Datastream
AWS: Powering the Internet and Amazon’s Profits
The Briefing
- Cloud computing has become a hugely important element of Amazon’s business
- In 2021, AWS accounted for 13% of Amazon’s revenue, but clocks in nearly three-quarters of their operating profit
AWS: Powering the Internet and Amazon’s Profits
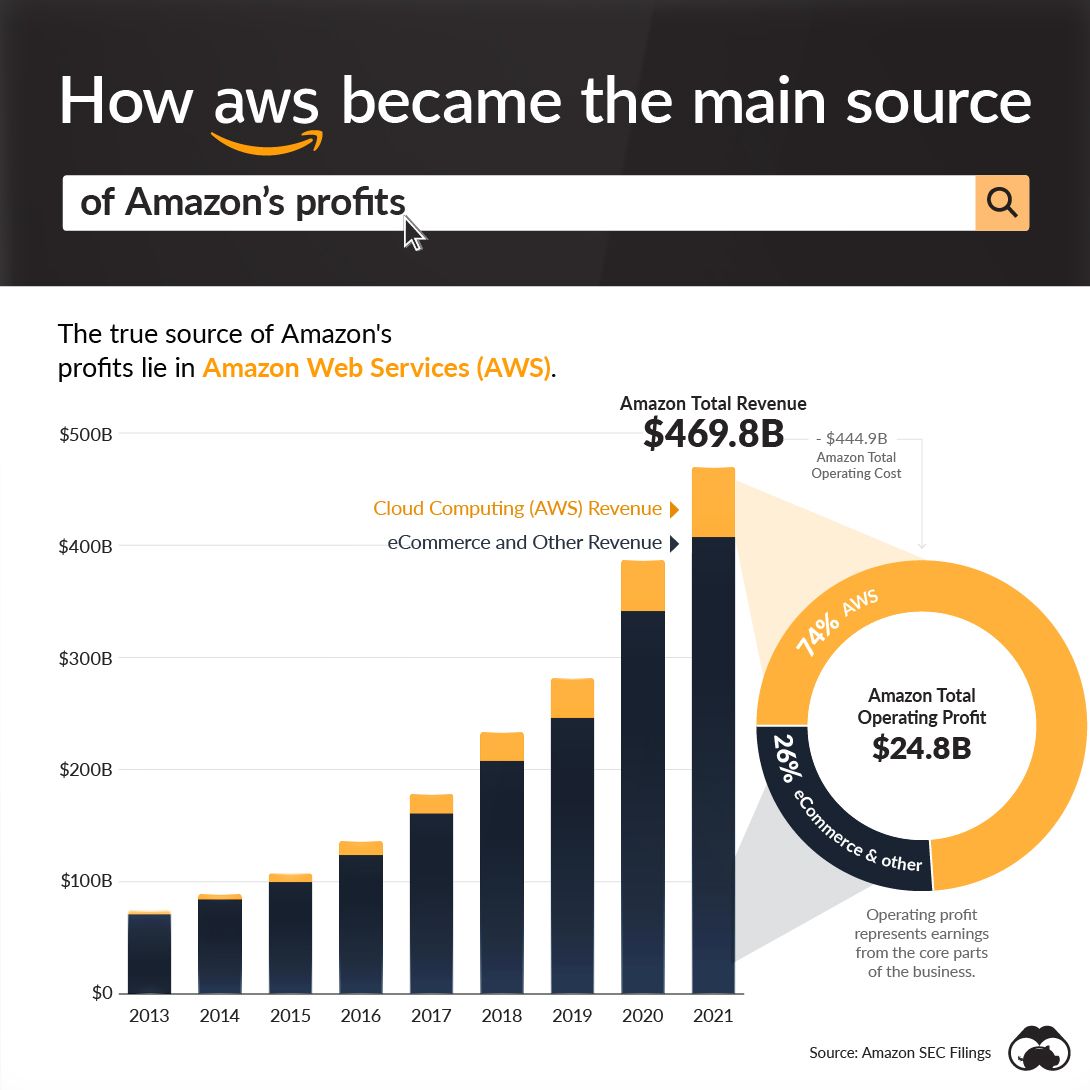
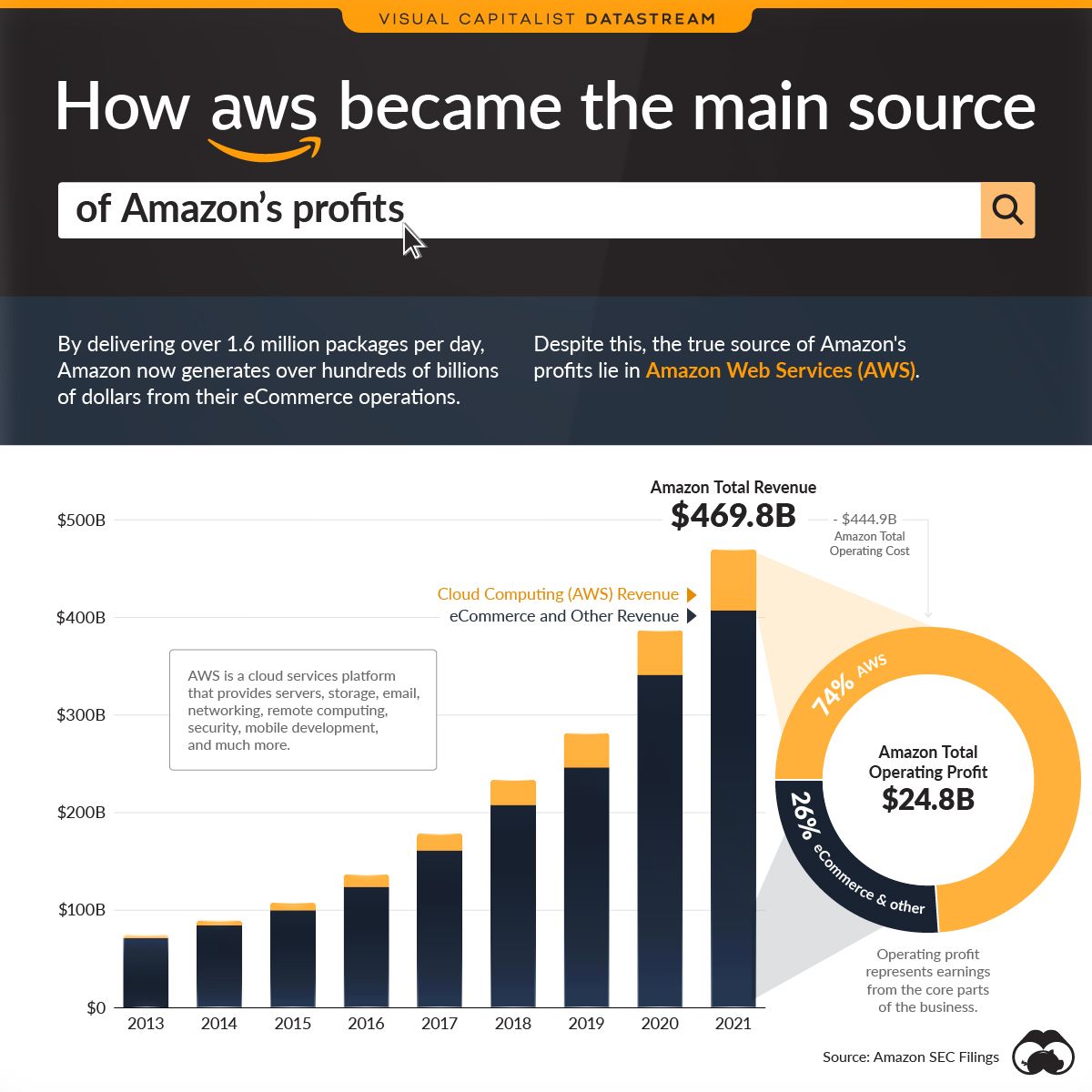
The Amazon growth story has been a remarkable one so far.
On the top line, the company has grown every single year since its inception. Even in going back to 2004, Amazon generated a much more modest $6.9 billion in revenue compared to the massive $469 billion for 2021.
Most of these sales come from their retail and ecommerce operations, which the company has come to be known for. However, on the bottom line, the source of profit paints a completely different picture. That’s because 74% of Amazon’s operating profit comes from Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Here’s a closer look at the financials around Amazon and AWS:
| Year | AWS Operating Profit ($B) | Total Operating Profit ($B) | AWS % of Operating Profit | Revenue ($B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | $18.5 | $24.8 | 74% | $469.8 |
| 2020 | $13.5 | $22.9 | 59% | $386.1 |
| 2019 | $9.2 | $14.5 | 63% | $280.5 |
| 2018 | $7.2 | $12.4 | 58% | $232.8 |
Ultimately, the data suggests that the cloud business has been, and possibly will always remain, a higher margin business and consistent profit center in comparison to ecommerce and the physical distribution of goods.
A Glance at AWS
AWS is Amazon’s cloud computing service that provides the critical infrastructure for an assortment of applications like data storage and networking. With this, they help fuel over a million organizations including businesses like Twitter and Netflix and even both the U.S. and Canadian Federal Governments.
Here are some other notable entities and the monthly payments they’ve made towards AWS:
| AWS Customer | Monthly Payments ($M) |
|---|---|
| Netflix | $19 |
| Twitch | $15 |
| $13 | |
| $11 | |
| Turner Broadcasting | $10 |
| BBC | $9 |
| Baidu | $9 |
| ESPN | $8 |
| Adobe | $8 |
| $7 |
Source: Continho (2020)
Based on these monthly figures from 2020, AWS collects $1.3 billion in sales a year just from these 10 customers, while raking in $62 billion of revenue overall. Moreover, this makes them the leader in the competitive cloud market.
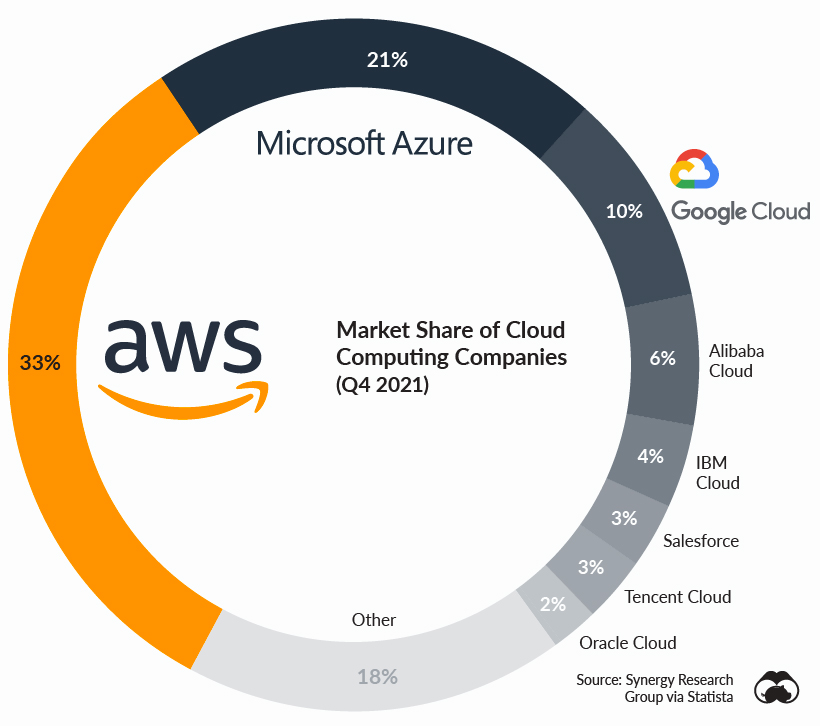
In an industry worth an excess of $180 billion, Amazon’s 33% market share position exceeds both Google and Microsoft (Azure) combined. Their market share also surpasses the bottom six shown on the chart combined, who are formidable tech giants in their own right.
The Future of AWS?
AWS has been a cash cow for years and there have even been rumors of an Amazon split up, where AWS would spin off as its own entity. It’s believed by some that if the cloud segment of the business separates, it will be seen as a pure play on the cloud industry and will be awarded a higher valuation multiple by the market.
One thing is for sure, from the perspective of profits, Amazon could be better be described as a cloud company, with an ecommerce business on the side.
Where does this data come from?
Source: Amazon SEC Filings
Notes: Operating profit is the profit from the business before the deduction of non-operating expenses like interest and taxes.
Datastream
Can You Calculate Your Daily Carbon Footprint?
Discover how the average person’s carbon footprint impacts the environment and learn how carbon credits can offset your carbon footprint.
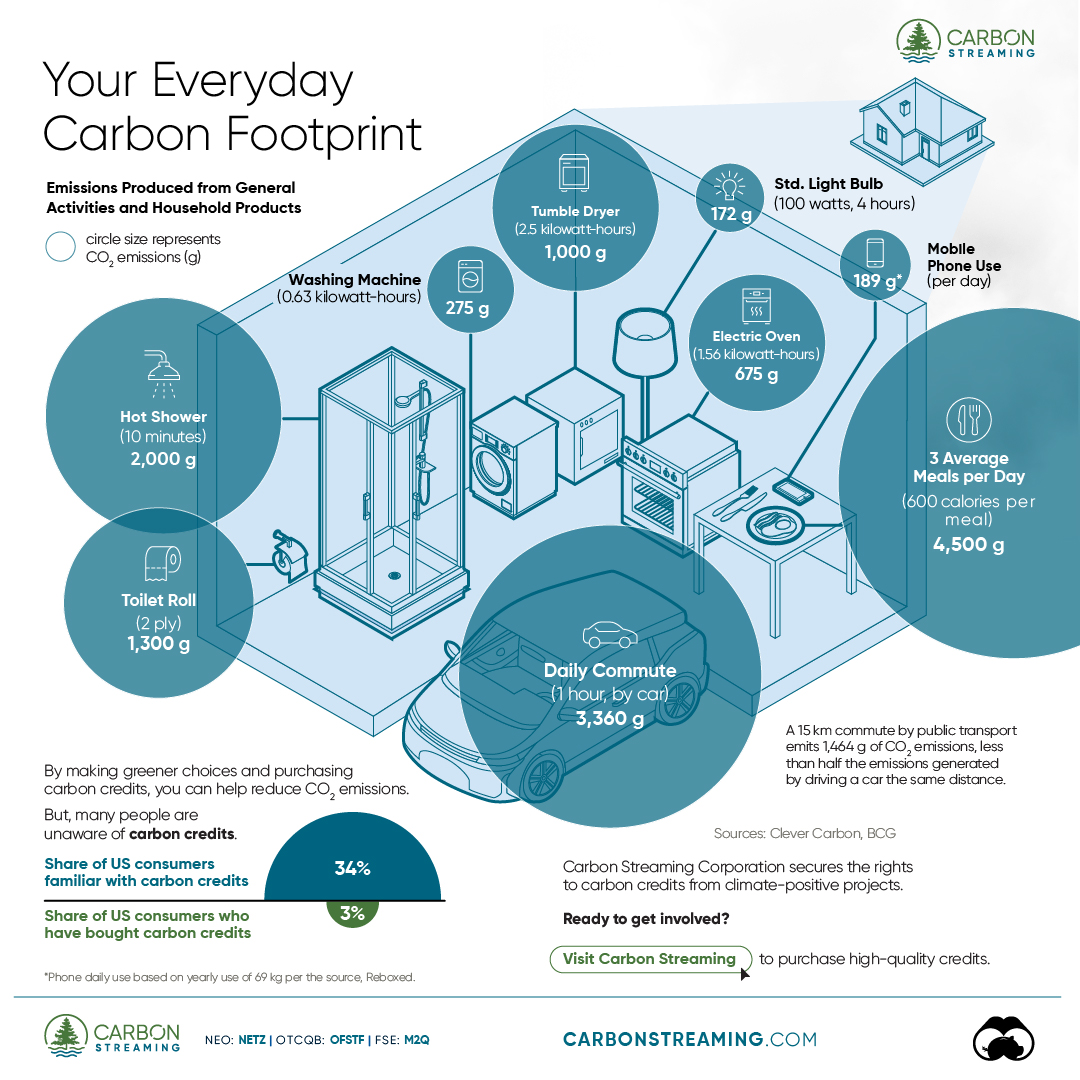
The Briefing
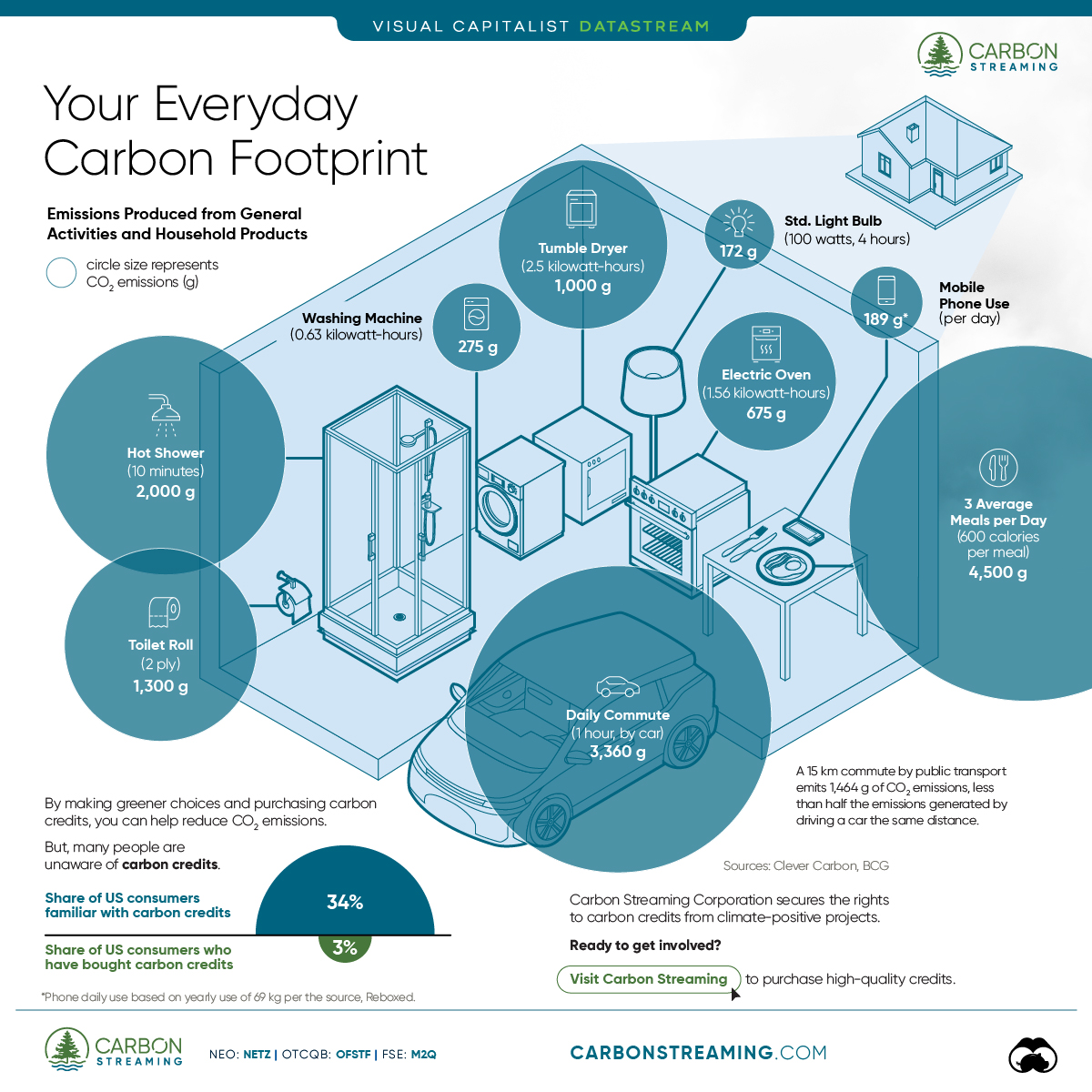
- A person’s carbon footprint is substantial, with activities such as food consumption creating as much as 4,500 g of CO₂ emissions daily.
- By purchasing carbon credits from Carbon Streaming Corporation, you can offset your own emissions and fund positive climate action.
Your Everyday Carbon Footprint
While many large businesses and countries have committed to net-zero goals, it is essential to acknowledge that your everyday activities also contribute to global emissions.
In this graphic, sponsored by Carbon Streaming Corporation, we will explore how the choices we make and the products we use have a profound impact on our carbon footprint.
Carbon Emissions by Activity
Here are some of the daily activities and products of the average person and their carbon footprint, according to Clever Carbon.
| Household Activities & Products | CO2 Emissions (g) |
|---|---|
| 💡 Standard Light Bulb (100 watts, four hours) | 172 g |
| 📱 Mobile Phone Use (195 minutes per day)* | 189 g |
| 👕 Washing Machine (0.63 kWh) | 275 g |
| 🔥 Electric Oven (1.56 kWh) | 675 g |
| ♨️ Tumble Dryer (2.5 kWh) | 1,000 g |
| 🧻 Toilet Roll (2 ply) | 1,300 g |
| 🚿 Hot Shower (10 mins) | 2,000 g |
| 🚙 Daily Commute (one hour, by car) | 3,360 g |
| 🍽️ Average Daily Food Consumption (three meals of 600 calories) | 4,500 g |
| *Phone use based on yearly use of 69kg per the source, Reboxed | |
Your choice of transportation plays a crucial role in determining your carbon footprint. For instance, a 15 km daily commute to work on public transport generates an average of 1,464 g of CO₂ emissions. Compared to 3,360 g—twice the volume for a journey the same length by car.
By opting for more sustainable modes of transport, such as cycling, walking, or public transportation, you can significantly reduce your carbon footprint.
Addressing Your Carbon Footprint
One way to compensate for your emissions is by purchasing high-quality carbon credits.
Carbon credits are used to help fund projects that avoid, reduce or remove CO₂ emissions. This includes nature-based solutions such as reforestation and improved forest management, or technology-based solutions such as the production of biochar and carbon capture and storage (CCS).
While carbon credits offer a potential solution for individuals to help reduce global emissions, public awareness remains a significant challenge. A BCG-Patch survey revealed that only 34% of U.S. consumers are familiar with carbon credits, and only 3% have purchased them in the past.
About Carbon Streaming
By financing the creation or expansion of carbon projects, Carbon Streaming Corporation secures the rights to future carbon credits generated by these sustainable projects. You can then purchase these carbon credits to help fund climate solutions around the world and compensate for your own emissions.
Ready to get involved?
>> Learn more about purchasing carbon credits at Carbon Streaming
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?