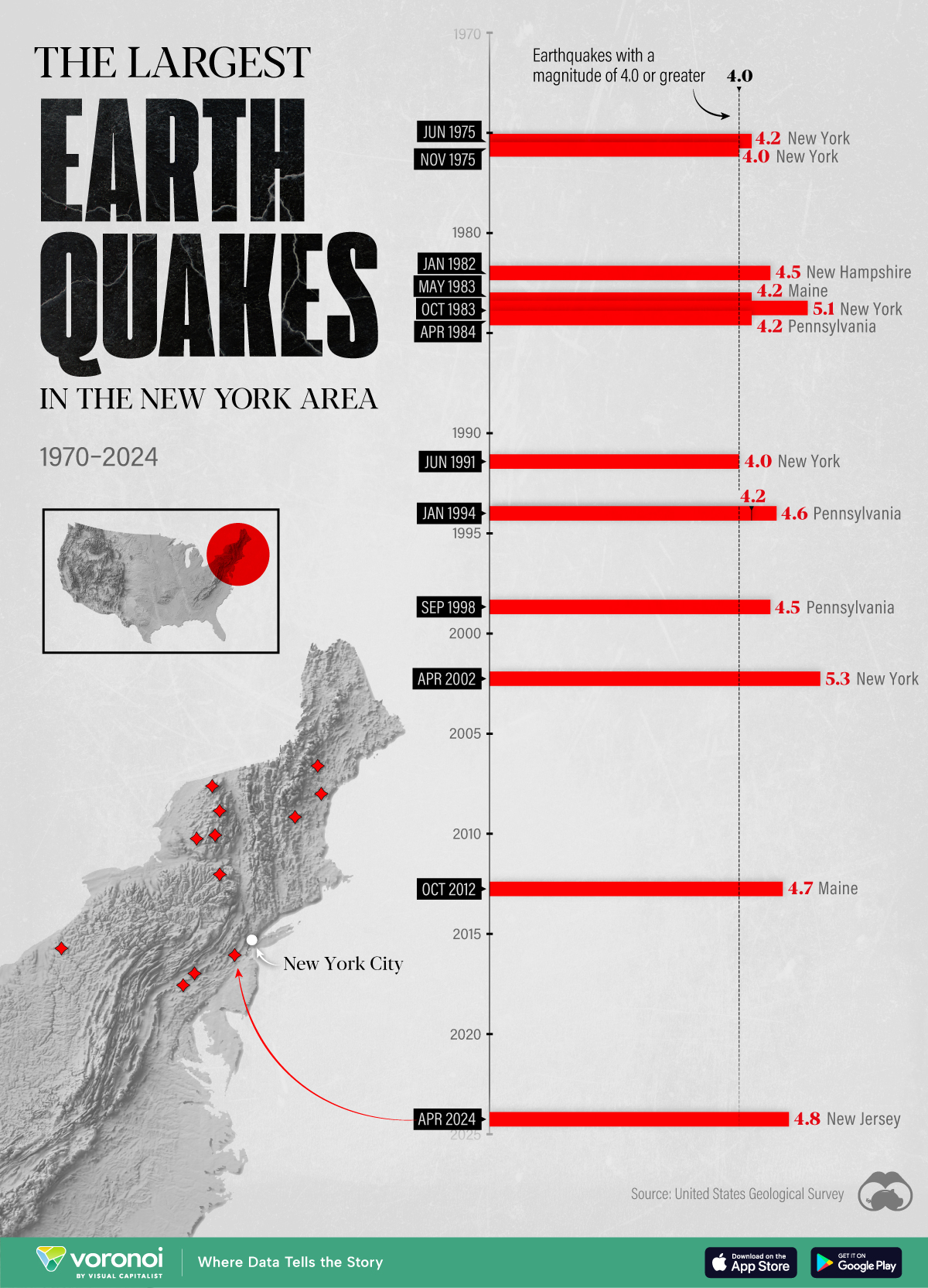
The Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area (1970-2024)
The earthquake that shook buildings across New York in April 2024 was the third-largest quake in the Northeast U.S. over the past 50 years.

The Largest Earthquakes in the New York Area
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The 4.8 magnitude earthquake that shook buildings across New York on Friday, April 5th, 2024 was the third-largest quake in the U.S. Northeast area over the past 50 years.
In this map, we illustrate earthquakes with a magnitude of 4.0 or greater recorded in the Northeastern U.S. since 1970, according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS).
Shallow Quakes and Older Buildings
The earthquake that struck the U.S. Northeast in April 2024 was felt by millions of people from Washington, D.C., to north of Boston. It even caused a full ground stop at Newark Airport.
The quake, occurring just 5 km beneath the Earth’s surface, was considered shallow, which is what contributed to more intense shaking at the surface.
According to the USGS, rocks in the eastern U.S. are significantly older, denser, and harder than those on the western side, compressed by time. This makes them more efficient conduits for seismic energy. Additionally, buildings in the Northeast tend to be older and may not adhere to the latest earthquake codes.
Despite disrupting work and school life, the earthquake was considered minor, according to the Michigan Technological University magnitude scale:
| Magnitude | Earthquake Effects | Estimated Number Each Year |
|---|---|---|
| 2.5 or less | Usually not felt, but can be recorded by seismograph. | Millions |
| 2.5 to 5.4 | Often felt, but only causes minor damage. | 500,000 |
| 5.5 to 6.0 | Slight damage to buildings and other structures. | 350 |
| 6.1 to 6.9 | May cause a lot of damage in very populated areas. | 100 |
| 7.0 to 7.9 | Major earthquake. Serious damage. | 10-15 |
| 8.0 or greater | Great earthquake. Can totally destroy communities near the epicenter. | One every year or two |
The largest earthquake felt in the area over the past 50 years was a 5.3 magnitude quake that occurred in Au Sable Forks, New York, in 2002. It damaged houses and cracked roads in a remote corner of the Adirondack Mountains, but caused no injuries.
| Date | Magnitude | Location | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| April 20, 2002 | 5.3 | Au Sable Forks | New York |
| October 7, 1983 | 5.1 | Newcomb | New York |
| April 5, 2024 | 4.8 | Whitehouse Station | New Jersey |
| October 16, 2012 | 4.7 | Hollis Center | Maine |
| January 16, 1994 | 4.6 | Sinking Spring | Pennsylvania |
| January 19, 1982 | 4.5 | Sanbornton | New Hampshire |
| September 25, 1998 | 4.5 | Adamsville | Pennsylvania |
| June 9, 1975 | 4.2 | Altona | New York |
| May 29, 1983 | 4.2 | Peru | Maine |
| April 23, 1984 | 4.2 | Conestoga | Pennsylvania |
| January 16, 1994 | 4.2 | Sinking Spring | Pennsylvania |
| November 3, 1975 | 4 | Long Lake | New York |
| June 17, 1991 | 4 | Worcester | New York |
The largest earthquake in U.S. history, however, was the 1964 Good Friday quake in Alaska, measuring 9.2 magnitude and killing 131 people.
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoVisualizing the Growth of $100, by Asset Class (1970-2023)
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoVisualizing the Size of the Global Senior Population
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoTesla Is Once Again the World’s Best-Selling EV Company