Entrepreneurship
How to Craft a Winning Value Proposition
The business landscape is perpetually shifting, but the basic fundamentals of business rarely change.
Whether your company is a scrappy startup or an international juggernaut, it needs to find a way to consistently provide value to customers – and just as important, it needs to communicate that message succinctly and effortlessly.
At the foundation of these efforts exists the value proposition, a deceptively simple set of key messages that serve as an anchor for all sales and communications efforts for an overall brand or a specific offering.
Crafting the Value Proposition
Today’s infographic comes to us from Quick Sprout, and it covers the steps in establishing and communicating an effective value proposition that can help differentiate you from your competitors.
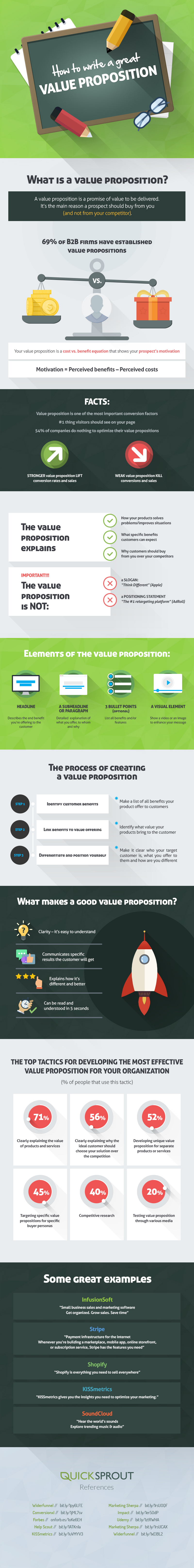
A quality value proposition is clear, easy to understand, and communicates the specific results a customer will get. It also must explain how the product or brand is different and better than competing ways to solve the same problem (i.e. competitors, legacy processes).
Nailing these criteria helps to create an effective foundation for all sales and marketing efforts, and it can also provide a useful compass for guiding any future messaging.
Discovering Value
While the concept behind a value proposition is pretty simple, that doesn’t make coming up with one a simple task.
There are literally millions of companies in the world, and likely tens of thousands that do something similar to your company. How do you stand apart from these competitors? How do you clearly articulate the value that you can provide?
One suggestion is to look at the customer experience methodically, and to fill out an exercise similar to this one created by digital brand strategist Peter Thomson:
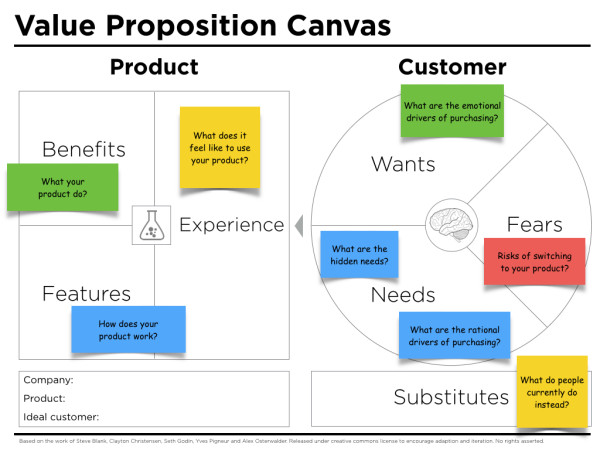
As Peter skillfully articulates, a value proposition is the intersection between what you make and why people buy it. This intersection is what connects business strategy and brand strategy.
Articulating Value
What good is discovering value if it can’t be articulated clearly and concisely?
After you’ve explored the customer experience, here’s a way to put it into words:
1. Identify customer benefits
Make a list of all benefits you offer to your customers
2. Link benefits to value offering
Identify what value your products bring to your customer
3. Differentiate and position yourself
Make it clear who the target customer is, what you offer to them, and how you are different
Using these points, a winning value proposition can be crafted – and if it’s something that is being shown online (i.e. landing page, product page) it may make sense to include the following elements: a headline, a subheadline or paragraph, three bullet points, and a visual element.
The Tactics
Finally, here are some tactics that are relied on to further the effectiveness of the value prop:
| Tactics for developing effective value props | % Use |
|---|---|
| Clearly explain the value of products and services | 71% |
| Clearly explain why the ideal customer should choose your solution | 56% |
| Develop unique value props for separate products or services | 52% |
| Target specific value props for specific buyer personas | 45% |
