Misc
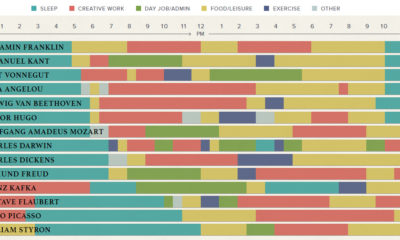
Visualized: The Daily Routines of Famous Creatives
View a higher resolution version of graphic.
Visualized: The Daily Routines of Famous Creatives
What is the best daily routine to unlock creativity, or is there such a thing?
Many modern suggestions for optimizing creativity—like scheduling time for “deep work,” and building small, sustainable “atomic habits”—can be traced back to famous creatives in many different eras. And though they all found success, they employed different methods as well.
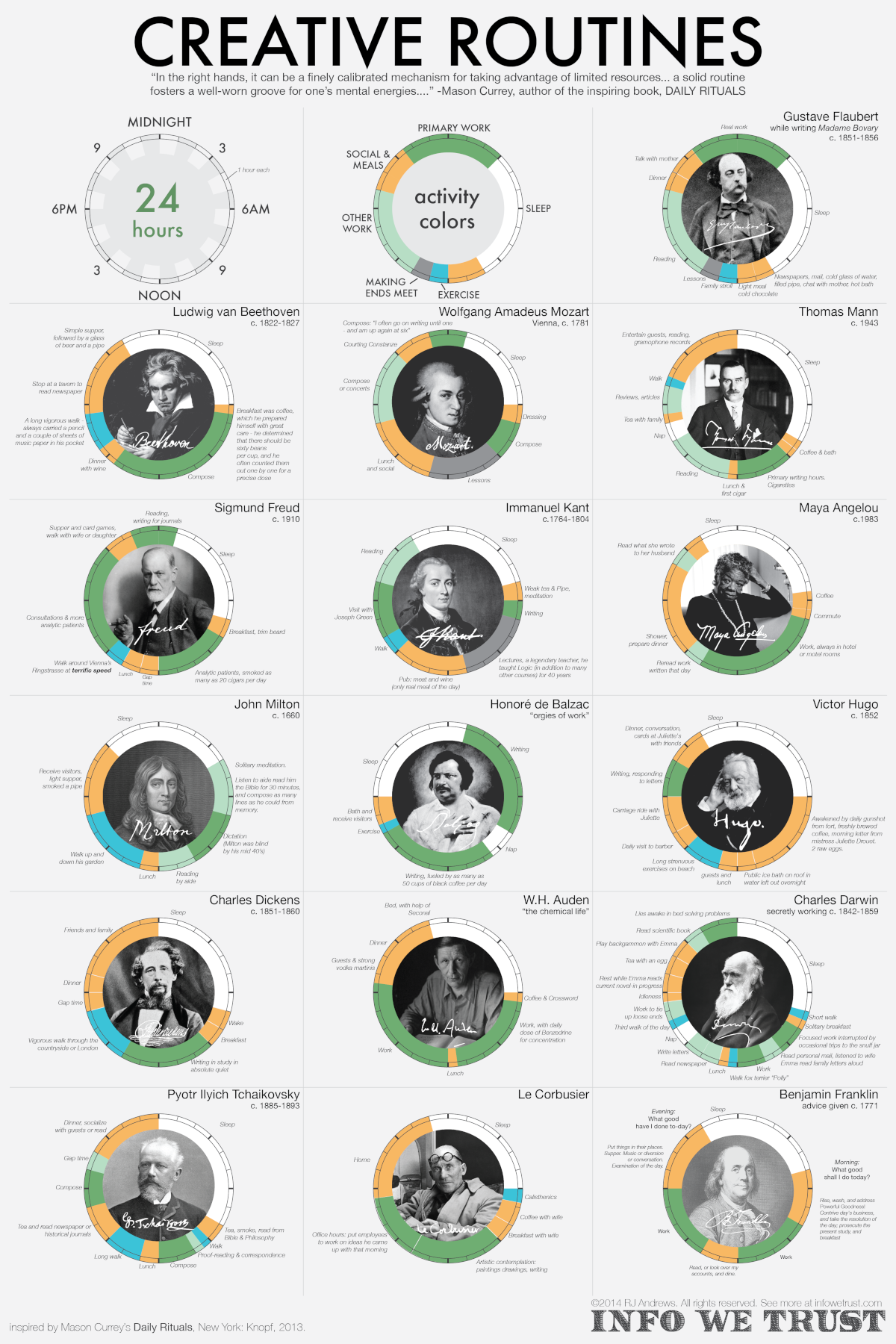
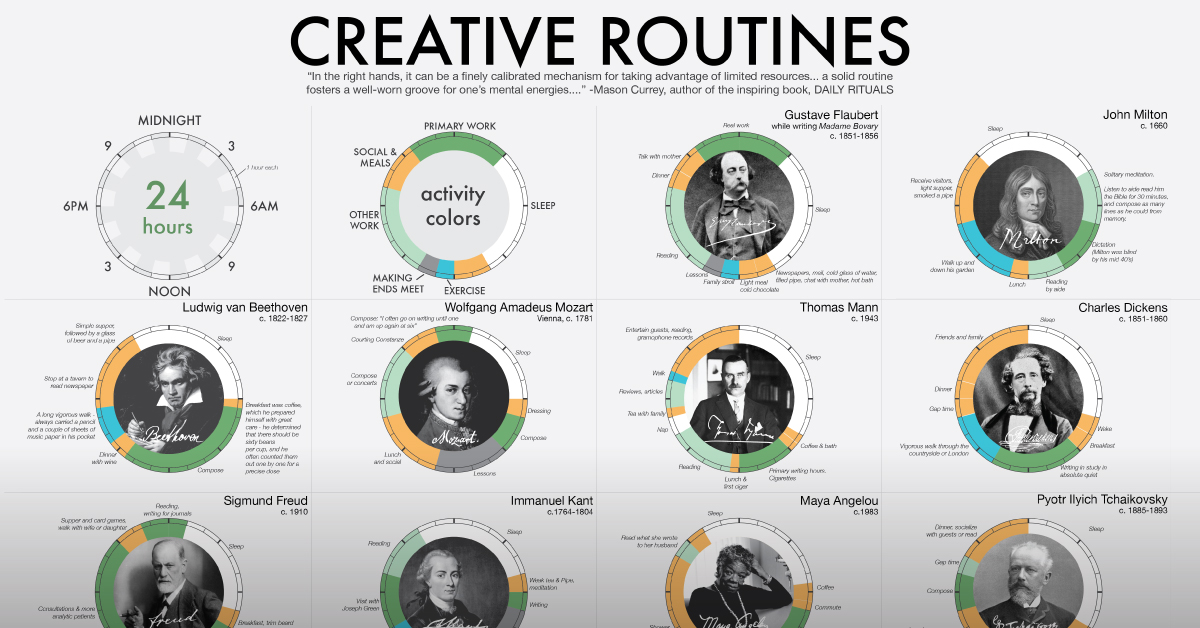
In this unique visualization, RJ Andrews from InfoWeTrust has charted how notable creatives in different fields spent their days. He picked 16 of the 161 “inspired minds” covered by Daily Rituals: How Artists Work, a book by writer and editor Mason Currey published in 2013.
How Much “Creativity Time” in Famous Daily Routines?
Dividing the day into 24 hours, Andrews denoted certain categories for daily activities like working creatively, sleeping, and other miscellaneous endeavors (meals, leisure, exercise, and social time).
For the creatives with a separate day job—Immanuel Kant and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart—their ordinary labor is also counted in miscellaneous activities.
Below is a breakdown of the daily routine of all 16 people featured above:
| Name | Occupation | Creative (hrs) | Sleep (hrs) | Miscellaneous (hrs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maya Angelou | Writer/Poet | 9 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| W.H. Auden | Poet | 11.5 | 7 | 5.5 |
| Honoré de Balzac | Novelist | 13.5 | 8.5 | 2 |
| L.V. Beethoven | Composer / Pianist | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Le Corbusier | Architect | 8.5 | 7 | 8.5 |
| Charles Darwin | Naturalist / Biologist/ Geologist | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| Charles Dickens | Writer | 5 | 7 | 12 |
| Gustave Flaubert | Novelist | 10.5 | 7 | 6.5 |
