Countries
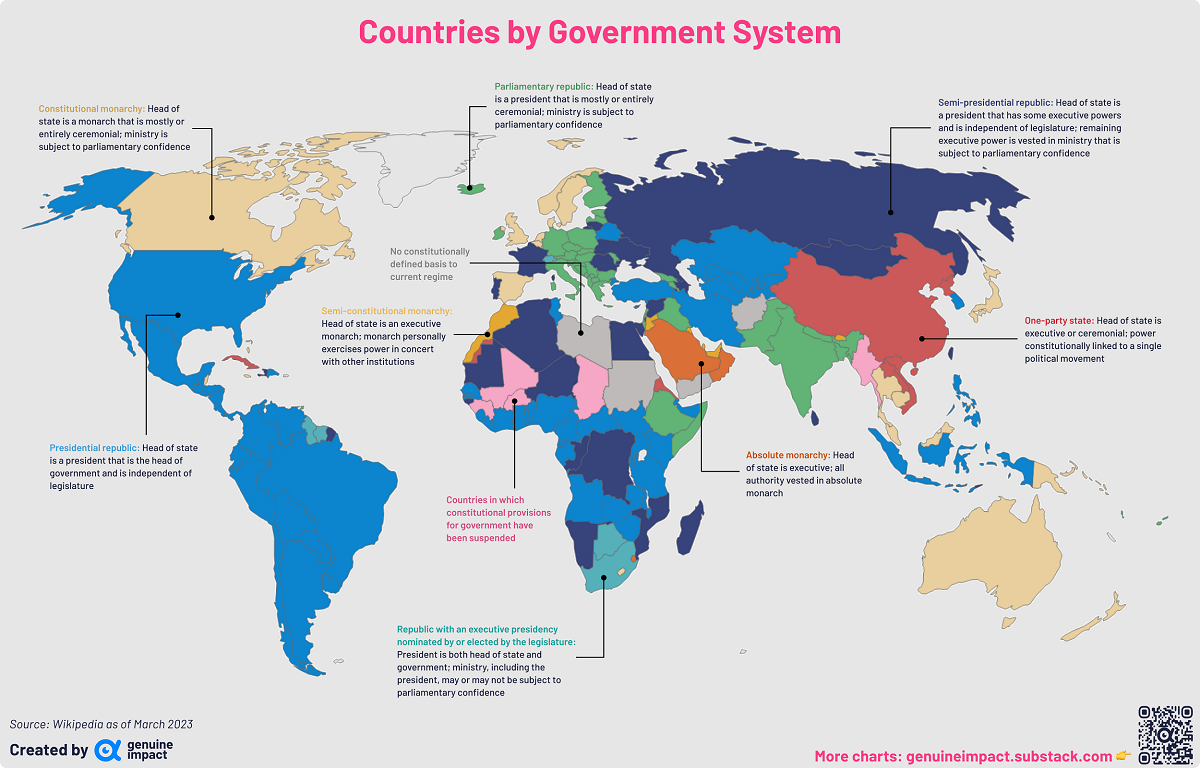
Mapped: The World’s Legal Government Systems
Click to view this graphic in a higher-resolution.
Mapping The World’s Legal Government Systems
With over 200 countries existing across the world with unique cultures and traditions, one might assume that there are hundreds of types of government systems. But both historically and in modern times, that’s not the case.
Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems.
This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework.
Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different.
Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023:
| Country | Constitutional form | Head of state |
|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | Provisional | n/a |
| Albania | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Algeria | Republic | Executive |
| Andorra | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Angola | Republic | Executive |
| Antigua and Barbuda | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Argentina | Republic | Executive |
| Armenia | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Australia | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Austria | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Azerbaijan | Republic | Executive |
| Bahamas, The | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Bahrain | Constitutional monarchy | Executive |
| Bangladesh | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Barbados | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Belarus | Republic | Executive |
| Belgium | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Belize | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Benin | Republic | Executive |
| Bhutan | Constitutional monarchy | Executive |
| Bolivia | Republic | Executive |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Botswana | Republic | Executive |
| Brazil | Republic | Executive |
| Brunei | Absolute monarchy | Executive |
| Bulgaria | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Burkina Faso | Provisional | n/a |
| Burundi | Republic | Executive |
| Cambodia | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Cameroon | Republic | Executive |
| Canada | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Cape Verde | Republic | Executive |
| Central African Republic | Republic | Executive |
| Chad | Provisional | n/a |
| Chile | Republic | Executive |
| China, People's Republic of | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Colombia | Republic | Executive |
| Comoros | Republic | Executive |
| Congo, Democratic Republic of the | Republic | Executive |
| Congo, Republic of the | Republic | Executive |
| Costa Rica | Republic | Executive |
| Côte d'Ivoire | Republic | Executive |
| Croatia | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Cuba | Republic | Executive |
| Cyprus | Republic | Executive |
| Czech Republic | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Denmark | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Djibouti | Republic | Executive |
| Dominica | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Dominican Republic | Republic | Executive |
| East Timor | Republic | Executive |
| Ecuador | Republic | Executive |
| Egypt | Republic | Executive |
| El Salvador | Republic | Executive |
| Equatorial Guinea | Republic | Executive |
| Eritrea | Republic | Executive |
| Estonia | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Eswatini | Absolute monarchy | Executive |
| Ethiopia | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Fiji | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Finland | Republic | Ceremonial |
| France | Republic | Executive |
| Gabon | Republic | Executive |
| Gambia, The | Republic | Executive |
| Georgia | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Germany | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Ghana | Republic | Executive |
| Greece | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Grenada | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Guatemala | Republic | Executive |
| Guinea | Provisional | n/a |
| Guinea-Bissau | Republic | Executive |
| Guyana | Republic | Executive |
| Haiti | Republic | Executive |
| Honduras | Republic | Executive |
| Hungary | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Iceland | Republic | Ceremonial |
| India | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Indonesia | Republic | Executive |
| Iran | Republic | Executive |
| Iraq | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Ireland | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Israel | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Italy | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Jamaica | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Japan | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Jordan | Constitutional monarchy | Executive |
| Kazakhstan | Republic | Executive |
| Kenya | Republic | Executive |
| Kiribati | Republic | Executive |
| Kuwait | Constitutional monarchy | Executive |
| Kyrgyzstan | Republic | Executive |
| Laos | Republic | Executive |
| Latvia | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Lebanon | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Lesotho | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Liberia | Republic | Executive |
| Libya | Provisional | n/a |
| Liechtenstein | Constitutional monarchy | Executive |
| Lithuania | Republic | Executive |
| Luxembourg | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Madagascar | Republic | Executive |
| Malawi | Republic | Executive |
| Malaysia | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Maldives | Republic | Executive |
| Mali | Provisional | n/a |
| Malta | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Marshall Islands | Republic | Executive |
| Mauritania | Republic | Executive |
| Mauritius | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Mexico | Republic | Executive |
| Micronesia | Republic | Executive |
| Moldova | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Monaco | Constitutional monarchy | Executive |
| Mongolia | Republic | Executive |
| Montenegro | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Morocco | Constitutional monarchy | Executive |
| Mozambique | Republic | Executive |
| Myanmar | Provisional | n/a |
| Namibia | Republic | Executive |
| Nauru | Republic | Executive |
| Nepal | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Netherlands | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| New Zealand | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Nicaragua | Republic | Executive |
| Niger | Republic | Executive |
| Nigeria | Republic | Executive |
| North Korea | Republic | Executive |
| North Macedonia | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Norway | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Oman | Absolute monarchy | Executive |
| Pakistan | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Palau | Republic | Executive |
| Palestine | Republic | Executive |
| Panama | Republic | Executive |
| Papua New Guinea | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Paraguay | Republic | Executive |
| Peru | Republic | Executive |
| Philippines | Republic | Executive |
| Poland | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Portugal | Republic | Executive |
| Qatar | Constitutional monarchy | Executive |
| Romania | Republic | Executive |
| Russia | Republic | Executive |
| Rwanda | Republic | Executive |
| Saint Kitts and Nevis | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Saint Lucia | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Samoa | Republic | Ceremonial |
| San Marino | Republic | Executive |
| São Tomé and Príncipe | Republic | Executive |
| Saudi Arabia | Absolute monarchy | Executive |
| Senegal | Republic | Executive |
| Serbia | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Seychelles | Republic | Executive |
| Sierra Leone | Republic | Executive |
| Singapore | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Slovakia | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Slovenia | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Solomon Islands | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Somalia | Republic | Ceremonial |
| South Africa | Republic | Executive |
| South Korea | Republic | Executive |
| South Sudan | Republic | Executive |
| Spain | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Sri Lanka | Republic | Executive |
| Sudan | Provisional | n/a |
| Suriname | Republic | Executive |
| Sweden | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Switzerland | Republic | Executive |
| Syria | Republic | Executive |
| Tajikistan | Republic | Executive |
| Tanzania | Republic | Executive |
| Thailand | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Togo | Republic | Executive |
| Tonga | Constitutional monarchy | Executive |
| Trinidad and Tobago | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Tunisia | Republic | Executive |
| Turkey | Republic | Executive |
| Turkmenistan | Republic | Executive |
| Tuvalu | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| Uganda | Republic | Executive |
| Ukraine | Republic | Executive |
| United Arab Emirates | Constitutional monarchy | Executive |
| United Kingdom | Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial |
| United States | Republic | Executive |
| Uruguay | Republic | Executive |
| Uzbekistan | Republic | Executive |
| Vanuatu | Republic | Ceremonial |
| Vatican City | Absolute monarchy | Executive |
| Venezuela | Republic | Executive |
| Vietnam | Republic | Executive |
| Yemen | Provisional | n/a |
| Zambia | Republic | Executive |
| Zimbabwe | Republic | Executive |
Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute.
A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government.
On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions.
Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary.
The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government.
In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government.
The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies.
It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries.
In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections.
In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government.
In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected.
Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
Demographics
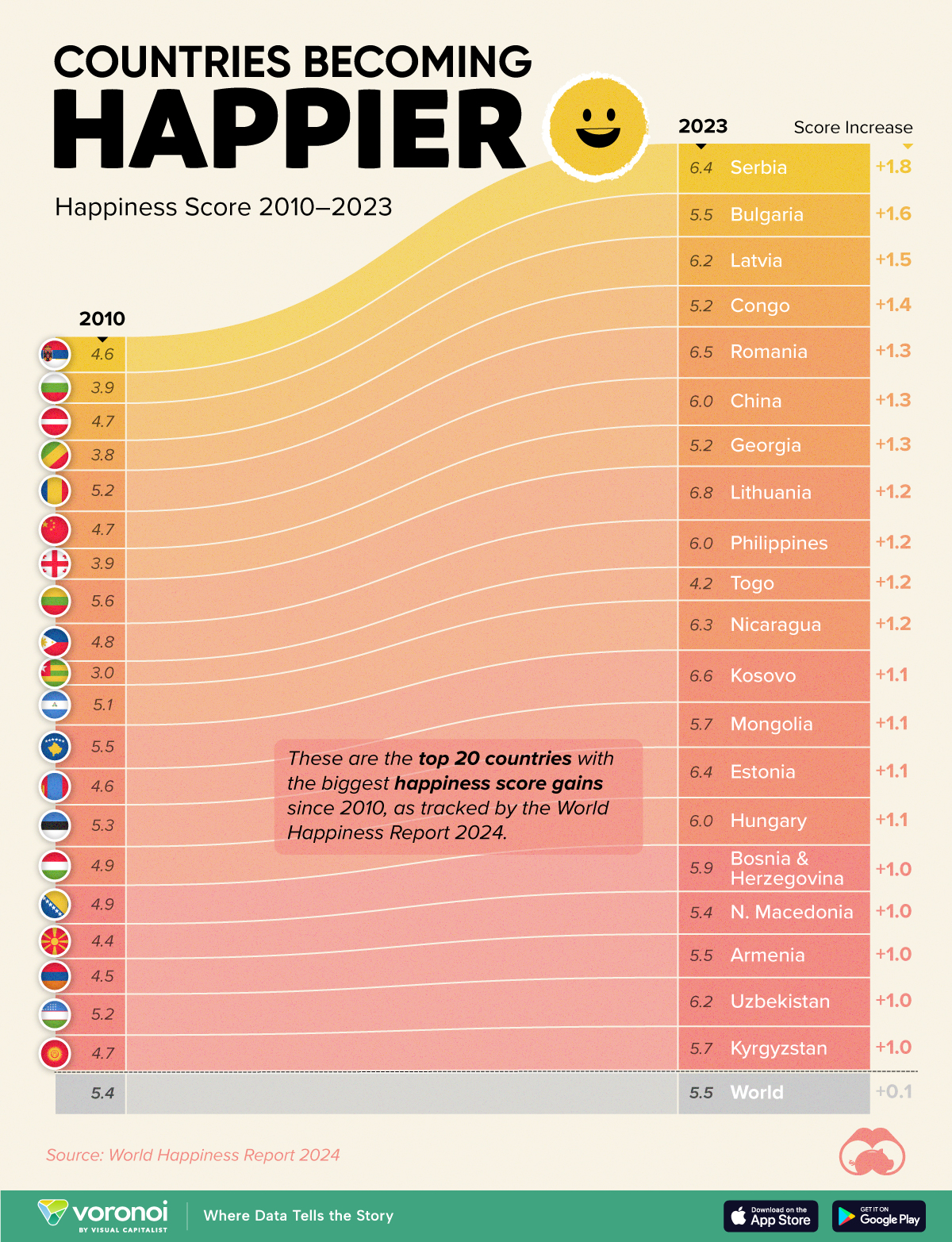
Countries With the Largest Happiness Gains Since 2010
Tracking Gallup survey data for more than a decade reveals insights into the regions seeing happiness gains.
Countries With the Largest Happiness Gains Since 2010
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
In 2011, Bhutan sponsored a UN resolution that invited governments to prioritize happiness and well-being as a way to measure social and economic development.
And thus, the World Happiness Report was born.
In 2012, the first report released, examining Gallup poll data from 2006–2010 that asked respondents in nearly every country to evaluate their life on a 0–10 scale. From this they extrapolated a single “happiness score” out of 10 to compare how happy countries are.
More than a decade later, the 2024 World Happiness Report continues the mission to quantify, measure, and compare well-being. Its latest findings also include how countries have become happier in the intervening years.
We visualize these findings in the above chart, which shows the 20 countries that have seen their happiness scores grow the most since 2010.
Which Countries Have Become Happier Since 2010?
Serbia leads a list of 12 Eastern European nations whose average happiness score has improved more than 20% in the last decade.
In the same time period, the Serbian economy has doubled to $80 billion, and its per capita GDP has nearly doubled to $9,538 in current dollar terms.
| Rank | Country | Happiness Score Gains (2010–2024) | 2024 Happiness Score (out of 10) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇷🇸 Serbia | +1.8 | 6.4 |
| 2 | 🇧🇬 Bulgaria | +1.6 | 5.5 |
| 3 | 🇱🇻 Latvia | +1.5 | 6.2 |
| 4 | 🇨🇬 Congo | +1.4 | 5.2 |
| 5 | 🇷🇴 Romania | +1.3 | 6.5 |
| 6 | 🇨🇳 China | +1.3 | 6.0 |
| 7 | 🇬🇪 Georgia | +1.3 | 5.2 |
| 8 | 🇱🇹 Lithuania | +1.2 | 6.8 |
| 9 | 🇵🇭 Philippines | +1.2 | 6.0 |
| 10 | 🇹🇬 Togo | +1.2 | 4.2 |
| 11 | 🇳🇮 Nicaragua | +1.2 | 6.3 |
| 12 | 🇽🇰 Kosovo | +1.1 | 6.6 |
| 13 | 🇲🇳 Mongolia | +1.1 | 5.7 |
| 14 | 🇪🇪 Estonia | +1.1 | 6.4 |
| 15 | 🇭🇺 Hungary | +1.1 | 6.0 |
| 16 | 🇧🇦 Bosnia & Herzegovina | +1.0 | 5.9 |
| 17 | 🇲🇰 North Macedonia | +1.0 | 5.4 |
| 18 | 🇦🇲 Armenia | +1.0 | 5.5 |
| 19 | 🇺🇿 Uzbekistan | +1.0 | 6.2 |
| 20 | 🇰🇬 Kyrgyzstan | +1.0 | 5.7 |
| N/A | 🌍 World | +0.1 | 5.5 |
Since the first report, Western Europe has on average been happier than Eastern Europe. But as seen with these happiness gains, Eastern Europe is now seeing their happiness levels converge closer to their Western counterparts. In fact, when looking at those under the age of 30, the most recent happiness scores are nearly the same across the continent.
All in all, 20 countries have increased their happiness score by a full point or more since 2010, on the 0–10 scale.
-

 Green1 week ago
Green1 week agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Travel2 weeks ago
Travel2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue