Agriculture
What are the Most Produced Cash Crops in Africa?
var divElement = document.getElementById(‘viz1649905023506’); var vizElement = divElement.getElementsByTagName(‘object’)[0]; vizElement.style.width=’1000px’;vizElement.style.height=’1574px’; var scriptElement = document.createElement(‘script’); scriptElement.src = ‘https://public.tableau.com/javascripts/api/viz_v1.js’; vizElement.parentNode.insertBefore(scriptElement, vizElement);
Open the large interactive version here
Open the large interactive version here
What are the Most Produced Cash Crops in Africa?
Agriculture makes up nearly 20% of Sub-Saharan Africa’s economy—a higher percentage than any other region worldwide.
From Nigeria to the fertile land across the East African Rift Valley, the continent is home to 60% of the world’s uncultivated arable land.
Given the massive role of agriculture across the region, this infographic from Zainab Ayodimeji shows the most produced cash crops in Africa and their share of total global production.
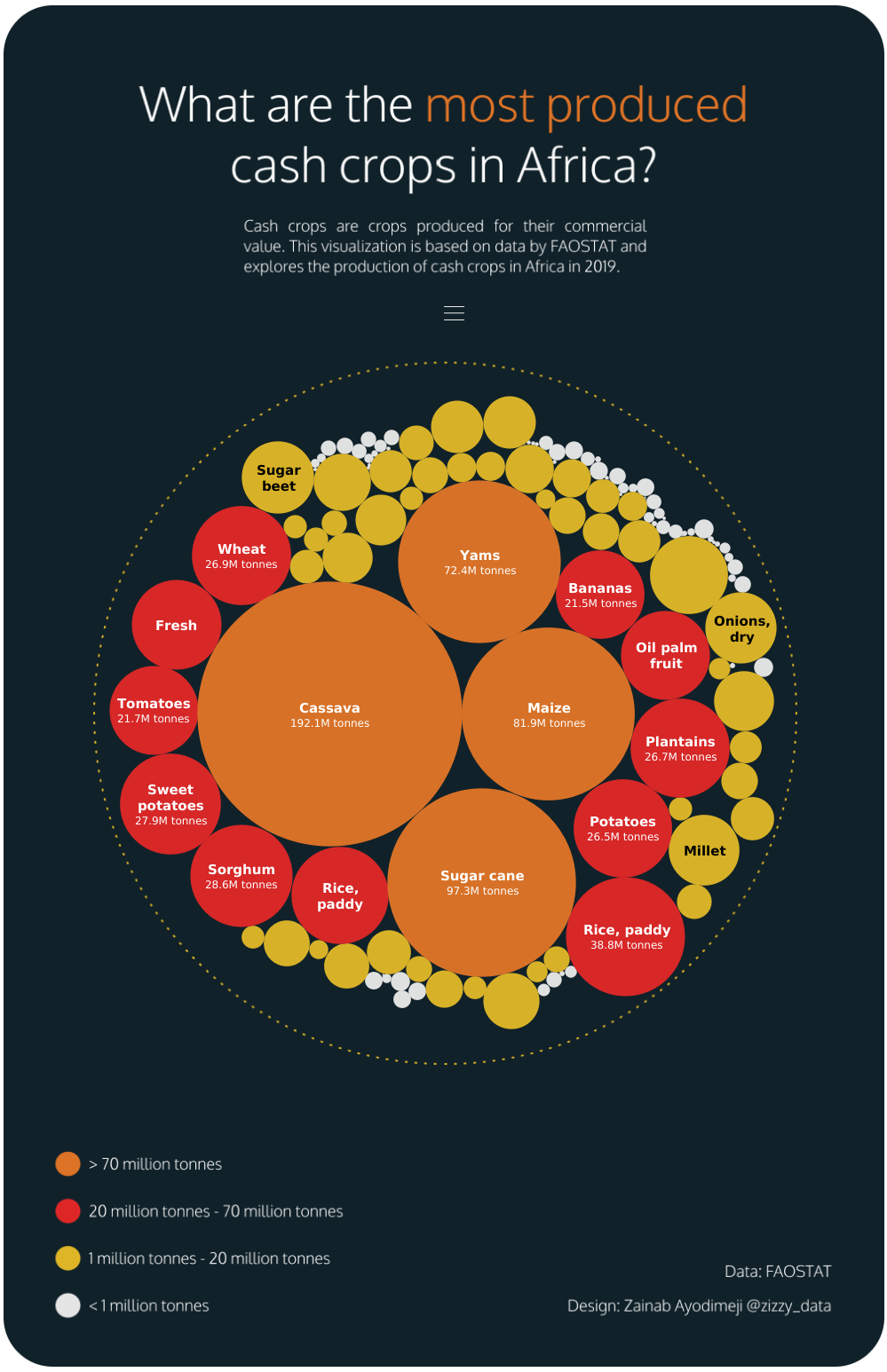
The Top 20 Cash Crops in Africa
Cash crops, such as coffee or rice, are crops that are produced for a salable market.
With data from the Food and Agriculture Organization Corporate Statistical Database (FAOSTAT), here are the most produced cash crops in Africa:
| Cash Crop | Tonnes Produced 2019 | % of World Production |
|---|---|---|
| Cassava | 192.1M | 63% |
| Sugar cane | 97.3M | 5% |
| Maize | 81.9M | 7% |
| Yams | 72.4M | 97% |
| Rice, paddy | 38.8M | 5% |
| Sorghum | 28.6M | 49% |
Rice, paddy (rice milled equivalent) | 25.9M | 5% |
| Sweet potatoes | 27.9M | 30% |
| Wheat | 26.9M | 4% |
| Plantains | 26.7M | 64% |
| Potatoes | 26.5M | 7% |
| Fresh vegetables | 22.0M | 7% |
| Oil palm fruit | 21.9M | 5% |
| Tomatoes | 21.7M | 12% |
| Bananas | 21.5M | 18% |
| Groundnuts, with shell | 16.6M | 34% |
| Sugar beet | 14.3M | 5% |
| Onions, dry | 13.9M | 14% |
| Millet | 13.7M | 48% |
| Oranges | 9.8M | 12% |
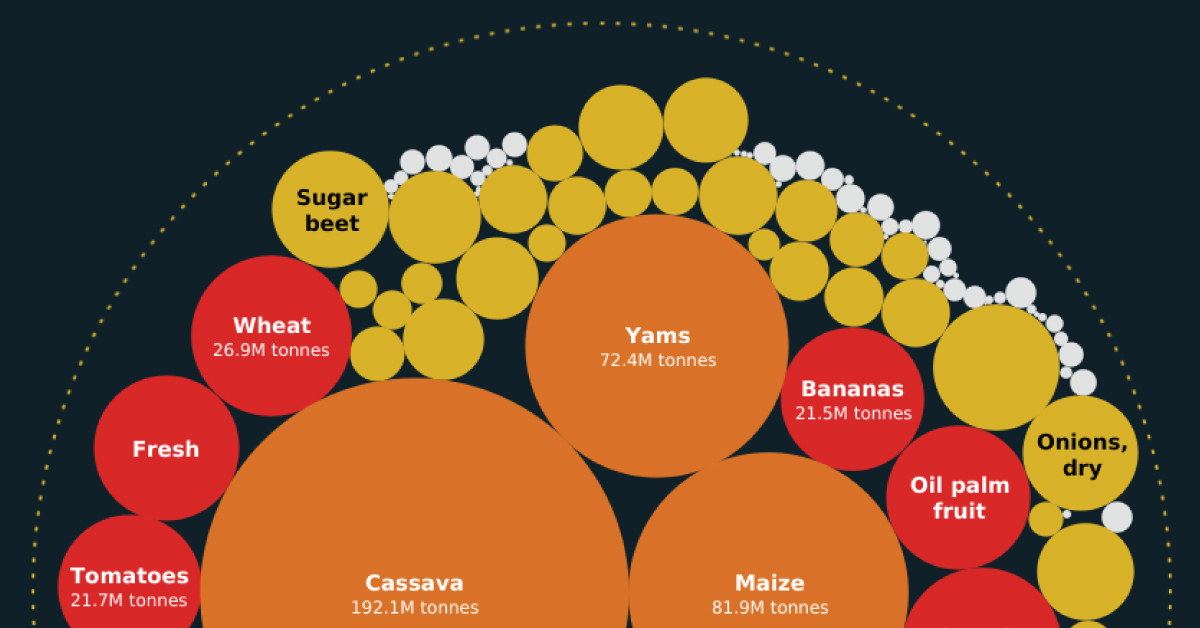
Cassava, also referred to as yuca, is the most produced cash crop by a wide margin. With nearly 200 million tonnes of it produced annually, Africa’s production of cassava makes up a majority (63%) of the global total.
While cassavas are not well known in the Western world, they feed 800 million people globally. Cassavas are an essential root vegetable that has similar uses to potatoes.
Sugar cane, maize, and yams are also significant cash crops.
Notably, Africa’s yam production is 97% of the global total. West Africa is known as the “yam belt,” covering Nigeria, Ghana, Benin, and Côte d’Ivoire. With over 60 million people across the yam belt directly or indirectly involved in its production, yam cultivation is an important component of the region’s economic vitality.
Agriculture Composition of GDP, by Region
While agriculture plays a significant role in Africa’s GDP, what role does it play across other regions around the world?
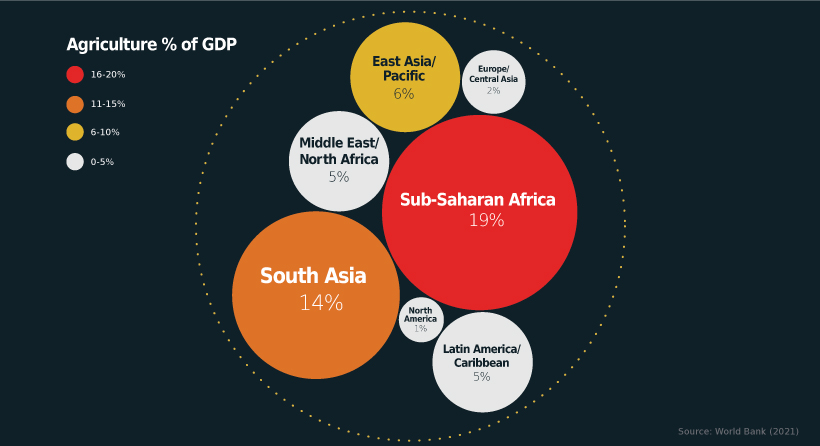
Like Sub-Saharan Africa, agriculture is a major part of South Asia’s economy. India produces nearly 24% of rice around the world, while Bangladesh produces over 7% of total global production. Meanwhile, over 14% of the global wheat supply is also produced by India.
On the other hand, agriculture makes up just 1% of North America’s GDP. The number of farms in the U.S. peaked in the 1930s and has sharply declined from almost 7 million to 2 million in 2020.
The Future of Africa’s Cash Crops
Despite Africa’s expansive agriculture sector, there remain bottlenecks to productivity.
In light of these challenges, several technological advances have the potential to improve farmers’ bottom lines. For instance, precision technology measures rainfall, soil information, and soil productivity. At the same time, remote sensing technology can provide information on weather and climate.
This, coupled with the majority of the world’s uncultivated arable land, presents a significant opportunity for cash crops going forward. By one estimate, cereal and grain production has the potential to increase threefold.

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
Markets
The World’s Top Cocoa Producing Countries
Here are the largest cocoa producing countries globally—from Côte d’Ivoire to Brazil—as cocoa prices hit record highs.

The World’s Top Cocoa Producing Countries
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
West Africa is home to the largest cocoa producing countries worldwide, with 3.9 million tonnes of production in 2022.
In fact, there are about one million farmers in Côte d’Ivoire supplying cocoa to key customers such as Nestlé, Mars, and Hershey. But the massive influence of this industry has led to significant forest loss to plant cocoa trees.
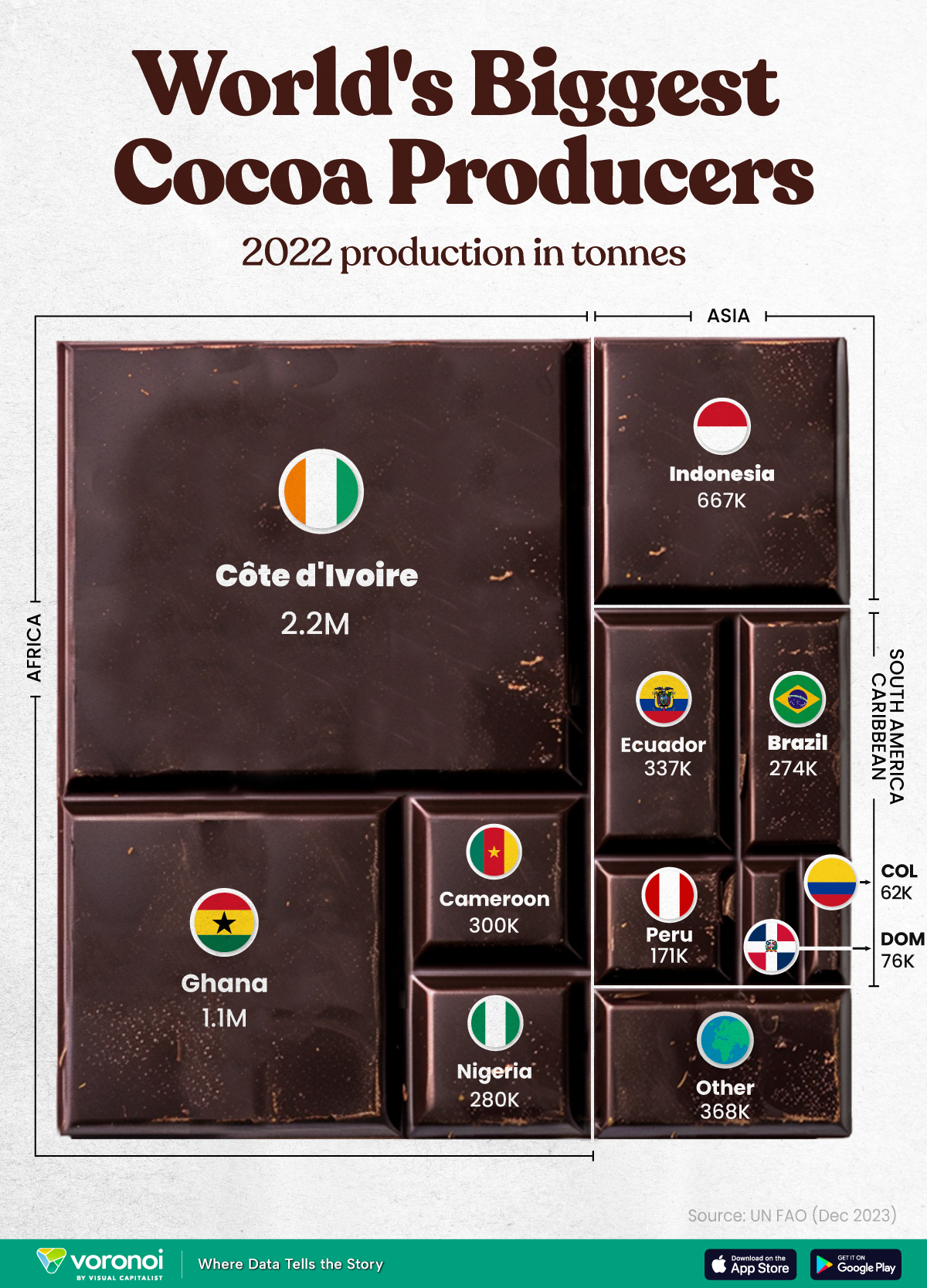
This graphic shows the leading producers of cocoa, based on data from the UN FAO.
Global Hotspots for Cocoa Production
Below, we break down the top cocoa producing countries as of 2022:
| Country | 2022 Production, Tonnes |
|---|---|
| 🇨🇮 Côte d'Ivoire | 2.2M |
| 🇬🇭 Ghana | 1.1M |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 667K |
| 🇪🇨 Ecuador | 337K |
| 🇨🇲 Cameroon | 300K |
| 🇳🇬 Nigeria | 280K |
| 🇧🇷 Brazil | 274K |
| 🇵🇪 Peru | 171K |
| 🇩🇴 Dominican Republic | 76K |
| 🌍 Other | 386K |
With 2.2 million tonnes of cocoa in 2022, Côte d’Ivoire is the world’s largest producer, accounting for a third of the global total.
For many reasons, the cocoa trade in Côte d’Ivoire and Western Africa has been controversial. Often, farmers make about 5% of the retail price of a chocolate bar, and earn $1.20 each day. Adding to this, roughly a third of cocoa farms operate on forests that are meant to be protected.
As the third largest producer, Indonesia produced 667,000 tonnes of cocoa with the U.S., Malaysia, and Singapore as major importers. Overall, small-scale farmers produce 95% of cocoa in the country, but face several challenges such as low pay and unwanted impacts from climate change. Alongside aging trees in the country, these setbacks have led productivity to decline.
In South America, major producers include Ecuador and Brazil. In the early 1900s, Ecuador was the world’s largest cocoa producing country, however shifts in the global marketplace and crop disease led its position to fall. Today, the country is most known for its high-grade single-origin chocolate, with farms seen across the Amazon rainforest.
Altogether, global cocoa production reached 6.5 million tonnes, supported by strong demand. On average, the market has grown 3% annually over the last several decades.
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?