| Competitive research | 40% |
| Testing value props through various media | 20% |
What other tactics do you use to craft a compelling message about your company or product?
Markets
Why Do People Start Businesses in Every U.S. State?
Is it for greater flexibility, more income, or something else? These graphics answer the question, why do people start businesses?
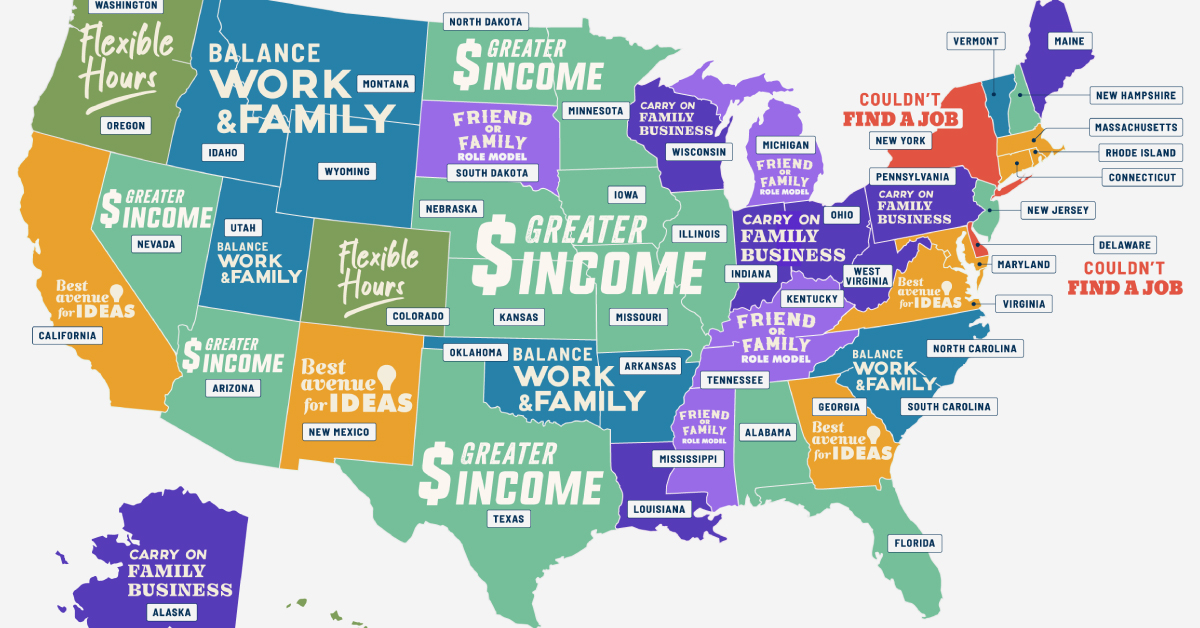
Why Do People Start Businesses in Every U.S. State?
People have various motivations for starting their businesses.
Some seek higher income. Others are looking for a balance between family life and career. In some situations, entrepreneurship may be the only way to fight unemployment.
In this infographic, OnDeck uses data from the U.S. Census Bureau’s 2020 Annual Business Survey to highlight the most unique reasons for why people start businesses in each U.S. state.
Editor’s note: The map tracks the most popular unique reasons to start a business. In this case, “unique” is defined by how much a particular reason stands out from the U.S. average across all states. For example, in Delaware, more respondents said they started businesses because they “couldn’t find jobs” (11.6%) than in any other state (U.S. average: 7.3%). So, even though it’s not numerically the most popular reason overall, it is the unique reason that stands out the most for that state.
The Most Popular Unique Reasons to Start a Business
According to the Global Entrepreneurship Monitor, entrepreneurship rates in the U.S. have been trending upward over the past two decades.
In fact, despite multi-billion dollar companies getting the spotlight, 99.9% of businesses across the U.S. are small businesses, employing over 60 million people.
Wanting to make more income is the biggest unique factor in starting a business in 14 states, including some of the states with the highest unemployment rates, like New Hampshire, North Dakota, and Alabama.

In Utah, a higher percentage (65.4%) of entrepreneurs start businesses to achieve a work-life balance than in any other state. Notably, Utah is known for having the largest average family size, as reported by the U.S. Census Bureau, and has a strong religious presence.
On the other hand, in Florida, more business founders (69.2%) start their businesses to become their own bosses than anywhere else.
New York and California are states where entrepreneurs mentioned that they couldn’t find a job as a key unique reason to start a business. In fact, both states lead as the worst for job seekers, as shown in another Visual Capitalist graphic.
Small Businesses to Remain Vital
Despite all the different reasons to start a business, the fact is that entrepreneurship is still crucial for the U.S. economy.
Over the last 25 years, small businesses have added over 12.9 million jobs. For perspective, that’s about two-thirds of the jobs added to the economy.
In 2021, a record-breaking 5.4 million new business applications were filed in the U.S.
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Popular Smartphone Brands in the U.S.
-

 Automotive1 week ago
Automotive1 week agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoVisualizing the Size of the Global Senior Population











 Creator Program
Creator Program
