Misc
Explainer: The Different Types of Volcanoes on Earth
Click to view a larger version of the graphic.
Explainer: The Different Types of Volcanoes on Earth
Even if you don’t live near a volcano, you’ve been impacted by their activity.
It’s estimated that more than 80% of our planet’s surface has been shaped by volcanic activity. They’ve helped create our mountain ranges, plains, and plateaus, and have even helped fertilize the land that we now use to grow crops.
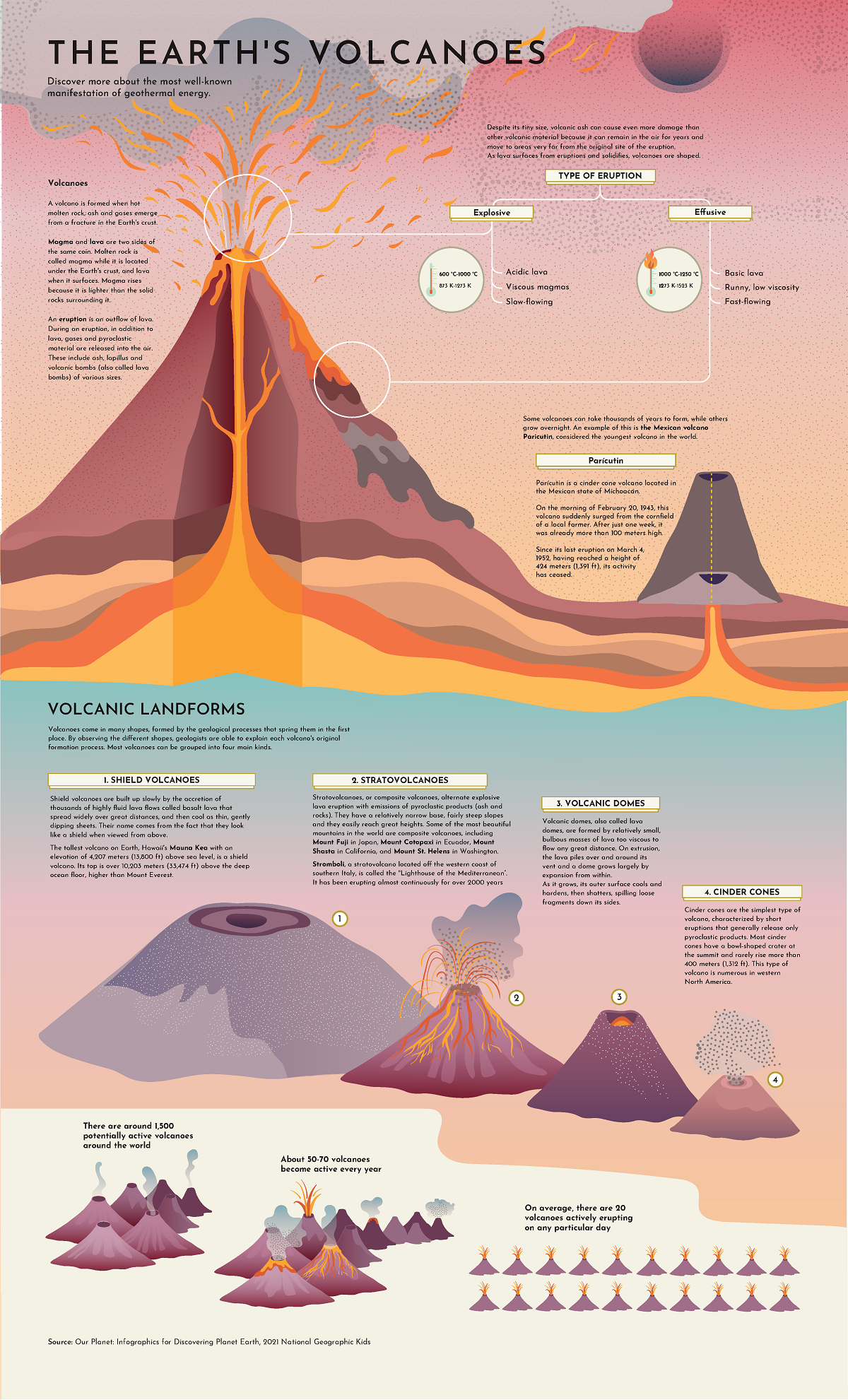
These critical mounds come in many shapes and sizes. This graphic by Giulia De Amicis provides a brief introduction to volcanoes, explaining their different types of shapes and eruptions.
Types of Eruptions
A volcano starts to form when molten rock rises from a crack in the Earth’s surface, which often emerge along tectonic plate boundaries.
Magma rises to the Earth’s surface because it’s lighter than rock. When it surfaces or erupts, it’s referred to as lava.
There are various types of volcanic eruptions, depending on the lava’s temperature, thickness, and composition. Generally speaking, high gas content and high viscosity lead to explosive eruptions, while low viscosity and gas content lead to an effusive, or steadily flowing, eruption.
The Four Main Types of Volcanoes
Volcanoes vary in size and structure, depending on how they’re formed. Most volcanoes types fall into four main groups:
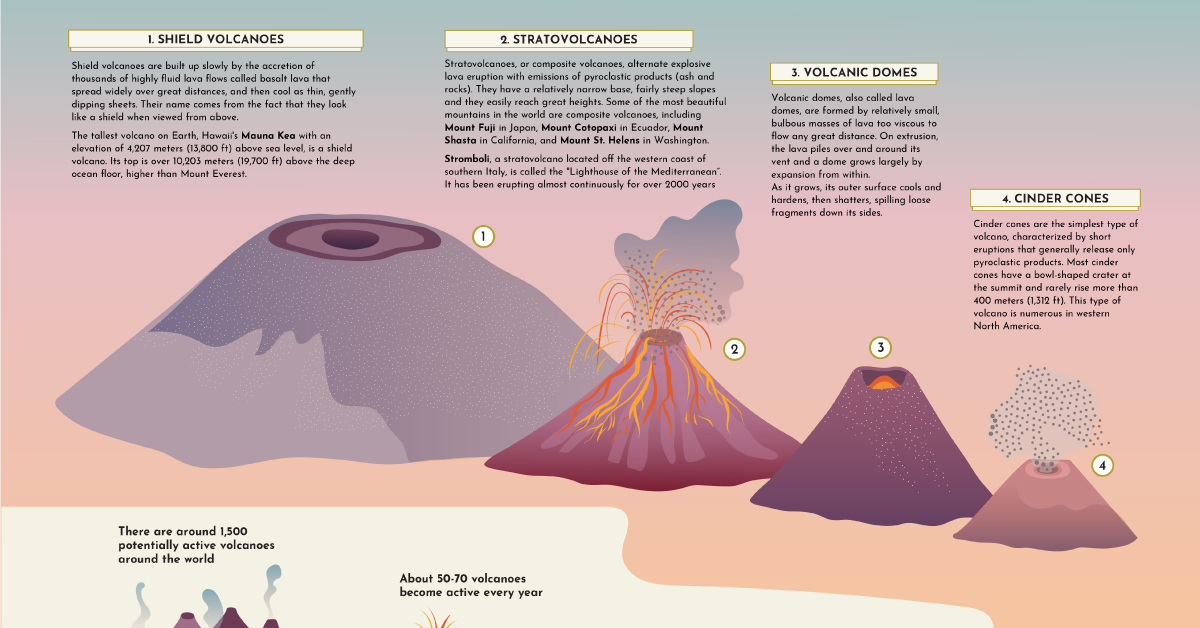
Shield Volcanoes
Shield volcanoes are built slowly, from low-viscosity lava that spreads far and quick. The lava eventually dries to form a thin, wide sheet, and after repeated eruptions, a mount starts to form.
From the top, these types of volcanoes look like a shield, hence the name. While these volcanoes take a while to form, they aren’t necessarily low. In fact, the world’s tallest active volcano, Mauna Kea in Hawaii, is a shield volcano.
Stratovolcanoes
Also known as composite volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are built relatively fast, at least compared to shield volcanoes. This is because, in between lava eruptions, composite volcanoes emit ash and rock, which helps add structure to the mound rather quickly.
Some well-known composite volcanoes are Mount Fuji in Japan, Mount St. Helens in Washington, and Mount Cotopaxi in Ecuador.
Volcanic Domes
Opposite to shield volcanoes, volcanic domes are formed when lava is highly-viscous. Because the thick lava can’t travel very far, it starts to pool around the volcano’s vent.
This can sometimes create a pressure build-up, meaning dome volcanoes are prone to explosive eruptions.
Cinder Cones
These types of volcanoes typically don’t release lava. Rather, their eruptions typically emit volcanic ash and rocks, known as pyroclastic products.
Cinder cones are characterized by a bowl-shaped crater at the top, and usually don’t exceed 400 m (1,312 ft) in height.
How Volcanoes Benefit the Earth
Volcanoes have a number of ecological benefits. Once broken down, volcanic materials create exceptionally fertile soil, which can help build prospering new habitats for animals and plants.
Volcanic eruptions can also help cool our climate. When a volcano explodes, ash and sulfur gas from the eruption combine with water droplets and get trapped in the atmosphere for years. This has a cooling effect which is extremely beneficial to us, especially given our current global warming situation.
Dr. Tracy Gregg, associate professor for the University at Buffalo’s geology department, told Accuweather that “volcanoes have actually helped to keep the world about 2 to 3 degrees cooler than it otherwise may be.”

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
Misc
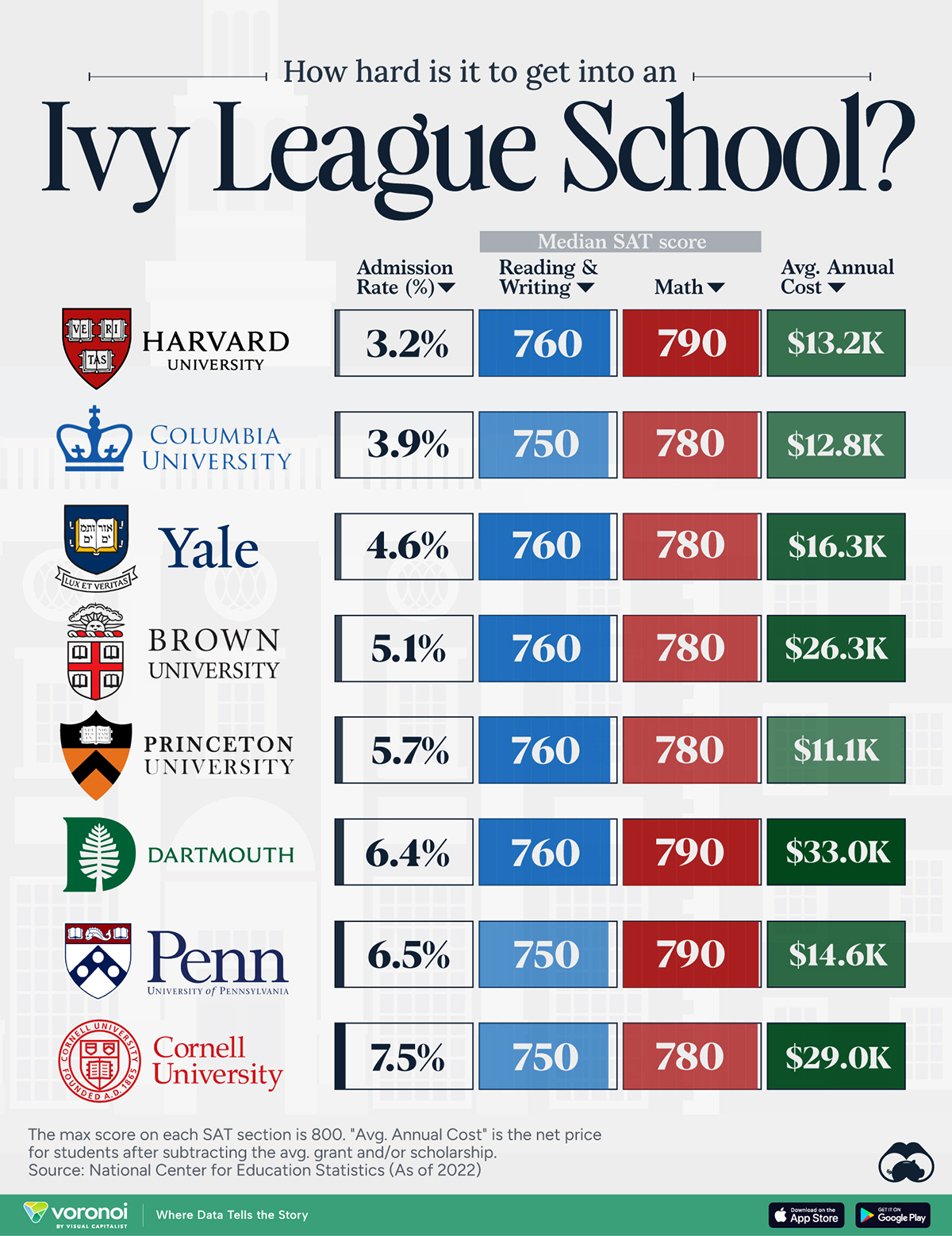
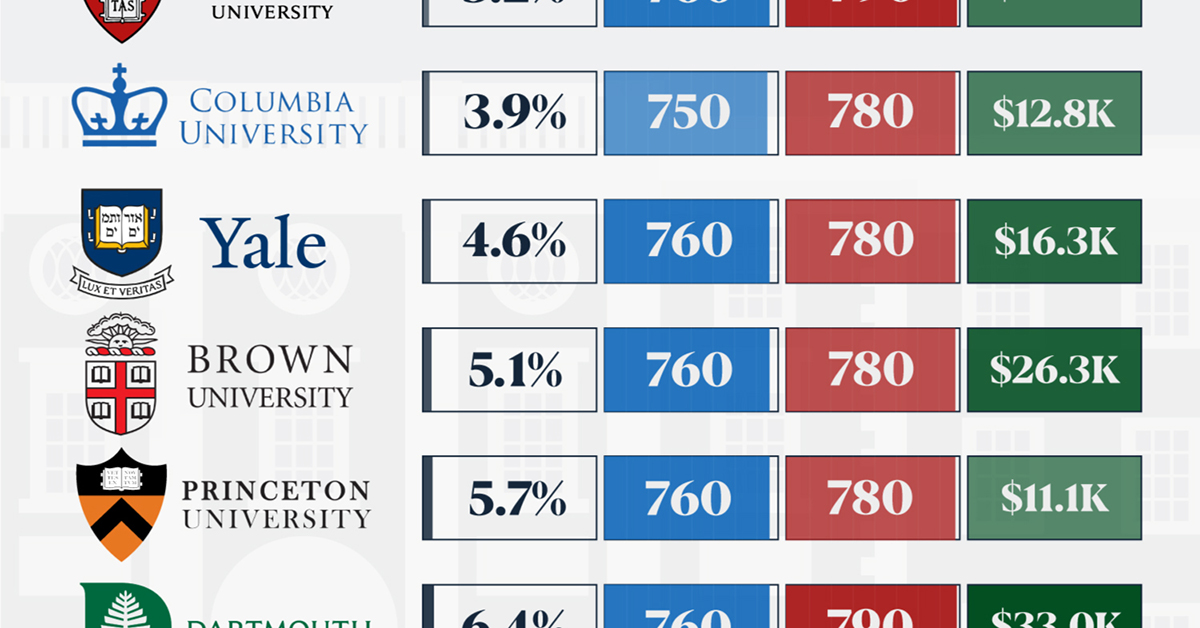
How Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
We detail the admission rates and average annual cost for Ivy League schools, as well as the median SAT scores required to be accepted.
How Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Ivy League institutions are renowned worldwide for their academic excellence and long-standing traditions. But how hard is it to get into one of the top universities in the U.S.?
In this graphic, we detail the admission rates and average annual cost for Ivy League schools, as well as the median SAT scores required to be accepted. The data comes from the National Center for Education Statistics and was compiled by 24/7 Wall St.
Note that “average annual cost” represents the net price a student pays after subtracting the average value of grants and/or scholarships received.
Harvard is the Most Selective
The SAT is a standardized test commonly used for college admissions in the United States. It’s taken by high school juniors and seniors to assess their readiness for college-level academic work.
When comparing SAT scores, Harvard and Dartmouth are among the most challenging universities to gain admission to. The median SAT scores for their students are 760 for reading and writing and 790 for math. Still, Harvard has half the admission rate (3.2%) compared to Dartmouth (6.4%).
| School | Admission rate (%) | SAT Score: Reading & Writing | SAT Score: Math | Avg Annual Cost* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harvard University | 3.2 | 760 | 790 | $13,259 |
| Columbia University | 3.9 | 750 | 780 | $12,836 |
| Yale University | 4.6 | 760 | 780 | $16,341 |
| Brown University | 5.1 | 760 | 780 | $26,308 |
| Princeton University | 5.7 | 760 | 780 | $11,080 |
| Dartmouth College | 6.4 | 760 | 790 | $33,023 |
| University of Pennsylvania | 6.5 | 750 | 790 | $14,851 |
| Cornell University | 7.5 | 750 | 780 | $29,011 |
*Costs after receiving federal financial aid.
Additionally, Dartmouth has the highest average annual cost at $33,000. Princeton has the lowest at $11,100.
While student debt has surged in the United States in recent years, hitting $1.73 trillion in 2023, the worth of obtaining a degree from any of the schools listed surpasses mere academics. This is evidenced by the substantial incomes earned by former students.
Harvard grads, for example, have the highest average starting salary in the country, at $91,700.
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001