| Sigmund Freud | Psychologist | 12.5 | 6 | 5.5 |
| Benjamin Franklin | Writer / Inventor / Scientist / Statesman | 8 | 7 | 9 |
| Victor Hugo | Writer | 2 | 8 | 14 |
| Immanuel Kant | Philosopher | 7 | 7 | 10 |
| Thomas Mann | Novelist | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| John Milton | Poet | 8 | 7 | 9 |
| W.A. Mozart | Composer / Pianist | 8 | 5 | 11 |
| P.I. Tchaikovsky | Composer | 4.5 | 8 | 11.5 |
The average and median amount of time spent on creative work for these individuals was just over 8 hours a day. At the extremes were two French novelists, Honoré de Balzac with 13.5 hours daily spent on creative work, and Victor Hugo with only 2 hours.
Interestingly, the allocation of creative work time was different in almost every daily routine. Maya Angelou’s routine resembles the modern work day, with the bulk of her writing between 7 a.m. to 2 p.m. Others like Kant and Mozart had creativity blocks when time allowed, such as before and after their teaching jobs.
Then there are outliers like Honoré de Balzac and Sigmund Freud, who worked as much as they could. Balzac wrote from 1:00 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. with just an hour and a half nap break in between, fueled by up to 50 cups of coffee. Freud split up his creative work into three different blocks: analyzing patients in the morning, consulting in the afternoon, and reading and writing journals into the late evening.
But somewhere in their days, most of these brilliant minds made sure to get a good rest, with an average of 7.25 hours of sleep across the board.
Schedule Yourself to Create Success
Creativity may ebb and flow, but these great minds had one clear thing in common: scheduling time for creative work.
The perfect daily routine was usually what fit in with their lifestyle (and their bodies), not based on an arbitrary amount of work. For example, night owls with later chronotypes worked late, while socialites and politicians found time outside of their commitments.
