Technology
Breaking Down How Amazon Makes Money
‘Tis the season for shopping.
For many of us, that means buying things online – and if you are like most internet denizens, you’ll be picking up at least one item this holiday season through the the world’s largest e-commerce giant, Amazon.
The company’s sales numbers are growing at a staggering pace. Last year, Amazon had $136 billion in sales, and the company is projected to finish at the $177 billion mark this year.
What are the exact sources of Amazon’s revenue, and how does it all break down?
How Amazon Makes Money
Today’s infographic comes to us from Sellbrite, and it dives into the company’s success, and how Amazon makes money:
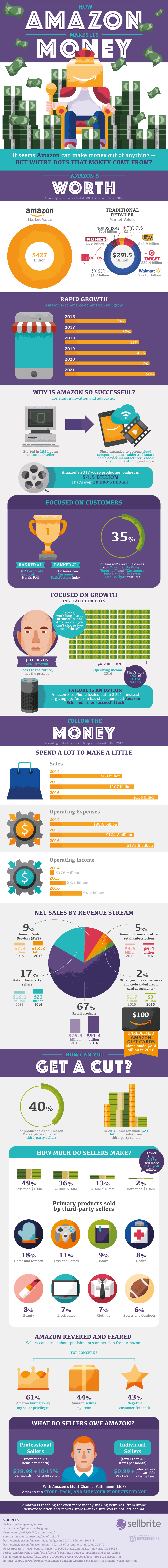
To the chagrin of many investors, Amazon has traditionally spent a lot to make a little.
In 2016, for example, the company brought in $136 billion in net sales, but it spent $131.8 billion on operating expenses. That gave the company an operating income of $4.2 billion.
However, that high-growth strategy seems to be paying off.
During the same period, e-commerce revenue jumped 25%, AWS revenue increased 55%, and net income skyrocketed 302%. The growth has continued through 2017 and it’s why Jeff Bezos is now the richest person in the world.
A Closer Look
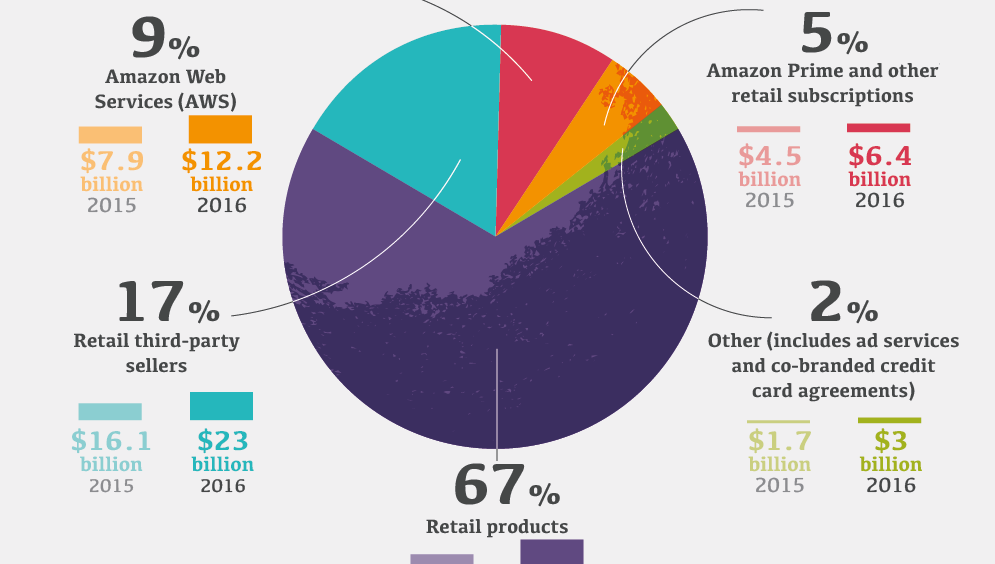
Here’s how Amazon makes money, according to the company’s last annual report for 2016:
| Revenue Stream | Net Sales (2016) | % of Total Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Retail products | $91.4B | 67.2% |
| Retail 3rd party sellers | $23.0B | 16.9% |
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | $12.2B | 9.0% |
| Subscriptions (Amazon Prime, etc.) | $6.4B | 4.7% |
| Other (ads, co-branded credit cards) | $3.0B | 2.2% |
| Total Revenue | $136.0B | 100.0% |
Which areas of Amazon’s business are growing the fastest – and where is the company investing in the future?
Here are just a few directions in which the Jeff Bezos Empire is expanding:
Ads
In 2017, the size of Amazon’s advertising business (forecasted at $1.65 billion) has already surpassed those belonging to Twitter ($1.21 billion) and Snapchat ($642 million). Of course, Amazon is still a longshot from impacting the Google and Facebook ad oligopoly, but the two leaders would be wise to take the emerging threat seriously.
Why would Amazon ads work well? The company has a vast database of user info to allow for effective targeting, as well as high margins.
Prime Video
In 2017, Amazon is spending $4.5 billion on creating original content. It has fewer dollars allocated to content than Netflix, but it’s still more than double what HBO spends each year. By the way, Amazon Prime Video is now live in an impressive 200 countries.
International
With 65% of U.S. households having access to Amazon Prime subscriptions, a focus on international sales is the biggest lever that Amazon can pull for future growth. The company is eyeing obvious countries, but less obvious ones as well. In India for example, Amazon’s marketplace is the fastest-growing in the country.
B2B
Amazon is also leveraging its strong logistics platform to provide goods for small businesses, rather than just consumers.
Shipping and Logistics
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is already a booming business that allows small businesses to tap into the scale of Amazon. Investing in shipping also betters the customer experience – a key objective for Amazon. However, it’s still possible that the company could take shipping and logistics a step further: domination in the $200 billion parcel shipping market would be a strategic and attainable prize.
With many other ways for the e-commerce giant to grow, it’ll be interesting to breakdown how Amazon makes money in 2018.
Technology
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
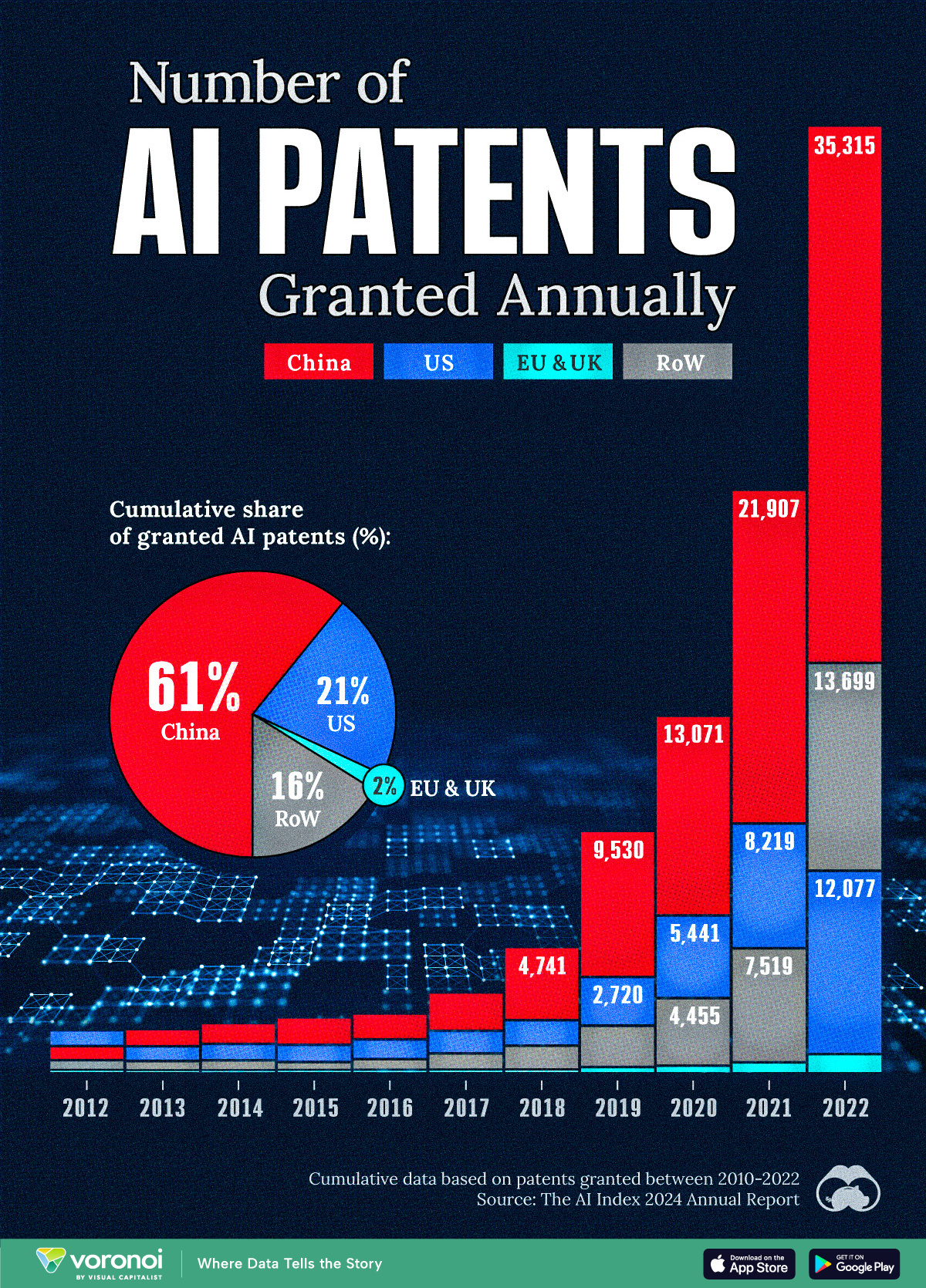
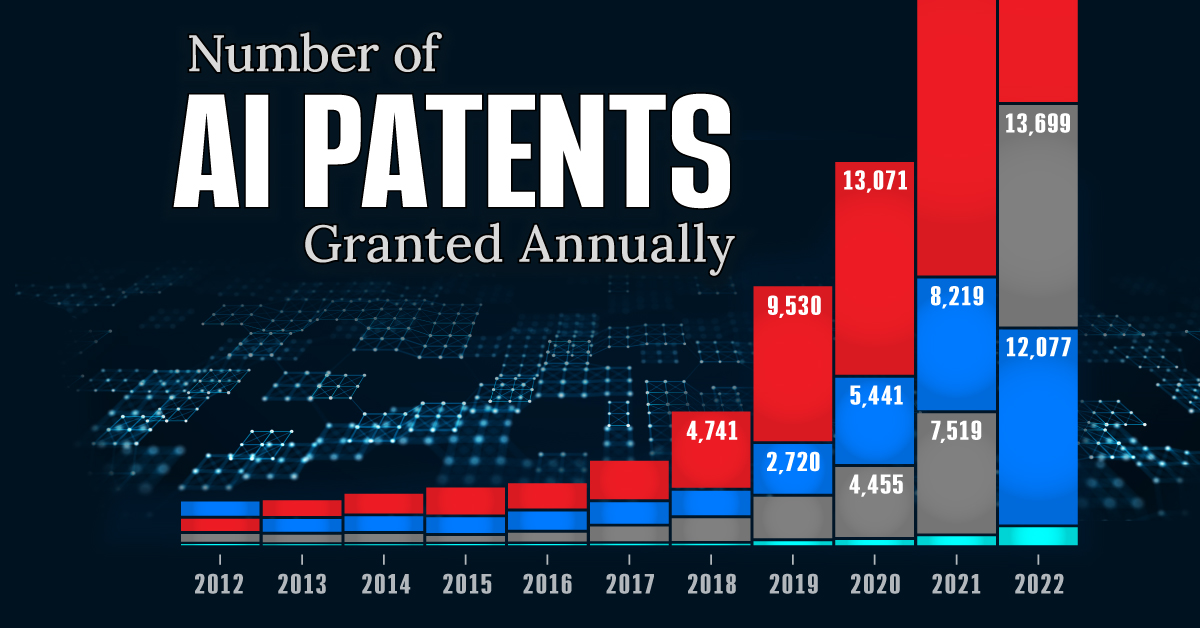
This infographic shows the number of AI-related patents granted each year from 2010 to 2022 (latest data available). These figures come from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET), accessed via Stanford University’s 2024 AI Index Report.
From this data, we can see that China first overtook the U.S. in 2013. Since then, the country has seen enormous growth in the number of AI patents granted each year.
| Year | China | EU and UK | U.S. | RoW | Global Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 307 | 137 | 984 | 571 | 1,999 |
| 2011 | 516 | 129 | 980 | 581 | 2,206 |
| 2012 | 926 | 112 | 950 | 660 | 2,648 |
| 2013 | 1,035 | 91 | 970 | 627 | 2,723 |
| 2014 | 1,278 | 97 | 1,078 | 667 | 3,120 |
| 2015 | 1,721 | 110 | 1,135 | 539 | 3,505 |
| 2016 | 1,621 | 128 | 1,298 | 714 | 3,761 |
| 2017 | 2,428 | 144 | 1,489 | 1,075 | 5,136 |
| 2018 | 4,741 | 155 | 1,674 | 1,574 | 8,144 |
| 2019 | 9,530 | 322 | 3,211 | 2,720 | 15,783 |
| 2020 | 13,071 | 406 | 5,441 | 4,455 | 23,373 |
| 2021 | 21,907 | 623 | 8,219 | 7,519 | 38,268 |
| 2022 | 35,315 | 1,173 | 12,077 | 13,699 | 62,264 |
In 2022, China was granted more patents than every other country combined.
While this suggests that the country is very active in researching the field of artificial intelligence, it doesn’t necessarily mean that China is the farthest in terms of capability.
Key Facts About AI Patents
According to CSET, AI patents relate to mathematical relationships and algorithms, which are considered abstract ideas under patent law. They can also have different meaning, depending on where they are filed.
In the U.S., AI patenting is concentrated amongst large companies including IBM, Microsoft, and Google. On the other hand, AI patenting in China is more distributed across government organizations, universities, and tech firms (e.g. Tencent).
In terms of focus area, China’s patents are typically related to computer vision, a field of AI that enables computers and systems to interpret visual data and inputs. Meanwhile America’s efforts are more evenly distributed across research fields.
Learn More About AI From Visual Capitalist
If you want to see more data visualizations on artificial intelligence, check out this graphic that shows which job departments will be impacted by AI the most.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023