Demographics
Mapped: The World’s Population Density by Latitude
Click to view a larger version of the graphic.
Mapped: The World’s Population Density by Latitude
When you think about areas with high population densities, certain regions spring to mind. This could be a populous part of Asia or a cluster of cities in North America or Europe.
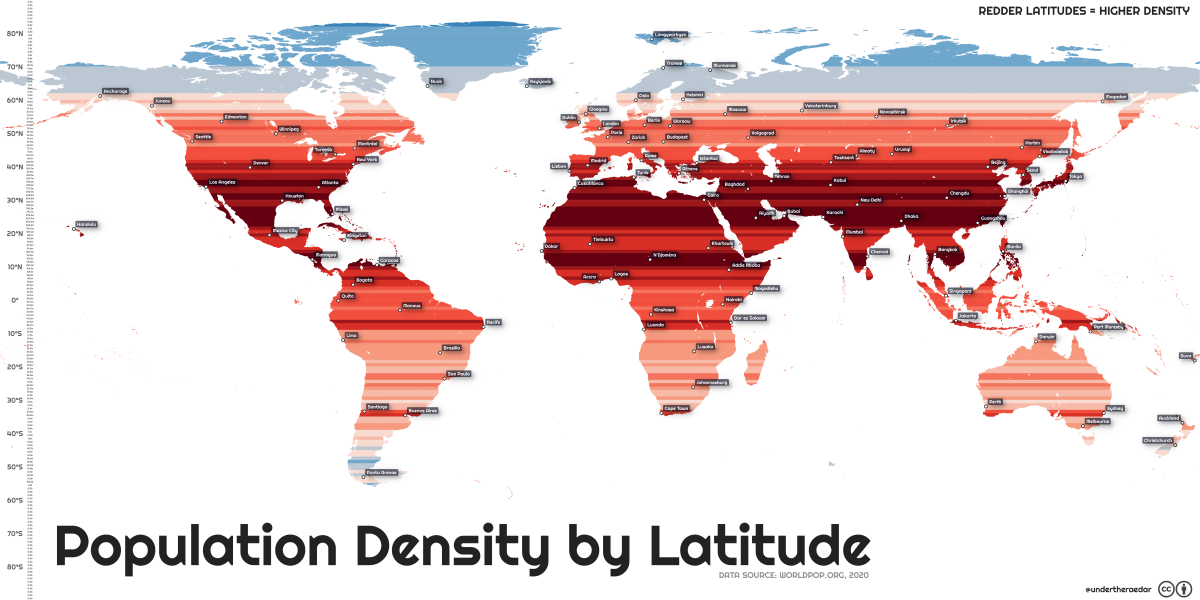
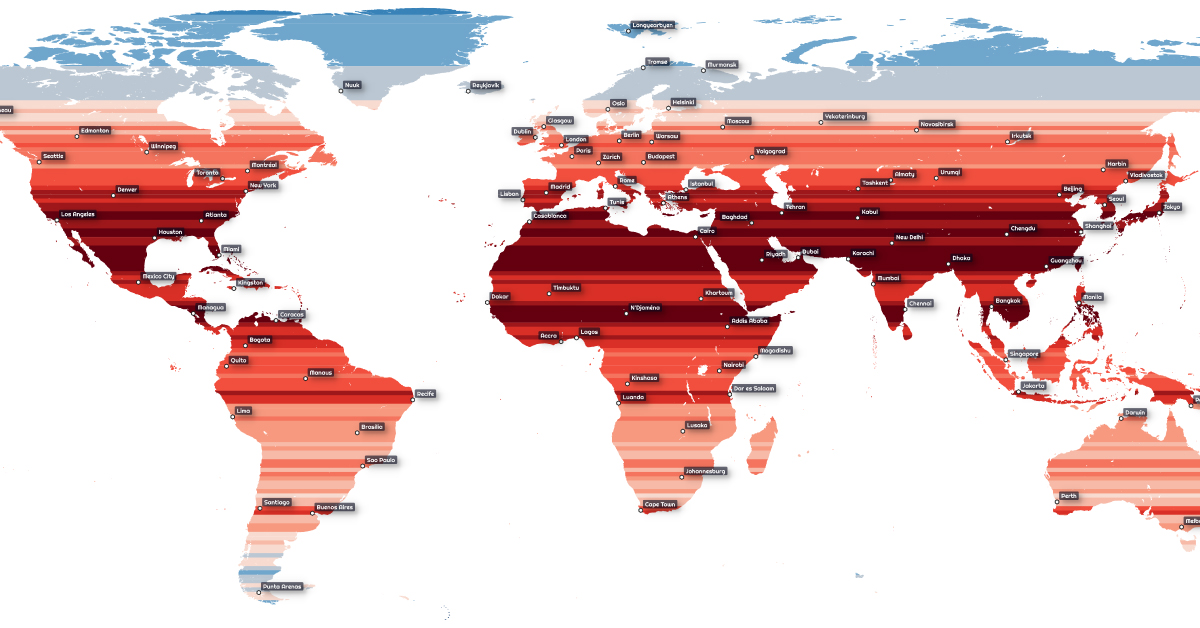
Usually density comparisons are made using cities or countries, but this map from Alasdair Rae provides another perspective. This world map depicts population density by latitude, going from the densest populated coordinates in deep red to the sparsest in light blue.
Why Certain Latitudes (and Regions) Are More Densely Populated
Numerous factors affect an area’s population density. These can range from topography, or the physical terrain characteristics of the place, to more direct factors like an area’s climate, which can impact both the survivability and agricultural potential.
Political, economic, and social factors are also at play—for example, there is a natural lack of livelihood opportunities in sparse areas such as the Amazon rainforest or the Himalayas.
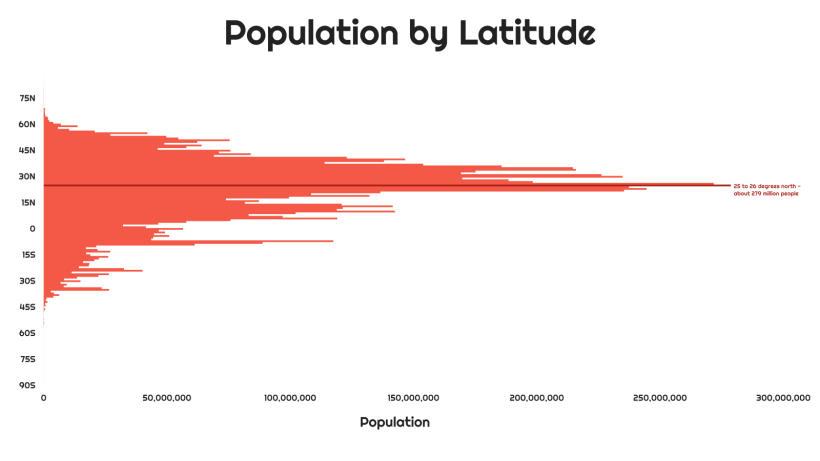
Breaking down the population by latitude, we see the population becomes more concentrated near the equator. In particular, the 25th and 26th parallel north are the most densely populated latitude circles. Around 279 million people reside in these latitude lines, which run through large countries like India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, China, the United States, Mexico, and others.
Despite their large landmasses, many of these countries do not themselves have very high population densities. Since density measures the ratio of people to physical space, countries with vast but sparse regions like China and India are less dense than imagined.
Out of the top 10 most densely populated countries in the world, only a couple can be found on the 25th and 26th parallel north—Bangladesh and Bahrain. For a size comparison, Bangladesh is 1.55% the size of China, and Bahrain is only 0.01%.
The Future of Population Density Near the Equator
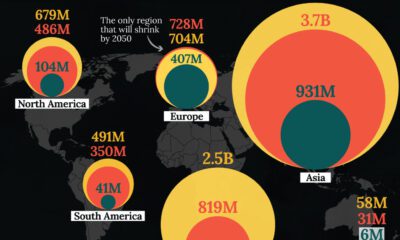
Looking ahead to 2100, the UN projects that the global population will rise to almost 11 billion. This would increase global population density from 59.11 people per square kilometer in 2022 to 80.82 per square kilometer in 2100.
However, the projections show that Asia will not be the biggest contributor to this growth. Instead, the most considerable jump in population is predicted for Africa, set to grow by almost 200% from almost 1.5 billion people today to 4.3 billion in 2100.
The equator runs right through the middle of Africa and crisscrosses countries like the Congo (both the Republic and DRC), Kenya, Gabon, Uganda, and Somalia.
As Africa’s population expands, this means that at latitudes near the equator, there could be even higher population densities coming. Or course, this largely depends on how the world’s fastest growing cities—most of which are in Africa—shape up over the coming decades.

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
Demographics
The Countries That Have Become Sadder Since 2010
Tracking Gallup survey data for more than a decade reveals some countries are witnessing big happiness declines, reflecting their shifting socio-economic conditions.
The Countries That Have Become Sadder Since 2010
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Can happiness be quantified?
Some approaches that try to answer this question make a distinction between two differing components of happiness: a daily experience part, and a more general life evaluation (which includes how people think about their life as a whole).
The World Happiness Report—first launched in 2012—has been making a serious go at quantifying happiness, by examining Gallup poll data that asks respondents in nearly every country to evaluate their life on a 0–10 scale. From this they extrapolate a single “happiness score” out of 10 to compare how happy (or unhappy) countries are.
More than a decade later, the 2024 World Happiness Report continues the mission. Its latest findings also include how some countries have become sadder in the intervening years.
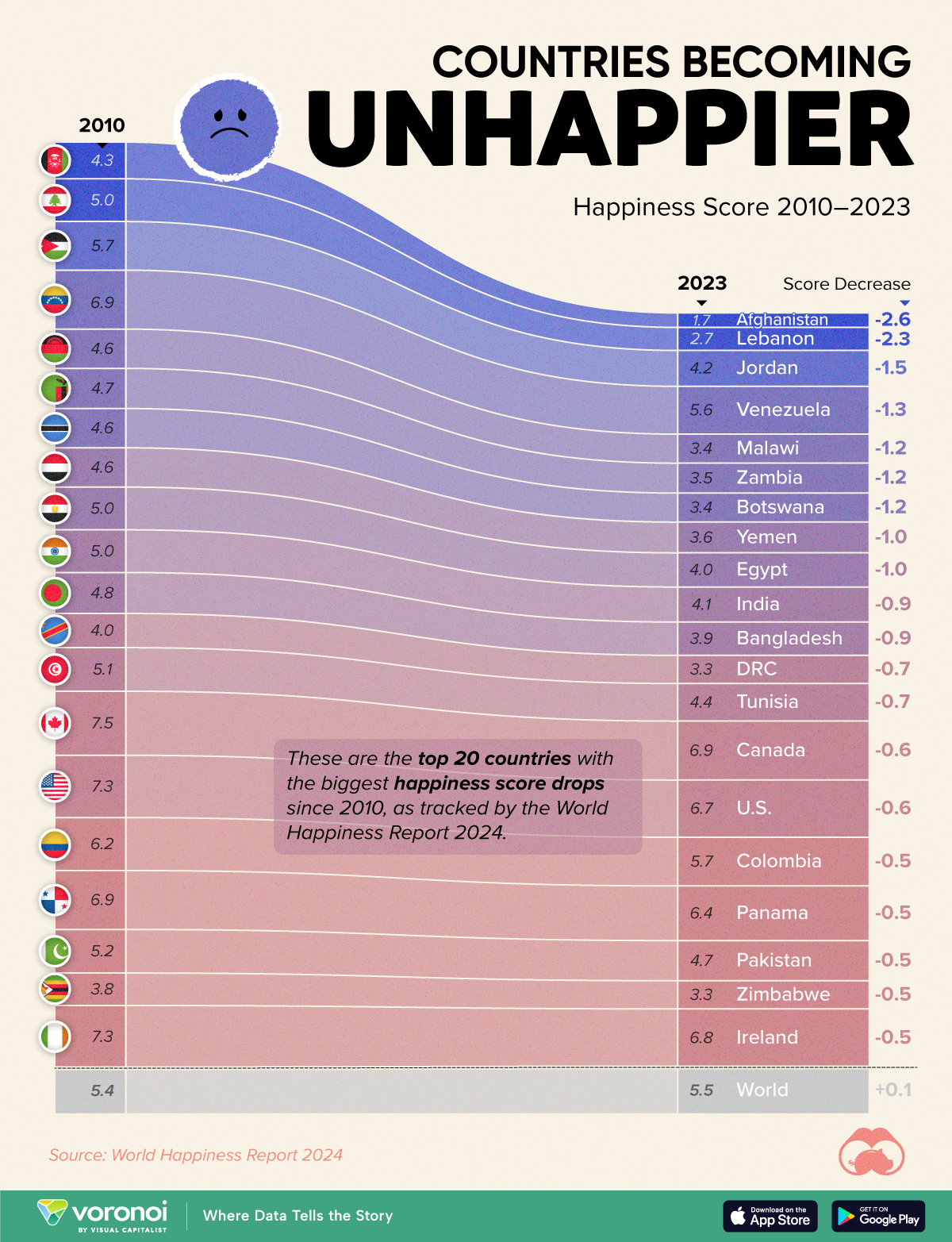
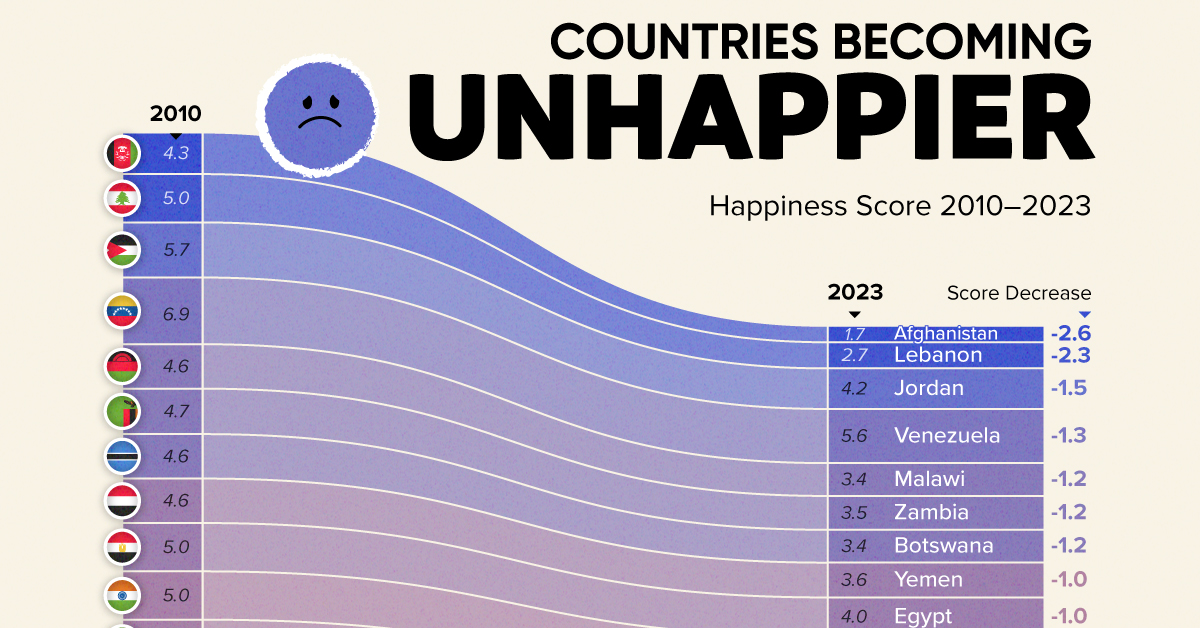
Which Countries Have Become Unhappier Since 2010?
Afghanistan is the unhappiest country in the world right now, and is also 60% unhappier than over a decade ago, indicating how much life has worsened since 2010.
In 2021, the Taliban officially returned to power in Afghanistan, after nearly two decades of American occupation in the country. The Islamic fundamentalist group has made life harder, especially for women, who are restricted from pursuing higher education, travel, and work.
On a broader scale, the Afghan economy has suffered post-Taliban takeover, with various consequent effects: mass unemployment, a drop in income, malnutrition, and a crumbling healthcare system.
| Rank | Country | Happiness Score Loss (2010–24) | 2024 Happiness Score (out of 10) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇦🇫 Afghanistan | -2.6 | 1.7 |
| 2 | 🇱🇧 Lebanon | -2.3 | 2.7 |
| 3 | 🇯🇴 Jordan | -1.5 | 4.2 |
| 4 | 🇻🇪 Venezuela | -1.3 | 5.6 |
| 5 | 🇲🇼 Malawi | -1.2 | 3.4 |
| 6 | 🇿🇲 Zambia | -1.2 | 3.5 |
| 7 | 🇧🇼 Botswana | -1.2 | 3.4 |
