Technology
Error 404: A Look At Digital Decay
In 2005, one of the most intriguing advertising stunts of the internet age was hatched.
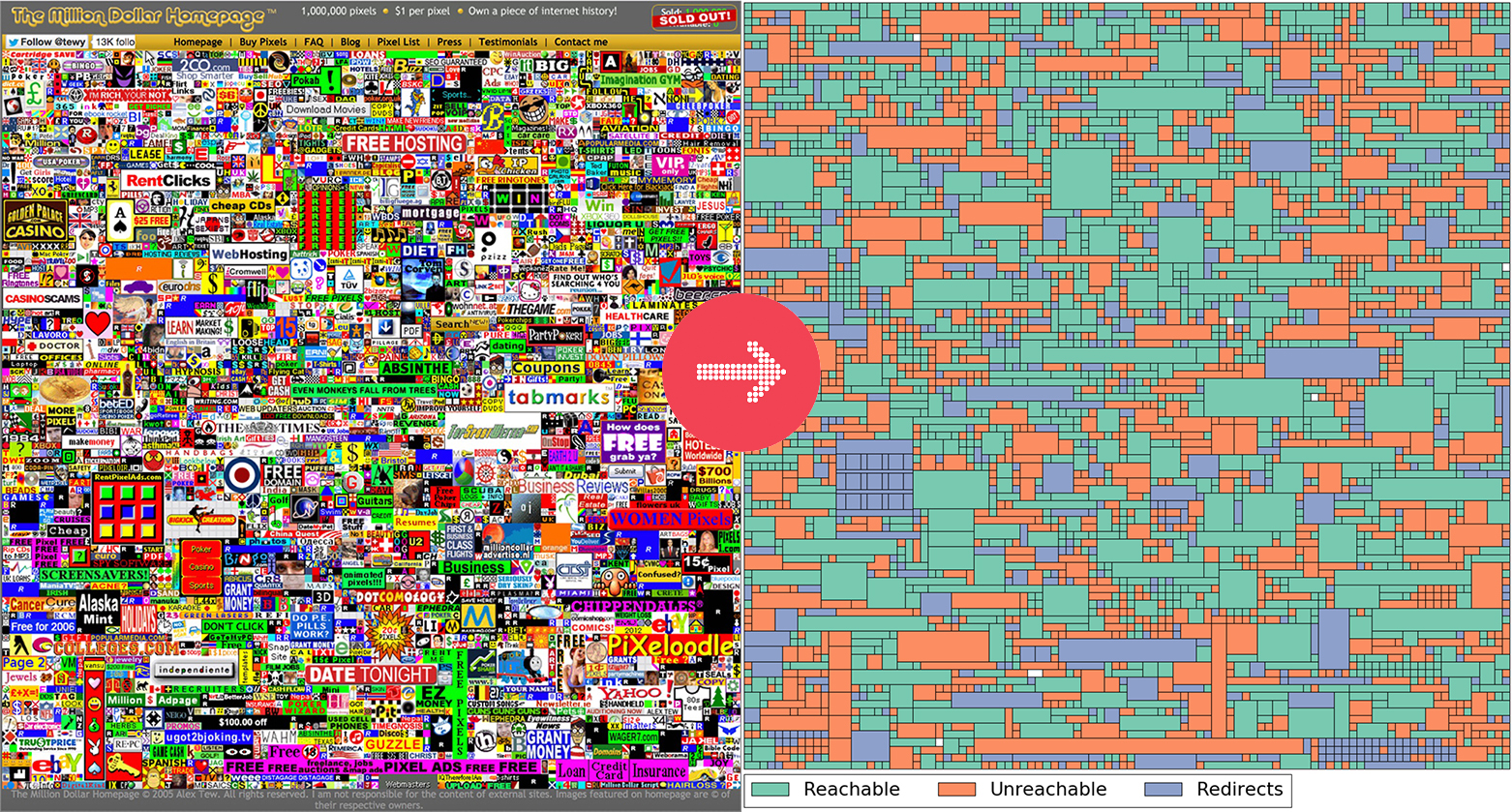
Alex Tew launched the The Million Dollar Homepage, where anyone could “own a piece of internet history” by purchasing pixels-plots (minimum of 10×10) on a massive digital canvas. At the price of just one dollar per pixel, everyone from individual internet users to well-known companies like Yahoo! raced to claim a space on the giant digital canvas.

Today, The Million Dollar Homepage lives on as a perfect record of that wacky time in internet history – or so it seems. However, the reality is that many of the hyperlinks on the canvas are now redirects that send incoming users to other sites, while over 20% of them are simply dead.
