Technology
Animation: Human Population Growth Over All of History
Imagine that for every million people on Earth, there was a single dot on a map.
In total, that would be about 7,600 dots – representing today’s global population of 7.6 billion.
But, what if we went back in time, and watched those dots accumulate over human history? When and where do the first dots appear, and when does population growth ramp up to get to the billions of people that are alive today?
The History of Population Growth
Today’s animation comes from the American Museum of Natural History, and it shows over 200,000 years of population growth and the major events along the way.
If you consider yourself on the more impatient side of things, we suggest starting at 1:50 which will zoom you to 400 AD – the time of India’s Golden Age. Alternatively, go to 3:25 to witness the Bubonic Plague’s rare negative impact on population growth, as well as the ensuing age of European exploration.
It took 200,000 years of human history to get to one billion people – and just 200 years to reach seven billion.
That’s partly how the exponential “hockey stick” growth curve works, but it is also a factor of improvements in living standards, sanitation, and medicine that came after the Industrial Revolution.
Key Population Moments
Here are a few moments that stood out to us in the video, that we think represent particularly interesting moments in human population history:
Agriculture
The impact of farming cannot be emphasized enough. For many thousands of years, the human population dwindled until we learned how to plant crops to provide a scalable and sustainable food supply for a hungry population.
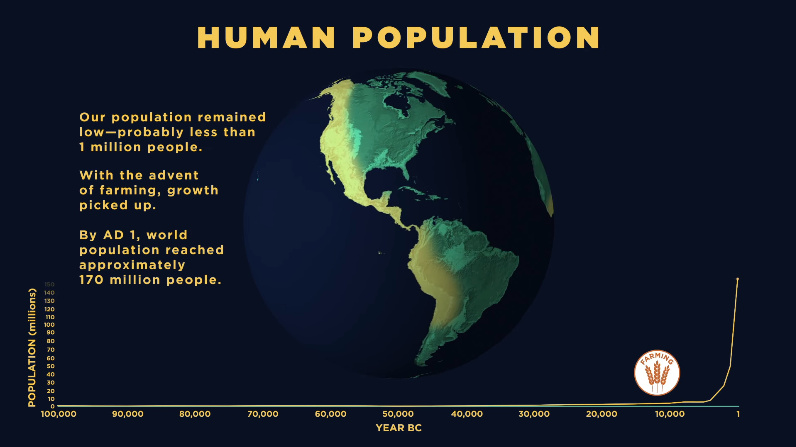
As you can see, after agriculture starts spreading, the human population quickly skyrockets. It is estimated to have reached roughly 170 million by the year 1 AD.
East vs. West
The Greeks and Romans were interesting cultures to us in many ways – but one thing that is sometimes missed with a Western education is the sheer size of Indian and Chinese civilizations.
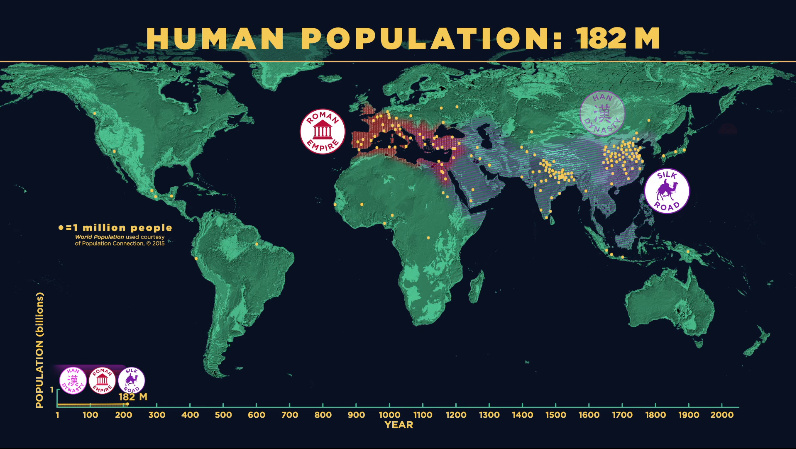
The above screenshot is from close to the territorial peak of the Roman Empire – notice its size in comparison to the Han Dynasty in China, as well as the area that is modern-day India.
Bubonic Plague
The Black Death, which started in 1347, didn’t do much to increase Europe’s population.
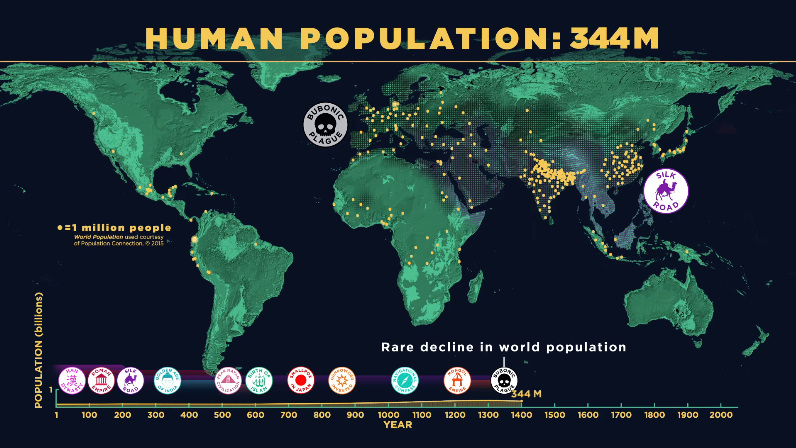
In fact, this was one of the rare times that global human population growth went backwards for multiple decades.
Post-Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution brought innovations to food and medicine, and kickstarted an era that would be usher in the birth of many new technologies.
This screenshot is from close to 1900, when these innovations started to make rapid global population growth a reality.
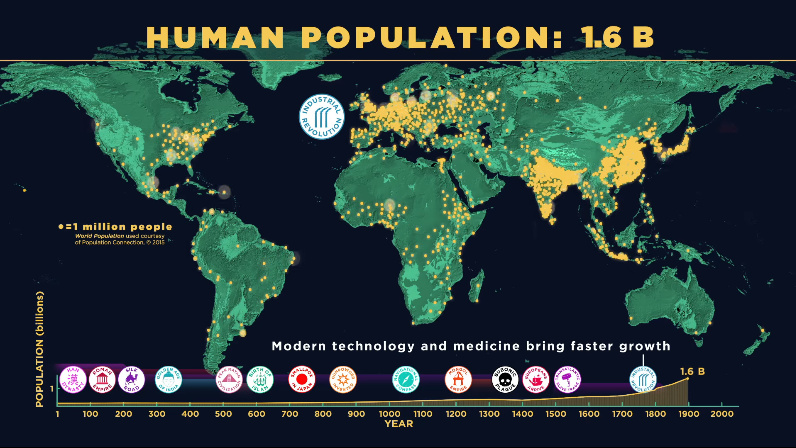
Over the next century, the population would more than quadruple to today’s seven billion plus people.
The Future of Population Growth
Naturally, this leads to thinking about the future of the human population.
For that, we recommend visiting these two prior animations: The 20 Most Populous Megacities in 2100 and The World’s Population by Region in 2100.
Technology
Ranked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Did you know that some computer chips are now retailing for the price of a new BMW?
As computers invade nearly every sphere of life, so too have the chips that power them, raising the revenues of the businesses dedicated to designing them.
But how did various chipmakers measure against each other last year?
We rank the biggest semiconductor companies by their percentage share of the industry’s revenues in 2023, using data from Omdia research.
Which Chip Company Made the Most Money in 2023?
Market leader and industry-defining veteran Intel still holds the crown for the most revenue in the sector, crossing $50 billion in 2023, or 10% of the broader industry’s topline.
All is not well at Intel, however, with the company’s stock price down over 20% year-to-date after it revealed billion-dollar losses in its foundry business.
| Rank | Company | 2023 Revenue | % of Industry Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intel | $51B | 9.4% |
| 2 | NVIDIA | $49B | 9.0% |
| 3 | Samsung Electronics | $44B | 8.1% |
| 4 | Qualcomm | $31B | 5.7% |
| 5 | Broadcom | $28B | 5.2% |
| 6 | SK Hynix | $24B | 4.4% |
| 7 | AMD | $22B | 4.1% |
| 8 | Apple | $19B | 3.4% |
| 9 | Infineon Tech | $17B | 3.2% |
| 10 | STMicroelectronics | $17B | 3.2% |
| 11 | Texas Instruments | $17B | 3.1% |
| 12 | Micron Technology | $16B | 2.9% |
| 13 | MediaTek | $14B | 2.6% |
| 14 | NXP | $13B | 2.4% |
| 15 | Analog Devices | $12B | 2.2% |
| 16 | Renesas Electronics Corporation | $11B | 1.9% |
| 17 | Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation | $10B | 1.9% |
| 18 | Microchip Technology | $8B | 1.5% |
| 19 | Onsemi | $8B | 1.4% |
| 20 | KIOXIA Corporation | $7B | 1.3% |
| N/A | Others | $126B | 23.2% |
| N/A | Total | $545B | 100% |
Note: Figures are rounded. Totals and percentages may not sum to 100.
Meanwhile, Nvidia is very close to overtaking Intel, after declaring $49 billion of topline revenue for 2023. This is more than double its 2022 revenue ($21 billion), increasing its share of industry revenues to 9%.
Nvidia’s meteoric rise has gotten a huge thumbs-up from investors. It became a trillion dollar stock last year, and broke the single-day gain record for market capitalization this year.
Other chipmakers haven’t been as successful. Out of the top 20 semiconductor companies by revenue, 12 did not match their 2022 revenues, including big names like Intel, Samsung, and AMD.
The Many Different Types of Chipmakers
All of these companies may belong to the same industry, but they don’t focus on the same niche.
According to Investopedia, there are four major types of chips, depending on their functionality: microprocessors, memory chips, standard chips, and complex systems on a chip.
Nvidia’s core business was once GPUs for computers (graphics processing units), but in recent years this has drastically shifted towards microprocessors for analytics and AI.
These specialized chips seem to be where the majority of growth is occurring within the sector. For example, companies that are largely in the memory segment—Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron Technology—saw peak revenues in the mid-2010s.
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc2 weeks ago
Misc2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?













