Technology
Computational Design: The Future of How We Make Things is Tech-Driven

Future Design is Computational
Design is always changing, and never stagnant.
In the late 20th century, it was the emergence of Design Thinking that upended how architects, engineers, and industrial design organizations made decisions about how to make new things.
Now, the rapid pace of technological advancement has brought forth a new design methodology that will again forever alter the course of design history. Computational design, which takes advantage of mass computing power, machine learning, and large amounts of data, is changing the fundamental role of humans in the design process.
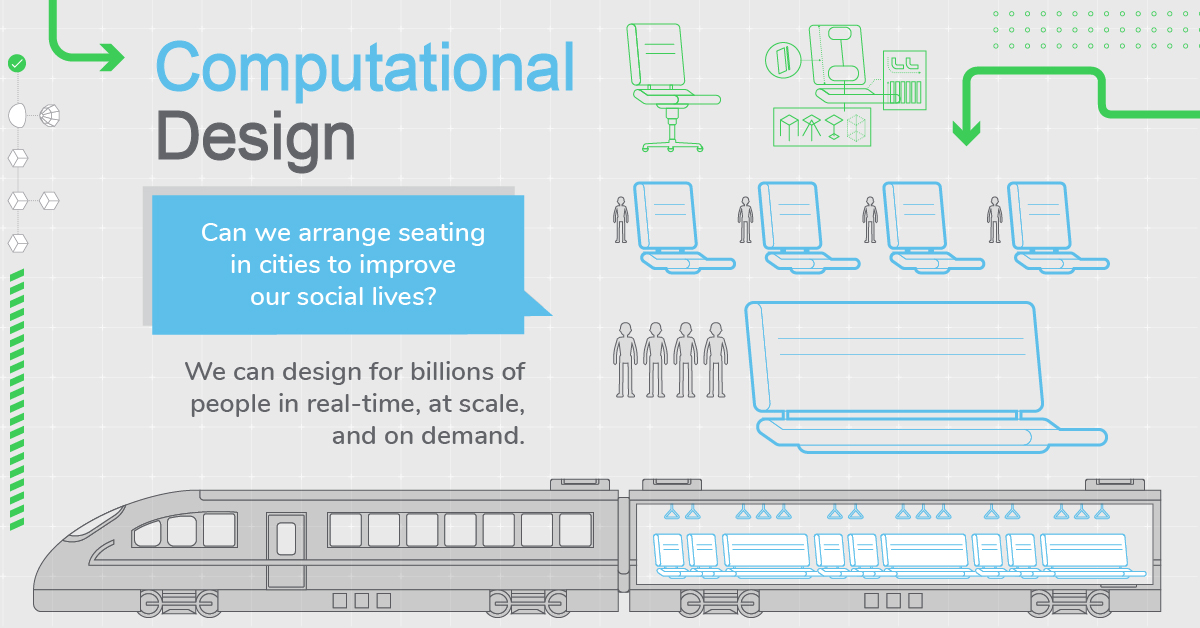
Designing With Billions of Data Points
Today’s infographic comes to us from Schneider Electric, and it looks at how the future of design will be driven by data and processing power.
While computational design is still a term with no real consensus, attempts to define it do have overlap:
Parameter setting
Algorithmic, “rules-based” code can be applied as constraints to test a wide variety of computer-driven designs
3d modelling and visualization tools
Complex 3d models can allow designers to test and create simulations for new ideas
Processing power
Using vast amounts of computational power and automation to make designs not before possible
Designing with data
Applying big data and powerful algorithms to create new designs
Generative design
By creating, testing, and analyzing thousands of design permutations, this approach mimics mother nature’s evolutionary path to design
While designers traditionally rely on intuition and experience to solve design problems, computational design is a new design methodology that can literally produce hundreds or thousands of design permutations to find the absolute best solution to a problem.
The Shifting Roles of Humans and Computers
Throughout history, humans have shaped the world with design.
But now that artificial intelligence is superior in taking on specific roles within the design process, humans will move towards shaping the things that shape the world.
Designers will be relinquishing control to technology, so that humans can do what they do best.
In other words, in the future, designers will work less on designing – and instead will supervise, mentor, and set the parameters for computational designs. Human designers would also interact with a broader group of stakeholders as additional inputs and the frequency of interactions increase.
A New Design Landscape
Disruption to traditional design methods brings more questions than answers:
- How will this change the value chain for design companies and professionals?
- Will AI-enabled computational design tools take the “craft” out of design?
- If automated design “assets” become commercial commodities, will that create new product and revenue channels for businesses?
- Who will own and manage all of this data, and does this create new roles and opportunities for companies?
As we give machines more design autonomy, it will be interesting to see how this literally changes the shape and design of objects that make up the real world.
Technology
Ranked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Did you know that some computer chips are now retailing for the price of a new BMW?
As computers invade nearly every sphere of life, so too have the chips that power them, raising the revenues of the businesses dedicated to designing them.
But how did various chipmakers measure against each other last year?
We rank the biggest semiconductor companies by their percentage share of the industry’s revenues in 2023, using data from Omdia research.
Which Chip Company Made the Most Money in 2023?
Market leader and industry-defining veteran Intel still holds the crown for the most revenue in the sector, crossing $50 billion in 2023, or 10% of the broader industry’s topline.
All is not well at Intel, however, with the company’s stock price down over 20% year-to-date after it revealed billion-dollar losses in its foundry business.
| Rank | Company | 2023 Revenue | % of Industry Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intel | $51B | 9.4% |
| 2 | NVIDIA | $49B | 9.0% |
| 3 | Samsung Electronics | $44B | 8.1% |
| 4 | Qualcomm | $31B | 5.7% |
| 5 | Broadcom | $28B | 5.2% |
| 6 | SK Hynix | $24B | 4.4% |
| 7 | AMD | $22B | 4.1% |
| 8 | Apple | $19B | 3.4% |
| 9 | Infineon Tech | $17B | 3.2% |
| 10 | STMicroelectronics | $17B | 3.2% |
| 11 | Texas Instruments | $17B | 3.1% |
| 12 | Micron Technology | $16B | 2.9% |
| 13 | MediaTek | $14B | 2.6% |
| 14 | NXP | $13B | 2.4% |
| 15 | Analog Devices | $12B | 2.2% |
| 16 | Renesas Electronics Corporation | $11B | 1.9% |
| 17 | Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation | $10B | 1.9% |
| 18 | Microchip Technology | $8B | 1.5% |
| 19 | Onsemi | $8B | 1.4% |
| 20 | KIOXIA Corporation | $7B | 1.3% |
| N/A | Others | $126B | 23.2% |
| N/A | Total | $545B | 100% |
Note: Figures are rounded. Totals and percentages may not sum to 100.
Meanwhile, Nvidia is very close to overtaking Intel, after declaring $49 billion of topline revenue for 2023. This is more than double its 2022 revenue ($21 billion), increasing its share of industry revenues to 9%.
Nvidia’s meteoric rise has gotten a huge thumbs-up from investors. It became a trillion dollar stock last year, and broke the single-day gain record for market capitalization this year.
Other chipmakers haven’t been as successful. Out of the top 20 semiconductor companies by revenue, 12 did not match their 2022 revenues, including big names like Intel, Samsung, and AMD.
The Many Different Types of Chipmakers
All of these companies may belong to the same industry, but they don’t focus on the same niche.
According to Investopedia, there are four major types of chips, depending on their functionality: microprocessors, memory chips, standard chips, and complex systems on a chip.
Nvidia’s core business was once GPUs for computers (graphics processing units), but in recent years this has drastically shifted towards microprocessors for analytics and AI.
These specialized chips seem to be where the majority of growth is occurring within the sector. For example, companies that are largely in the memory segment—Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron Technology—saw peak revenues in the mid-2010s.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoAmerica’s Top Companies by Revenue (1994 vs. 2023)
-

 Environment1 week ago
Environment1 week agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoVisualizing the Size of the Global Senior Population
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoTesla Is Once Again the World’s Best-Selling EV Company
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Popular Smartphone Brands in the U.S.