Markets
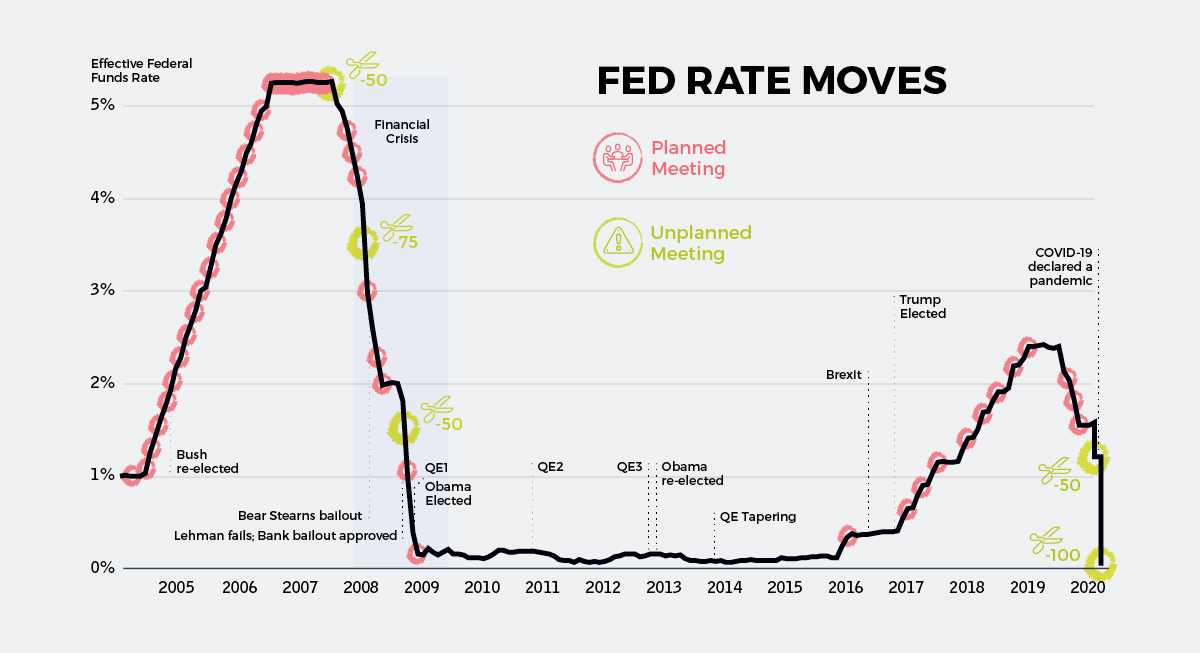
Chart: The Downward Spiral in Interest Rates
During the onset of an economic crisis, national governments are thought to have two chief policy tools at their disposal:
- Fiscal Policy
How the central government collects money through taxation, and how it spends that money - Monetary Policy
How central banks choose to manage the supply of money and interest rates
Major fiscal policy changes can take time to be implemented — but since central banks can make moves unilaterally, monetary policy is often the first line of defense in settling markets.
As the ripple effect of the COVID-19 pandemic rages on, central banks have been quick to act in slashing interest rates. However, with rates already sitting at historic lows before the crisis, it is possible that banks may be forced to employ more unconventional and controversial techniques to try and calm the economy as time goes on.
The Fed: Firing at Will
The most meaningful rate cuts happened on March 3rd and March 15th after emergency meetings in the United States.
First, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) cut the target rate from 1.5% to 1.0% — and then on Sunday (March 15th) the rate got chopped by an entire percentage point to rub up against the lower bound of zero.

As you can see on the chart, this puts us back into familiar territory: a policy environment analogous to that seen during the recovery from the financial crisis.
ZIRP or NIRP?
It’s been awhile, but with interest rates again bumping up against the lower bound, you’ll begin to see discussions pop up again about the effectiveness of zero interest rate policy (ZIRP) and even negative interest rate policy (NIRP).
Although the latter has been used by some European banks in recent years, NIRP has never been experimented with in the United States or Canada.
Here’s a quick primer on both:
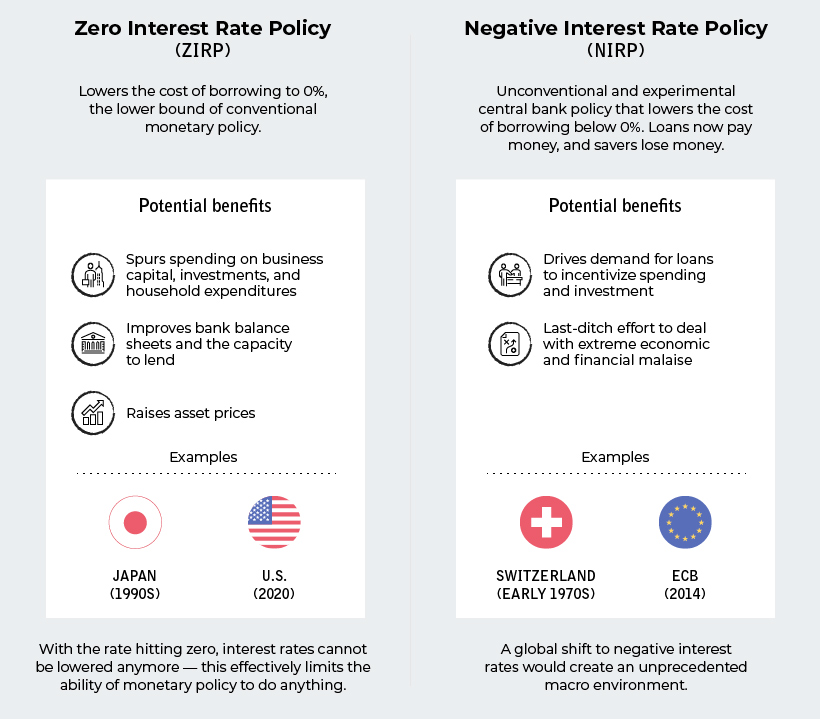
With rates sitting at zero, it’s not impossible for the Fed and other central banks to begin toying more seriously with the idea of negative rates. Such a move would be bold, but also seen as highly experimental and risky with unforeseen consequences.
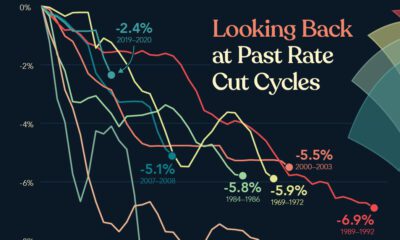
Global Rate Slashing
Since only the beginning of March, the world’s central banks have cut interest rates on 37 separate occasions.
The only exception to this rule was the National Bank of Kazakhstan, which raised its key rate by 2.75% to support its currency in light of current oil prices. Even so, the Kazakhstani tenge has lost roughly 15% of its value against the U.S. dollar since February.
Here’s a look at cumulative interest rate cuts by some of the world’s most important central banks, from January 1, 2020 until today:
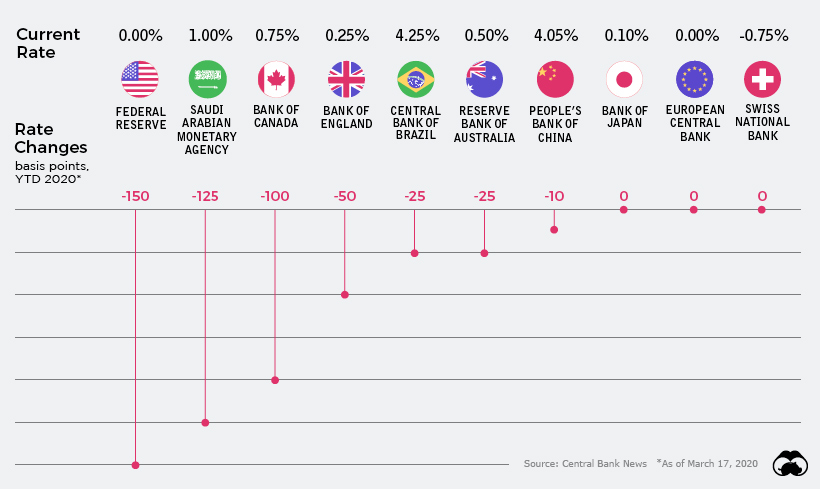
Going into the year, rates in developed economies were already between 0% and 2%.
Despite not having much room to work with, banks have slashed rates where they can — and now out of major developed economies, Canada has the “highest” interest rate at just 0.75%.
Helicopters on the Horizon
With central banks running out of ammo for the use of traditional measures, the conversation is quickly shifting to unconventional measures such as “helicopter money” and NIRP.
Life is already surreal as societal measures to defend against the spread of COVID-19 unfold; pretty soon, monetary measures taken around the globe may seem just as bizarre.
Put another way, unless something changes fast and miraculously, we could be moving into an unprecedented monetary environment where up is down, and down is up. At that point, it’s anybody’s guess as to how things will shake out going forward.
Economy
Economic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?

G7 & BRICS Real GDP Growth Forecasts for 2024
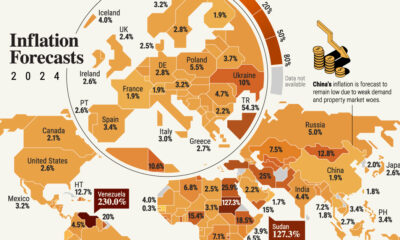
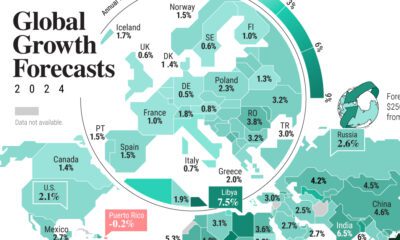
The International Monetary Fund’s (IMF) has released its real gross domestic product (GDP) growth forecasts for 2024, and while global growth is projected to stay steady at 3.2%, various major nations are seeing declining forecasts.
This chart visualizes the 2024 real GDP growth forecasts using data from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook for G7 and BRICS member nations along with Saudi Arabia, which is still considering an invitation to join the bloc.
Get the Key Insights of the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
Want a visual breakdown of the insights from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook report?
This visual is part of a special dispatch of the key takeaways exclusively for VC+ members.
Get the full dispatch of charts by signing up to VC+.
Mixed Economic Growth Prospects for Major Nations in 2024
Economic growth projections by the IMF for major nations are mixed, with the majority of G7 and BRICS countries forecasted to have slower growth in 2024 compared to 2023.
Only three BRICS-invited or member countries, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and South Africa, have higher projected real GDP growth rates in 2024 than last year.
| Group | Country | Real GDP Growth (2023) | Real GDP Growth (2024P) |
|---|---|---|---|
| G7 | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 2.5% | 2.7% |
| G7 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 1.1% | 1.2% |
| G7 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 1.9% | 0.9% |
| G7 | 🇫🇷 France | 0.9% | 0.7% |
| G7 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 0.9% | 0.7% |
| G7 | 🇬🇧 UK | 0.1% | 0.5% |
| G7 | 🇩🇪 Germany | -0.3% | 0.2% |
| BRICS | 🇮🇳 India | 7.8% | 6.8% |
| BRICS | 🇨🇳 China | 5.2% | 4.6% |
| BRICS | 🇦🇪 UAE | 3.4% | 3.5% |
| BRICS | 🇮🇷 Iran | 4.7% | 3.3% |
| BRICS | 🇷🇺 Russia | 3.6% | 3.2% |
| BRICS | 🇪🇬 Egypt | 3.8% | 3.0% |
| BRICS-invited | 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | -0.8% | 2.6% |
| BRICS | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 2.9% | 2.2% |
| BRICS | 🇿🇦 South Africa | 0.6% | 0.9% |
| BRICS | 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | 7.2% | 6.2% |
| 🌍 World | 3.2% | 3.2% |
China and India are forecasted to maintain relatively high growth rates in 2024 at 4.6% and 6.8% respectively, but compared to the previous year, China is growing 0.6 percentage points slower while India is an entire percentage point slower.
On the other hand, four G7 nations are set to grow faster than last year, which includes Germany making its comeback from its negative real GDP growth of -0.3% in 2023.
Faster Growth for BRICS than G7 Nations
Despite mostly lower growth forecasts in 2024 compared to 2023, BRICS nations still have a significantly higher average growth forecast at 3.6% compared to the G7 average of 1%.
While the G7 countries’ combined GDP is around $15 trillion greater than the BRICS nations, with continued higher growth rates and the potential to add more members, BRICS looks likely to overtake the G7 in economic size within two decades.
BRICS Expansion Stutters Before October 2024 Summit
BRICS’ recent expansion has stuttered slightly, as Argentina’s newly-elected president Javier Milei declined its invitation and Saudi Arabia clarified that the country is still considering its invitation and has not joined BRICS yet.
Even with these initial growing pains, South Africa’s Foreign Minister Naledi Pandor told reporters in February that 34 different countries have submitted applications to join the growing BRICS bloc.
Any changes to the group are likely to be announced leading up to or at the 2024 BRICS summit which takes place October 22-24 in Kazan, Russia.
Get the Full Analysis of the IMF’s Outlook on VC+
This visual is part of an exclusive special dispatch for VC+ members which breaks down the key takeaways from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook.
For the full set of charts and analysis, sign up for VC+.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries