Misc
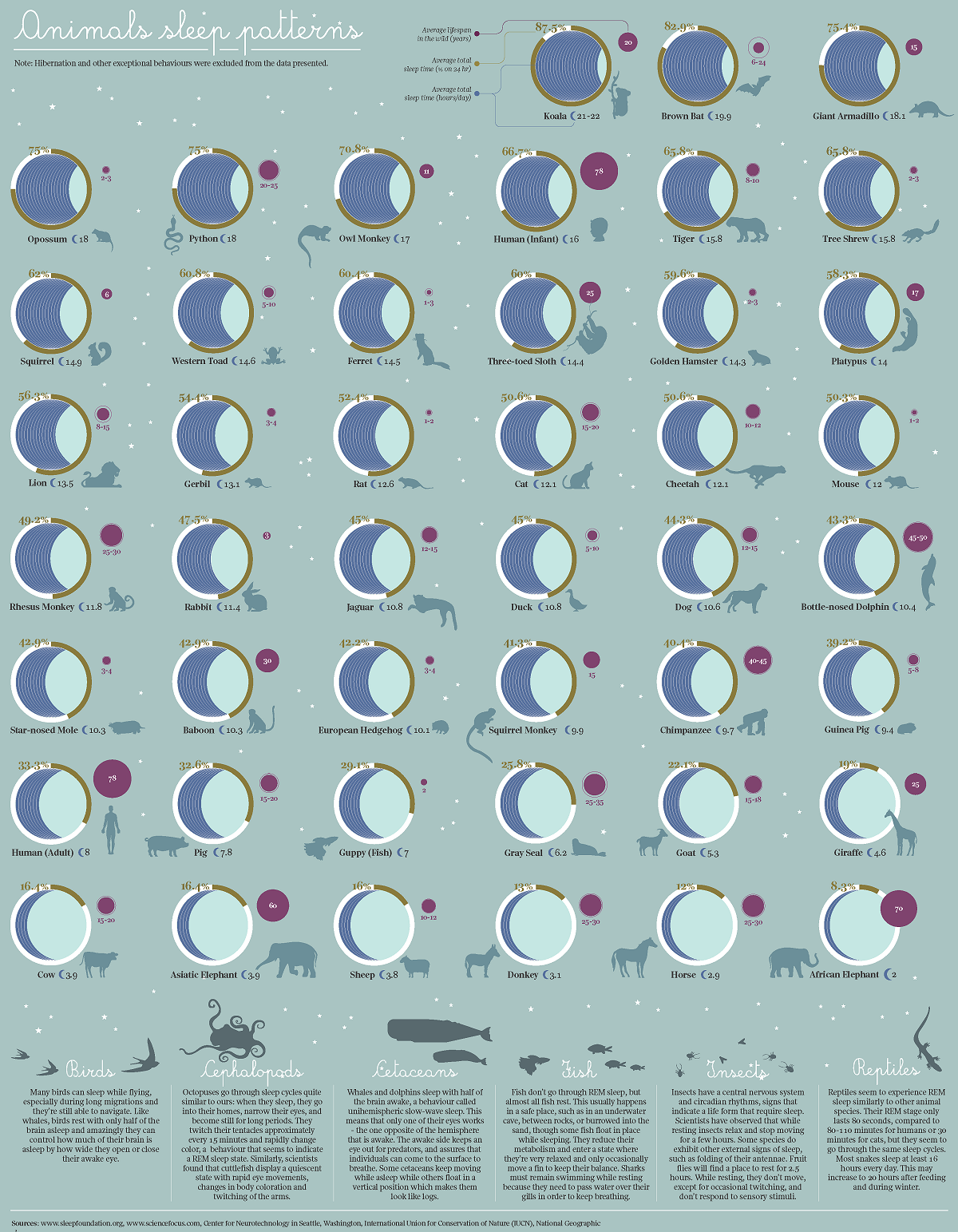
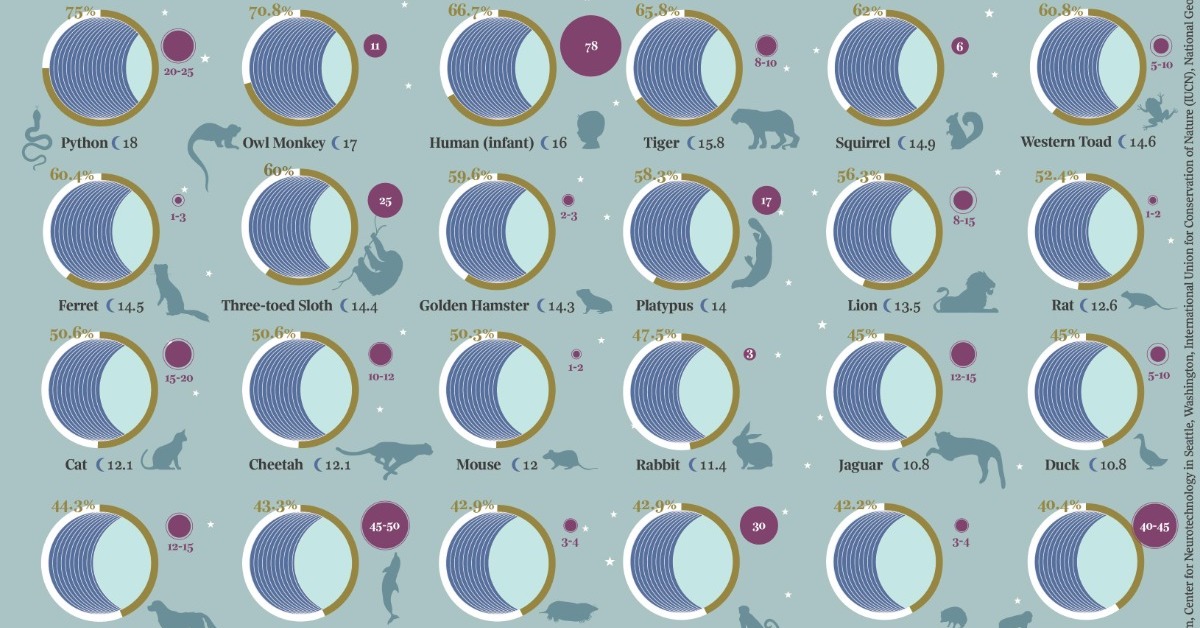
Visualizing 40 Different Animal Sleep Patterns
Click to view a larger version of the graphic.
Visualizing 40 Different Animal Sleep Patterns
Every animal has to rest in some way, but some animals need a lot more sleep than others.
This graphic by Giulia De Amicis uses data from startsleeping.com to show the typical sleeping patterns of 40 different animals, highlighting their average sleep times, and what percentage of each 24-hour day they spend resting.
Compared to the rest of the animals featured in the graphic, humans need a relatively small amount of sleep. We sleep for an average of eight hours—or 33% of our day.
| Animal | Average Sleep Time (hrs/day) | Average Sleep Time (% of 24 hours) |
|---|---|---|
| Koala | 21-22 | 87.5% |
| Brown Bat | 19.9 | 82.9% |
| Giant Armadillo | 18.1 | 75.4% |
| Opossum | 18.0 | 75.0% |
| Python | 18.0 | 75.0% |
| Owl Monkey | 17.0 | 70.8% |
| Human (Infant) | 16.0 | 66.7% |
| Tiger | 15.8 | 65.8% |
| Tree Shrew | 15.8 | 65.8% |
| Squirrel | 14.9 | 62.0% |
| Western Toad | 14.6 | 60.8% |
| Ferret | 14.5 | 60.4% |
| Three-toed Sloth | 14.4 | 60.0% |
| Golden Hamster | 14.3 | 59.6% |
| Platypus | 14.0 | 58.3% |
| Lion | 13.5 | 56.3% |
| Gerbil | 13.1 | 54.4% |
| Rat | 12.6 | 52.4% |
| Cat | 12.1 | 50.6% |
| Cheetah | 12.1 | 50.6% |
| Mouse | 12.0 | 50.3% |
| Rhesus Monkey | 11.8 | 49.2% |
| Rabbit | 11.4 | 47.5% |
| Jaguar | 10.8 | 45.0% |
| Duck | 10.8 | 45.0% |
| Dog | 10.6 | 44.3% |
| Bottle-nose Dolphin | 10.4 | 43.3% |
| Star-nosed Mole | 10.3 | 42.9% |
| Baboon | 10.3 | 42.9% |
| European Hedgehog | 10.1 | 42.2% |
| Squirrel Monkey | 9.9 | 41.3% |
| Chimpanzee | 9.7 | 40.4% |
| Guinea Pig | 9.4 | 39.2% |
| Human (Adult) | 8.0 | 33.3% |
| Pig | 7.8 | 32.6% |
| Guppy (Fish) | 7.0 | 29.1% |
| Gray Seal | 6.2 | 25.8% |
| Goat | 5.3 | 22.1% |
| Giraffe | 4.6 | 19.0% |
| Cow | 3.9 | 16.4% |
| Asiatic Elephant | 3.9 | 16.4% |
| Sheep | 3.8 | 16.0% |
| Donkey | 3.1 | 13.0% |
| Horse | 2.9 | 12.0% |
| African Elephant | 2.0 | 8.3% |
In contrast, Koalas sleep up to 22 hours a day, or 87.5% of the day. This is mostly because of the Koala’s diet—Koalas eat Eucalyptus leaves, which are toxic and take a lot of energy to digest.

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
VC+
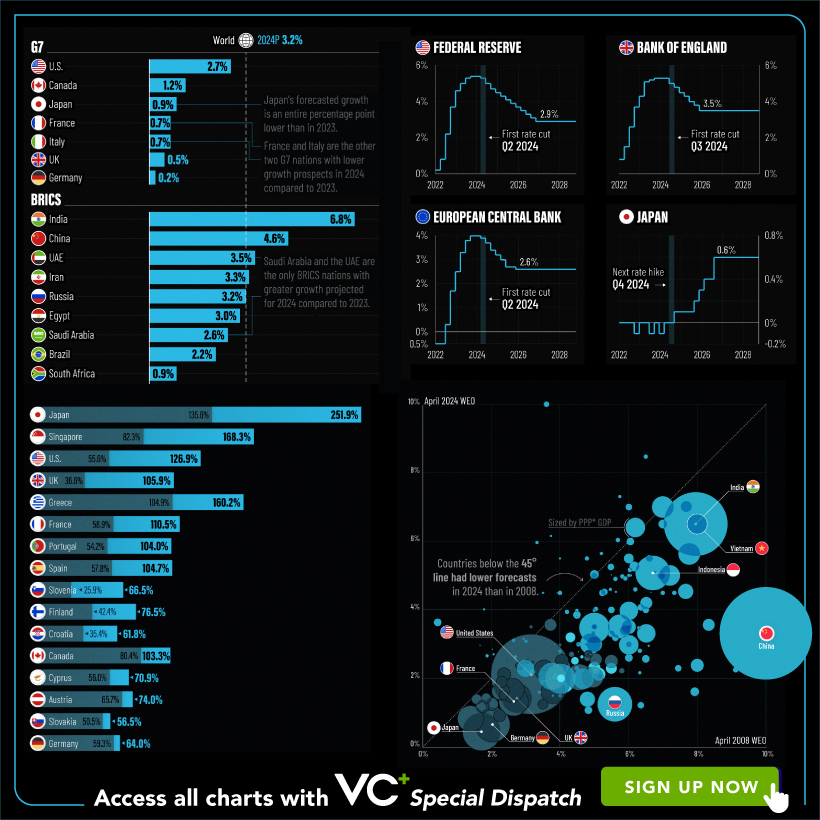
VC+: Get Our Key Takeaways From the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
A sneak preview of the exclusive VC+ Special Dispatch—your shortcut to understanding IMF’s World Economic Outlook report.

Have you read IMF’s latest World Economic Outlook yet? At a daunting 202 pages, we don’t blame you if it’s still on your to-do list.
But don’t worry, you don’t need to read the whole April release, because we’ve already done the hard work for you.
To save you time and effort, the Visual Capitalist team has compiled a visual analysis of everything you need to know from the report—and our upcoming VC+ Special Dispatch will be available exclusively to VC+ members on Thursday, April 25th.
If you’re not already subscribed to VC+, make sure you sign up now to receive the full analysis of the IMF report, and more (we release similar deep dives every week).
For now, here’s what VC+ members can expect to receive.
Your Shortcut to Understanding IMF’s World Economic Outlook
With long and short-term growth prospects declining for many countries around the world, this Special Dispatch offers a visual analysis of the key figures and takeaways from the IMF’s report including:
- The global decline in economic growth forecasts
- Real GDP growth and inflation forecasts for major nations in 2024
- When interest rate cuts will happen and interest rate forecasts
- How debt-to-GDP ratios have changed since 2000
- And much more!
Get the Full Breakdown in the Next VC+ Special Dispatch
VC+ members will receive the full Special Dispatch on Thursday, April 25th.
Make sure you join VC+ now to receive exclusive charts and the full analysis of key takeaways from IMF’s World Economic Outlook.
Don’t miss out. Become a VC+ member today.
What You Get When You Become a VC+ Member
VC+ is Visual Capitalist’s premium subscription. As a member, you’ll get the following:
- Special Dispatches: Deep dive visual briefings on crucial reports and global trends
- Markets This Month: A snappy summary of the state of the markets and what to look out for
- The Trendline: Weekly curation of the best visualizations from across the globe
- Global Forecast Series: Our flagship annual report that covers everything you need to know related to the economy, markets, geopolitics, and the latest tech trends
- VC+ Archive: Hundreds of previously released VC+ briefings and reports that you’ve been missing out on, all in one dedicated hub
You can get all of the above, and more, by joining VC+ today.
-

 Green1 week ago
Green1 week agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Travel2 weeks ago
Travel2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue