Misc
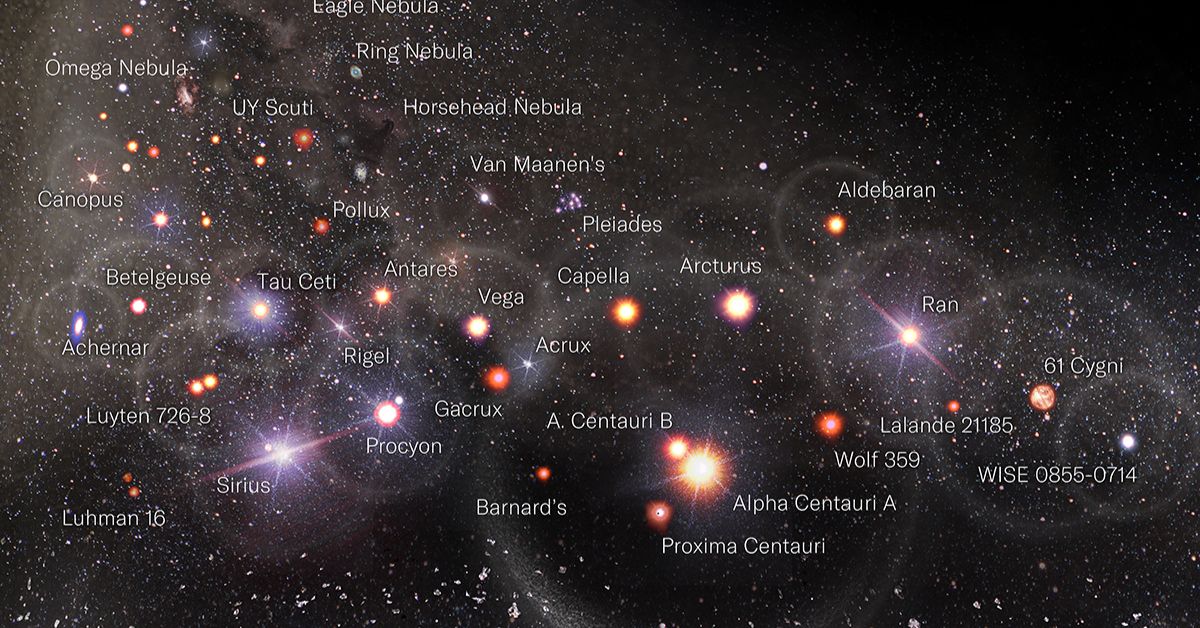
A Logarithmic Map of the Entire Observable Universe

For a full-size option or to inquire about posters, please visit Pablo Carlos Budassi’s website.
A Logarithmic Map of the Entire Observable Universe
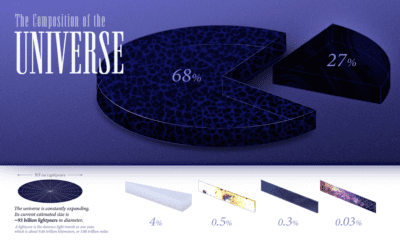
Among the scientific community, it’s widely believed that so far humans have only discovered about 5% of the universe.
Yet, despite knowing about just a fraction of what’s out there, we’ve still managed to discover galaxies billions of light-years away from Earth.
This graphic by Pablo Carlos Budassi provides a logarithmic map of the entire known universe, using data by researchers at Princeton University and updated as of May 2022.
How Does the Map Work?
Before diving in, it’s worth touching on a few key details about the map.
First off, it’s important to note that the celestial objects shown on this map are not shown to scale. If it was made to scale with sizes relative to how we see them from Earth, nearly all of the objects would be miniscule dots (except the Moon, the Sun, and some nebulae and galaxies).
Secondly, each object’s distance from the Earth is measured on a logarithmic scale, which increases exponentially, in order to fit in all the data.
Within our Solar System, the map’s scale spans astronomical units (AU), roughly the distance from the Earth to the Sun. Beyond, it grows to measure millions of parsecs, with each one of those equal to 3.26 light-years, or 206,000 AU.
Exploring the Map
The map highlights a number of different celestial objects, including:
- The Solar System
- Comets and asteroids
- Star systems and clusters
- Nebulae
- Galaxies, including the Milky Way
- Galaxy clusters
- Cosmic microwave background—radiation leftover from the Big Bang
Featured are some recently discovered objects, such as the most distant known galaxy to date, HD1. Scientists believe this newly-discovered galaxy was formed just 330 million years after the Big Bang, or roughly 8.4 billion years before Earth.
It also highlights some newly deployed spacecraft, including the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), which is NASA’s latest infrared telescope, and the Tiangong Space Station, which was made by China and launched in April 2021.
Why is it called the “Observable” Universe?
Humanity has been interested in space for thousands of years, and many scientists and researchers have dedicated their lives to furthering our collective knowledge about space and the universe.
Most people are familiar with Albert Einstein and his theory of relativity, which became a cornerstone of both physics and astronomy. Another well-known scientist was Edwin Hubble, whose findings of galaxies moving away from Earth is considered to be the first observation of the universe expanding.
But the massive logarithmic map above, and any observations from Earth or probes in space, are limited in nature. The universe is currently dated to be around 13.8 billion years old, and nothing in the universe can travel faster than the speed of light.
When accounting for the expansion of the universe and observed objects moving away from us, that means that the farthest we can “see” is currently calculated at around 47.7 billion light-years. And since light takes time to travel, much of what we’re observing actually happened many millions of years ago.
But our understanding of the universe is evolving constantly with new discoveries. What will we discover next?

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
Misc
How Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
We detail the admission rates and average annual cost for Ivy League schools, as well as the median SAT scores required to be accepted.
How Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
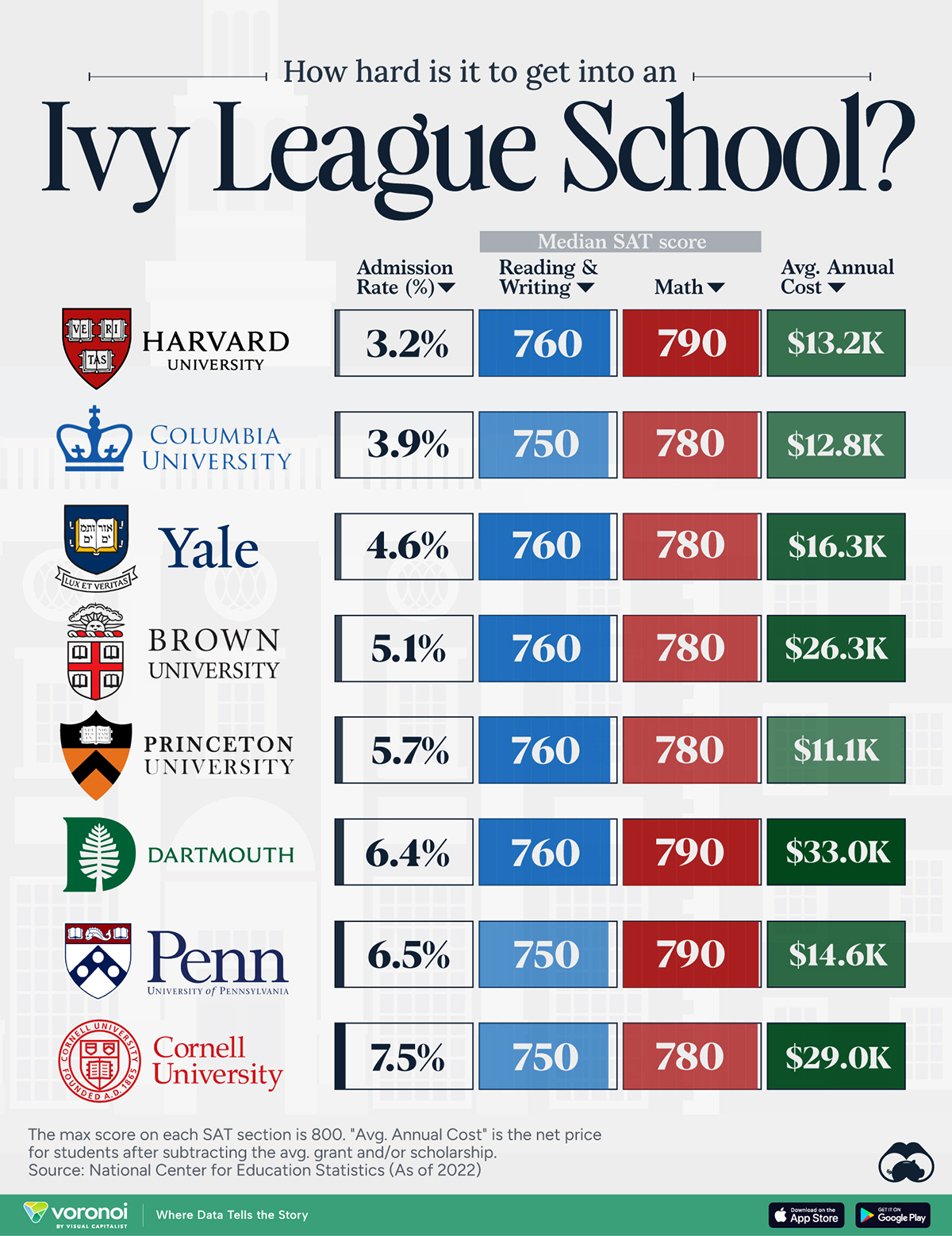
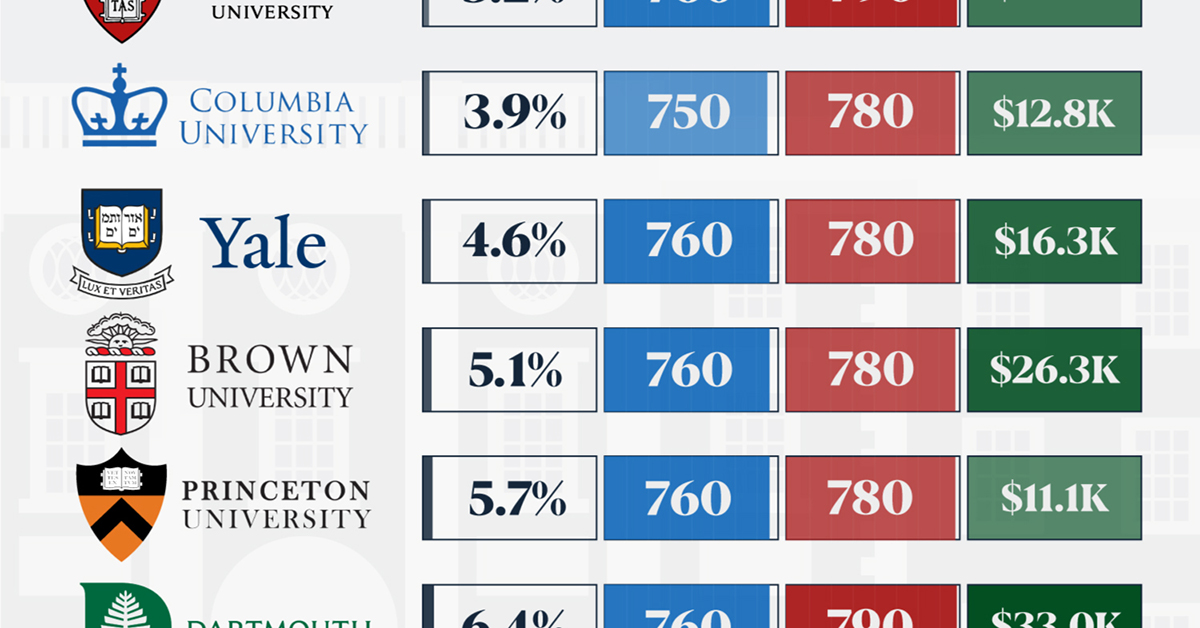
Ivy League institutions are renowned worldwide for their academic excellence and long-standing traditions. But how hard is it to get into one of the top universities in the U.S.?
In this graphic, we detail the admission rates and average annual cost for Ivy League schools, as well as the median SAT scores required to be accepted. The data comes from the National Center for Education Statistics and was compiled by 24/7 Wall St.
Note that “average annual cost” represents the net price a student pays after subtracting the average value of grants and/or scholarships received.
Harvard is the Most Selective
The SAT is a standardized test commonly used for college admissions in the United States. It’s taken by high school juniors and seniors to assess their readiness for college-level academic work.
When comparing SAT scores, Harvard and Dartmouth are among the most challenging universities to gain admission to. The median SAT scores for their students are 760 for reading and writing and 790 for math. Still, Harvard has half the admission rate (3.2%) compared to Dartmouth (6.4%).
| School | Admission rate (%) | SAT Score: Reading & Writing | SAT Score: Math | Avg Annual Cost* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harvard University | 3.2 | 760 | 790 | $13,259 |
| Columbia University | 3.9 | 750 | 780 | $12,836 |
| Yale University | 4.6 | 760 | 780 | $16,341 |
| Brown University | 5.1 | 760 | 780 | $26,308 |
| Princeton University | 5.7 | 760 | 780 | $11,080 |
| Dartmouth College | 6.4 | 760 | 790 | $33,023 |
| University of Pennsylvania | 6.5 | 750 | 790 | $14,851 |
| Cornell University | 7.5 | 750 | 780 | $29,011 |
*Costs after receiving federal financial aid.
Additionally, Dartmouth has the highest average annual cost at $33,000. Princeton has the lowest at $11,100.
While student debt has surged in the United States in recent years, hitting $1.73 trillion in 2023, the worth of obtaining a degree from any of the schools listed surpasses mere academics. This is evidenced by the substantial incomes earned by former students.
Harvard grads, for example, have the highest average starting salary in the country, at $91,700.
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc1 week ago
Misc1 week agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes