Misc
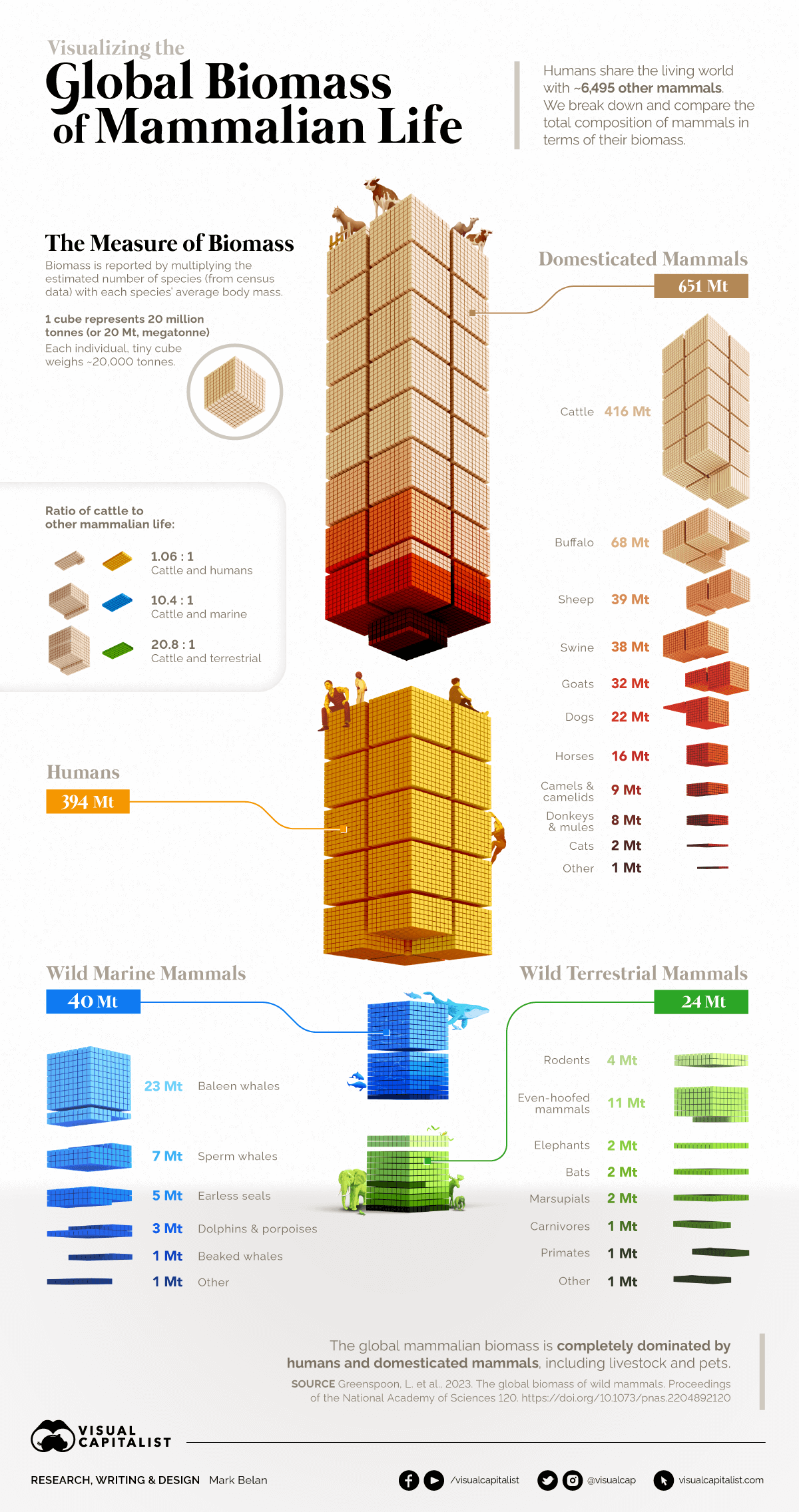
Visualizing the Biomass of All the World’s Mammals
Visualizing the Biomass of All the World’s Mammals
Even as we understand more about the world we live in, certain aspects of it remain undefined or hard to comprehend.
One such example is in the scale and distribution of Earth’s life. What’s the ratio of wild to domesticated animals? How much do all of the world’s humans weigh?
Until recently, such questions were nearly unanswerable. A new report titled The Global Biomass of Wild Mammals helps shed more light on the composition and scale of life on our planet. The research provides an estimate of the biomass of all mammals, globally—including humans.
So, What is Biomass Anyway?
Biomass is simply the weight of living things.
In this study, researchers
created rough estimates for four major categories of mammals: humans, domesticated animals, and those that were found in wild terrestrial and marine environments. A further breakdown of mammal groups are found within each category.
To achieve this, they took the estimated number of species from census data and multiplied it with each species’ average body mass.
One component worth pointing out is that animals contribute very different amounts to the world’s biomass total. For example, whales significantly outweigh rodents in terms of biomass, even though there are fewer species and populations of whales. The fact that whales are so much larger than rodents means that even smaller populations can contribute a meaningful portion to overall biomass.
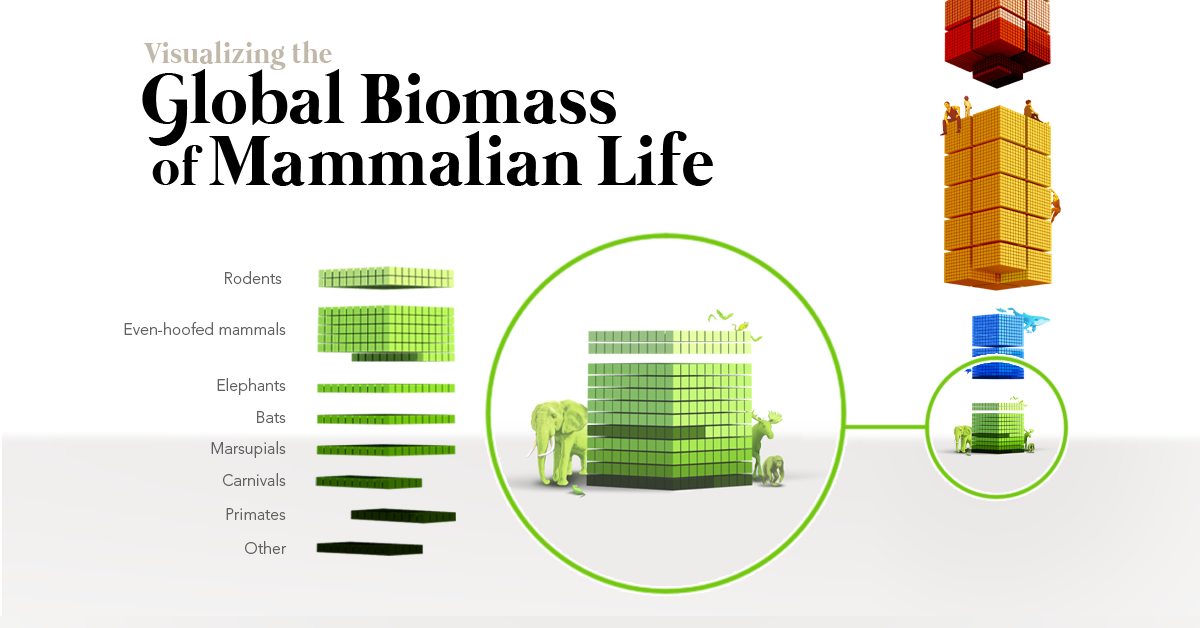
Mammalian Biomass, Organized Neatly
Each larger cube above represents 20 million metric tons of carbon, and the entirety of the visualization represents all living mammalian life on Earth.
The paper separates mammals into four distinct categories:
| Category | Total Mass (Mt) | Top Sub-Category |
|---|---|---|
| Domesticated Mammals | 651 | Cattle (416 Mt) |
| Humans | 394 | n/a |
| Wild Marine Mammals | 40 | Baleen Whales (23 Mt) |
| Wild Terrestrial Mammals | 24 | Even-Hoofed Mammals (11 Mt) |
| Total | 1,109 |
One of the most obvious takeaways from this data is that humans make up one-third of total mammalian biomass.
Perhaps even more strikingly, the animals we’ve domesticated for food, companionship, and labor make up close to 60% of the total weight of Earth’s mammals. Domesticated dogs and cats alone equal the total weight of all other wild land mammals combined.
The world’s sheep, on their own, weigh as much as all the whales and seals in the ocean. Domesticated buffalo such as the water buffalo, a species commonly found in Asia, combine to have the third largest biomass of all mammals.
Finally, there’s one category of mammal that comes way out on top.
Cattle Planet
The global livestock population has risen along with the human population, and cattle are now the top mammal in the world by weight.
In fact, just the United States’ share of cattle matches the biomass of all wild mammals on Earth.
As the standard of living continues to rise for people around the world, beef consumption has been increasing in many developing countries. Of course, raising cattle is a resource and land intensive operation, and there have been very real impacts on a global scale. For one, cows are a major source of methane emissions. As well, in Brazil, which accounts for around 25% of the world’s cattle population, pasture has directly replaced large swaths of rainforest habitat.
Waning Wildlife
At the very bottom of the visualization, dwarfed by humans and domesticated mammals, lies the vast array of wild mammals that live on planet Earth.
It’s sobering to see that the biomass of North America’s human population alone compares closely with that of all terrestrial wild mammals in the world. This includes plentiful creatures like rats and mice, as well as large mammals like elephants and bears.
Below are the top 10 wild mammalian contributors to biomass in the natural world.
| Rank | Contributor | Total Mass (Mt) | Individuals (millions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Fin Whales | 8 | 0.1 |
| #2 | Sperm Whales | 7 | 0.4 |
| #3 | Humpback Whales | 4 | 0.1 |
| #4T | Antarctic Minke Whales | 3 | 0.5 |
| #4T | Blue Whales | 3 | 0.05 |
| #6 | White-Tailed Deer | 2.7 | 45 |
| #7 | Crabeater Seals | 2.0 | 10 |
| #8 | Wild Boar | 1.9 | 30 |
| #9T | African Elephants | 1.3 | 0.5 |
| #9T | Bryde's Whales | 1.3 | 0.1 |
In the ocean, whales and seals are the heavyweight champions. On land, deer, and boar come out on top as they are both heavy and plentiful.
Humans have a complicated relationship with large mammals. We feel a very clear connection to these creatures, and they are often the key figures in conservation efforts. That said, even small populations of humans have wiped out large mammal species in the past.
The news that cattle outweigh wild land animals by a factor of 20:1 is a reminder that human influence is perhaps even more powerful than we think.
The more we’re exposed to nature’s full splendor […] the more we might be tempted to imagine that nature is an endless and inexhaustible resource. In reality, the weight of all remaining wild land mammals is less than 10% of humanity’s combined weight. – Ron Milo, Professor of Systems Biology
Source: The global biomass of wild mammals
Data notes: To come up with the numbers above, scientists estimated the total biomass of wild mammals on Earth by manually collecting population estimates for 392 land mammal species, which make up about 6% of all wild land mammal species, and using machine learning to infer the global populations of the remaining 94%. Their estimate includes 4,805 wild land mammal species out of approximately 6,400 known and extant wild land mammal species, excluding low-abundance species for which data are scarce.
Misc
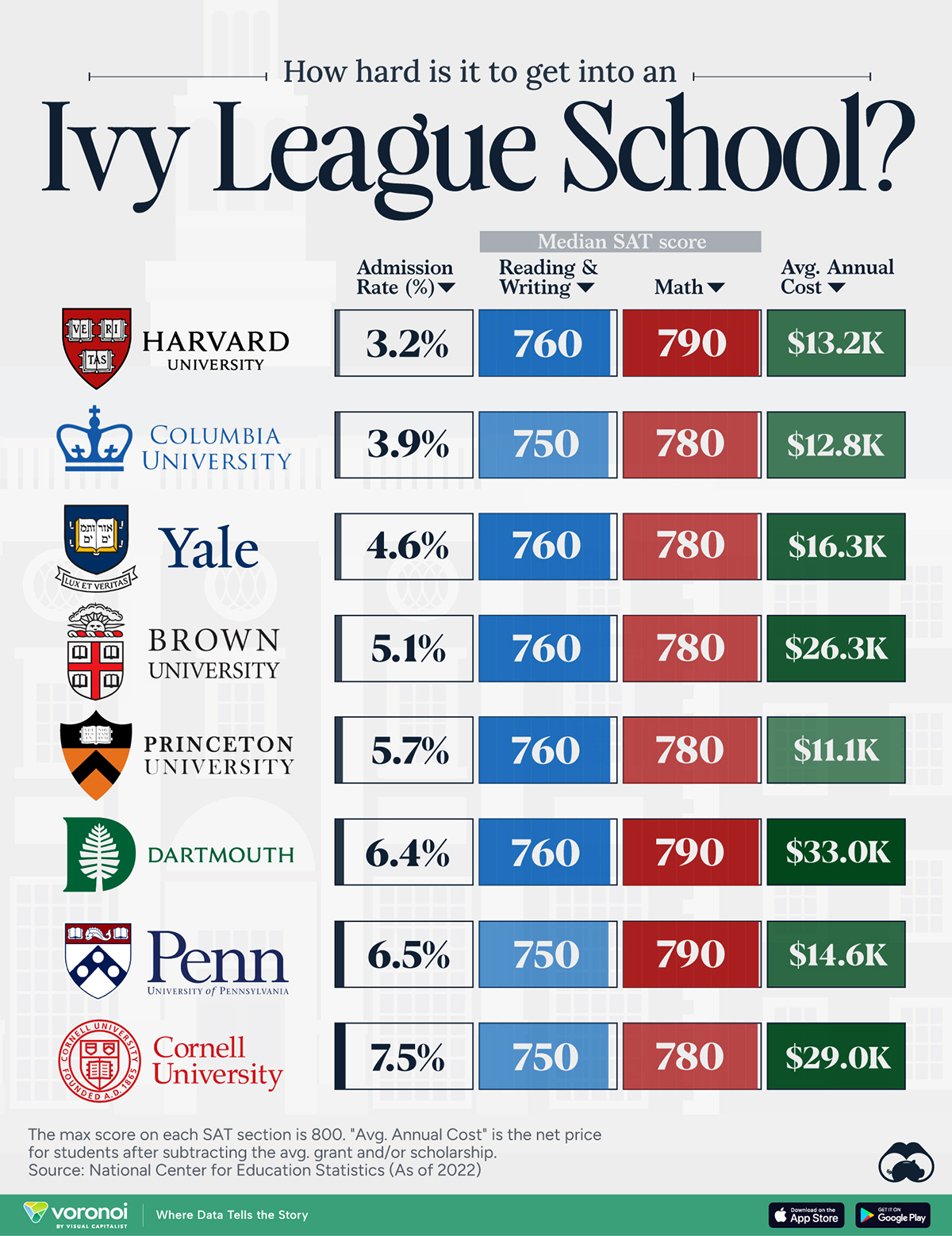
How Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
We detail the admission rates and average annual cost for Ivy League schools, as well as the median SAT scores required to be accepted.
How Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Ivy League institutions are renowned worldwide for their academic excellence and long-standing traditions. But how hard is it to get into one of the top universities in the U.S.?
In this graphic, we detail the admission rates and average annual cost for Ivy League schools, as well as the median SAT scores required to be accepted. The data comes from the National Center for Education Statistics and was compiled by 24/7 Wall St.
Note that “average annual cost” represents the net price a student pays after subtracting the average value of grants and/or scholarships received.
Harvard is the Most Selective
The SAT is a standardized test commonly used for college admissions in the United States. It’s taken by high school juniors and seniors to assess their readiness for college-level academic work.
When comparing SAT scores, Harvard and Dartmouth are among the most challenging universities to gain admission to. The median SAT scores for their students are 760 for reading and writing and 790 for math. Still, Harvard has half the admission rate (3.2%) compared to Dartmouth (6.4%).
| School | Admission rate (%) | SAT Score: Reading & Writing | SAT Score: Math | Avg Annual Cost* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harvard University | 3.2 | 760 | 790 | $13,259 |
| Columbia University | 3.9 | 750 | 780 | $12,836 |
| Yale University | 4.6 | 760 | 780 | $16,341 |
| Brown University | 5.1 | 760 | 780 | $26,308 |
| Princeton University | 5.7 | 760 | 780 | $11,080 |
| Dartmouth College | 6.4 | 760 | 790 | $33,023 |
| University of Pennsylvania | 6.5 | 750 | 790 | $14,851 |
| Cornell University | 7.5 | 750 | 780 | $29,011 |
*Costs after receiving federal financial aid.
Additionally, Dartmouth has the highest average annual cost at $33,000. Princeton has the lowest at $11,100.
While student debt has surged in the United States in recent years, hitting $1.73 trillion in 2023, the worth of obtaining a degree from any of the schools listed surpasses mere academics. This is evidenced by the substantial incomes earned by former students.
Harvard grads, for example, have the highest average starting salary in the country, at $91,700.
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001