Demographics
Visualizing the World’s Most Popular Religions

Visualizing the World’s Most Popular Religions
According to some estimates, there are over 4,000 religions, faiths groups, and denominations that exist around the world today. Researchers and academics generally categorize the world’s religions into five major groups: Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Hinduism, and Judaism.
This graphic by Chit Chart visualizes the most popular religions around the world, using the latest available data from Index Mundi’s world demographics.
In addition to the five major religious groups, the graphic includes two more categories: one for a collective of Folk religions and another for people who are unaffiliated with a religion.
The Religions with the Most Followers
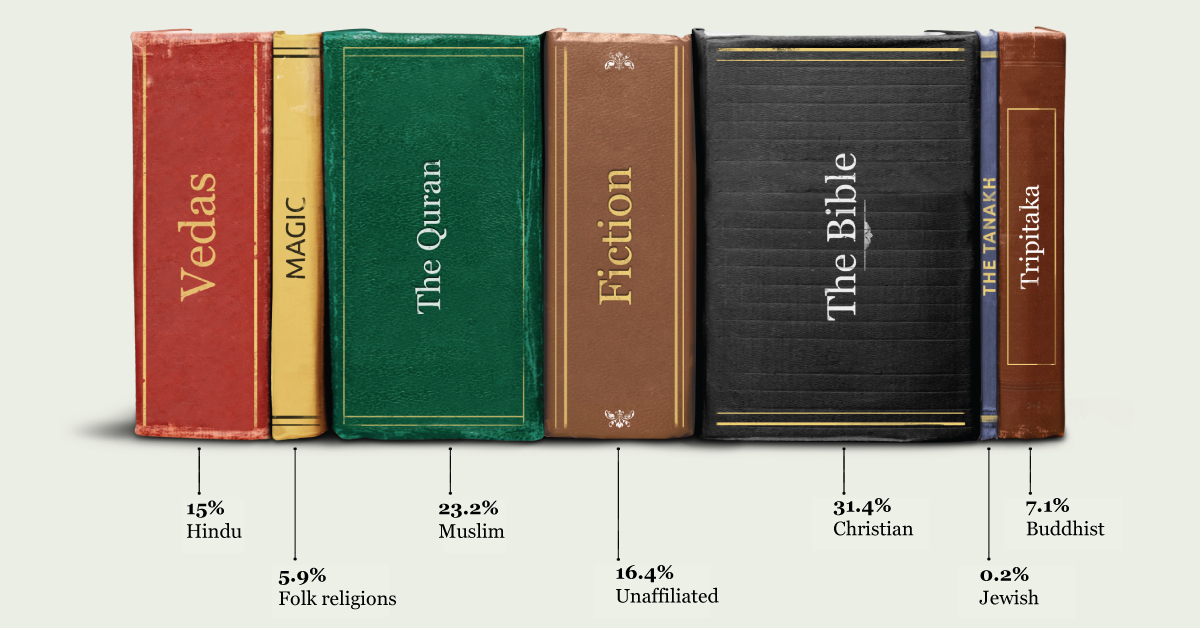
Although the number of people who follow a religion has decreased in recent decades, 82.8% of the global population still identifies with one of the world’s major religions.
Here’s a breakdown of the most popular religions, ranked by their following as a percentage of the world’s population:
| Rank | Religion | % of World’s Population |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Christian | 31.4% |
| 2 | Muslim | 23.2% |
| 3 | Unaffiliated | 16.4% |
| 4 | Hindu | 15.0% |
| 5 | Buddhist | 7.1% |
| 6 | Folk Religions | 5.9% |
| 7 | Jewish | 0.2% |
| 8 | Other | 0.8% |
Christianity has the largest following with approximately 31% of the global population. Muslims make up the second-largest religious group, accounting for 23.2% of the world’s population.
Roughly 16.4% of the global population is unaffiliated with a religion. This figure exceeds the percentage of people who identify with Hinduism (15%), Buddhism (7.1%), Folk Religions (5.9%), or Judaism (0.2%).
The World’s Religions from Oldest to Newest
Hinduism is considered the oldest religion in the world, originating in the Indus River Valley (modern-day Pakistan) circa 7000 BCE.
While Judaism came after Hinduism, it is thought to be the oldest of the three monotheistic Abrahamic faiths, making it older than Christianity and Islam.
It began circa 2000 BCE in the Southern Levant (modern-day Israel, Palestine, and Jordan). By contrast, Christianity was founded in the 1st century and began as a movement within Judaism.
Scholars typically date the creation of Islam to the 7th century, making it the youngest of the world’s major religions on this list. Islam was established in Mecca (modern-day Saudi-Arabia).
One religion that’s not included on this list is Sikhism. Founded in the late 15th century, it’s relatively new, especially compared to other religions like Hinduism or Judaism. Yet, despite being new, Sikhism has a large following—according to some estimates, there are over 25 million Sikhs worldwide.
What are Folk Religions?
A folk religion is defined as an ethnic or cultural practice that exists outside the theological doctrine of organized religions.
Lacking sacred texts, Folk religions are more concerned with spirituality than rituals or rites. Examples of Folk religions include Native American traditions, Chinese folk religions, and traditional African religions.
Since Folk religions are less institutionalized, they are especially challenging to measure and often excluded from surveys. With that said, an estimated 5.9% of the global population (approximately 430 million people) practice a Folk religion.
The Fastest-Growing Religions
While Islam is the newest of the big five religions, it’s currently the world’s fastest-growing one too. For context, here’s the estimated percent change among the seven religion categories, between 2015 and 2060:
| Rank | Religious Group | Est. % change in population size (2015-2060) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Muslims | 70% |
| 2 | Christians | 34% |
| 3 | Hindus | 27% |
| 4 | Jews | 15% |
| 5 | Folk religions | 5% |
| 6 | Unaffiliated | 3% |
| 7 | Buddhists | -7% |
Islam’s rapid growth means it may surpass Christianity as the world’s largest religion within the next half-century. What’s causing this growth?
According to Pew Research Center, the main reason is simply demographics—on average, Muslim women have 2.9 children, which the average of all non-Muslims is 2.2.
Muslims are also concentrated in Africa and the Middle East, the two regions predicted to have the highest population increases in the next few decades.

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
Demographics
The Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
Which OECD countries have the smallest gender wage gaps? We look at the 10 countries with gaps lower than the average.
The Smallest Gender Pay Gaps in OECD Countries
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Among the 38 member countries in the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), several have made significant strides in addressing income inequality between men and women.
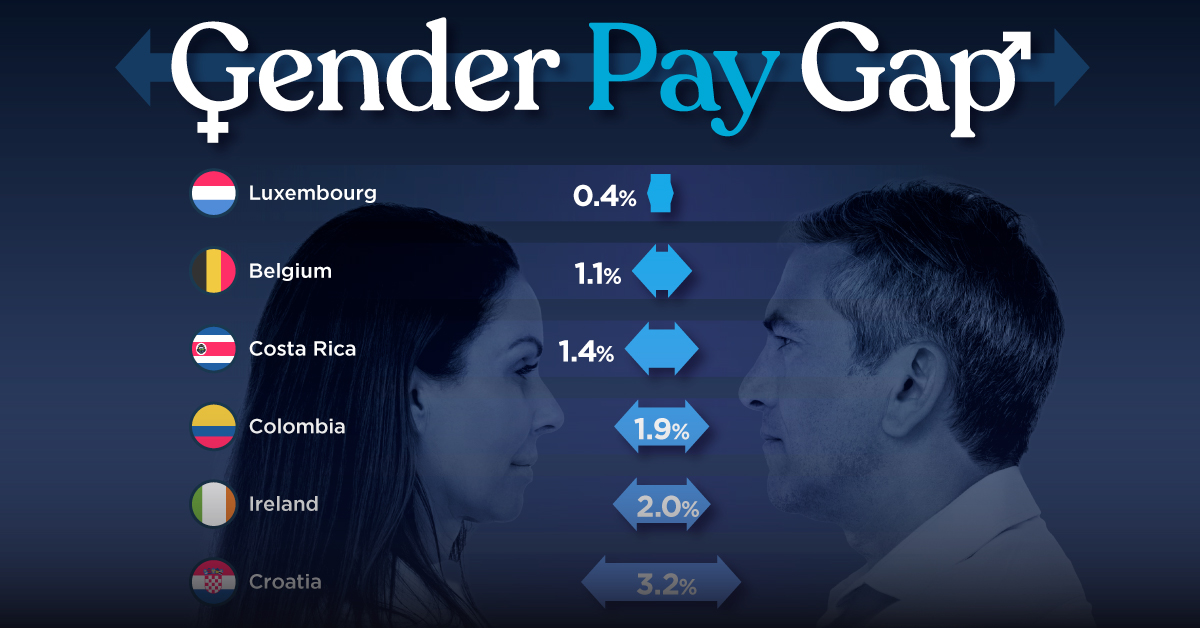
In this graphic we’ve ranked the OECD countries with the 10 smallest gender pay gaps, using the latest data from the OECD for 2022.
The gender pay gap is calculated as the difference between median full-time earnings for men and women divided by the median full-time earnings of men.
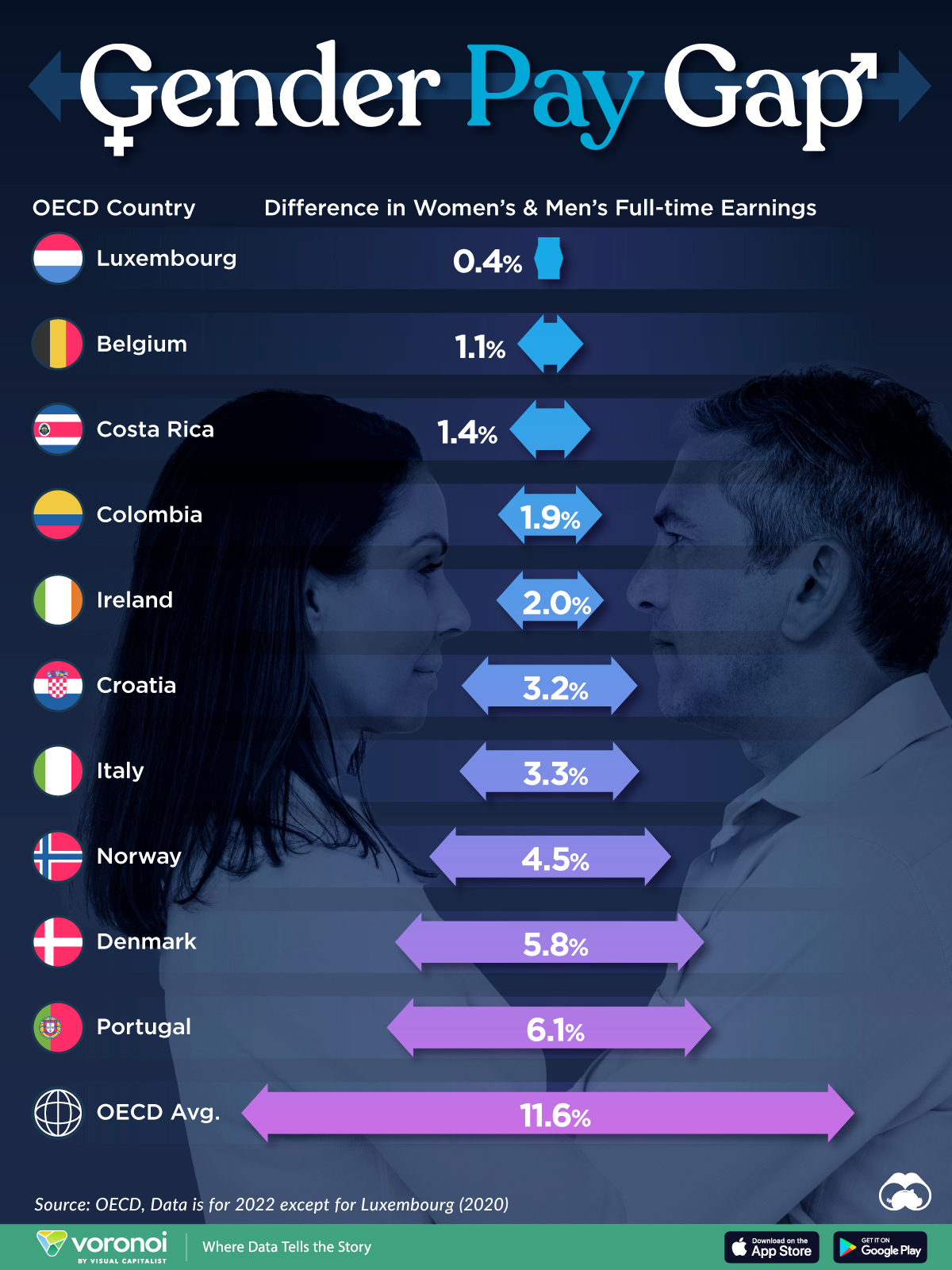
Which Countries Have the Smallest Gender Pay Gaps?
Luxembourg’s gender pay gap is the lowest among OECD members at only 0.4%—well below the OECD average of 11.6%.
| Rank | Country | Percentage Difference in Men's & Women's Full-time Earnings |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | 0.4% |
| 2 | 🇧🇪 Belgium | 1.1% |
| 3 | 🇨🇷 Costa Rica | 1.4% |
| 4 | 🇨🇴 Colombia | 1.9% |
| 5 | 🇮🇪 Ireland | 2.0% |
| 6 | 🇭🇷 Croatia | 3.2% |
| 7 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 3.3% |
| 8 | 🇳🇴 Norway | 4.5% |
| 9 | 🇩🇰 Denmark | 5.8% |
| 10 | 🇵🇹 Portugal | 6.1% |
| OECD Average | 11.6% |
Notably, eight of the top 10 countries with the smallest gender pay gaps are located in Europe, as labor equality laws designed to target gender differences have begun to pay off.
The two other countries that made the list were Costa Rica (1.4%) and Colombia (1.9%), which came in third and fourth place, respectively.
How Did Luxembourg (Nearly) Eliminate its Gender Wage Gap?
Luxembourg’s virtually-non-existent gender wage gap in 2020 can be traced back to its diligent efforts to prioritize equal pay. Since 2016, firms that have not complied with the Labor Code’s equal pay laws have been subjected to penalizing fines ranging from €251 to €25,000.
Higher female education rates also contribute to the diminishing pay gap, with Luxembourg tied for first in the educational attainment rankings of the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Index Report for 2023.
See More Graphics about Demographics and Money
While these 10 countries are well below the OECD’s average gender pay gap of 11.6%, many OECD member countries including the U.S. are significantly above the average. To see the full list of the top 10 OECD countries with the largest gender pay gaps, check out this visualization.
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive1 week ago
Automotive1 week agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001