Here are the links that still work on the Million Dollar Homepage today:
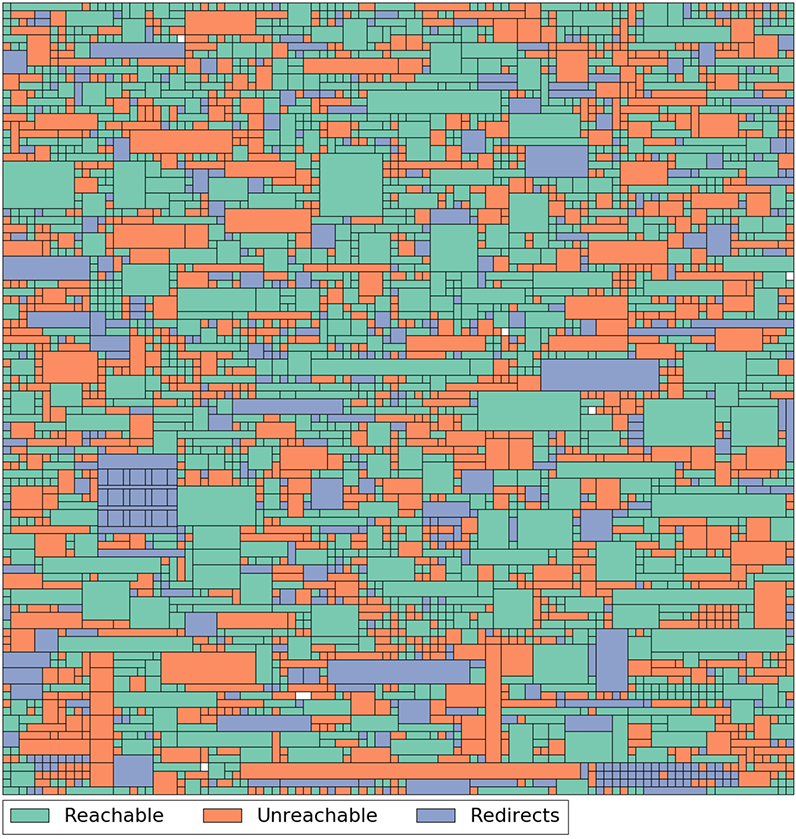
The revealing graphic above, via John Bowers, raises the question – how do hyperlinks disappear, and what implications does this “digital decay” have?
Digital Decay
The internet is stitched together by an incalculable number of hyperlinks, but much like cells in an organism, the sources and destinations have a finite lifespan. Essentially, links can and do die.
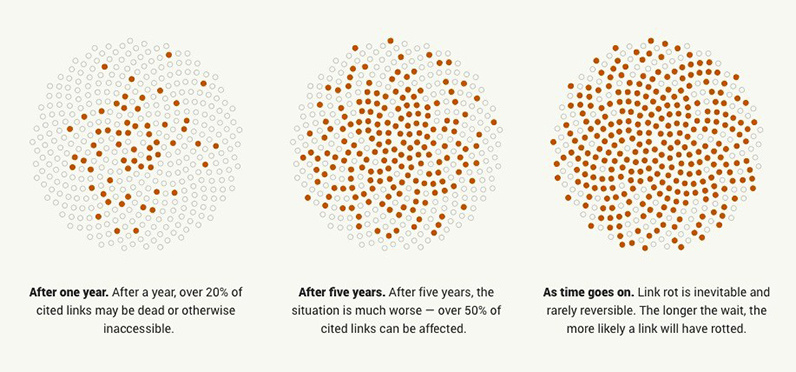
Most “link rot” is the result of website restructuring, or entities going out of business and pulling their website offline.
A high-impact example of this is when Yahoo! pulled the plug on GeoCities, one of the first popular web hosting services. In one fell swoop, roughly 7 million websites (containing a plethora of animated gifs, auto-playing midi files, and traffic counters) went dark forever.
Links can also die because of more deliberate reasons, as well. In 2015, the editor-in-chief of Buzzfeed, Ben Smith, came under fire for deleting thousands of posts from the site (including content that was critical of Buzzfeed advertisers). Journalism has traditionally acted as a public record, so this type of “decay” has serious implications on the credibility of media brands.
Who Cares?
This idea of a public record is at the heart of why digital decay is an issue worth addressing. Once millions of links simply burn out, what will people in the future know about society in the early-ish days of the internet? What record will remain of people’s thoughts and feelings in that era?
I worry that the twenty-first century will become an informational black hole.
– Vint Cerf, Internet pioneer
Perhaps more urgent are public records that live in the digital realm. Supreme Court decisions and academia lean heavily on citations to build their arguments. What happens when those citations simply vanish? A Harvard study found that 49% of the hyperlinks in Supreme Court decisions are now broken.
Even that ubiquitous resource, Wikipedia, has serious issues caused by digital decay. Over 130,000 entries link to dead pages – a troubling development, as linked citations are what lend entries their credibility.
Backing Up The Internet
A handful of people are taking steps to archive the internet.
The most well-known solution is Internet Archive’s Wayback Machine, which has archived hundreds of billions webpages over the past 20 years. Even the The Library of Congress – which is well known for archiving digital information such as tweets – contracts Internet Archive to do its web crawling.
The academia-focused Perma is another example of a company looking to create permanent records of the web sources (particularly citations).
Many of the weird and wonderful forums and hand-coded homepages of early internet lore may be gone, but we’re finally taking steps to combat digital decay. As awareness grows, avoiding an “informational black hole” may be possible.
Technology
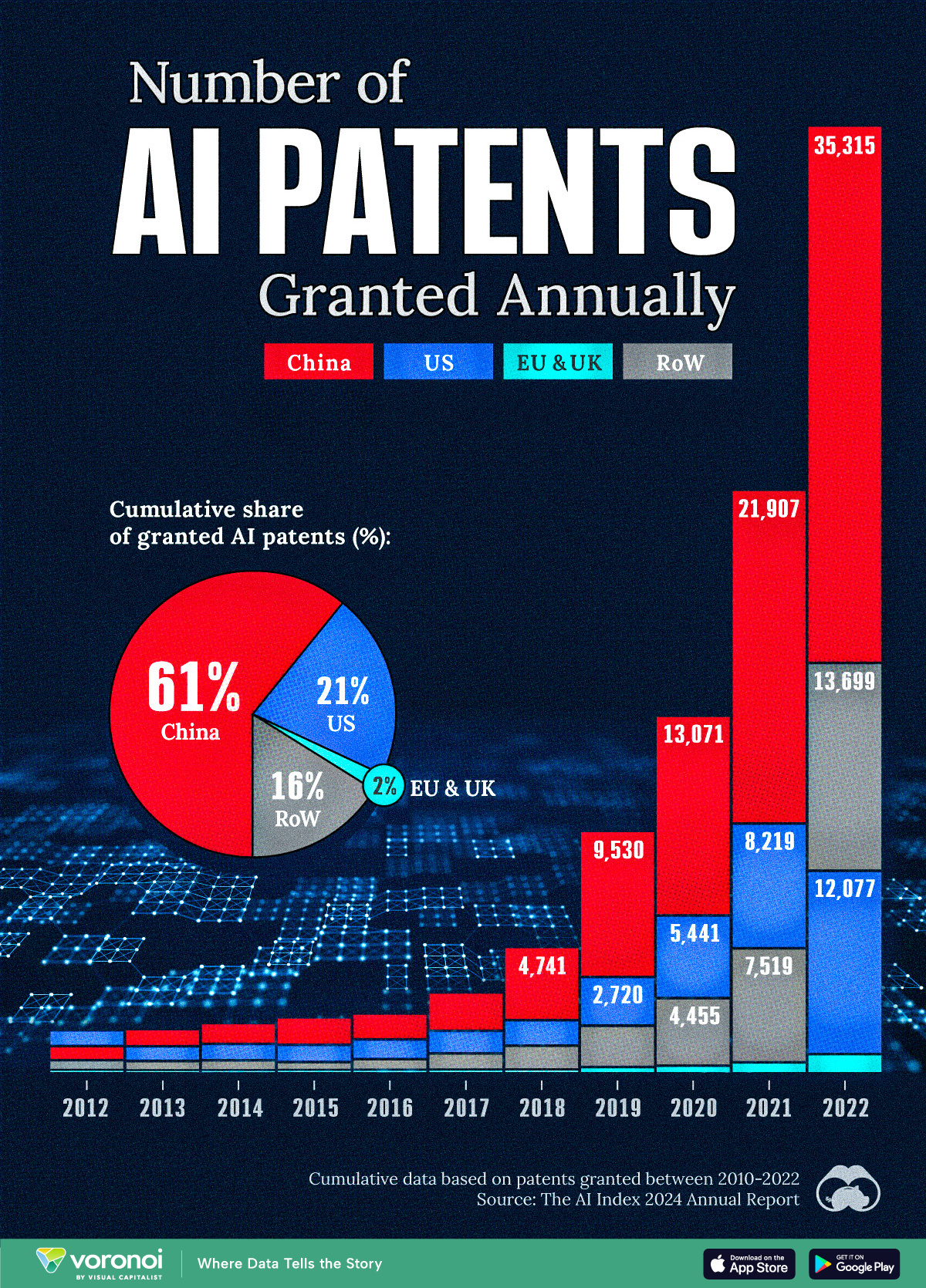
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
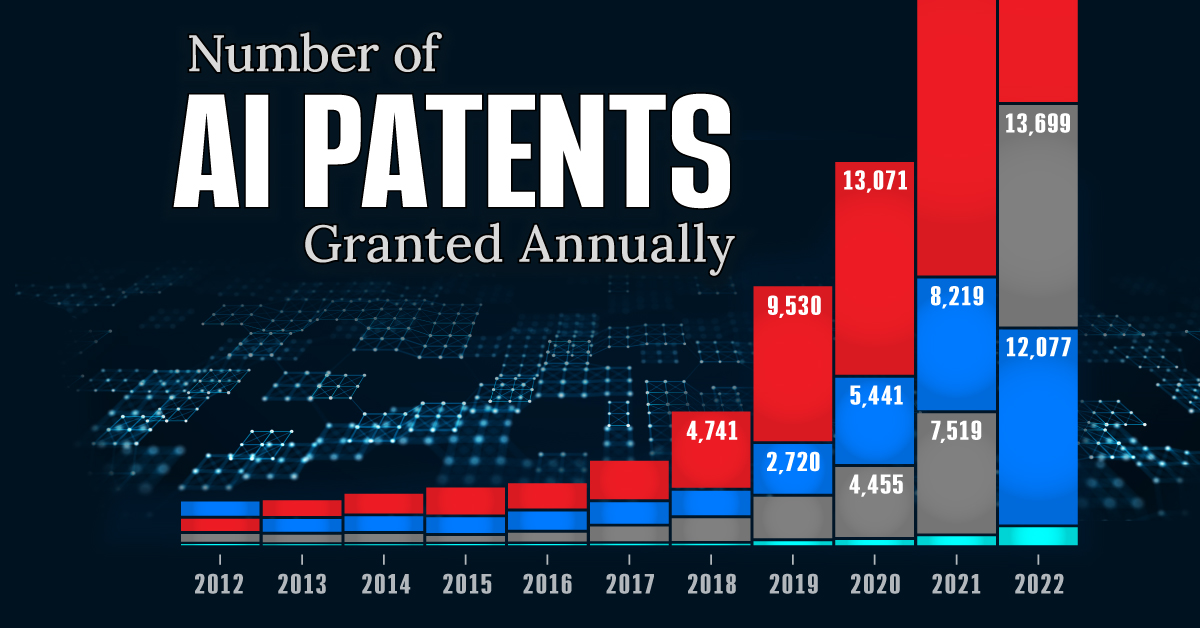
This infographic shows the number of AI-related patents granted each year from 2010 to 2022 (latest data available). These figures come from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET), accessed via Stanford University’s 2024 AI Index Report.
From this data, we can see that China first overtook the U.S. in 2013. Since then, the country has seen enormous growth in the number of AI patents granted each year.
| Year | China | EU and UK | U.S. | RoW | Global Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 307 | 137 | 984 | 571 | 1,999 |
| 2011 | 516 | 129 | 980 | 581 | 2,206 |
| 2012 | 926 | 112 | 950 | 660 | 2,648 |
| 2013 | 1,035 | 91 | 970 | 627 | 2,723 |
| 2014 | 1,278 | 97 | 1,078 | 667 | 3,120 |
| 2015 | 1,721 | 110 | 1,135 | 539 | 3,505 |
| 2016 | 1,621 | 128 | 1,298 | 714 | 3,761 |
| 2017 | 2,428 | 144 | 1,489 | 1,075 | 5,136 |
| 2018 | 4,741 | 155 | 1,674 | 1,574 | 8,144 |
| 2019 | 9,530 | 322 | 3,211 | 2,720 | 15,783 |
| 2020 | 13,071 | 406 | 5,441 | 4,455 | 23,373 |
| 2021 | 21,907 | 623 | 8,219 | 7,519 | 38,268 |
| 2022 | 35,315 | 1,173 | 12,077 | 13,699 | 62,264 |
In 2022, China was granted more patents than every other country combined.
While this suggests that the country is very active in researching the field of artificial intelligence, it doesn’t necessarily mean that China is the farthest in terms of capability.
Key Facts About AI Patents
According to CSET, AI patents relate to mathematical relationships and algorithms, which are considered abstract ideas under patent law. They can also have different meaning, depending on where they are filed.
In the U.S., AI patenting is concentrated amongst large companies including IBM, Microsoft, and Google. On the other hand, AI patenting in China is more distributed across government organizations, universities, and tech firms (e.g. Tencent).
In terms of focus area, China’s patents are typically related to computer vision, a field of AI that enables computers and systems to interpret visual data and inputs. Meanwhile America’s efforts are more evenly distributed across research fields.
Learn More About AI From Visual Capitalist
If you want to see more data visualizations on artificial intelligence, check out this graphic that shows which job departments will be impacted by AI the most.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries