AI
Which Jobs Will Be Most Impacted by ChatGPT?

Jobs Most Impacted by ChatGPT and Similar AI Models
On November 30, 2022, OpenAI heralded a new era of artificial intelligence (AI) by introducing ChatGPT to the world.
The AI chatbot stunned users with its human-like and thorough responses. ChatGPT could comprehend and answer a variety of different questions, make suggestions, research and write essays and briefs, and even tell jokes (amongst other tasks).
Many of these skills are used by workers in their jobs across the world, which begs the question: which jobs will be transformed, or even replaced, by generative AI in the coming future?
This infographic from Harrison Schell visualizes the March 2023 findings of OpenAI on the potential labor market impact of large language models (LLMs) and various applications of generative AI, including ChatGPT.
Methodology
The OpenAI working paper specifically examined the U.S. industries and jobs most “exposed” to large language models like GPT, which the chatbot ChatGPT operates on.
Key to the paper is the definition of what “exposed” actually means:
“A proxy for potential economic impact without distinguishing between labor-augmenting or labor-displacing effects.” – OpenAI
Thus, the results include both jobs where humans could possibly use AI to optimize their work, along with jobs that could potentially be automated altogether.
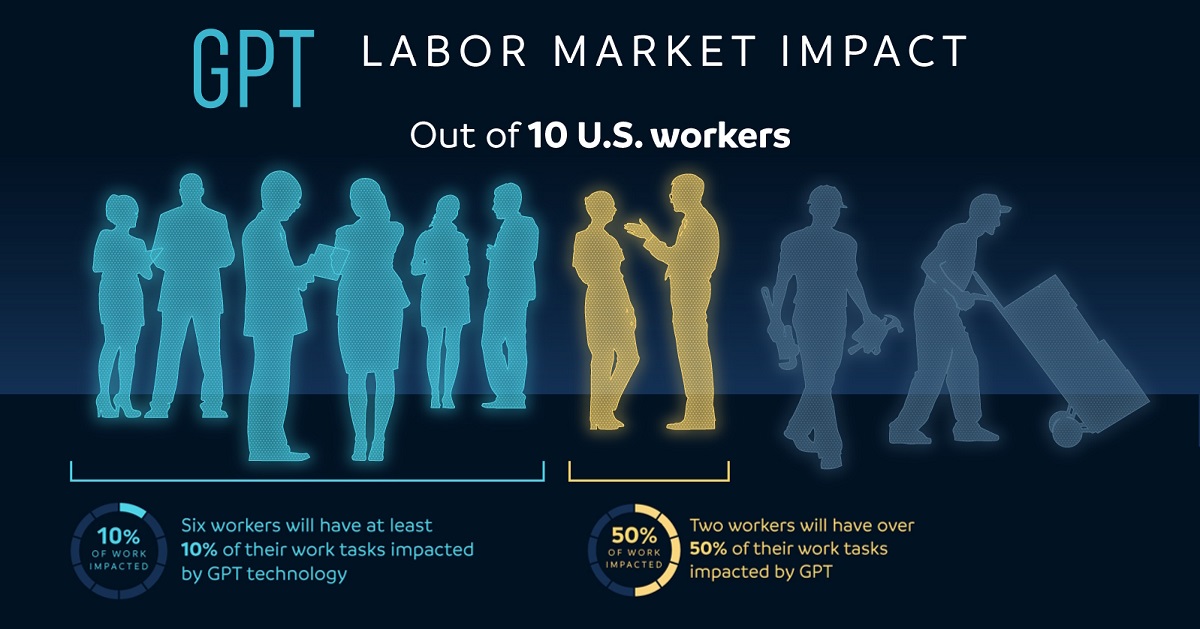
OpenAI found that 80% of the American workforce belonged to an occupation where at least 10% of their tasks can be done (or aided) by AI. One-fifth of the workforce belonged to an occupation where 50% of work tasks would be impacted by artificial intelligence.
The Jobs Most and Least at Risk of AI Disruption
Here is a list of jobs highlighted in the paper as likely to see (or already seeing) AI disruption, where AI can reduce the time to do tasks associated with the occupation by at least 50%.
Analysis was provided by a variety of human-made models as well as ChatGPT-4 models, with results from both showing below:
| Jobs | Categorized By | AI Exposure |
|---|---|---|
| Accountants | AI | 100% |
| Admin and legal assistants | AI | 100% |
| Climate change policy analysts | AI | 100% |
| Reporters & journalists | AI | 100% |
| Mathematicians | Human & AI | 100% |
| Tax preparers | Human | 100% |
| Financial analysts | Human | 100% |
| Writers & authors | Human | 100% |
| Web designers | Human | 100% |
| Blockchain engineers | AI | 97.1% |
| Court reporters | AI | 96.4% |
| Proofreaders | AI | 95.5% |
| Correspondence clerks | AI | 95.2% |
| Survey researchers | Human | 84.0% |
| Interpreters/translators | Human | 82.4% |
| PR specialists | Human | 80.6% |
| Animal scientists | Human | 77.8% |
Editor’s note: The paper only highlights some jobs impacted. One AI model found a list of 84 additional jobs that were “fully exposed”, but not all were listed. One human model found 15 additional “fully exposed” jobs that were not listed.
Generally, jobs that require repetitive tasks, some level of data analysis, and routine decision-making were found to face the highest risk of exposure.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, “information processing industries” that involve writing, calculating, and high-level analysis have a higher exposure to LLM-based artificial intelligence. However, science and critical-thinking jobs within those industries negatively correlate with AI exposure.
On the flipside, not every job is likely to be affected. Here’s a list of jobs that are likely least exposed to large language model AI disruption.
| Jobs Least Exposed to AI | |
|---|---|
| Athletes | Short-order cooks |
| Large equipment operators | Barbers/hair stylists |
| Glass installers & repairers | Dredge operators |
| Automotive mechanics | Power-line installers/repairers |
| Masons, carpenters, roofers | Oil field maintenance workers |
| Plumbers, painters, pipefitters | Servers, dishwashers, bartenders |
Naturally, hands-on industries like manufacturing, mining, and agriculture were more protected, but still include information processing roles at risk.
Likewise, the in-person service industry is also expected to see minimal impact from these kinds of AI models. But, patterns are beginning to emerge for job-seekers and industries that may have to contend with artificial intelligence soon.
Artificial Intelligence Impacts on Different Levels of Jobs
OpenAI analyzed correlations between AI exposure in the labor market against a job’s requisite education level, wages, and job-training.
The paper found that jobs with higher wages have a higher exposure to LLM-based AI (though there were numerous low-wage jobs with high exposure as well).
| Job Parameter | AI Exposure Correlation |
|---|---|
| Wages | Direct |
| Education | Direct |
| Training | Inverse |
Professionals with higher education degrees also appeared to be more greatly exposed to AI impact, compared to those without.
However, occupations with a greater level of on-the-job training had the least amount of work tasks exposed, compared to those jobs with little-to-no training.
Will AI’s Impact on the Job Market Be Good or Bad?
The potential impact of ChatGPT and similar AI-driven models on individual job titles depends on several factors, including the nature of the job, the level of automation that is possible, and the exact tasks required.
However, while certain repetitive and predictable tasks can be automated, others that require intangibles like creative input, understanding cultural nuance, reading social cues, or executing good judgement cannot be fully hands-off yet.
And keep in mind that AI exposure isn’t limited to job replacement. Job transformation, with workers utilizing the AI to speed up or improve tasks output, is extremely likely in many of these scenarios. Already, there are employment ads for “AI Whisperers” who can effectively optimize automated responses from generalist AI.
As the AI arms race moves forward at a rapid pace rarely seen before in the history of technology, it likely won’t take long for us to see the full impact of ChatGPT and other LLMs on both jobs and the economy.

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
Technology
Ranked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Did you know that some computer chips are now retailing for the price of a new BMW?
As computers invade nearly every sphere of life, so too have the chips that power them, raising the revenues of the businesses dedicated to designing them.
But how did various chipmakers measure against each other last year?
We rank the biggest semiconductor companies by their percentage share of the industry’s revenues in 2023, using data from Omdia research.
Which Chip Company Made the Most Money in 2023?
Market leader and industry-defining veteran Intel still holds the crown for the most revenue in the sector, crossing $50 billion in 2023, or 10% of the broader industry’s topline.
All is not well at Intel, however, with the company’s stock price down over 20% year-to-date after it revealed billion-dollar losses in its foundry business.
| Rank | Company | 2023 Revenue | % of Industry Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intel | $51B | 9.4% |
| 2 | NVIDIA | $49B | 9.0% |
| 3 | Samsung Electronics | $44B | 8.1% |
| 4 | Qualcomm | $31B | 5.7% |
| 5 | Broadcom | $28B | 5.2% |
| 6 | SK Hynix | $24B | 4.4% |
| 7 | AMD | $22B | 4.1% |
| 8 | Apple | $19B | 3.4% |
| 9 | Infineon Tech | $17B | 3.2% |
| 10 | STMicroelectronics | $17B | 3.2% |
| 11 | Texas Instruments | $17B | 3.1% |
| 12 | Micron Technology | $16B | 2.9% |
| 13 | MediaTek | $14B | 2.6% |
| 14 | NXP | $13B | 2.4% |
| 15 | Analog Devices | $12B | 2.2% |
| 16 | Renesas Electronics Corporation | $11B | 1.9% |
| 17 | Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation | $10B | 1.9% |
| 18 | Microchip Technology | $8B | 1.5% |
| 19 | Onsemi | $8B | 1.4% |
| 20 | KIOXIA Corporation | $7B | 1.3% |
| N/A | Others | $126B | 23.2% |
| N/A | Total | $545B | 100% |
Note: Figures are rounded. Totals and percentages may not sum to 100.
Meanwhile, Nvidia is very close to overtaking Intel, after declaring $49 billion of topline revenue for 2023. This is more than double its 2022 revenue ($21 billion), increasing its share of industry revenues to 9%.
Nvidia’s meteoric rise has gotten a huge thumbs-up from investors. It became a trillion dollar stock last year, and broke the single-day gain record for market capitalization this year.
Other chipmakers haven’t been as successful. Out of the top 20 semiconductor companies by revenue, 12 did not match their 2022 revenues, including big names like Intel, Samsung, and AMD.
The Many Different Types of Chipmakers
All of these companies may belong to the same industry, but they don’t focus on the same niche.
According to Investopedia, there are four major types of chips, depending on their functionality: microprocessors, memory chips, standard chips, and complex systems on a chip.
Nvidia’s core business was once GPUs for computers (graphics processing units), but in recent years this has drastically shifted towards microprocessors for analytics and AI.
These specialized chips seem to be where the majority of growth is occurring within the sector. For example, companies that are largely in the memory segment—Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron Technology—saw peak revenues in the mid-2010s.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoAmerica’s Top Companies by Revenue (1994 vs. 2023)
-

 Environment1 week ago
Environment1 week agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoVisualizing the Size of the Global Senior Population
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoTesla Is Once Again the World’s Best-Selling EV Company
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Popular Smartphone Brands in the U.S.