Money
Charted: Income Distributions in 16 Different Countries
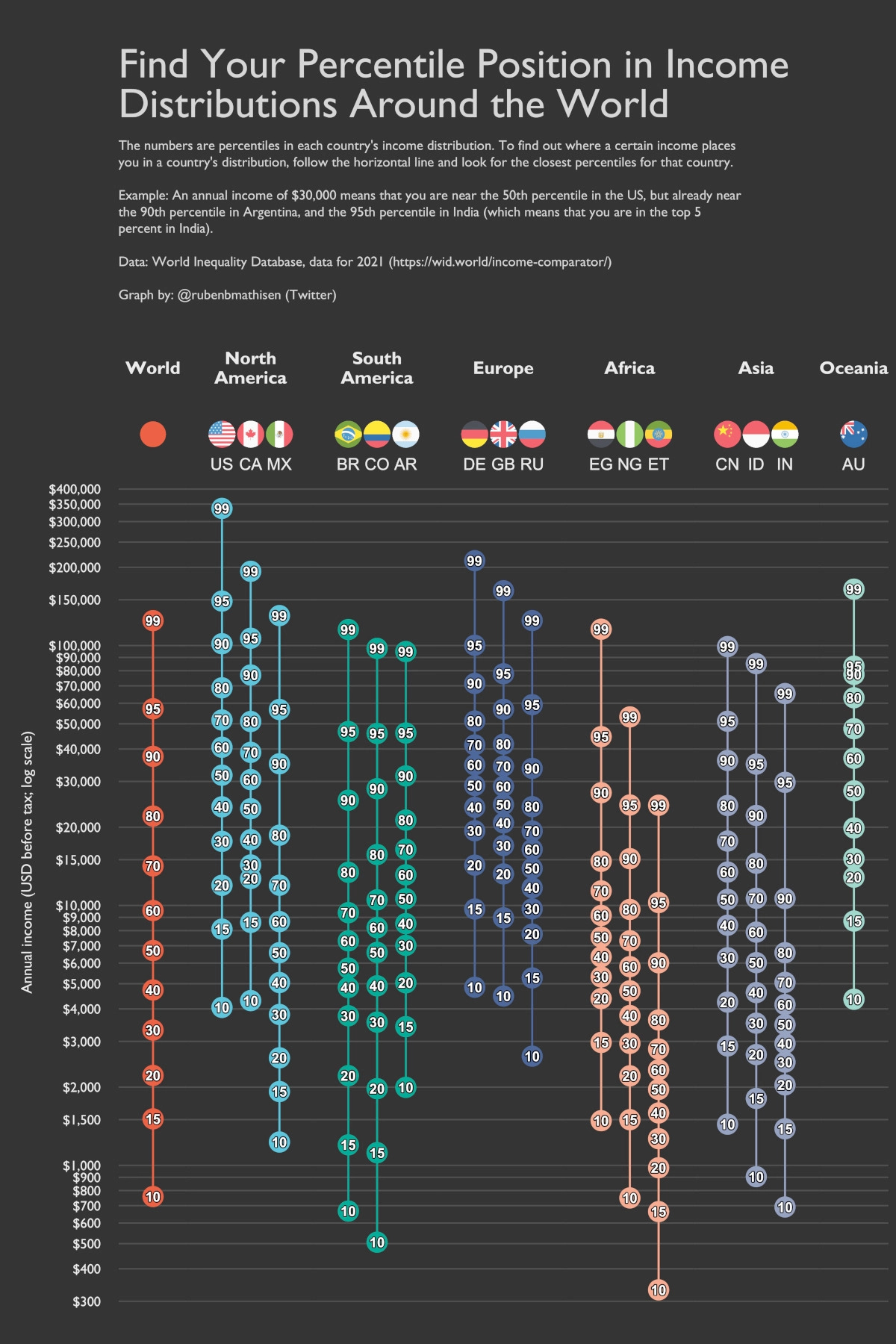
Charting Income Distributions in 16 Different Countries
Throughout the 19th century, roughly 80% of the global population lived in what we’d now consider extreme poverty.
And as earnings and living conditions have improved dramatically since then, they haven’t done so evenly across the world. There are still vast income gaps, both between different countries and within them.
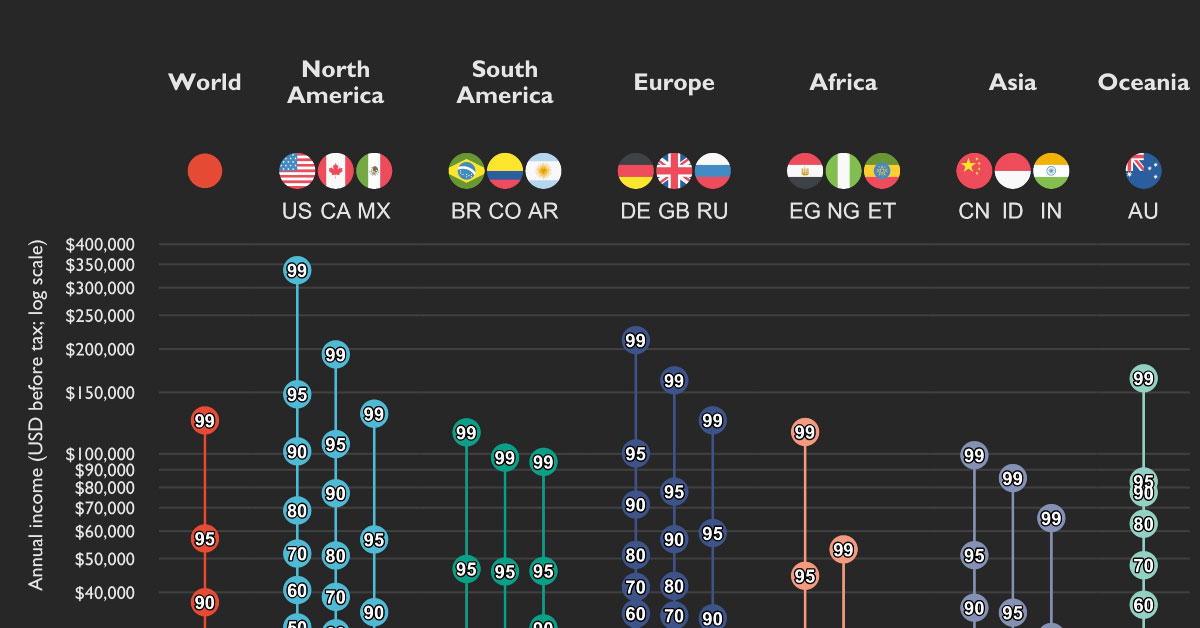
To highlight these global income discrepancies, this chart by Ruben Berge Mathisen shows income distributions around the world, using 2021 income data from the World Inequality Database (WID) on a per adult basis.
Global Income Distributions
This graphic shows the adult income distributions of 16 different countries in U.S. dollars, along with the world average.
On a global scale, adults making an annual income greater than $124,720 make it into the 99th percentile, meaning they make more than 99% of the worldwide population.
However, things change when you zoom in on specific countries. Here’s a look at all the countries on the list, and how much annual income is needed (at minimum) to be in the top 1%:
| Region | Country | Adult income (2021, 99th percentile) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 🇺🇸 United States | $336,953.19 |
| North America | 🇨🇦 Canada | $193,035.55 |
| North America | 🇲🇽 Mexico | $130,388.19 |
| South America | 🇧🇷 Brazil | $115,257.86 |
| South America | 🇨🇴 Colombia | $97,500.37 |
| South America | 🇦🇷 Argentina | $94,794.89 |
| Asia | 🇨🇳 China | $99,095.34 |
| Asia | 🇮🇳 India | $65,370.51 |
| Asia | 🇮🇩 Indonesia | $85,176.35 |
| Europe | 🇷🇺 Russia | $124,805.86 |
| Europe | 🇩🇪 Germany | $212,106.53 |
| Europe | 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | $162,547.56 |
| Africa | 🇳🇬 Nigeria | $53,144.36 |
| Africa | 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | $24,295.66 |
| Africa | 🇪🇬 Egypt | $115,546.44 |
| Oceania | 🇦🇺 Australia | $164,773.40 |
| 🌎 World | $124,719.60 |
People in America’s top 1% make at least $336,953 in annual pre-tax income. That’s more than $100,000 above the 1% of next closest countries, Germany ($212,107) and Canada ($193,036).
On the flip side, adults in Ethiopia only need to make $24,297 to fall into the country’s 99th percentile. Ethiopia is one of the poorest nations in the world—according to estimates by the World Bank, about 27% of Ethiopia’s population is thought to be currently living under the poverty line.
Income Gaps Within Countries
It is also noticeable how much income varies within each country.
One example is Colombia, which has one of the largest wealth gaps of any country on the list. The 99th percentile in Colombia is making an annual income that’s 192x higher than its 10th percentile. In contrast, an income in the 99th percentile in the United States is 83x higher than the 10th percentile.
Colombia’s high level of income inequality stems from early childhood disadvantages, such as lack of access to education, which can limit opportunities later on in life.

This article was published as a part of Visual Capitalist's Creator Program, which features data-driven visuals from some of our favorite Creators around the world.
Money
Charted: Who Has Savings in This Economy?
Older, better-educated adults are winning the savings game, reveals a January survey by the National Opinion Research Center at the University of Chicago.
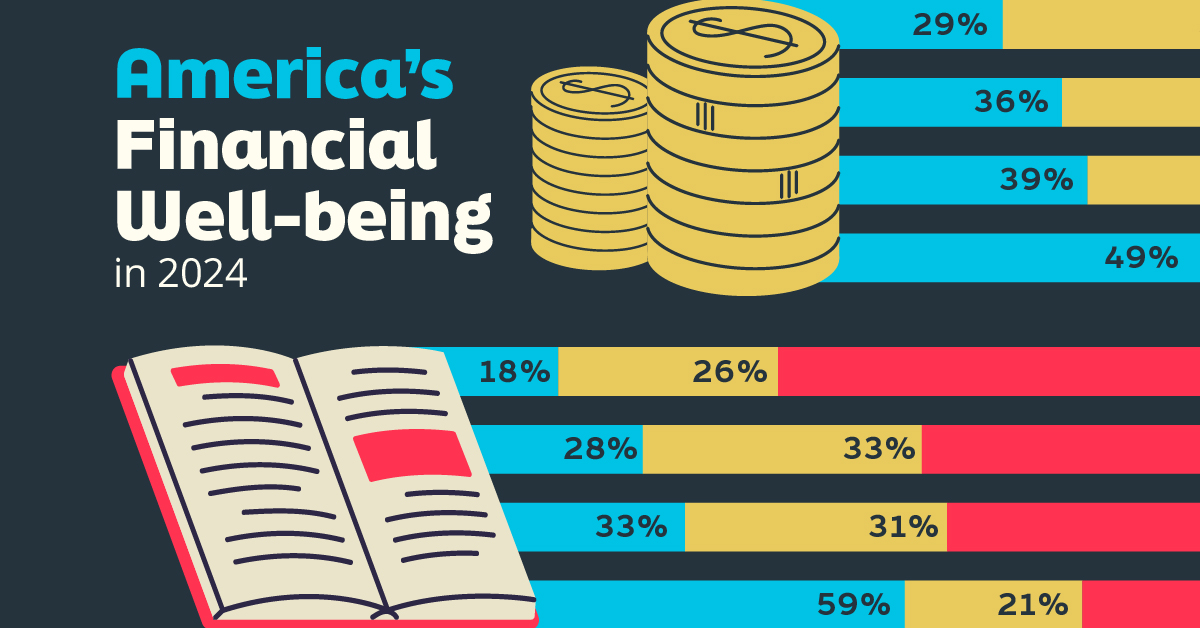
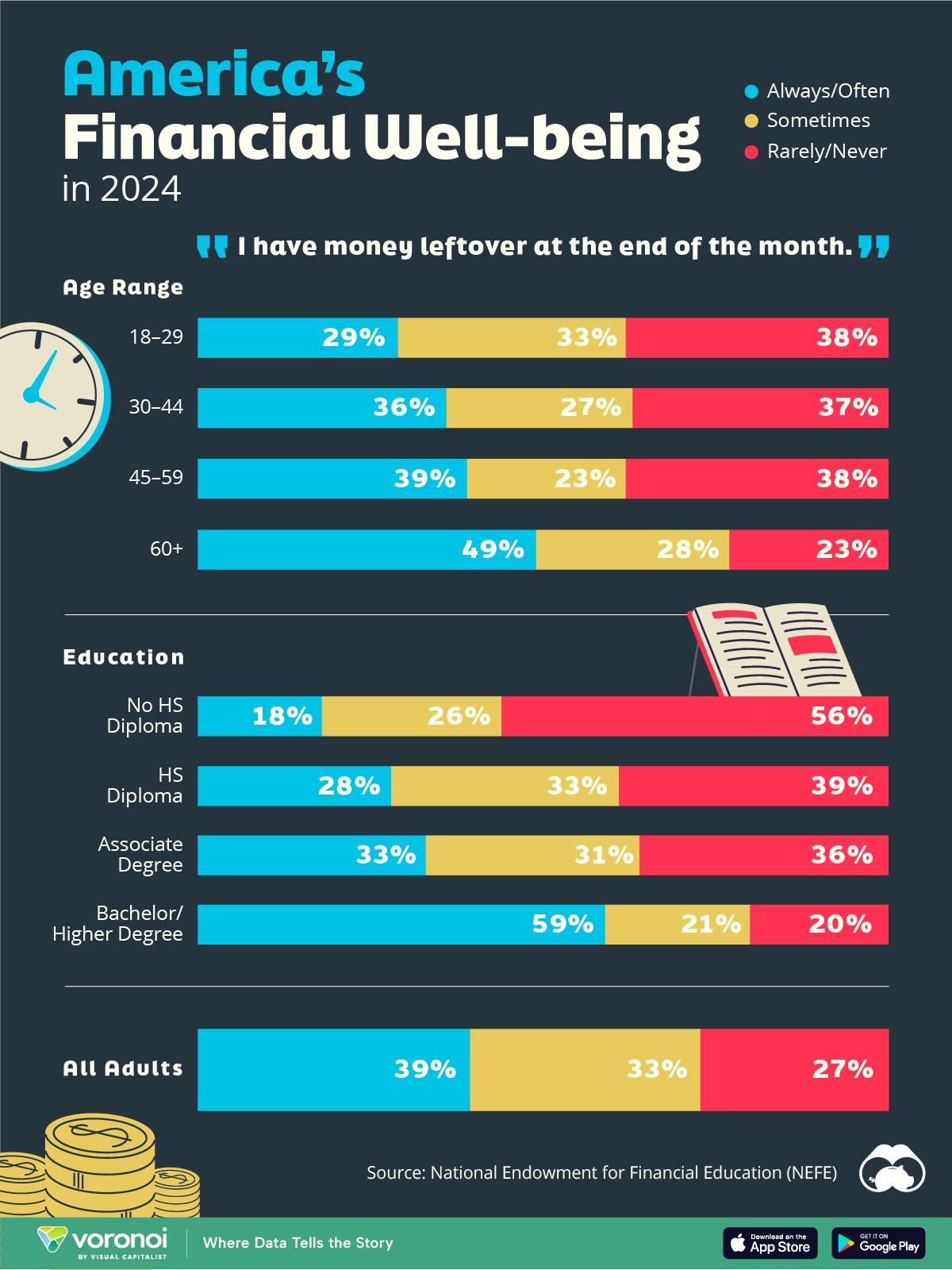
Who Has Savings in This Economy?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Two full years of inflation have taken their toll on American households. In 2023, the country’s collective credit card debt crossed $1 trillion for the first time. So who is managing to save money in the current economic environment?
We visualize the percentage of respondents to the statement “I have money leftover at the end of the month” categorized by age and education qualifications. Data is sourced from a National Endowment for Financial Education (NEFE) report, published last month.
The survey for NEFE was conducted from January 12-14, 2024, by the National Opinion Research Center at the University of Chicago. It involved 1,222 adults aged 18+ and aimed to be representative of the U.S. population.
Older Americans Save More Than Their Younger Counterparts
General trends from this dataset indicate that as respondents get older, a higher percentage of them are able to save.
| Age | Always/Often | Sometimes | Rarely/Never |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18–29 | 29% | 33% | 38% |
| 30–44 | 36% | 27% | 37% |
| 45–59 | 39% | 23% | 38% |
| Above 60 | 49% | 28% | 23% |
| All Adults | 39% | 33% | 27% |
Note: Percentages are rounded and may not sum to 100.
Perhaps not surprisingly, those aged 60+ are the age group with the highest percentage saying they have leftover money at the end of the month. This age group spent the most time making peak earnings in their careers, are more likely to have investments, and are more likely to have paid off major expenses like a mortgage or raising a family.
The Impact of Higher Education on Earnings and Savings
Based on this survey, higher education dramatically improves one’s ability to save. Shown in the table below, those with a bachelor’s degree or higher are three times more likely to have leftover money than those without a high school diploma.
| Education | Always/Often | Sometimes | Rarely/Never |
|---|---|---|---|
| No HS Diploma | 18% | 26% | 56% |
| HS Diploma | 28% | 33% | 39% |
| Associate Degree | 33% | 31% | 36% |
| Bachelor/Higher Degree | 59% | 21% | 20% |
| All Adults | 39% | 33% | 27% |
Note: Percentages are rounded and may not sum to 100.
As the Bureau of Labor Statistics notes, earnings improve with every level of education completed.
For example, those with a high school diploma made 25% more than those without in 2022. And as the qualifications increase, the effects keep stacking.
Meanwhile, a Federal Reserve study also found that those with more education tended to make financial decisions that contributed to building wealth, of which the first step is to save.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023