Misc
Visualized: The Biggest Ponzi Schemes in Modern History

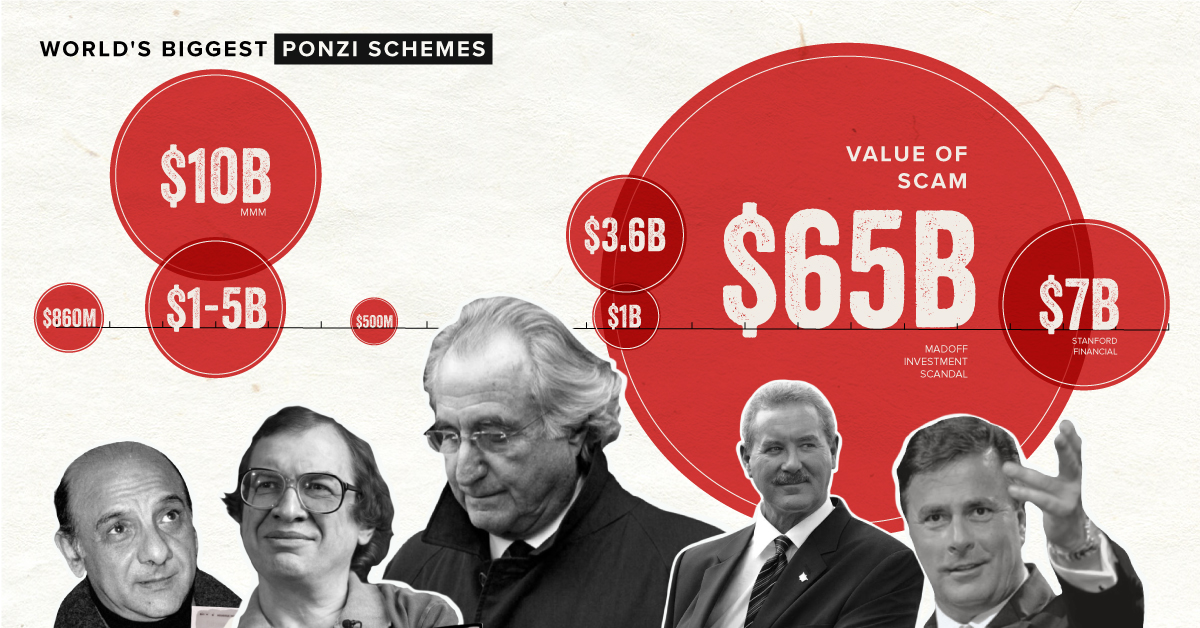
The Biggest Ponzi Schemes in Modern History
Some things simply sound too good to be true, but when money is involved, our judgement can become clouded.
This is often the case with Ponzi schemes, a type of financial fraud that lures investors by promising abnormally high returns. Money brought in by new members is used to pay the scheme’s founders, as well as its earlier investors.
The scheme is named after Charles Ponzi, an Italian who became infamous in the 1920s for claiming he could double his clients’ money within 90 days. Since then, numerous Ponzi schemes have been orchestrated around the globe.
To help you learn more about these sophisticated crimes, this infographic examines some of the biggest Ponzi schemes in modern history.
Ponzi Schemes in the 20th Century
The 1990s saw a number of large Ponzi schemes worth upwards of $500 million.
| Country | Date Ended | Name of Scheme and Founder | Value (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Belgium | 1991 | Moneytron, Jean-Pierre Van Rossem | $860M |
| Romania | 1994 | Caritas, Ioan Stoica | $1B - $5B |
| Russia | 1994 | MMM, Sergei Mavrodi | $10B |
| U.S. | 1997 | Great Ministries International, Geral Payne | $500M |
In many cases, these schemes thrived by taking advantage of the unsuspecting public who often lacked any knowledge of investing. Caritas, for example, was a Ponzi scheme based in Romania that marketed itself as a “self-help game” for the poor.
The scheme was initially very successful, tricking millions of people into making deposits by offering the chance to earn an 800% return after three months. This was not sustainable, and Caritas was eventually unable to distribute further winnings.
Caritas operated for only two years, but its “success” was undeniable. In 1993, it was estimated that a third of the country’s money was circulating through the scheme.
Ponzi Schemes in the 21st Century
The American public has fallen victim to numerous multi-billion dollar Ponzi schemes since the beginning of the 21st century.
| Country | Date Ended | Name of Scheme and Founder | Value (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| U.S. | 2003 | Mutual Benefits Company, Joel Steinger | $1B |
| U.S. | 2003 | Petters Group Worldwide, Tom Petters | $4B |
| U.S. | 2008 | Madoff Investment Scandal, Bernie Madoff | $65B |
| U.S. | 2012 | Stanford Financial Group, Allen Stanford | $7B |
Many of these schemes have made major headlines, but much less is said about the thousands of everyday Americans that were left in financial ruin.
For victims of the Madoff Investment Scandal, receiving any form of compensation has been a drawn-out process. In 2018, 10 years after the scheme was uncovered, a court-appointed trustee managed to recover $13 billion by liquidating Madoff’s firm and personal assets.
As NPR reported, investors may recover up to 60 to 70 percent of their initial investment only. For victims who had to delay retirement or drastically alter their lifestyles, this compensation likely provides little solace.
Do the Crime, Pay the Time
Running a Ponzi scheme is likely to land you in jail for a long time, at least in the U.S.
In 2009, for example, 71-year-old Bernie Madoff pled guilty to 11 federal felonies and was sentenced to 150 years in prison. That’s 135 years longer than the average U.S. murder conviction.
Outside of the U.S., it’s a much different story. Weaker regulation and enforcement, particularly in developing countries, means a number of schemes are ongoing today.
Sergei Mavrodi, known for running the Russian Ponzi scheme MMM, started a new organization named MMM Global after being released from prison in 2011. Although he died in March 2018, his self-described “social financial network” has established a base in several Southeast Asian and African countries.
If you or someone you know is worried about falling victim to a Ponzi scheme, this checklist from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) may be a useful resource.
Misc
How Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
We detail the admission rates and average annual cost for Ivy League schools, as well as the median SAT scores required to be accepted.
How Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Ivy League institutions are renowned worldwide for their academic excellence and long-standing traditions. But how hard is it to get into one of the top universities in the U.S.?
In this graphic, we detail the admission rates and average annual cost for Ivy League schools, as well as the median SAT scores required to be accepted. The data comes from the National Center for Education Statistics and was compiled by 24/7 Wall St.
Note that “average annual cost” represents the net price a student pays after subtracting the average value of grants and/or scholarships received.
Harvard is the Most Selective
The SAT is a standardized test commonly used for college admissions in the United States. It’s taken by high school juniors and seniors to assess their readiness for college-level academic work.
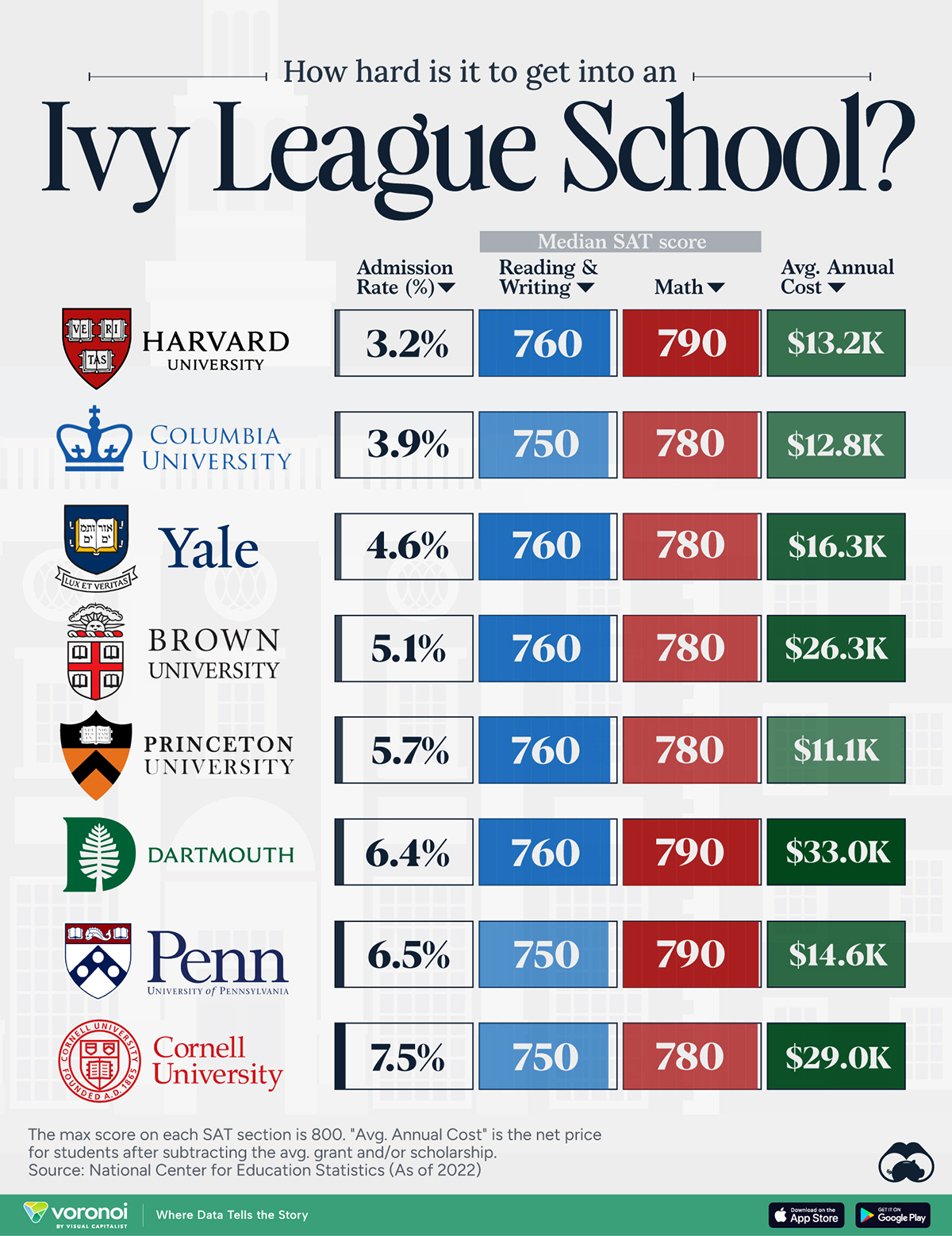
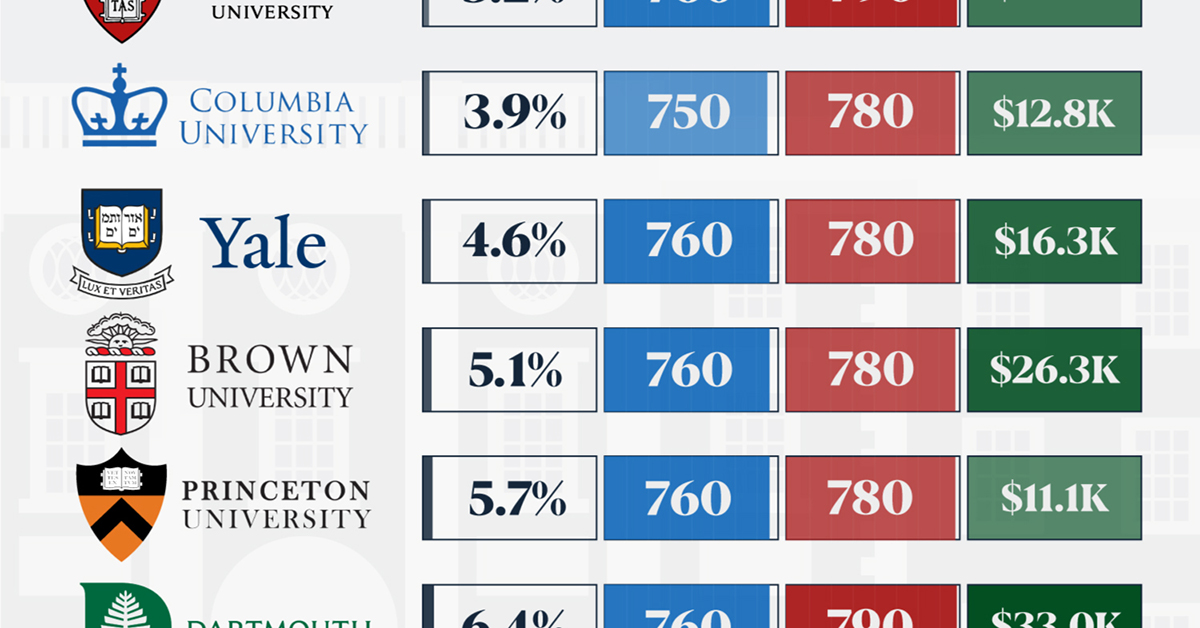
When comparing SAT scores, Harvard and Dartmouth are among the most challenging universities to gain admission to. The median SAT scores for their students are 760 for reading and writing and 790 for math. Still, Harvard has half the admission rate (3.2%) compared to Dartmouth (6.4%).
| School | Admission rate (%) | SAT Score: Reading & Writing | SAT Score: Math | Avg Annual Cost* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harvard University | 3.2 | 760 | 790 | $13,259 |
| Columbia University | 3.9 | 750 | 780 | $12,836 |
| Yale University | 4.6 | 760 | 780 | $16,341 |
| Brown University | 5.1 | 760 | 780 | $26,308 |
| Princeton University | 5.7 | 760 | 780 | $11,080 |
| Dartmouth College | 6.4 | 760 | 790 | $33,023 |
| University of Pennsylvania | 6.5 | 750 | 790 | $14,851 |
| Cornell University | 7.5 | 750 | 780 | $29,011 |
*Costs after receiving federal financial aid.
Additionally, Dartmouth has the highest average annual cost at $33,000. Princeton has the lowest at $11,100.
While student debt has surged in the United States in recent years, hitting $1.73 trillion in 2023, the worth of obtaining a degree from any of the schools listed surpasses mere academics. This is evidenced by the substantial incomes earned by former students.
Harvard grads, for example, have the highest average starting salary in the country, at $91,700.
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001