Markets
Charting the Rise and Fall of the Global Luxury Goods Market
The Rise and Fall of the Global Luxury Goods Market
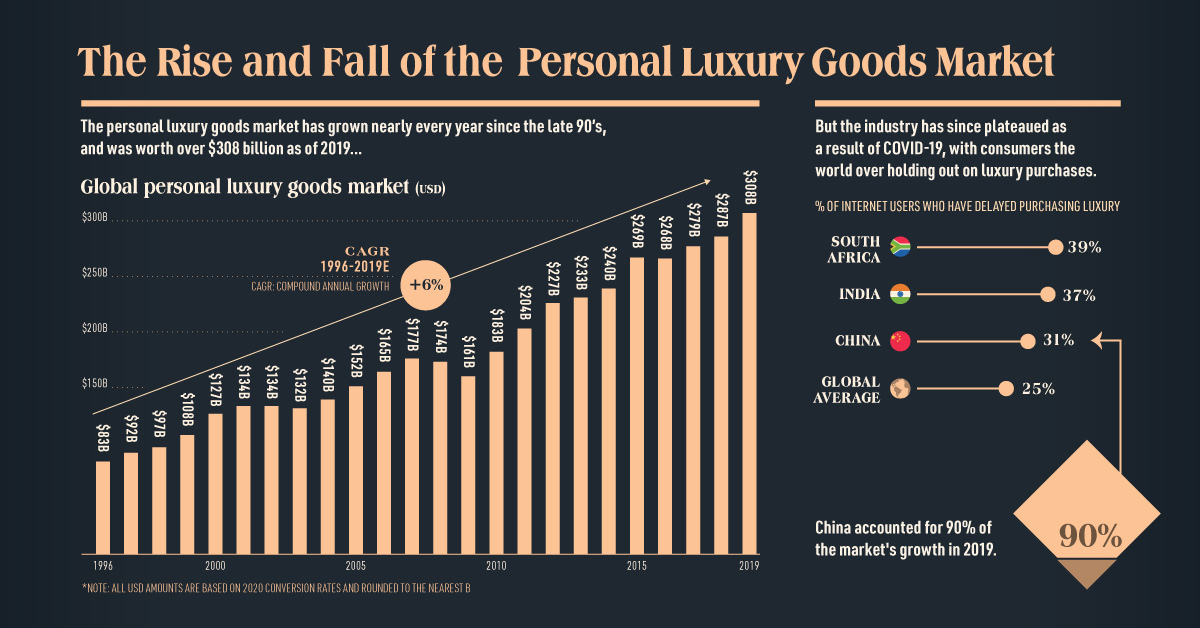
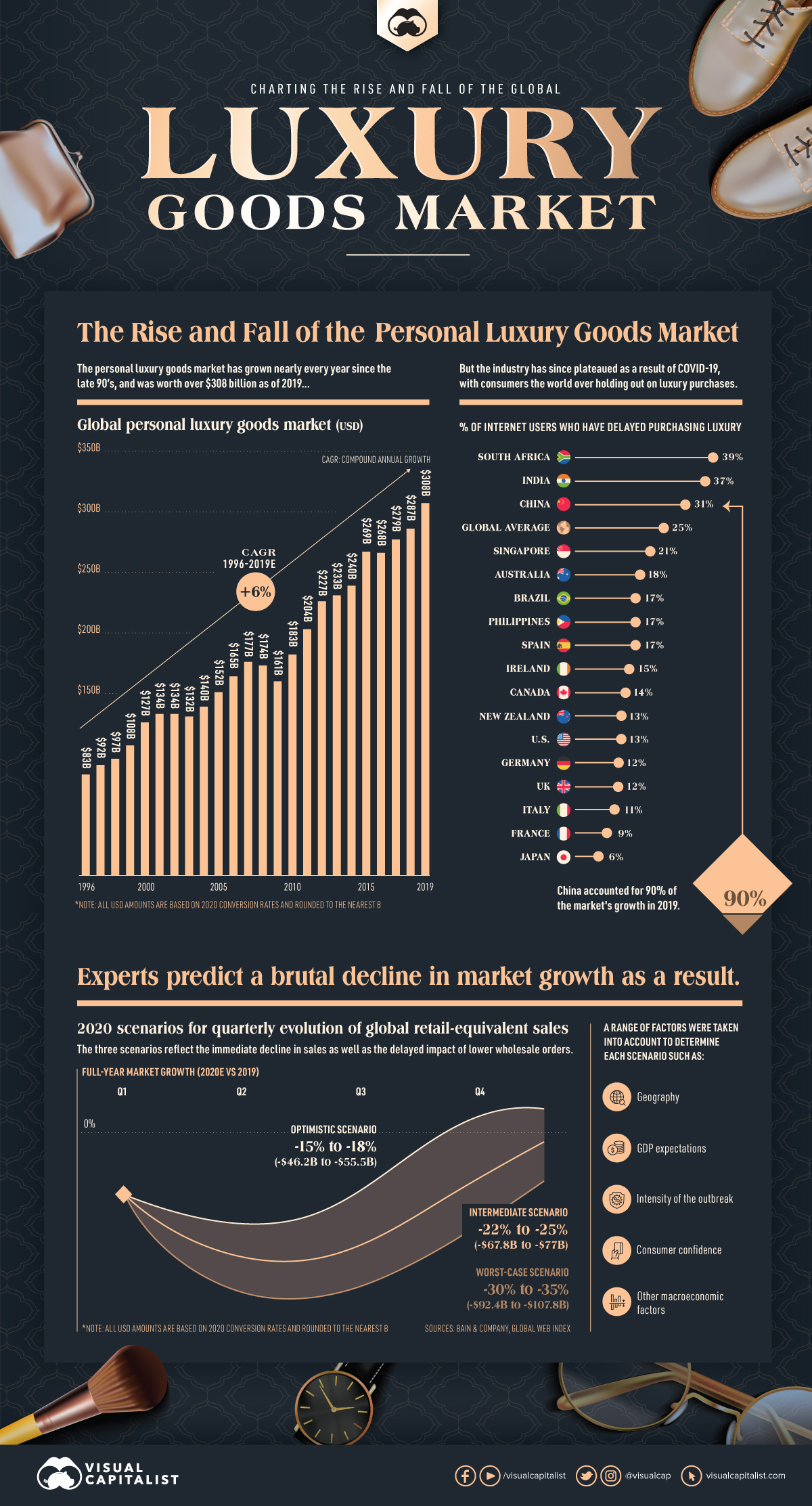
Global demand for personal luxury goods has been steadily increasing for decades, resulting in an industry worth $308 billion in 2019.
However, the insatiable desire for consumers to own nice things was suddenly interrupted by the coming of COVID-19, and experts are predicting a brutal contraction of up to one-third of the current luxury good market size this year.
Will the industry bounce back? Or will it return as something noticeably different?
A Once Promising Trajectory
The global luxury goods market—which includes beauty, apparel, and accessories—has compounded at a 6% pace since the 1990s.
Recent years of growth in the personal luxury goods market can be mostly attributed to Chinese consumers. This geographic market accounted for 90% of total sales growth in 2019, followed by the Europe and the Americas.
Analysts suggest that China’s younger luxury goods consumers in particular have significant spending power, with an average spend of $6,000 (¥41,000) per person in pre-COVID times.
An Industry Now in Distress
The lethal combination of reduced foot traffic and decreased consumer spending in the first quarter of 2020 has brought the retail industry to its knees.
In fact, more than 80% of fashion and luxury players will experience financial distress as a result of extended store closures.
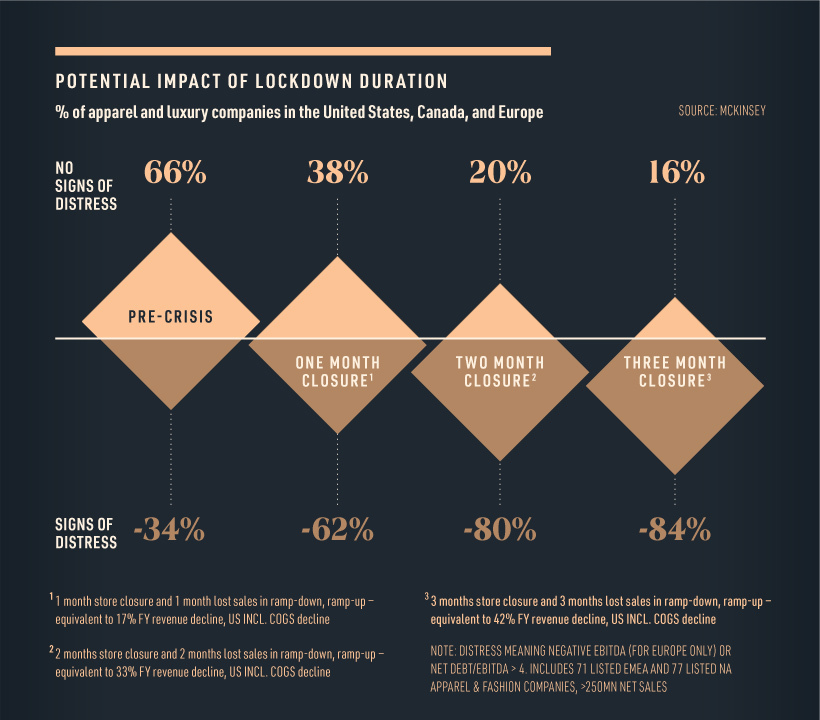
With iconic luxury retailers such as Neiman Marcus filing for bankruptcy, the pressure on the luxury industry is clear. It should be noted however, that companies who were experiencing distress before the COVID-19 outbreak will be the hardest hit.
Predicting the Collapse
In a recent report, Bain & Company estimated a 25% to 30% global luxury market contraction for the first quarter of 2020 based on several economic variables. They have also modeled three scenarios to predict the performance for the remainder of 2020.
- Optimistic scenario: A limited market contraction of 15% to 18%, assuming increased consumer demand for the second and third quarter of the year, roughly equating to a sales decline of $46 billion to $56 billion.
- Intermediate scenario: A moderate market contraction of between 22% and 25%, or $68 to $77 billion.
- Worst-case scenario: A steep contraction of between 30% and 35%, equating to $92 billion to $108 billion. This assumes a longer period of sales decline.
Although there are signs of recovery in China, the industry is not expected to fully return to 2019 levels until 2022 at the earliest. By that stage, the industry could have transformed entirely.
Changing Consumer Mindsets
Since the beginning of the pandemic, one-quarter of consumers have delayed purchasing luxury items. In fact, a portion of those who have delayed purchasing luxury goods are now considering entirely new avenues, such as seeking out cheaper alternatives.
However, most people surveyed claim that they will postpone buying luxury items until they can get a better deal on price.
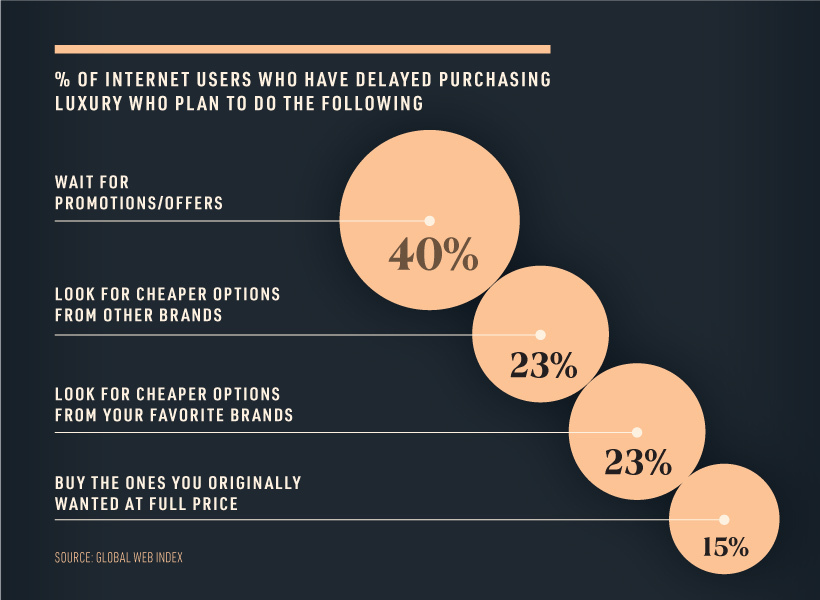
This frugal mindset could spark an interesting behavioral shift, and set the stage for a new category to emerge from the ashes—the second-hand luxury market.
Numerous sources claim that pre-owned luxury could in fact overtake the traditional luxury market, and the pandemic economy could very well be a tipping point.
The Future of Luxury
Medium-term market growth could be driven by a number of factors, from a global growing middle class and their demand for luxury products, as well as retailers’ sudden shift to e-commerce.
While analysts can only rely on predictions to determine the future of personal luxury, it is clear that the industry is at a crossroads.
Markets
Ranked: The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
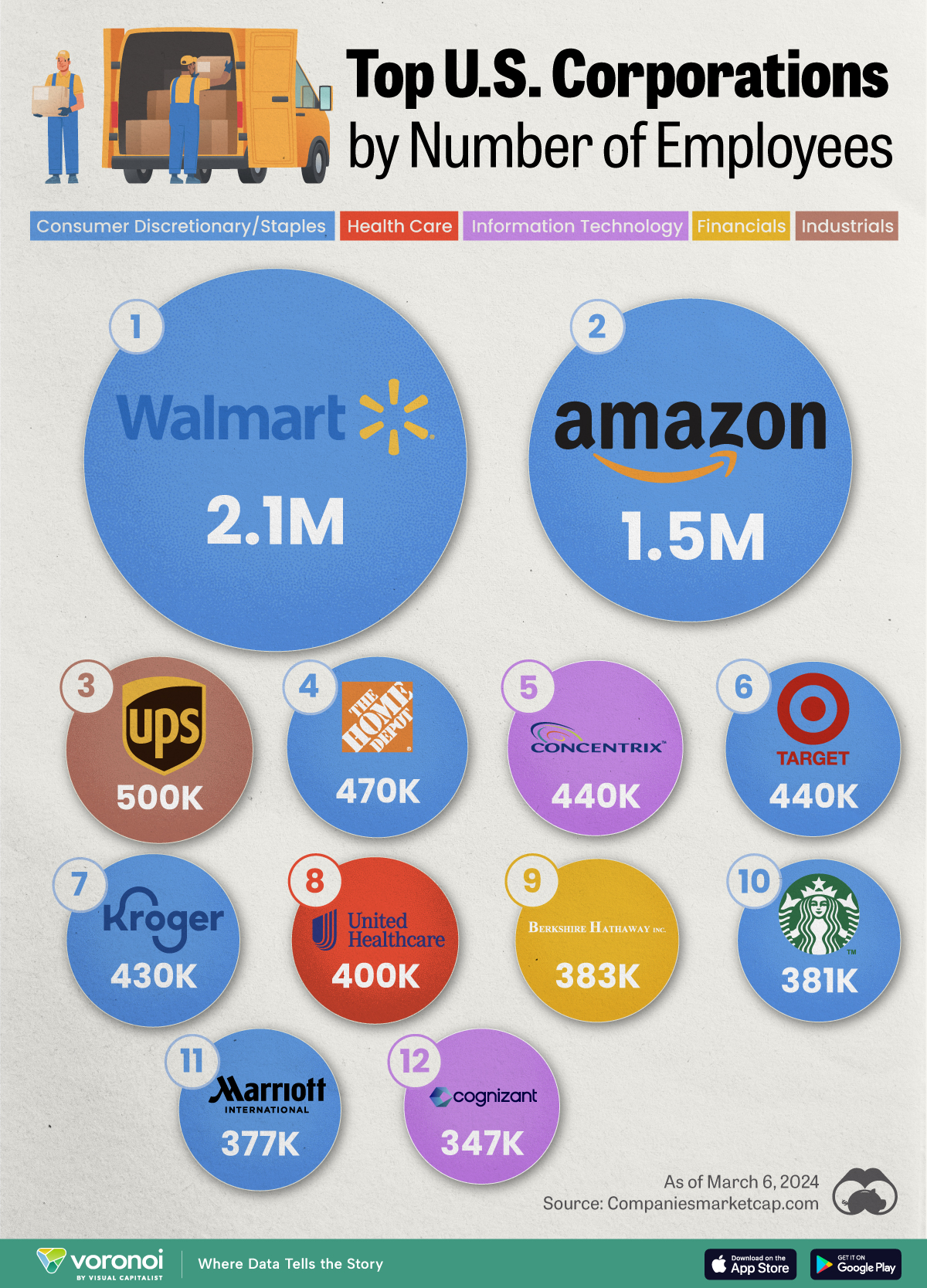
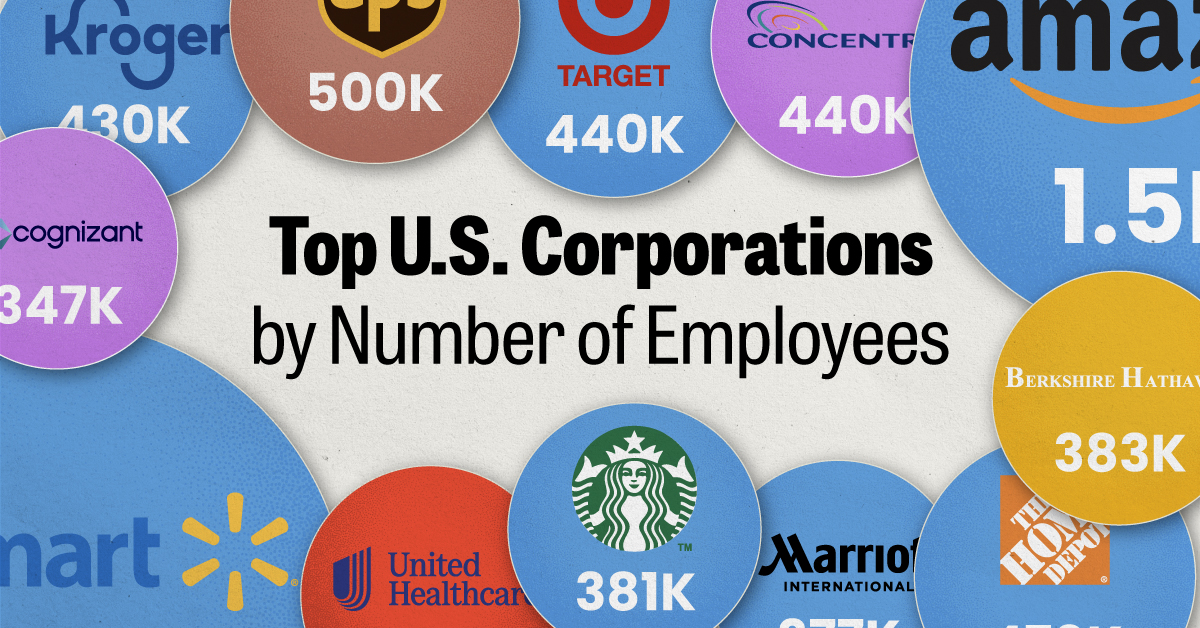
We visualized the top U.S. companies by employees, revealing the massive scale of retailers like Walmart, Target, and Home Depot.
The Largest U.S. Corporations by Number of Employees
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Revenue and profit are common measures for measuring the size of a business, but what about employee headcount?
To see how big companies have become from a human perspective, we’ve visualized the top U.S. companies by employees. These figures come from companiesmarketcap.com, and were accessed in March 2024. Note that this ranking includes publicly-traded companies only.
Data and Highlights
The data we used to create this list of largest U.S. corporations by number of employees can be found in the table below.
| Company | Sector | Number of Employees |
|---|---|---|
| Walmart | Consumer Staples | 2,100,000 |
| Amazon | Consumer Discretionary | 1,500,000 |
| UPS | Industrials | 500,000 |
| Home Depot | Consumer Discretionary | 470,000 |
| Concentrix | Information Technology | 440,000 |
| Target | Consumer Staples | 440,000 |
| Kroger | Consumer Staples | 430,000 |
| UnitedHealth | Health Care | 400,000 |
| Berkshire Hathaway | Financials | 383,000 |
| Starbucks | Consumer Discretionary | 381,000 |
| Marriott International | Consumer Discretionary | 377,000 |
| Cognizant | Information Technology | 346,600 |
Retail and Logistics Top the List
Companies like Walmart, Target, and Kroger have a massive headcount due to having many locations spread across the country, which require everything from cashiers to IT professionals.
Moving goods around the world is also highly labor intensive, explaining why UPS has half a million employees globally.
Below the Radar?
Two companies that rank among the largest U.S. corporations by employees which may be less familiar to the public include Concentrix and Cognizant. Both of these companies are B2B brands, meaning they primarily work with other companies rather than consumers. This contrasts with brands like Amazon or Home Depot, which are much more visible among average consumers.
A Note on Berkshire Hathaway
Warren Buffett’s company doesn’t directly employ 383,000 people. This headcount actually includes the employees of the firm’s many subsidiaries, such as GEICO (insurance), Dairy Queen (retail), and Duracell (batteries).
If you’re curious to see how Buffett’s empire has grown over the years, check out this animated graphic that visualizes the growth of Berkshire Hathaway’s portfolio from 1994 to 2022.
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoAmerica’s Top Companies by Revenue (1994 vs. 2023)
-

 Environment1 week ago
Environment1 week agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoVisualizing the Size of the Global Senior Population
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoTesla Is Once Again the World’s Best-Selling EV Company
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Popular Smartphone Brands in the U.S.