| 8 | 🇾🇪 Yemen | -1.0 | 3.6 |
| 9 | 🇪🇬 Egypt | -1.0 | 4.0 |
| 10 | 🇮🇳 India | -0.9 | 4.1 |
| 11 | 🇧🇩 Bangladesh | -0.9 | 3.9 |
| 12 | 🇨🇩 DRC | -0.7 | 3.3 |
| 13 | 🇹🇳 Tunisia | -0.7 | 4.4 |
| 14 | 🇨🇦 Canada | -0.6 | 6.9 |
| 15 | 🇺🇸 U.S. | -0.6 | 6.7 |
| 16 | 🇨🇴 Colombia | -0.5 | 5.7 |
| 17 | 🇵🇦 Panama | -0.5 | 6.4 |
| 18 | 🇵🇰 Pakistan | -0.5 | 4.7 |
| 19 | 🇿🇼 Zimbabwe | -0.5 | 3.3 |
| 20 | 🇮🇪 Ireland | -0.5 | 6.8 |
| N/A | 🌍 World | +0.1 | 5.5 |
Nine countries in total saw their happiness score drop by a full point or more, on the 0–10 scale.
Noticeably, many of them have seen years of social and economic upheaval. Lebanon, for example, has been grappling with decades of corruption, and a severe liquidity crisis since 2019 that has resulted in a banking system collapse, sending poverty levels skyrocketing.
In Jordan, unprecedented population growth—from refugees leaving Iraq and Syria—has aggravated unemployment rates. A somewhat abrupt change in the line of succession has also raised concerns about political stability in the country.
-

 Green1 week ago
Green1 week agoRanked: The Countries With the Most Air Pollution in 2023
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Travel2 weeks ago
Travel2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075