They also found time to move and enjoy life. Half of the people in the dataset specified exercise in their accounts—either leisurely strolls or fast walks. Many also scheduled social time with partners, friends, or children, often paired with a meal.
Perhaps the greatest insight, however, is that the day-to-day routine doesn’t have to look extraordinary to be able to create extraordinary work.

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
VC+
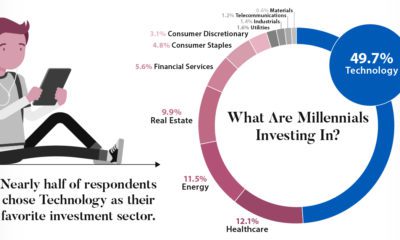
VC+: Get Our Key Takeaways From the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
A sneak preview of the exclusive VC+ Special Dispatch—your shortcut to understanding IMF’s World Economic Outlook report.

Have you read IMF’s latest World Economic Outlook yet? At a daunting 202 pages, we don’t blame you if it’s still on your to-do list.
But don’t worry, you don’t need to read the whole April release, because we’ve already done the hard work for you.
To save you time and effort, the Visual Capitalist team has compiled a visual analysis of everything you need to know from the report—and our upcoming VC+ Special Dispatch will be available exclusively to VC+ members on Thursday, April 25th.
If you’re not already subscribed to VC+, make sure you sign up now to receive the full analysis of the IMF report, and more (we release similar deep dives every week).
For now, here’s what VC+ members can expect to receive.
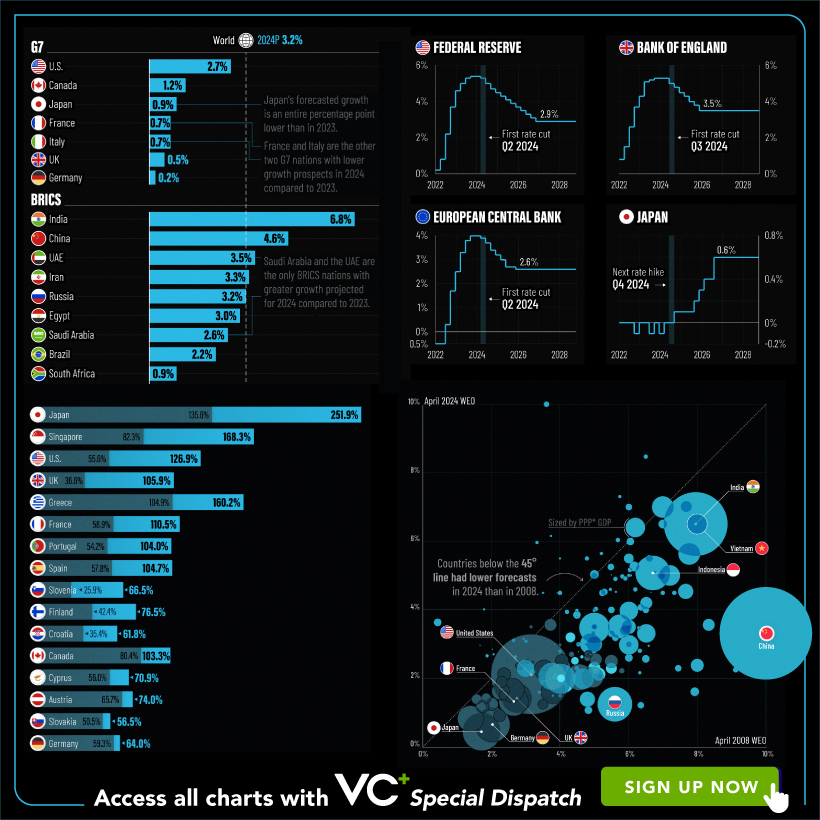
Your Shortcut to Understanding IMF’s World Economic Outlook
With long and short-term growth prospects declining for many countries around the world, this Special Dispatch offers a visual analysis of the key figures and takeaways from the IMF’s report including:
- The global decline in economic growth forecasts
- Real GDP growth and inflation forecasts for major nations in 2024
- When interest rate cuts will happen and interest rate forecasts
- How debt-to-GDP ratios have changed since 2000
- And much more!
Get the Full Breakdown in the Next VC+ Special Dispatch
VC+ members will receive the full Special Dispatch on Thursday, April 25th.
Make sure you join VC+ now to receive exclusive charts and the full analysis of key takeaways from IMF’s World Economic Outlook.
Don’t miss out. Become a VC+ member today.
What You Get When You Become a VC+ Member
VC+ is Visual Capitalist’s premium subscription. As a member, you’ll get the following:
- Special Dispatches: Deep dive visual briefings on crucial reports and global trends
- Markets This Month: A snappy summary of the state of the markets and what to look out for
- The Trendline: Weekly curation of the best visualizations from across the globe
- Global Forecast Series: Our flagship annual report that covers everything you need to know related to the economy, markets, geopolitics, and the latest tech trends
- VC+ Archive: Hundreds of previously released VC+ briefings and reports that you’ve been missing out on, all in one dedicated hub
You can get all of the above, and more, by joining VC+ today.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries