Politics
Cheat Sheet: The Third Party Presidential Candidates

Cheat Sheet: The Third Party Presidential Candidates
It’s coming closer to election time, and it’s hard to shake the feeling that something crazy or unprecedented could happen in the coming months.
Trump and Clinton are the most disliked presidential candidates in history, both having an “unfavorable” image with the majority of the U.S. population. Meanwhile, according to a recent Pew Research poll, only 24% of registered voters feel that the next generation of Americans will be better off than folks today.
Picking up Steam
For the first time in almost 20 years, the third-party candidates are getting attention across the board. Gary Johnson (Libertarian) and Jill Stein (Green) are even getting regular mainstream coverage from outlets such as CNN, Vox, The Washington Post, The NY Times, Forbes, and The Wall Street Journal.
The poll numbers for Johnson and Stein are respectable, especially among the millennial crowd where they garner around 40% of voter support. When it comes to the general electorate, however, average poll numbers are more muted with Johnson averaging 9% and Stein 3%.
The numbers are not enough to meet the arbitrary 15% threshold for the first round of debates, but the third-party candidates are starting to pick up steam in other areas. For example, Gary Johnson just shattered a fundraising record for the Libertarian Party by raising $5 million in August. Meanwhile, Stein is preparing for a major publicity stunt at Hofstra University in New York – the site of the first Presidential Debate on September 26th.
An End to the Two-Party Duopoly?
Regardless of how Johnson and Stein fare, this year could symbolize a resurgence for third-party candidates in the national conversation. After all, it seems that growing discontent with the two-party duopoly can be found in a variety of places.
More people are now aware that the committee that set the arbitrary debate threshold of 15% was established jointly by RNC and DNC officials. This makes it almost impossible to get a third-party candidate onto the debate stage. However, if you ask actual voters about the third-party candidates, the answer is clear: 52% of Americans want to see Gary Johnson in the debates, while 47% would like to have Jill Stein’s voice heard.
Further, supporters of Bernie Sanders found out first-hand that the elections are not as democratic as they once seemed. Leaked emails from the DNC showed that the party worked against Sanders to ensure a Clinton nomination. Sanders supporters also found out the true power of superdelegates, which were initially created by the DNC elites to ensure their choices were considered disproportionately.
Lastly, it’s also worth noting that the media landscape has changed. There is no longer a few television networks that dominate the conversation, and people now have more access to independent media than ever before. This fragmentation increases competition and gives outsiders the opportunity to express opinions – it also allows groups like Wikileaks to do their thing by uncovering scandals or other unfair play. The new generation of media will lead to the exploration of different alternatives in both opinion and policy. With that will come more support for third-party candidates that align themselves with those viewpoints.
Some people will consider a vote for a third-party candidate as a waste, and others will condemn it as a mere “protest” vote. Likely, some people will also consider Johnson and Stein as the candidates that best reflect their values, and they’ll consider the “lesser of two evils” argument to be one without merit.
Regardless of what happens, for better or worse, the Libertarians and Greens will likely leave their stamp on this election. Hopefully it’s one that ends up being a net positive for the future.
War
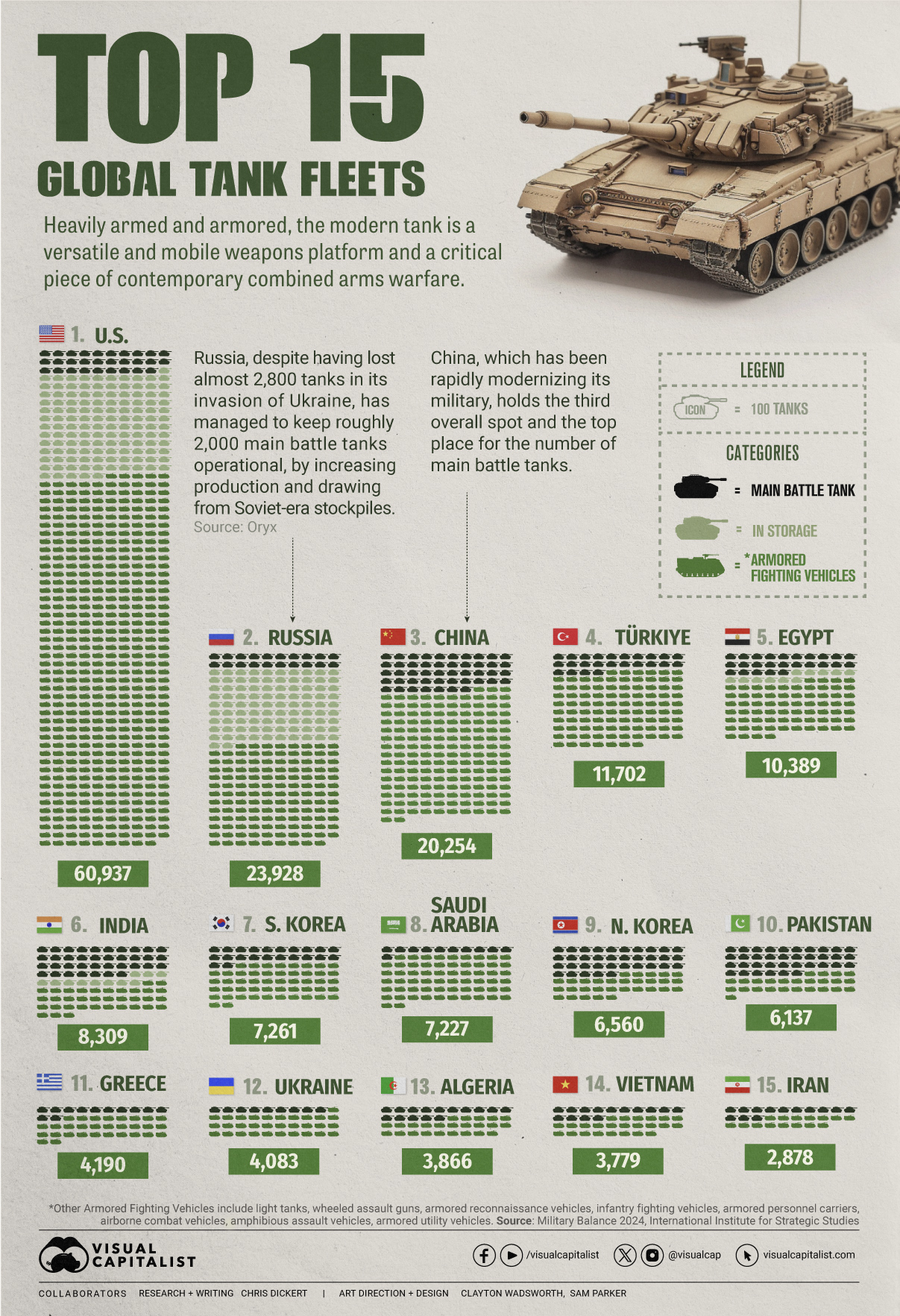
Visualized: Top 15 Global Tank Fleets
Heavily armed and armored, the modern tank is a versatile and mobile weapons platform, and a critical piece of contemporary warfare.

The Top 15 Global Tank Fleets
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Heavily armed and armored, the modern tank is a versatile and mobile weapons platform, and a critical piece of contemporary warfare.
This visualization shows the top 15 global tank fleets, using data from the 2024 Military Balance report from the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS).
Let’s take an in-depth look at the top three fleets:
1. United States
As the world’s pre-eminent military power, it’s perhaps no surprise that the United States also has the largest tank fleet, by a wide margin.
In total, they have just over 45,000 armored fighting vehicles in operation, along with 2,640 main battle tanks (MBTs), and 12,800 vehicles in storage, of which 2,000 are main battle tanks.
| Category | Vehicles | Global rank |
|---|---|---|
| Main battle tanks | 2,640 | 4 |
| Armored reconnaissance | 1,745 | 1 |
| Infantry fighting vehicles | 3,262 | 3 |
| Armored personnel carriers | 10,644 | 1 |
| Amphibious assault vehicles | 1,401 | 1 |
| Armored utility vehicles | 28,445 | 1 |
| Storage | 12,800 | 1 |
| Total | 60,937 | 1 |
The U.S. is internalizing the lessons from the ongoing invasion of Ukraine, where Western-supplied anti-tank weapons and massed Ukrainian artillery have been cutting Russian tanks to pieces. As a result, the U.S. recently canceled an upgrade of the M1 Abrams in favor of a more ambitious upgrade.
Meanwhile, the U.S. is nervously eyeing a more confident China and a potential clash over Taiwan, where air and naval forces will be critical. However, a recent war game showed that Taiwanese mechanized ground forces, kitted out with American-made tanks and armored fighting vehicles, were critical in keeping the island autonomous.
2. Russia
According to Oryx, a Dutch open-source intelligence defense website, at time of writing, Russia has lost almost 2,800 main battle tanks since invading Ukraine. Considering that in the 2022 edition of the Military Balance, Russia was estimated to have 2,927 MBTs in operation, those are some hefty losses.
Russia has been able to maintain about 2,000 MBTs in the field, in part, by increasing domestic production. Many defense plants have been taken over by state-owned Rostec and now operate around the clock. Russia is also now spending a full third of their budget on defense, equivalent to about 7.5% of GDP.
At the same time, they’ve also been drawing down their Soviet-era stockpiles, which are modernized before being sent to the front. Just how long they can keep this up is an open question; their stockpiles are large, but not limitless. Here is what their storage levels look like:
| Category | 2023 | 2024 | YOY change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main battle tanks | 5,000 | 4,000 | -20.0% |
| Armored reconnaissance | 1,000 | 100 | -90.0% |
| Infantry fighting vehicles | 4,000 | 2,800 | -30.0% |
| Armored personnel carriers | 6,000 | 2,300 | -61.7% |
| Total | 16,000 | 9,200 | -42.5% |
3. China
China holds the third overall spot and top place globally for the number of main battle tanks in operation. Untypically, the People’s Liberation Army has no armored vehicles in storage, which perhaps isn’t surprising when you consider that China has been rapidly modernizing its military and that stockpiles usually contain older models.
China also has one of the world’s largest fleets of armored fighting vehicles, second only to the United States. Breaking down that headline number, we can also see that they have the largest number of light tanks, wheeled guns, and infantry fighting vehicles.
| Category | Vehicles | Global rank |
|---|---|---|
| Main battle tanks | 4,700 | 1 |
| Light tanks | 1,330 | 1 |
| Wheeled guns | 1,250 | 1 |
| Infantry fighting vehicles | 8,200 | 1 |
| Armored personnel carriers | 3,604 | 5 |
| Airborne combat vehicles | 180 | 2 |
| Amphibious assault vehicles | 990 | 2 |
| Total | 20,254 | 3 |
This is equipment that would be integral if China were to make an attempt to reunify Taiwan with the mainland by force, where lightly armored mechanized units need to move with speed to occupy the island before Western allies can enter the fray. It’s worth noting that China also has one of the world’s largest fleets of amphibious assault vehicles.
End of the Tank?
Many commentators at the outset of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, were quick to predict the end of the tank, however, to paraphrase Mark Twain, reports of the tank’s demise are greatly exaggerated.
With the U.S. and China both developing remote and autonomous armored vehicles, tanks could be quite different in the future, but there is nothing else that matches them for firepower, mobility, and survivability on the modern battlefield today.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoRanked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
-

 Green3 weeks ago
Green3 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?